What is Flash and why do you need it?
Flash is a multimedia software platform that allows you to create and view interactive content on the web. Developed by Adobe, Flash was once widely used for animations, games, and streaming videos. While its popularity has declined in recent years with the rise of HTML5, there are still websites and applications that rely on Flash to function properly.
Flash provides a range of features that make it popular among developers. It enables the creation of visually appealing and interactive content, making websites more engaging for visitors. With Flash, you can incorporate animations, videos, audio, and interactive elements into your web pages, enhancing the user experience and bringing your vision to life.
Although Flash has faced criticism for its security vulnerabilities and resource-heavy nature, there are still instances where you may need it. Some older websites and applications continue to rely on Flash for their functionality, and without it, you may not be able to access certain content or features. Additionally, some websites and online services, such as web-based games and educational platforms, may still use Flash as their primary technology, requiring you to have it installed and enabled on your Chrome browser.
While HTML5 has become the standard for web development, certain legacy sites and applications may not have made the transition, and thus still require Flash. Additionally, if you frequently visit Flash-based websites or interact with Flash content, having Flash enabled on your Chrome browser allows you to enjoy a seamless browsing experience without any compatibility issues.
It’s important to note that as of December 2020, Adobe has officially announced that Flash will reach its end-of-life and will no longer be supported or updated. This means that the need for Flash will decrease over time, and developers are encouraged to transition to alternative technologies. However, until Flash is completely phased out, it remains necessary for certain online experiences.
+
Installing Flash on Chrome
To install Flash on Google Chrome, follow these simple steps:
- Open the Google Chrome browser on your computer.
- Visit the official Adobe Flash Player download page (https://get.adobe.com/flashplayer/) in a new tab.
- Make sure to uncheck any optional offers and click on the “Install now” button.
- Choose the operating system you are using (Windows, Mac, or Linux).
- Click the “Download now” button to start the download.
- Once the download is complete, locate the installation file on your computer and double-click on it to run the installer.
- Follow the prompts provided by the installer to complete the installation process.
- After the installation is complete, restart your Google Chrome browser.
Congratulations, you have successfully installed Flash on your Chrome browser! You can now enjoy Flash-based content and websites without any issues. However, keep in mind that Flash will be phased out in the near future, so it’s advisable to transition to alternative technologies whenever possible to ensure continued compatibility with modern web standards.
It’s worth noting that starting from Chrome version 76, Flash is disabled by default. This is a security measure taken by Google to protect users from potential vulnerabilities. Therefore, even after installing Flash, you may need to manually enable it in Chrome to use Flash content. Don’t worry, we will cover that in the next section.
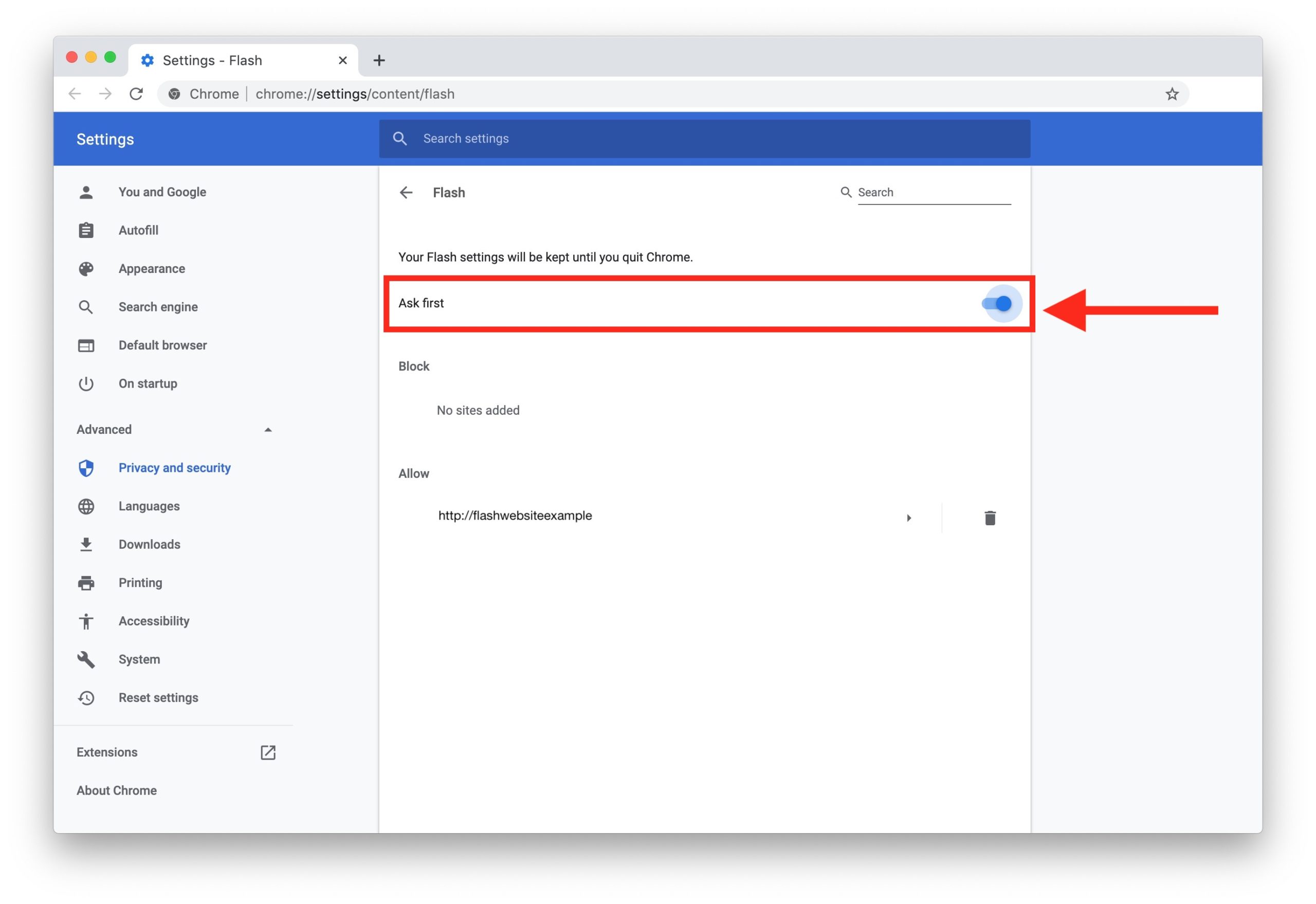
