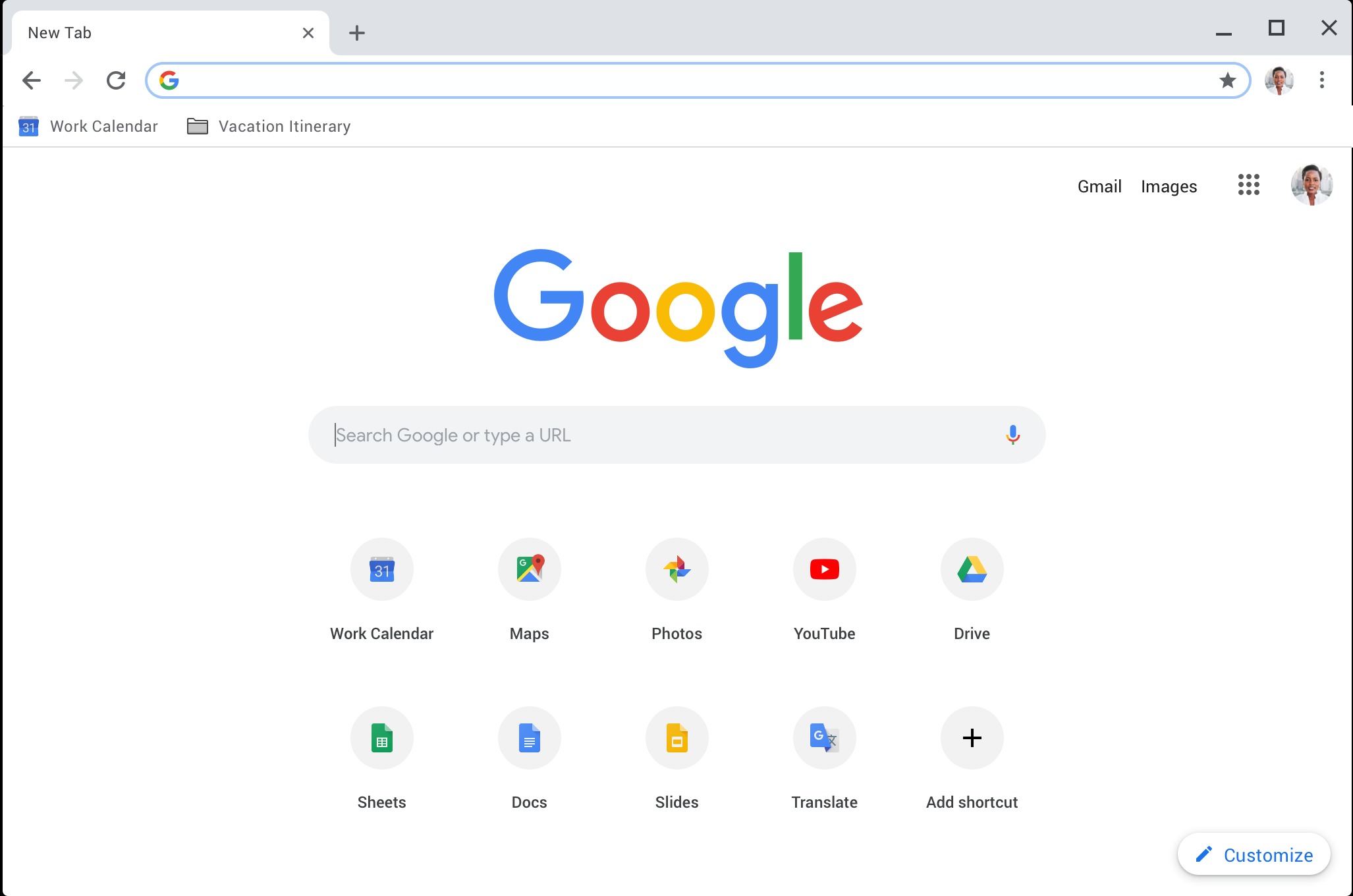
What is a web browser?
A web browser is a software application that allows users to access and navigate the internet. It serves as a gateway between users and the vast array of information available online. With a web browser, users can visit websites, view webpages, download files, stream videos, and engage in various online activities.
Web browsers utilize a rendering engine to interpret and display the content of webpages. They interpret the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code behind each webpage, allowing users to view text, images, videos, and interactive elements in a visually appealing and interactive manner.
