Choosing the Right Method for Wiping Your Hard Drive
When it comes to wiping your hard drive, there are several methods available, each with its own level of effectiveness and complexity. Choosing the right method depends on your specific needs and the level of security you require. Let’s explore some of the options:
1. Formatting: Formatting your hard drive is a quick and easy way to erase all the data on it. However, it’s important to note that formatting alone does not completely erase the data. It simply marks the space on the drive as empty, making the data recoverable by specialized software. This method is suitable if you plan to reuse the drive or if you’re not concerned about someone potentially recovering your data.
2. Factory Reset: If you’re using a device such as a smartphone or tablet, a factory reset will wipe the data and restore the device to its original settings. This method is convenient but may not be as secure as other methods when it comes to permanent data erasure.
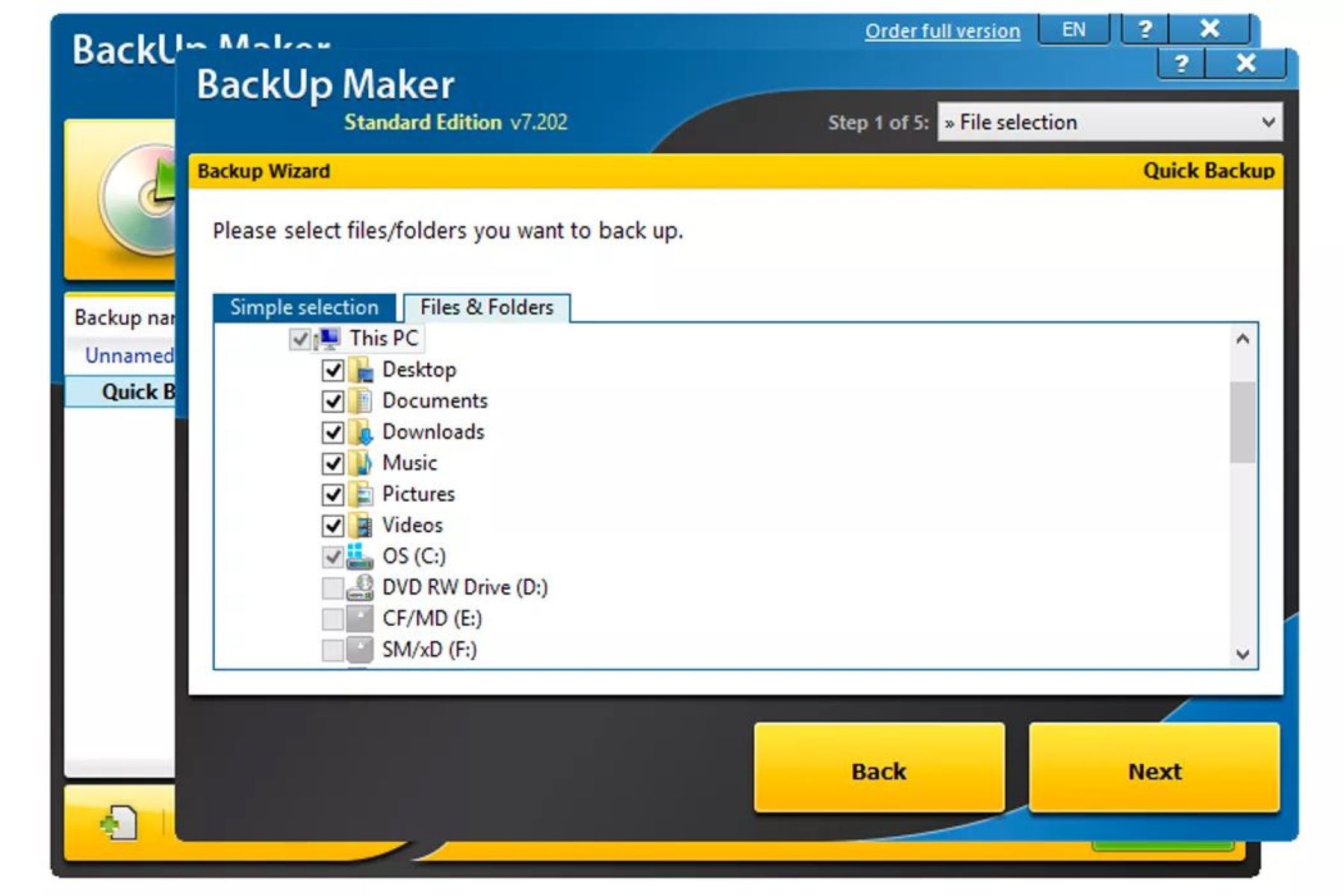
3. Data Wiping Software: Using specialized data wiping software ensures a more thorough and secure erasure of your hard drive. These programs overwrite the entire drive with random data multiple times, making it nearly impossible to recover the original data. Popular data wiping software options include DBAN (Darik’s Boot and Nuke), CCleaner, and Eraser.
