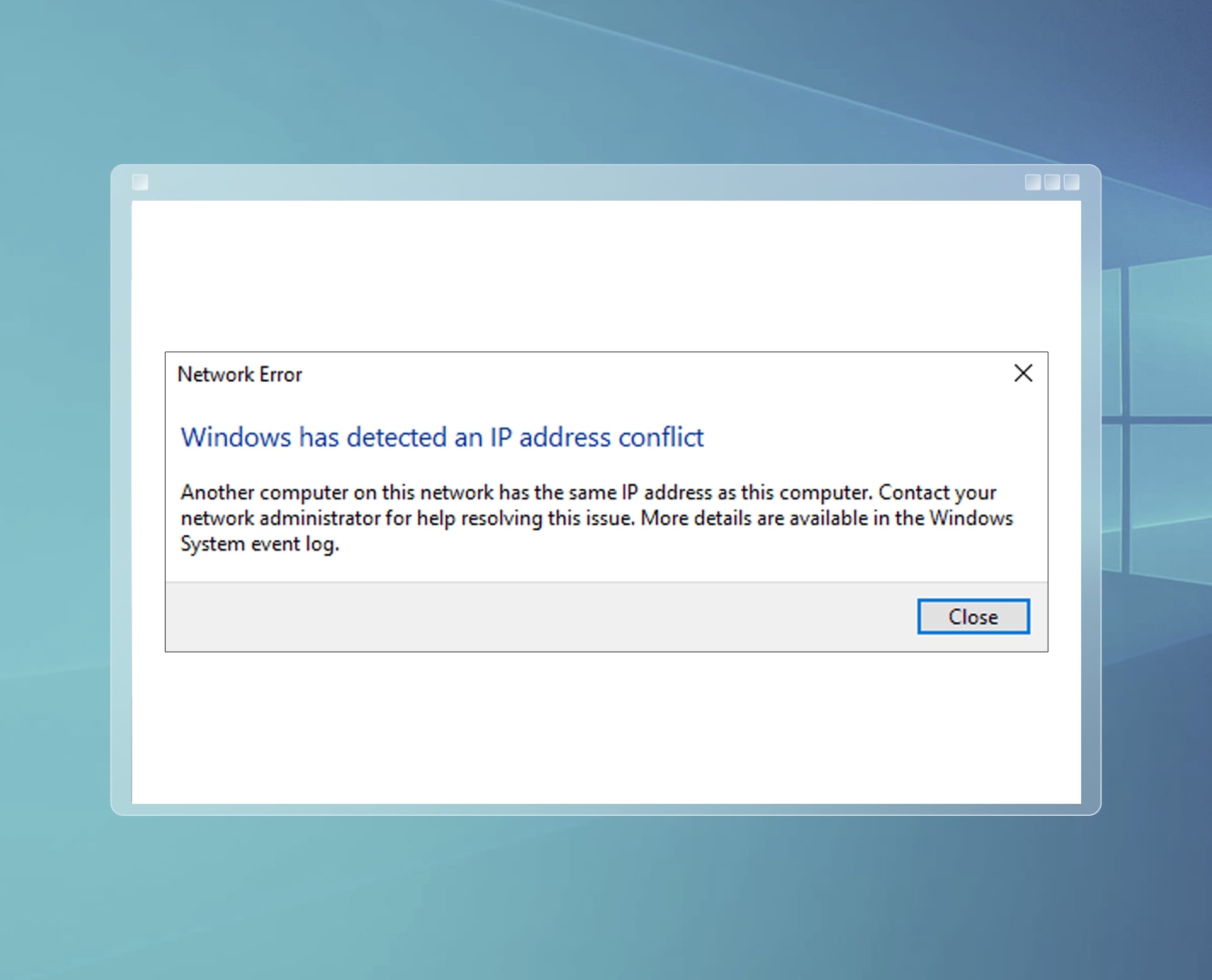
What Is an IP Address?
An IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It serves as the device’s identifier, allowing it to send and receive data over the internet or a local network. Think of it as a physical address for your device in the virtual world.
IP addresses are composed of four sets of numbers, separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.1. Each set can range from 0 to 255, providing a total of over 4 billion possible combinations. This addressing system ensures that every device on the network has a unique identification.
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6). IPv4, the most widely used protocol, assigns addresses in the familiar dotted-decimal format. However, with the proliferation of internet-enabled devices, the world is transitioning to IPv6 to accommodate the growing demand for unique IP addresses.