Web browsers also provide essential functionalities such as bookmarking, history tracking, and tab management. They enable users to save their favorite websites for quick access, keep track of previously visited sites, and organize multiple webpages in separate tabs for efficient multitasking.
Commonly used web browsers include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari, and Opera. Each browser offers its unique set of features and capabilities, catering to different user preferences and requirements.
Web browsers have evolved significantly over the years, becoming faster, more secure, and user-friendly. With the advancements in web technologies, such as HTML5 and CSS3, browsers can now support complex web applications, interactive media, and responsive designs.
Additionally, web browsers play a vital role in ensuring a seamless and secure online experience. They incorporate various security measures, including built-in phishing and malware protection, secure data transmission (HTTPS), and options to clear browsing history and cookies.
The birth of Google Chrome
Google Chrome, developed by Google, is one of the most popular web browsers in the world. It was first released on September 2, 2008, as a fresh and innovative addition to the browser market. Google designed Chrome with a vision to provide users with a faster, more secure, and user-friendly browsing experience.
One of the notable factors that set Google Chrome apart from its competitors was its minimalist design. Chrome featured a clean and simple user interface, with a single search and address bar, known as the Omnibox, at the top. This allowed users to perform searches and enter website addresses in the same space, making navigation and searching more streamlined.
Another significant aspect of Google Chrome was its focus on speed. The browser introduced a new JavaScript engine, called V8, which was designed to execute JavaScript code faster than other browsers. This improvement resulted in quicker webpage loading times, smoother browsing, and enhanced performance.
Furthermore, Google Chrome pioneered the concept of tabbed browsing, taking it to a new level. Users could open multiple tabs within a single browser window, allowing them to switch between different websites effortlessly. Chrome also introduced individual tab processes, isolating each tab to prevent one crashing tab from affecting the entire browsing experience.
Google Chrome gained popularity rapidly, surpassing other browsers in terms of usage and market share. Its constant updates and improvements further solidified its position as a top choice among internet users.
In recent years, Chrome has expanded its reach beyond traditional desktop platforms. Google developed versions of the browser for mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, enabling users to enjoy a seamless browsing experience across different devices and operating systems.
With its continuous innovation and commitment to user satisfaction, Google Chrome remains a dominant force in the web browser market. It continues to push boundaries, introducing new features, improving performance, and ensuring a secure browsing environment for millions of users worldwide.
Features and advantages of Google Chrome
Google Chrome is renowned for its impressive array of features and advantages that enhance the browsing experience. Here are some of the standout features that make Chrome a popular choice among users:
1. Speed and Performance: Chrome’s cutting-edge technologies, such as the V8 JavaScript engine, ensure fast and responsive browsing. It prioritizes efficiency and delivers quick page loading times, enabling users to navigate the web with ease.
2. Simplicity and User-Friendly Interface: Chrome’s minimalist design makes it easy to use for both beginners and experienced users. The clean interface focuses on essential elements, allowing users to navigate effortlessly and find what they need quickly.
3. Tab Management: Chrome revolutionized tabbed browsing by introducing features like tab stacking and tab pinning. Users can group related tabs together, collapse them into a single tab, or pin frequently accessed tabs for instant access.
4. Customization: Chrome offers numerous customization options, allowing users to personalize their browsing experience. Users can customize the browser’s appearance by choosing from a wide range of themes, extensions, and wallpapers.
5. Syncing and Integration: Chrome’s sync feature enables users to synchronize their bookmarks, history, passwords, and settings across multiple devices. It seamlessly integrates with other Google services, such as Gmail and Google Drive, making it convenient for users with Google accounts.
6. Web Developer Tools: Developers appreciate Chrome’s built-in developer tools, which provide powerful functionalities for coding, debugging, and analyzing web applications. The Inspect tool allows for real-time examination and modification of webpage elements.
7. Security and Privacy: Chrome prioritizes user safety by proactively protecting against malware, phishing attempts, and other online threats. It offers features like Safe Browsing, automatic updates, and sandboxing for a secure browsing environment.
8. Incognito Mode: Chrome’s Incognito mode allows users to browse privately, without leaving any traces of their browsing history, cookies, or form data. This feature is ideal for those who want to keep their online activities private.