Enabling Flash in Chrome
After installing Flash on Chrome, you need to enable it to ensure Flash content can be played. Here’s how you can enable Flash on Chrome:
- Launch Google Chrome on your computer.
- In the address bar, type “chrome://settings/content/flash” and press Enter.
- Alternatively, you can access the settings by clicking the three-dot menu icon in the top right corner of the Chrome window, selecting “Settings,” then scrolling down and clicking on “Advanced,” followed by “Content settings.”
- On the Flash settings page, toggle the switch next to “Ask first (recommended)” to enable Flash.
By choosing “Ask first,” Chrome will prompt you to allow Flash to run whenever you visit a website that requires it. This provides an additional layer of security, as you can decide whether to enable or disable Flash on a per-site basis.
It’s important to note that starting from Chrome version 88, Adobe Flash Player is permanently disabled and cannot be enabled again. This is in line with Adobe’s end-of-life announcement for Flash and the industry-wide shift away from Flash-based technologies.
However, if you are using an earlier version of Chrome and need to enable Flash, keep in mind that Flash is a deprecated technology and has security implications. It’s crucial to be cautious when allowing Flash to run and only enable it on trusted websites. Additionally, it’s recommended to regularly update both Chrome and Flash to ensure you have the latest security fixes.
Allowing Flash on specific websites
In Chrome, Flash is disabled by default for security reasons. However, you can manually allow specific websites to run Flash if you trust them. Here’s how you can do it:
- Launch Google Chrome and navigate to the website that requires Flash.
- Once on the website, click on the padlock icon to the left of the URL in the address bar.
- In the drop-down menu, locate the “Flash” option.
- Click on the drop-down menu and select “Allow.”
- Refresh the page, and Flash content on that specific website should now load and run.
By allowing Flash on specific websites, you have more control over which sites can use Flash and can prevent Flash content from running on sites you do not trust or are unfamiliar with. This helps to enhance the security of your browsing experience.
It’s important to remember that allowing Flash on websites should be done with caution. Flash is known for its security vulnerabilities, and enabling it on untrusted sites can expose your computer to potential risks. Be sure to only enable Flash on trusted websites and keep your browser and Flash Player up to date to minimize security risks.
As more websites transition away from Flash and adopt newer web technologies, the need to allow Flash on specific websites will become less common. It is recommended to explore alternative solutions to Flash whenever possible to ensure compatibility with modern web standards and maintain a secure browsing experience.
Disabling Flash in Chrome
With the deprecation of Flash and the shift towards more modern web technologies, it is advisable to disable Flash in Chrome for security and performance reasons. Here’s how you can disable Flash in Chrome:
- Open Google Chrome on your computer.
- In the address bar, type “chrome://settings/content/flash” and press Enter.
- Alternatively, you can access the settings by clicking the three-dot menu icon in the top right corner of the Chrome window, selecting “Settings,” then scrolling down and clicking on “Advanced,” followed by “Content settings.”