IP addresses play a crucial role in enabling communication between devices on the internet. They allow data packets to be routed accurately, ensuring that information reaches its intended destination. In addition, IP addresses are vital for various network tasks, such as port forwarding, remote access, and network troubleshooting.
Understanding IP addresses is essential for managing networks, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and securing network resources. Whether you’re setting up a home network or working in an IT environment, having a basic understanding of IP addresses is beneficial.
Understanding IP Address Conflict
An IP address conflict occurs when two or more devices in a network are assigned the same IP address. This conflict can disrupt network connectivity and cause various issues, such as intermittent internet connection, inability to access certain resources, or even complete network failure.
The primary reason for IP address conflicts is the dynamic assignment of IP addresses by network routers or DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) servers. When a device connects to a network, it requests an IP address from the DHCP server. In some cases, two or more devices may request the same IP address simultaneously, resulting in a conflict.
IP address conflicts can also arise due to misconfigurations or manual assignment of static IP addresses. This occurs when an administrator manually assigns an IP address to a device without first checking if it is already in use by another device on the network.
It’s important to note that IP address conflicts are more likely to occur in larger networks with numerous devices or in environments where there is a frequent influx of new devices connecting to the network, such as a bustling office or a busy public Wi-Fi hotspot.
When an IP address conflict occurs, the devices involved may experience connectivity issues, and network services may become unstable or inaccessible. Identifying and resolving IP address conflicts in a timely manner is crucial to maintain a smoothly running network.
In the next sections, we will explore how to identify and resolve IP address conflicts, as well as steps you can take to prevent them from happening in the first place.
Causes of IP Address Conflict
IP address conflicts can occur due to a variety of reasons. Understanding these causes can help you identify and resolve conflicts more effectively. Here are some common causes:
- Duplicate IP Address Assignment: One of the main causes of IP address conflicts is when multiple devices are assigned the same IP address. This can happen if the network router or DHCP server mistakenly assigns the same IP address to different devices at the same time.
- Misconfigured Network Settings: Improper network configurations can lead to IP address conflicts. This can include incorrectly configured subnet masks, gateway addresses, or DNS settings. These misconfigurations can result in devices using the same IP address, causing conflicts.
- Manual IP Address Assignment: When IP addresses are manually assigned to devices on a network, there is a greater chance of conflicts if proper precautions are not taken. Manual assignment without checking for existing IP address usage can lead to devices using the same IP address, causing conflicts.
- Faulty Network Hardware: Malfunctioning network hardware, such as routers or switches, can cause IP address conflicts. This can occur if the hardware fails to properly assign or manage IP addresses in the network. If a device receives an incorrect IP assignment from faulty hardware, conflicts may occur.
- Network Changes and Reconfiguration: When network changes or reconfigurations are made, such as adding new devices or modifying network settings, improper handling can lead to IP address conflicts. Failing to update DHCP server settings, forgetting to release previously assigned IP addresses, or not properly configuring new devices can all contribute to conflicts.
- IP Address Lease Renewal Failures: IP addresses are typically assigned on lease, allowing devices to use them for a certain period. If a device fails to renew the lease properly, it may attempt to use an IP address that has already been assigned to another device, leading to a conflict.
By understanding the causes of IP address conflicts, you can take proactive measures to prevent them and be better equipped to troubleshoot and resolve conflicts when they do occur.
How to Identify an IP Address Conflict
Identifying an IP address conflict is essential for resolving network connectivity issues and maintaining a smoothly running network. Here are a few ways to identify if an IP address conflict is occurring:
- Network Error Messages: Look out for error messages or warnings on your devices or network management tools that indicate an IP address conflict. These messages may mention duplicate IP addresses or failures in obtaining an IP address.
- Intermittent Network Connectivity: If you experience intermittent network connectivity, where the connection drops or becomes unstable at certain times, it could be a sign of an IP address conflict. Conflicting IP addresses can disrupt network communication and cause intermittent connection issues.
- Inability to Access Specific Resources: If you can’t access specific resources, such as shared drives, printers, or network services, it could be indicative of an IP address conflict. Conflicting IP addresses can prevent devices from properly accessing or communicating with network resources.
- IP Conflict Error Message: Some operating systems or network management tools may display error messages explicitly stating an IP address conflict. These messages will typically inform you that there is an IP address conflict and provide details about the conflicting IP addresses.
- Unexpected Device Behavior: Conflicting IP addresses can cause unexpected behavior in devices. This can include devices suddenly losing network connectivity, being unable to acquire or maintain an IP address, or experiencing frequent drops in connection.