9. Cross-Platform Support: Chrome is available on various platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. This cross-platform compatibility ensures consistent browsing experiences across different devices and operating systems.
10. Rich Selection of Extensions: The Chrome Web Store offers a vast library of extensions and apps that enhance functionality and expand the browser’s capabilities. These extensions range from productivity tools to ad-blockers and can be easily installed to cater to individual needs.
With its impressive features and continuous updates, Google Chrome remains a top choice for users seeking a fast, secure, and customizable web browsing experience.
How to download and install Google Chrome
Downloading and installing Google Chrome is a simple and straightforward process. Follow these steps to get started:
- Open your current web browser: Start by opening your existing web browser, such as Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, or Safari.
- Go to the Google Chrome website: In the address bar of your current browser, type in “www.google.com/chrome” and press Enter. This will take you to the official Google Chrome website.
- Download Chrome: On the Google Chrome website, you will see a large blue button that says “Download Chrome.” Click on this button to start the download process.
- Review the Terms of Service: Before the download begins, you may be asked to review and accept the Google Chrome Terms of Service. Make sure to read through the terms and click on the “Accept and Install” button if you agree to them.
- Run the installer: Once the download is complete, locate the downloaded file (usually in your “Downloads” folder) and double-click on it to run the installer.
- Allow permissions: If prompted by your operating system or security software, allow the installer to make changes to your device. This step is necessary to complete the installation process.
- Follow the installation prompts: The Google Chrome installer will guide you through the installation process. You may be asked to select an installation location, create desktop shortcuts, or set Chrome as your default browser. Follow the prompts and make your preferred selections.
- Complete the installation: Once you have made your selections and confirmed any additional settings, click on the “Install” button to proceed with the installation. The installer will then install Google Chrome on your device.
- Launch Google Chrome: Once the installation is complete, you can launch Google Chrome by clicking on the “Open” button or by finding the Chrome icon on your desktop or in the Start menu.
Congratulations! You have successfully downloaded and installed Google Chrome. You can now enjoy the fast, secure, and feature-rich browsing experience that Chrome offers.
The Chrome user interface
Google Chrome offers a clean and intuitive user interface that prioritizes simplicity and ease of use. Understanding the various elements of the Chrome user interface can help you navigate the browser efficiently. Here’s an overview of the key components:
1. Omnibox: Located at the top of the Chrome window, the Omnibox functions as both the address bar and search bar. You can enter website URLs or search queries directly into the Omnibox to quickly navigate to a webpage or perform a search.
2. Tab bar: Below the Omnibox is the tab bar, where you can see all the open tabs in your browser. Each tab represents a separate webpage or website. You can click on a tab to switch to it or use keyboard shortcuts to navigate between tabs.
3. New Tab button: To open a new empty tab, click on the “+” icon located at the end of the tab bar or use the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + T” (Windows) or “Command + T” (Mac).
4. Back and forward buttons: These buttons, usually located next to the Omnibox, allow you to navigate backward and forward through previously visited pages. You can also use the keyboard shortcuts “Alt + Left Arrow” (Windows) or “Command + [ ” (Mac) to go back and “Alt + Right Arrow” (Windows) or “Command + ]” (Mac) to go forward.
5. Bookmarks bar: The bookmarks bar, located below the Omnibox, allows you to save and access your favorite websites with just one click. You can drag and drop bookmarks onto the bar for quick access to your most frequently visited sites.
6. Menu icon: The menu icon, represented by three vertical dots at the top right corner of the Chrome window, opens up a drop-down menu with various options and settings. Here, you can access features like history, downloads, settings, extensions, and more.
7. Customize and control Chrome: Clicking on the menu icon and selecting the “Settings” option will take you to the Chrome settings page. Here, you can customize and personalize your browsing experience by adjusting options related to appearance, search engine preferences, privacy and security settings, extensions, and more.
8. Incognito mode: Chrome’s Incognito mode allows you to browse privately, without leaving traces of your browsing history, cookies, or form data. You can open an Incognito window by clicking on the menu icon and selecting “New Incognito Window” or by using the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + Shift + N” (Windows) or “Command + Shift + N” (Mac).
Understanding the different components of the Chrome user interface will help you navigate the browser seamlessly and make the most of its features and functionalities.
