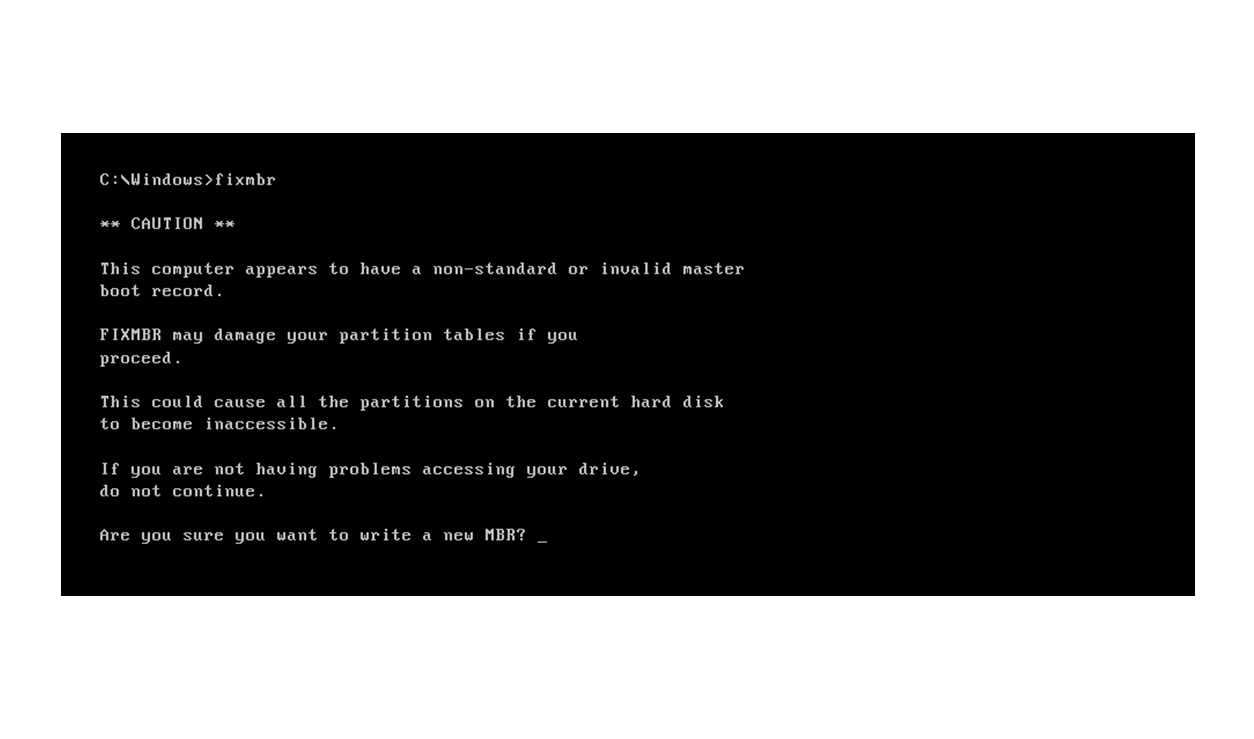
What is the Fixmbr Command?
The Fixmbr command is a powerful tool available in the Recovery Console of the Windows operating system. It is designed to fix issues related to the Master Boot Record (MBR) and helps restore the system’s ability to boot properly. The MBR is a small section of the hard drive that contains crucial information for the computer to start up.
When you turn on your computer, the MBR is the first thing the system looks for. It contains the instructions on where to find the operating system and how to load it into memory. If the MBR is damaged or corrupted, your computer may fail to start, displaying error messages or entering an endless boot loop.
The Fixmbr command provides a solution to these issues by rewriting the MBR with a new, clean configuration. It replaces any corrupted or faulty data, allowing the system to successfully initiate the boot process. However, it’s essential to exercise caution when using this command, as any mistakes during the process can result in the system becoming unbootable.
The Fixmbr command has proven to be particularly useful in situations where the MBR has been affected by malware, such as viruses or rootkits. These malicious programs can manipulate the MBR, making it difficult for the computer to start up correctly. By using the Fixmbr command, you can eliminate the malicious code and restore the MBR to its original state.
It’s important to note that the Fixmbr command should only be used in specific cases where there is a known issue with the MBR. If your computer is experiencing other boot-related problems, it’s advisable to explore other troubleshooting methods or seek professional assistance.