- Monitoring Network Traffic: Network monitoring tools can help identify IP address conflicts by capturing and analyzing network traffic. Look for duplicate IP address usage or multiple devices using the same IP address in the network traffic logs.
By keeping an eye out for these signs, you can quickly identify if an IP address conflict is occurring in your network. Once identified, you can take the necessary steps to resolve the conflict and restore network stability.
Consequences of IP Address Conflict
IP address conflicts can have several consequences that can impact both individual devices and the entire network. Understanding these consequences is crucial for realizing the importance of resolving IP address conflicts promptly. Here are some common consequences of IP address conflicts:
- Intermittent Network Connectivity: One of the most noticeable consequences of an IP address conflict is intermittent network connectivity. Devices involved in the conflict may experience frequent drops in connection or irregular network behavior, making it difficult to perform tasks that require a stable network connection.
- Inability to Access Network Resources: IP address conflicts can disrupt the communication between devices and network resources, such as shared drives, printers, or network-attached services. When conflicts occur, affected devices may lose access to these resources or experience difficulties in interacting with them.
- Unexpected Device Behavior: Conflicting IP addresses can cause devices to behave unexpectedly. This can manifest as devices suddenly losing network connectivity, experiencing slowdowns in performance, or encountering random errors and interruptions while accessing network services.
- Network Disruptions: In severe cases, conflicts between crucial network devices can lead to complete network disruptions. Network servers, routers, or switches involved in an IP address conflict may fail to function properly, impacting the overall network performance and resource availability.
- Data Packet Collisions: IP address conflicts can result in data packet collisions within the network. When multiple devices use the same IP address, data packets can get misrouted or collide as they compete for the same IP address. This can lead to packet loss, delays, and reduced overall network efficiency.
- Security Vulnerabilities: IP address conflicts can introduce security vulnerabilities to the network. Conflicting IP addresses may allow unauthorized access to network resources if the conflicting device has different network permissions or authentication credentials. This can compromise network security and expose sensitive data.
It is important to address IP address conflicts promptly to mitigate these consequences and ensure a stable and secure network environment. Resolving conflicts will restore network connectivity, prevent disruptions, and safeguard the integrity of network resources and data.
Resolving IP Address Conflicts
Resolving IP address conflicts is essential to restore network connectivity and prevent further disruptions. Here are some steps you can take to resolve IP address conflicts:
- Release and Renew IP Addresses: In some cases, simply releasing and renewing IP addresses can resolve conflicts. To do this, go to the network settings on the affected device and release the current IP address. Then, request a new IP address from the DHCP server or assign a static IP address that is not in conflict with other devices on the network.
- Power Cycle Devices: Power cycling the devices involved in the IP address conflict can sometimes resolve the issue. Turn off the affected devices, including the modem, router, and any other networking equipment. After a few minutes, power them back on and allow them to reestablish connections and renegotiate IP address assignments.
- Check Network Configurations: Ensure that all network configurations, such as subnet masks, gateway addresses, and DNS settings, are correct. Incorrect configurations can lead to IP address conflicts. Verify that devices are using the appropriate settings and adjust them if necessary.
- Use Static IP Address Assignment: Instead of relying on dynamic IP address assignments from DHCP servers, consider assigning static IP addresses to devices on your network. Ensure that each device has a unique IP address and that there are no conflicts with other devices. Keep a record of all assigned static IP addresses to avoid future conflicts.
- Update DHCP Server Settings: If you are using a DHCP server, review and update its settings. Ensure that the range of IP addresses available for assignment does not overlap or conflict with statically assigned IP addresses or other devices on the network. Adjust the DHCP server’s configuration as needed.
- Configure IP Address Reservations: Some routers allow you to reserve specific IP addresses for certain devices. By creating IP address reservations in the router’s settings, you can ensure that certain devices always receive the same IP address, eliminating the possibility of conflicts with other devices.
- Reset Network Hardware: If all else fails, you may need to reset your network hardware to its factory settings. This can involve performing a factory reset on your router or modem, which will erase all customized settings and enable you to set up the network from scratch.
By following these steps, you can effectively resolve IP address conflicts and restore network connectivity. It’s essential to address conflicts promptly to ensure a stable and reliable network environment.
Basic Troubleshooting Steps for IP Address Conflicts
When encountering an IP address conflict, there are several basic troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the issue. These steps can help identify the conflicting devices and restore network connectivity. Here are some basic troubleshooting steps for IP address conflicts:
- Identify the Affected Devices: Determine which devices are experiencing connectivity issues or displaying IP address conflict messages. Make a note of the IP addresses involved in the conflict, as well as the devices associated with those IP addresses.