Customizing Google Chrome
Google Chrome offers various customization options that allow you to personalize your browsing experience. By customizing Chrome, you can enhance its appearance, improve functionality, and tailor it to your specific preferences. Here are some ways you can customize Google Chrome:
1. Themes: Chrome allows you to change its appearance by applying different themes. You can access the Themes page by clicking on the menu icon, selecting “Settings,” and then navigating to the “Appearance” section. Choose a theme from the Chrome Web Store or create a custom theme using your own background image and color scheme.
2. Extensions: Chrome offers a vast library of extensions that provide additional functionality and features. These can be found in the Chrome Web Store. From ad blockers to productivity tools, there are extensions to suit every need. To install an extension, simply click on the menu icon, go to “More tools,” and select “Extensions.” From there, you can browse, search, and install extensions to enhance your browsing experience.
3. Bookmarks bar: The bookmarks bar in Chrome allows you to save and access your favorite websites with ease. To add a website to the bookmarks bar, simply click on the star icon located at the right side of the Omnibox and select the “Bookmarks bar” option. You can organize your bookmarks by right-clicking on the bookmarks bar and selecting “Add folder” or “New bookmark.”
4. Startup page: You can customize the page that Chrome displays when you open a new tab or launch the browser. To do this, click on the menu icon, select “Settings,” and go to the “On startup” section. Choose whether you want to open a specific set of pages, open the pages that were open last, or use the default Chrome start page.
5. Chrome flags: Chrome flags are experimental features that allow you to enable or disable certain functionalities in Chrome. To access Chrome flags, type “chrome://flags” in the Omnibox and press Enter. Here, you can enable or disable various experimental features. However, be cautious as these features may be in development and can impact the stability of the browser. Make changes to flags with care.
6. Default search engine: Chrome allows you to choose your preferred search engine. To change the default search engine, click on the menu icon, select “Settings,” and go to the “Search engine” section. Here, you can select your preferred search engine from the list or add a custom search engine of your choice.
7. Clear browsing data: If you want to customize the browsing experience by removing your browsing history, cookies, or other saved data, you can do so by clicking on the menu icon, selecting “More tools,” and choosing “Clear browsing data.” From there, you can select the types of data you want to delete and the time range you want to clear.
By exploring and utilizing these customization options, you can make Google Chrome a personalized and tailored browser that suits your preferences and enhances your browsing experience.
Working with tabs in Google Chrome
Google Chrome offers a powerful tabbed browsing experience that allows users to open multiple webpages simultaneously within a single browser window. Tabs in Chrome offer a convenient way to organize and manage your browsing sessions. Here are some tips and tricks for working with tabs in Google Chrome:
Opening a new tab: To open a new tab, you can click on the “+” icon located at the end of the tab bar or press “Ctrl + T” (Windows) or “Command + T” (Mac) on your keyboard. Alternatively, you can middle-click on a link to open it in a new tab.
Switching between tabs: To switch between open tabs, simply click on the tab you want to navigate to. You can also use the keyboard shortcuts “Ctrl + Tab” (Windows) or “Command + Option + Right Arrow” (Mac) to cycle through tabs in the forward direction, and “Ctrl + Shift + Tab” (Windows) or “Command + Option + Left Arrow” (Mac) to cycle through tabs in the backward direction.
Opening a link in a new tab: You can open a link in a new tab by either right-clicking on the link and selecting “Open link in new tab” or by holding down the Ctrl key (Windows) or Command key (Mac) while clicking on the link.
Duplicating a tab: To duplicate an existing tab, right-click on the tab and select “Duplicate” from the context menu. This creates an exact copy of the current webpage in a new tab.
Reordering tabs: You can rearrange the order of tabs by simply clicking and dragging them to a new position on the tab bar. This allows you to organize your tabs based on your preference.
Pin tabs: If you have frequently accessed websites or web applications, you can pin them to the left side of the tab bar by right-clicking on the tab and selecting “Pin tab” from the context menu. Pinned tabs take up less space and can be easily accessed with a single click.
Merging all windows: If you have multiple Chrome windows open and want to consolidate them into a single window with separate tabs, you can do so by right-clicking on a tab in one window and selecting “Move all to new window” from the context menu.