- On the Flash settings page, toggle the switch next to “Ask first (recommended)” to disable Flash.
By disabling Flash in Chrome, you can protect your computer from potential security vulnerabilities associated with Flash. Additionally, disabling Flash can help improve the performance and stability of your browser, as Flash content is resource-intensive and can slow down your browsing experience.
It’s worth noting that starting from Chrome version 76, Flash is disabled by default and cannot be enabled again. This is part of the ongoing efforts by both Google and Adobe to phase out Flash and encourage the adoption of more secure and efficient web technologies.
If you still come across websites or applications that rely on Flash, you may need to consider alternative solutions or reach out to the website’s developer to encourage them to transition to modern web technologies.
Updating Flash in Chrome
Keeping your Flash Player up to date is essential for security and compatibility reasons. To update Flash in Chrome, follow these steps:
- Open Google Chrome on your computer.
- In the address bar, type “chrome://components” and press Enter.
- Scroll down the list of components to find “Adobe Flash Player.”
- If an update is available, you’ll see an “Update” button next to Adobe Flash Player.
- Click on the “Update” button.
- Wait for the update process to complete.
- After the update is finished, restart your Chrome browser to apply the changes.
It’s recommended to regularly check for updates and install them promptly to ensure you have the latest security patches and performance improvements. Flash updates are crucial, as they often fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors.
However, it’s important to note that as Flash is being phased out, Adobe will eventually stop providing updates and support for Flash Player. This means that in the near future, Flash updates may no longer be available, further emphasizing the need to transition to alternative technologies.
As a responsible internet user, it’s important to keep your software, including Flash Player, up to date to protect yourself from potential security risks. Additionally, staying updated ensures compatibility with the latest web standards and technologies.
Troubleshooting common Flash issues
While Flash can enhance your web browsing experience, it can sometimes encounter issues that may prevent it from working correctly. Here are some common Flash issues you may encounter and how to troubleshoot them:
- Flash is not working: If Flash isn’t working on certain websites, try clearing your browser cache and cookies. If the issue persists, verify that Flash is enabled in Chrome settings. Additionally, make sure you have the latest version of Flash installed. If none of these steps work, the website itself may have compatibility issues with Flash or be using outdated Flash content.
- Flash crashes or freezes: If Flash crashes or freezes frequently, try disabling any browser extensions that may be conflicting with Flash. It’s also recommended to update both Chrome and Flash Player to the latest versions. If the problem persists, you can try disabling hardware acceleration in Flash settings or seek assistance from Adobe’s Flash Player forums for further troubleshooting steps.
- Security warnings for Flash: If you receive security warnings about Flash, it’s crucial to update Flash to the latest version as soon as possible. These warnings usually indicate that there are vulnerabilities in the current version of Flash that could be exploited by malicious actors. Keeping Flash up to date is essential to ensure the security of your computer and browsing experience.
If you continue to experience issues with Flash, it may be worthwhile to consider transitioning to alternative technologies that offer similar functionalities but with fewer security vulnerabilities and better performance. HTML5 has become the standard for web development and offers a wide range of multimedia capabilities, reducing the reliance on Flash.
Additionally, as Flash reaches its end-of-life, more websites and applications are moving away from it and adopting modern web technologies. It’s important to stay updated with the latest trends in web development to ensure a seamless and secure browsing experience.
Using alternative solutions to Flash on Chrome
With the gradual phasing out of Flash and the industry-wide transition to more modern web technologies, it’s important to explore alternative solutions that provide similar functionality without the security risks associated with Flash. Here are some alternative solutions you can use on Chrome:
- HTML5: HTML5 is a markup language that has become the standard for web development. It offers a wide range of multimedia capabilities, including audio and video playback, animations, and interactive elements. Many websites and applications have already migrated to HTML5, making it the go-to choice for delivering rich content on the web.
- WebAssembly: WebAssembly is a binary instruction format that allows for high-performance execution of code on the web. It enables developers to run complex applications, including games and simulations, directly in the browser without the need for plugins like Flash.
- JavaScript libraries and frameworks: JavaScript libraries and frameworks, such as React, Angular, and Vue.js, provide powerful tools for building interactive web applications. They offer a wide range of features, including animation libraries, media players, and UI components that can replace Flash-based functionalities.
- Browser extensions: Some browser extensions can help emulate or replace Flash functionality. However, exercise caution when using extensions, and ensure they come from trusted sources to avoid potential security risks. Remember, Flash is still a deprecated technology, and it’s advisable to transition away from it whenever possible.
It’s important for both developers and users to stay updated with the latest web development trends and technologies. By embracing modern solutions such as HTML5, WebAssembly, and JavaScript libraries, we can move away from the reliance on Flash and ensure a safer, more efficient, and future-proof web experience.