- Release and Renew IP Addresses: For devices experiencing conflicts, release their current IP addresses and request new ones. This can be done through the device’s network settings or by restarting the device. Ensure that the new IP addresses are not in conflict with any other devices on the network.
- Restart Network Devices: Restart the network router, modem, and any other networking equipment. Sometimes, a simple restart can help resolve IP address conflicts by allowing the devices to renegotiate their IP address assignments.
- Check Network Settings: Verify the network settings of the devices involved in the conflict. Ensure that the subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS settings are configured correctly. Incorrect settings can contribute to IP address conflicts. Make any necessary adjustments to align the settings properly.
- Disable and Enable Network Adapters: Disable and then enable the network adapters on the devices experiencing conflicts. This can refresh the network connection and help obtain a new IP address without conflicts.
- Connect Devices to Different Network Segments: If possible, connect the devices experiencing conflicts to different segments of the network. For example, if your network has multiple switches, connect the conflicting devices to different switches. This can help isolate the conflict to a specific network segment and minimize its impact on other devices.
- Use a Network Scanner: Utilize a network scanning tool to identify devices using conflicting IP addresses. The network scanner can provide a comprehensive view of all connected devices and their assigned IP addresses. This can help pinpoint the devices causing the conflicts.
- Factory Reset Network Hardware: As a last resort, consider performing a factory reset on your network router or modem. This will revert the device to its default settings and remove any custom configurations. Be aware that a factory reset will erase all settings, so make sure you have the necessary information to reconfigure the device accordingly.
By following these basic troubleshooting steps, you can effectively address IP address conflicts and restore network connectivity. However, if the conflicts persist or the issue is more complex, it may be necessary to seek advanced troubleshooting or IT support.
Advanced Troubleshooting Steps for IP Address Conflicts
If basic troubleshooting steps fail to resolve IP address conflicts, you may need to employ more advanced techniques. These steps can help identify and troubleshoot complex conflicts that are not easily resolved. Here are some advanced troubleshooting steps for IP address conflicts:
- Check DHCP Server Configuration: Verify the configuration of your DHCP server. Ensure that it is properly assigning IP addresses and that there are no conflicts in the DHCP scope. If necessary, adjust the DHCP server settings to prevent overlapping IP address assignments.
- Inspect Network Traffic: Analyze network traffic using a network monitoring tool. Look for duplicate IP address usage or multiple devices using the same IP address. This can help pinpoint the devices causing conflicts and identify potential patterns or anomalies in IP address assignment.
- Use ARP Cache Clearing: Clear the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) cache on the affected devices. The ARP cache maps IP addresses to MAC (Media Access Control) addresses. Clearing the cache can help refresh the mapping and potentially resolve IP address conflicts.
- Verify MAC Address Cloning: Check if any devices on the network are using MAC address cloning. MAC address cloning allows a device to impersonate another device on the network. Conflicts can occur if multiple devices are using the same MAC address. Ensure that each device has a unique MAC address to prevent conflicts.
- Change DHCP Lease Duration: Adjust the lease duration on the DHCP server. A shorter lease duration will allow IP addresses to be released and renewed more frequently, minimizing the chances of conflicts due to IP address exhaustion or lease renewal failures.
- Configure IP Address Exclusions: Set up IP address exclusions on the DHCP server to reserve specific IP addresses for devices that require a static IP assignment. By reserving these addresses, you can avoid conflicts with dynamically assigned IP addresses and ensure that important devices always retain their assigned IP addresses.
- Separate Subnets: If your network is large and complex, consider dividing it into separate subnets. This can help isolate devices and minimize the possibility of IP address conflicts. Devices on separate subnets will typically use different IP address ranges, reducing the likelihood of conflicts.
- Consult with Network Professionals: If the IP address conflicts persist or if the network environment is highly complex, it may be beneficial to seek assistance from network professionals or IT specialists. They can provide advanced troubleshooting techniques tailored to your specific network setup and help resolve complex IP address conflicts.
By employing these advanced troubleshooting steps, you can tackle more complex IP address conflicts and ensure the stability and integrity of your network. Remember to document any changes made during the troubleshooting process for future reference and network maintenance purposes.