Saving tabs for later: If you want to save a set of open tabs to revisit later, you can create a new bookmark folder by right-clicking on a tab and selecting “Bookmark all tabs.” This will save all the open tabs as bookmarks within a new folder that you can access from the bookmarks bar or bookmarks menu.
Closing tabs: To close a single tab, click on the small “x” icon on the right side of the tab. You can also use the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + W” (Windows) or “Command + W” (Mac) to close the current tab. To close multiple tabs simultaneously, press “Ctrl + Shift + W” (Windows) or “Command + Shift + W” (Mac).
By mastering these tab management techniques, you can optimize your browsing experience and efficiently navigate through multiple webpages using Google Chrome.
Managing bookmarks and history
Google Chrome offers convenient features for managing your bookmarks and browsing history, allowing for easy access to your favorite websites and the ability to revisit previously visited pages. Here are some tips on how to effectively manage bookmarks and history in Google Chrome:
Bookmarks:
Adding a bookmark: To bookmark a webpage, click on the star icon located at the end of the Omnibox. A dialog box will appear, allowing you to choose the name and location for the bookmark. You can also add tags or select a folder to organize your bookmarks efficiently.
Organizing bookmarks into folders: To keep your bookmarks organized, right-click on the bookmarks bar or the bookmarks menu, and select “Add folder.” Give the folder a name and drag and drop bookmarks into the folder for easy access.
Editing and deleting bookmarks: To edit or delete a bookmark, right-click on the bookmark and select the appropriate option from the context menu. You can edit the name, URL, and folder location of a bookmark or choose to delete it altogether.
Importing and exporting bookmarks: Chrome allows you to import bookmarks from other browsers or export your bookmarks for backup or use on a different device. To import or export bookmarks, go to the Chrome menu, select “Bookmarks,” and choose the “Import bookmarks and settings” or “Export bookmarks” option.
History:
Viewing browsing history: To view your browsing history, click on the menu icon, go to “History,” and select the “History” option. A new tab will open, displaying your entire browsing history organized by date. You can search for specific websites or use the filter options to narrow down your search.
Clearing browsing history: If you want to delete specific items or clear your entire browsing history, go to the Chrome menu, select “History,” and click on the “Clear browsing data” option. From the dialog box, you can choose the time range and the types of data you want to clear, such as browsing history, cookies, and cached images and files.
Searching browsing history: If you want to find a specific webpage you’ve visited in the past, you can use the search bar at the top of the history page. Enter keywords related to the website or page you’re looking for, and Chrome will populate the results based on your search query.
Opening closed tabs: Accidentally closed a tab? You can quickly reopen recently closed tabs by right-clicking on the tab bar and selecting the “Reopen closed tab” option. You can also use the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + Shift + T” (Windows) or “Command + Shift + T” (Mac) to reopen the most recently closed tab.
By effectively managing your bookmarks and browsing history in Google Chrome, you can keep track of your favorite websites, organize your bookmarks efficiently, and easily revisit previously visited pages.
Privacy and security features in Google Chrome
Google Chrome prioritizes user privacy and security, offering a range of features and settings to protect your browsing experience. Here are some privacy and security features in Google Chrome:
Safe Browsing: Chrome’s Safe Browsing feature helps protect you from malicious websites and downloads. It automatically warns you if you’re about to visit a harmful site or download potentially dangerous files, helping to keep your computer and personal information safe.
Sandboxing: Chrome utilizes a sandboxing technique that isolates each tab and browser process. This means that if a tab or process encounters malware or other security threats, it remains contained and does not affect the rest of your browsing experience. Sandboxing adds an extra layer of protection against potential threats.
Automatic updates: Chrome regularly updates itself in the background to ensure that you have the latest security patches and bug fixes. This helps protect you from newly discovered vulnerabilities and keeps your browser up to date with the latest security features.
Privacy settings: Chrome offers various privacy settings that allow you to control how your browsing data is collected and used. In the Chrome settings, you can manage options such as clearing your browsing history, disabling third-party cookies, managing website permissions, and controlling how Chrome handles your passwords and autofill data.
Incognito mode: Chrome’s Incognito mode provides a private browsing experience. When you open a new Incognito window, Chrome does not save your browsing history, cookies, or form data. It also blocks websites from tracking your activity. To open an Incognito window, click on the menu icon and select “New Incognito Window,” or use the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + Shift + N” (Windows) or “Command + Shift + N” (Mac).