When to Use the Fixmbr Command
The Fixmbr command should be used when you are experiencing issues with your computer’s boot process that are specifically related to the Master Boot Record (MBR). Here are some situations where using the Fixmbr command may be necessary:
Corrupted or Damaged MBR: If the MBR is corrupted or damaged due to malware or other reasons, your computer may fail to start properly. You may encounter error messages or see your system stuck in a boot loop. In such cases, using the Fixmbr command can help restore the MBR and allow your computer to boot successfully.
Virus or Malware Infections: Some viruses or malware programs target the MBR, making it difficult for the system to start up. If you suspect that your computer is infected and experiencing boot-related issues, running the Fixmbr command can help eliminate the malicious code and restore the MBR to its original state.
Error Messages Related to MBR: If you receive error messages indicating MBR-related problems when you try to boot your computer, it suggests that the MBR may be corrupted or misconfigured. The Fixmbr command can be used to overwrite the existing MBR with a fresh configuration, eliminating any errors and enabling proper booting.
MBR Modification by Third-party Software: Some software, particularly disk partitioning tools, can unintentionally modify the MBR, causing boot issues. If you have recently used any such software and are experiencing problems starting your computer, running the Fixmbr command can help restore the MBR to its original state and resolve the boot-related issues.
It’s important to note that the Fixmbr command should only be used when you are certain that the MBR is the root cause of the boot problems. If you are unsure about the specific issue or don’t have experience using the Recovery Console, it’s advisable to seek assistance from a knowledgeable professional to avoid any potential risks or data loss.
How to Access the Recovery Console
The Recovery Console is a command-line tool in Windows that provides various troubleshooting options, including the ability to use the Fixmbr command. To access the Recovery Console, you will need a Windows installation disc or a system repair disc. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to access the Recovery Console:
Step 1: Insert the Windows Installation Disc: Insert the Windows installation disc into the CD/DVD drive of your computer. If you don’t have a physical disc, you can create a system repair disc using another Windows computer with the same operating system.
Step 2: Boot from the Installation Disc: Restart your computer and boot from the Windows installation disc. To do this, you may need to change the boot order in the BIOS settings or use a designated key (such as F12 or ESC) during the startup process to select the boot device.
Step 3: Select Language and Keyboard Layout: After the computer boots from the installation disc, choose your preferred language and keyboard layout, and click “Next” to proceed.
Step 4: Click on “Repair your Computer”: On the next screen, click on “Repair your Computer” or a similar option. This will launch the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
Step 5: Choose the Operating System: In the WinRE, you may be asked to select the operating system you want to repair. Choose the appropriate operating system and click “Next” to continue.
Step 6: Select “Command Prompt”: In the next set of options, choose “Command Prompt” to open a command-line window.
Once you have successfully accessed the Recovery Console, you can proceed to use the Fixmbr command or any other available troubleshooting options to resolve the boot-related issues.
It’s worth noting that the steps to access the Recovery Console may vary slightly depending on the version of Windows you are using. If you are unsure or have specific concerns, referring to the official documentation or seeking guidance from a knowledgeable source is recommended.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Fixmbr Command
Using the Fixmbr command in the Windows Recovery Console can help resolve boot-related issues caused by a damaged Master Boot Record (MBR). Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use the Fixmbr command:
Step 1: Access the Recovery Console: Follow the steps outlined in the previous section to access the Windows Recovery Console using a Windows installation disc or a system repair disc.
Step 2: Choose the Operating System: If prompted, select the operating system you want to repair from the list displayed in the Recovery Console.
Step 3: Select “Command Prompt”: In the available options, choose “Command Prompt” to open a command-line window.
Step 4: Identify the Drive: In the Command Prompt, you may need to identify the drive that contains the Windows installation you want to repair. Use the appropriate drive letter (e.g., C:, D:, etc.) followed by a colon to switch to the desired drive.
Step 5: Run the Fixmbr Command: Once you are in the correct drive, type “fixmbr” (without quotes) and press Enter to execute the Fixmbr command.
Step 6: Confirm the Action: Before proceeding, you may be prompted to confirm that you want to repair the MBR. Type “y” (without quotes) and press Enter to confirm and initiate the repair process.