Preventing IP Address Conflicts
Preventing IP address conflicts is key to maintaining a stable and smoothly running network. By implementing preventive measures, you can minimize the occurrence of conflicts and ensure seamless connectivity. Here are some effective strategies for preventing IP address conflicts:
- Configure DHCP Server Properly: Ensure that your DHCP server is correctly configured to assign IP addresses within a specific range that does not overlap with statically assigned addresses. Set the DHCP lease duration appropriately to avoid IP address conflicts caused by expired leases or lease renewal failures.
- Use Static IP Address Assignments: Assign static IP addresses to devices that require permanent or highly stable connections, such as servers, printers, and network equipment. Keep a record of all assigned static IP addresses to avoid assigning duplicate addresses or overlapping with DHCP-assigned addresses.
- Implement IP Address Reservations: If your network infrastructure supports it, set up IP address reservations in the DHCP server. This allows you to reserve specific IP addresses for certain devices, ensuring consistent IP assignments and minimizing the chances of conflicts.
- Monitor Network Changes: Keep track of any changes made to the network, such as adding new devices or adjusting network settings. Document these changes and ensure that IP address assignments are updated accordingly to prevent conflicts.
- Perform Regular IP Address Audits: Conduct periodic audits to identify and resolve any IP address conflicts proactively. Use network scanning tools or management software to identify devices using duplicate or conflicting IP addresses.
- Implement VLANs or Subnets: If your network is large or complex, consider implementing VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) or subnets. By segmenting the network into smaller logical groups, you reduce the likelihood of IP address conflicts between devices within each segment.
- Train Network Users: Educate network users, especially employees in an office environment, about the importance of not manually assigning IP addresses without proper authorization. Encourage them to report any network connectivity issues promptly to the IT department for resolution.
- Document Network Configuration: Maintain a detailed inventory of your network infrastructure and document all IP address assignments, both static and dynamic. This documentation will help you quickly identify potential conflicts and troubleshoot network issues more effectively.
- Regularly Update Network Firmware: Ensure that your network devices, such as routers, switches, and DHCP servers, have up-to-date firmware. Firmware updates often contain bug fixes and enhancements that can improve the overall stability of the network and reduce the risk of IP address conflicts.
- Plan for Future Network Growth: Anticipate future network growth and allocate IP address ranges accordingly. Leave room for expanding device counts and additional network segments to avoid IP address exhaustion and potential conflicts as your network evolves.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of IP address conflicts and maintain a more efficient and reliable network infrastructure.
IP Address Conflict FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about IP address conflicts:
- What is an IP address conflict?
- How do I know if there is an IP address conflict?
- What causes IP address conflicts?
- How can I resolve an IP address conflict?
- How can I prevent IP address conflicts?
- Are IP address conflicts a security concern?
- Should I use static or dynamic IP addresses?
- Is IPv4 or IPv6 more prone to IP address conflicts?
- Why should I resolve IP address conflicts promptly?
An IP address conflict occurs when two or more devices on a network are assigned the same IP address. This conflict can disrupt network connectivity and cause various issues.
Common signs of an IP address conflict include intermittent network connectivity, inability to access specific resources, error messages indicating duplicate IP addresses, and unexpected device behavior.
IP address conflicts can be caused by duplicate IP address assignment, misconfigured network settings, manual IP address assignment without checking for conflicts, faulty network hardware, network changes or reconfiguration, and lease renewal failures.
Basic troubleshooting steps include releasing and renewing IP addresses, power cycling devices, checking network settings, disabling and enabling network adapters, and connecting devices to different network segments. Advanced troubleshooting steps may involve checking DHCP server configuration, analyzing network traffic, and using ARP cache clearing.
To prevent IP address conflicts, configu
re DHCP servers properly, use static IP addresses for specific devices, implement IP address reservations, monitor network changes, perform regular IP address audits, implement VLANs or subnets, train network users, document network configuration, update network firmware, and plan for future network growth.
IP address conflicts can introduce security vulnerabilities to the network. Conflicting IP addresses may allow unauthorized access to network resources when the conflicting device has different network permissions or authentication credentials.
Both dynamic and static IP addressing have their advantages. Dynamic IP addressing is more flexible and can accommodate a large number of devices, while static IP addressing provides stability and is useful for devices that require consistent connections, such as servers or printers.
Both IPv4 and IPv6 can experience IP address conflicts. However, due to the limited number of available IPv4 addresses, conflicts may be more common in IPv4 networks. The larger address space of IPv6 helps reduce the likelihood of conflicts.
Resolving IP address conflicts promptly is crucial to restore network connectivity, prevent disruptions, ensure proper communication between devices, and maintain network stability and security.
By understanding IP address conflicts and their resolution, you can effectively manage your network and address any conflicts that may arise.