Privacy Sandbox: Google is working on developing the Privacy Sandbox, an initiative aimed at improving privacy on the web while still allowing personalized experiences. This includes exploring alternative methods for targeted advertising and reducing reliance on third-party cookies.
Extensions and permissions: When installing extensions from the Chrome Web Store, Chrome prompts you to review the requested permissions. This allows you to make informed decisions about the access and data that extensions have. Be cautious when installing extensions and only grant permissions to trusted sources.
Clear browsing data: Chrome allows you to easily clear your browsing data, including your browsing history, cookies, cached images, and files. You can customize the time range and types of data you want to delete by going to the Chrome menu, selecting “History,” and clicking on the “Clear browsing data” option.
By leveraging these privacy and security features in Google Chrome, you can browse the web with confidence, knowing that your personal information is protected and your browsing experience is secure.
Using Chrome extensions and apps
Google Chrome offers a wide range of extensions and apps that expand the functionality and enhance the browsing experience. These extensions and apps can help with productivity, security, entertainment, and much more. Here’s how you can make the most out of Chrome extensions and apps:
Accessing the Chrome Web Store: To explore and install extensions and apps, visit the Chrome Web Store. You can find the web store by clicking on the menu icon, selecting “More tools,” and choosing “Extensions” or “Web Store.” From there, you can browse the featured, popular, or recommended extensions and apps, or search for specific ones using keywords.
Installing Chrome extensions: Once you find an extension you want to install, click on the “Add to Chrome” button. A confirmation dialog box will appear, providing you with details about the extension and the permissions it requires. Review the details, and if you’re satisfied, click “Add extension” to install it. The extension will then appear in your browser’s toolbar or menu bar.
Managing Chrome extensions: To manage your installed extensions, click on the menu icon, go to “More tools,” and select “Extensions.” Here, you can enable or disable extensions, remove them completely, or access their unique settings or options. Remember to regularly review your installed extensions to ensure they are still useful and trustworthy.
Using Chrome apps: Chrome apps are separate applications that you can install through the Chrome Web Store. These apps provide standalone functionality and can be accessed from your desktop or the Chrome App Launcher. To install a Chrome app, visit the Chrome Web Store, search for the desired app, and click the “Add to Chrome” button, similar to installing extensions.
Managing Chrome apps: Installed Chrome apps can be managed by clicking on the menu icon, going to “More tools,” and selecting “Extensions.” At the top of the Extensions page, you will find a section for Chrome apps. From here, you can enable or disable apps, remove them, or rearrange their order in the Chrome App Launcher.
Updating Chrome extensions and apps: Chrome automatically keeps your installed extensions and apps up to date. Updates are installed in the background without requiring any manual intervention. However, you can check for pending updates by going to the Chrome menu, selecting “More tools,” and choosing “Extensions” or “Updates” from the list.
Exploring popular extensions and apps: The Chrome Web Store offers various categories of extensions and apps, including productivity, communication, entertainment, education, and more. Popular extensions include ad-blockers, password managers, note-taking tools, grammar checkers, and video downloaders. Explore the store to find extensions and apps that suit your needs and interests.
Reading extension reviews and ratings: Before installing an extension, be sure to check the reviews and ratings provided by other users. This can help you determine if the extension is reliable, effective, and free from any potential security risks.
By utilizing the wide range of extensions and apps available in the Chrome Web Store, you can enhance your browsing experience, increase productivity, and customize Chrome to suit your specific needs and preferences.
Syncing and using Google services in Chrome
Google Chrome offers seamless integration with various Google services, allowing you to sync your data, access your Google account, and utilize Google’s suite of tools and features. Here’s how you can sync and make the most of Google services in Chrome:
Signing in to Chrome:
Syncing your data: By signing in to Chrome with your Google account, you can sync your browsing data across multiple devices. This includes bookmarks, history, passwords, autofill information, open tabs, and even installed extensions and apps. To sign in, click on the menu icon, select “Settings,” and click “Sign in to Chrome.”
Managing Chrome data: You can control which types of data are synced by going to the Chrome settings, clicking on your profile icon, and selecting “Sync and Google services.” From there, you can enable or disable sync for specific categories, such as passwords or browsing history.