Step 7: Wait for the Fixmbr Command to Complete: The Fixmbr command will analyze the MBR and apply the necessary fixes. Wait for the process to complete, which may take a few moments.
Step 8: Restart the Computer: Once the Fixmbr command has finished running, type “exit” (without quotes) and press Enter to close the Command Prompt. Restart your computer to see if the boot issues have been resolved.
It’s important to note that the Fixmbr command modifies the MBR, so it’s essential to use it only when necessary and with caution. Any mistakes or errors during the execution of the command can lead to further issues, including an unbootable system. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with performing these steps yourself, it’s recommended to seek assistance from a professional or knowledgeable source.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While the Fixmbr command can be an effective solution for resolving boot-related issues caused by a damaged MBR, there are some common issues that you might encounter during the process. Here are a few common issues and their troubleshooting steps:
Issue 1: Fixmbr Command Not Recognized: In some cases, when you enter the Fixmbr command, it may not be recognized by the Recovery Console. This can happen if the version of Windows you are using does not have the Fixmbr command available. In such cases, it’s advisable to explore alternative methods to fix the MBR, such as using the bootrec command or reinstalling the operating system.
Issue 2: Error Messages While Running Fixmbr Command: During the execution of the Fixmbr command, you may encounter error messages indicating that the command cannot be completed. This can be due to several reasons, including incompatible hardware or software configurations. To troubleshoot this issue, you can try disconnecting any external devices, such as USB drives or printers, and disabling any non-essential software or drivers that may interfere with the Fixmbr process.
Issue 3: No Improvement in Boot Issues: After successfully running the Fixmbr command, your computer may still experience boot-related problems. This can indicate that the issue is not solely related to the MBR, but may be caused by other factors such as hardware failures or software conflicts. In such cases, it’s recommended to explore other troubleshooting options, such as performing a system restore, running a malware scan, or seeking professional assistance.
Issue 4: Data Loss: It’s important to note that running the Fixmbr command can potentially lead to data loss if not executed correctly. As the Fixmbr command modifies the MBR, there is a risk of inadvertently overwriting or deleting critical data. To mitigate this risk, it’s essential to ensure that you have an up-to-date backup of all important files and data before attempting to use the Fixmbr command.
It’s crucial to approach troubleshooting boot-related issues with caution and to have a backup plan in case anything goes wrong. If you are uncertain or uncomfortable with performing advanced troubleshooting steps, it’s recommended to consult with a professional or seek guidance from Microsoft support forums or communities.
Alternatives to the Fixmbr Command
While the Fixmbr command can be effective in resolving boot-related issues caused by a damaged Master Boot Record (MBR), there are alternative methods you can try if the Fixmbr command is not suitable or does not resolve the problem. Here are some alternatives to consider:
1. Bootrec Command: The bootrec command is another tool available in the Windows Recovery Console that can help repair the MBR and resolve boot issues. It offers a range of options, including fixing the MBR, rebuilding the Boot Configuration Data (BCD), and fixing boot-related errors. To use the bootrec command, access the Recovery Console and enter the desired command: bootrec /fixmbr, bootrec /fixboot, or bootrec /rebuildbcd.
2. System Restore: If you have enabled System Restore on your computer and created restore points, you can use this feature to revert your system back to a previous working state. This can help resolve boot-related issues caused by changes or modifications to system files or settings. Access the System Restore feature either through the Recovery Console or by booting into Safe Mode and selecting the appropriate restore point.
3. Startup Repair: The Startup Repair tool is available in the Windows Recovery Environment and is designed to automatically fix common boot issues. It can detect and repair problems with the MBR, system files, and configuration settings that may be causing boot failures. To access Startup Repair, follow the steps outlined in the section on accessing the Recovery Console and select the Startup Repair option.
4. Reinstalling the Operating System: If all else fails and you are unable to resolve the boot issues, you may consider reinstalling the operating system. This option should be a last resort, as it will result in the loss of all data and installed applications. Before proceeding with a reinstallation, ensure you have backed up all important files and have the necessary installation media or recovery options available.
It’s important to note that the appropriate alternative method will depend on the specific issue you are facing and your level of comfort with advanced troubleshooting techniques. If you are unsure or need assistance, seeking help from a qualified professional or contacting Microsoft support can provide further guidance tailored to your specific situation.