Accessing Google services:
Gmail, Google Drive, and other services: Once you are signed in to Chrome, you can easily access your Google services like Gmail, Google Drive, Google Calendar, and Google Docs by clicking on the “Apps” icon in the bookmarks bar or by visiting the respective websites. These services allow for seamless collaboration, file storage, and productivity in your browser.
Chrome and Google search integration: Chrome offers a built-in search box in the Omnibox, which is powered by Google search. You can enter your search queries directly into the Omnibox and receive instant search suggestions and results. This integration ensures a consistent and reliable search experience.
Using Chrome with Google Assistant: If you have Google Assistant enabled on your device, you can use voice commands to perform various actions in Chrome. This includes opening websites, conducting searches, navigating to specific tabs, and more. Simply activate Google Assistant and issue voice commands to control your browsing experience.
Chrome Remote Desktop: Google offers a service called Chrome Remote Desktop that allows you to access and control your computer remotely using Chrome. With this feature, you can securely connect to your home or work computer from anywhere, enabling you to retrieve files, troubleshoot issues, or access applications on the go.
Extensions and apps from the Chrome Web Store: The Chrome Web Store offers a vast range of extensions and apps, including those developed by Google. From tools like Google Keep for note-taking, Google Translate for language assistance, to Google Calendar for managing your schedule, these extensions and apps enhance your productivity and access to Google’s services.
Google Smart Lock: Google Smart Lock is a feature that allows you to securely store your passwords and sign in to websites automatically. When you’re signed in to Chrome, you can enable this feature to save and sync your passwords across devices. This saves you from the hassle of remembering and entering passwords manually.
By syncing your data and utilizing Google services within Chrome, you can streamline your workflow, access your information seamlessly, and benefit from the wide range of tools and features that Google offers.
Keyboard shortcuts and other tips and tricks
Google Chrome offers a variety of keyboard shortcuts and hidden features that can help you navigate the browser more efficiently and perform tasks quickly. Discover these shortcuts and tips to enhance your Chrome browsing experience:
1. Tab management:
- Ctrl + 1-8: Switch to a specific tab based on its position from left to right.
- Ctrl + 9: Switch to the last tab.
- Ctrl + Tab: Cycle through open tabs in the forward direction.
- Ctrl + Shift + Tab: Cycle through open tabs in the backward direction.
- Ctrl + W: Close the current tab.
- Ctrl + Shift + T: Reopen the most recently closed tab.
2. Page navigation:
- Space bar: Scroll down a full page length in a webpage.
- Shift + Space bar: Scroll up a full page length in a webpage.
- Alt + Left Arrow: Go back to the previous page.
- Alt + Right Arrow: Go forward to the next page.
- Ctrl + F: Open the find bar to search for text on the current page.
3. Address bar and search:
- Ctrl + L: Highlight the URL in the address bar for quick editing.
- Ctrl + Enter: Automatically add “www.” and “.com” to whatever is typed in the address bar, then load the website.
- Ctrl + K: Move the cursor to the address bar for a quick search.
4. Webpage actions:
- Ctrl + S: Save the current webpage as a bookmark.
- Ctrl + P: Print the current webpage.
- Ctrl + Shift + B: Toggle the bookmarks bar on or off.
- Ctrl + + (Plus key): Zoom in on the webpage.
- Ctrl + – (Minus key): Zoom out on the webpage.
- Ctrl + 0 (Zero key): Reset the webpage zoom level to default.
5. Miscellaneous tips and tricks:
- Drag and drop: Rearrange tabs by clicking and dragging them to a new location on the tab bar.
- Customize the new tab page: Access the Chrome settings, click on “Appearance,” and select a custom URL, image, or set of shortcuts for your new tab page.
- Right-click menu options: Right-click on various elements on a webpage or within the browser to access context-specific options and settings.
- Manage multiple user profiles: Click on the profile icon on the top right corner of Chrome to add and switch between user profiles. Each profile can have its own set of bookmarks, extensions, and settings.
- Task Manager: Open the Chrome Task Manager by pressing “Shift + Esc” to view and manage individual processes and tabs, monitor memory usage, and identify and close any problematic tabs or extensions.
By utilizing these keyboard shortcuts and applying these tips and tricks, you can navigate Chrome more efficiently, streamline your browsing tasks, and uncover additional functionalities that enhance your overall browsing experience.
Troubleshooting common issues with Google Chrome
While Google Chrome is a reliable and widely-used browser, occasional issues may arise. Here are some common problems users encounter with Chrome and their possible solutions:
1. Slow performance or freezing:
- Clear browsing data: Go to the Chrome menu, select “More tools,” and click on “Clear browsing data.” Clearing your history, cookies, and cached files can improve performance.
- Disable extensions: Some extensions can slow down Chrome. Go to the Chrome menu, select “More tools,” then “Extensions.” Disable or remove any extensions that may be causing the issue.
- Hardware acceleration: In Chrome settings, go to “Advanced,” then under the “System” section, toggle off “Use hardware acceleration when available.”
2. Crashing or not responding:
- Update Chrome: Make sure Chrome is up to date. Go to the Chrome menu, select “Help,” then “About Google Chrome.” Chrome will automatically check for updates and install if available.
- Disable conflicting software: Certain software, such as antivirus or firewall programs, can conflict with Chrome. Temporarily disable these programs and see if Chrome works properly.
- Reset Chrome settings: Go to Chrome settings, click on “Advanced,” then select “Restore settings to their original defaults” under the “Reset and clean up” section.
3. Error messages or pages not loading:
- Check your internet connection: Ensure that you have a stable and working internet connection. Try accessing other websites to see if the problem is specific to Chrome or your connection.
- Clear DNS cache: Open the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac), then type “ipconfig /flushdns” (Windows) or “sudo dscacheutil -flushcache” (Mac) and press Enter or Return.
- Disable proxy settings: In Chrome settings, go to “Advanced,” then under the “System” section, click on “Open proxy settings.” In the new window, disable any proxy settings that may be enabled.
4. Incompatibility with websites or web applications:
- Use Incognito mode: Open the website or web application in Chrome’s Incognito mode to eliminate any conflicts caused by extensions or cached data.
- Try a different browser: If a website or web application consistently has issues in Chrome, try accessing it in another browser to see if the problem persists.
- Check for browser updates: Make sure Chrome is updated to the latest version by going to the Chrome menu, selecting “Help,” then “About Google Chrome.”
Remember that troubleshooting steps may vary depending on the specific issue you are facing. If the problem persists, it is recommended to visit the Chrome Help Center or Google Support pages for more detailed and specific guidance.
Keeping Chrome up to date
Keeping your Google Chrome browser up to date is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, security, and access to the latest features and improvements. Here’s how you can keep Chrome up to date:
Automatic updates:
Chrome is designed to update automatically in the background, so you don’t have to worry about manually checking for updates. However, to ensure that automatic updates are enabled:
- Windows: Click on the menu icon, go to “Settings,” scroll down and click on “Advanced,” then under the “Privacy and security” section, select “Chrome updates.” Ensure that “Update Chrome automatically” is toggled on.
- Mac: Click on the menu icon, go to “Settings,” scroll down, and click on “Advanced,” then under the “Privacy and security” section, select “Chrome updates.” Ensure that “Update Chrome automatically” is toggled on.
- Linux: Chrome updates are managed through your system’s package manager. Make sure to regularly update your Linux distribution to receive the latest Chrome updates.
Manually checking for updates:
If you want to manually check for updates or ensure that you’re running the latest version of Chrome:
- Windows and Mac: Click on the menu icon, go to “Help,” then select “About Google Chrome.” Chrome will automatically check for updates and prompt you to install them if available. If an update is available, click on the “Relaunch” button to apply the update.
- Linux: Chrome updates are managed through your system’s package manager. Check with your Linux distribution’s documentation for instructions on how to update Chrome.
Benefits of keeping Chrome up to date:
Regularly updating Chrome offers several key benefits:
- Security: Updates often include important security patches that address vulnerabilities and protect you against emerging threats.
- Performance and stability: Updates can improve the overall performance and stability of the browser, allowing for smoother and more efficient browsing.
- New features and enhancements: Updates may introduce new features, tools, and enhancements that enhance your browsing experience and provide additional functionalities.
- Compatibility: Staying up to date with Chrome ensures compatibility with the latest web technologies and standards, allowing you to access and interact with websites and web applications seamlessly.
By enabling automatic updates or regularly checking for updates manually, you can ensure that you’re running the latest version of Google Chrome and enjoy the benefits of enhanced security, performance, and access to new features.