4. Physical Destruction: For the utmost security, physically destroying your hard drive is the most effective method. This involves physically damaging the drive, rendering it unreadable and unrecoverable. However, this option is irreversible and should only be considered if you have no intention of reusing the drive.
It’s important to assess your specific needs and consider the sensitivity of the data you’re disposing of when selecting a method for wiping your hard drive. If you’re unsure about which method to choose, consulting with an IT professional can provide valuable guidance based on your unique circumstances.
Backing Up Your Data Before Wiping Your Hard Drive
Before wiping your hard drive and permanently deleting all your data, it’s crucial to back up any important files and documents. This step prevents the loss of valuable information and ensures you can access your files after the wipe. Here are some key points to consider:
Identify Important Data: Take the time to identify and prioritize the files and data you need to back up. This may include personal documents, photos, videos, and important work files. Make a list of these files to ensure nothing is overlooked.
Choose a Backup Method: There are several backup methods available, depending on your preferences and resources. External hard drives, cloud storage services, or even backing up to a separate computer or network drive are all viable options. Select the method that suits your needs and provides a secure and easily accessible backup solution.
Create a Backup Schedule: Regularly backing up your data is a good practice to ensure you don’t lose any recent files. Determine a schedule that works for you and stick to it. This could be daily, weekly, or monthly backups, depending on the frequency of data changes and your own preferences.
Verify Backup Integrity: After performing a backup, it’s essential to verify the integrity of the files. Double-check that all your important data has been successfully copied and ensure the backup is accessible and functional. This step helps prevent any surprises or disappointments when you try to retrieve your files after the hard drive wipe.
Store Backups Securely: Treat your backups with the same level of security as your original data. If using an external hard drive, keep it in a safe location and consider encrypting the backup for an extra layer of protection. If using cloud storage, ensure you have strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
Test Data Restoration: Before proceeding with the hard drive wipe, test the restoration process to ensure you can successfully retrieve your backed-up data. This practice offers peace of mind and allows you to address any potential issues or complications before it’s too late.
By following these steps, you can safeguard your valuable data and reduce the risk of losing important files during the hard drive wipe. Taking the time to back up your data ensures you can continue working seamlessly or enjoy your personal files without any interruptions.
Formatting vs. Wiping: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to cleaning your hard drive, you may come across the terms “formatting” and “wiping.” While both methods involve erasing data from your drive, there are crucial differences to consider. Let’s take a closer look:
Formatting: Formatting a hard drive involves preparing it for data storage by creating a file system. This process essentially clears the existing file structure, marking the space as available for new data. While formatting removes the directory information and file references, it doesn’t thoroughly erase the actual data. With specialized software, the formatted data can still be recovered.
Wiping: On the other hand, wiping, also known as secure erasing, involves overwriting the entire hard drive with random data multiple times. This process ensures that the original data becomes unrecoverable, as the overwritten data makes it extremely difficult for anyone to retrieve the original files. Wiping provides a higher level of security, particularly when dealing with sensitive or confidential information.
So, what are the key differences between formatting and wiping?
Data Integrity: Formatting primarily concentrates on clearing the file structure, leaving the actual data intact. Wiping, however, focuses on thoroughly erasing the data by overwriting it multiple times, providing a higher level of data integrity and security.
Data Recovery: With formatting, data recovery is possible using specialized software. Wiping, on the other hand, makes data recovery extremely challenging, as the overwritten data makes it significantly harder to retrieve the original files.
Security: If you’re concerned about the security of your data, wiping is the recommended method. It ensures that your sensitive information remains unrecoverable, protecting you from potential data breaches or identity theft. Formatting alone may not provide the same level of security.
Intended Use: Formatting is often used when preparing a hard drive for reuse or when troubleshooting certain issues. Wiping is preferred when disposing of a drive or transferring it to someone else, especially when dealing with confidential data that should never be recovered.
Understanding the differences between formatting and wiping enables you to make an informed decision based on the level of data security required. If you’re unsure, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and opt for wiping to ensure the complete removal of sensitive information.
Wiping a Hard Drive on Windows OS
If you’re using a Windows operating system and need to wipe your hard drive for security or privacy reasons, there are several methods you can utilize. Here are some effective ways to wipe your hard drive on a Windows OS:
1. Built-in Windows Tools: Windows provides built-in tools that can help you wipe your hard drive. You can use the “Disk Cleanup” utility to delete unnecessary files and free up space. Additionally, the “Format” option in Windows allows you to format the drive, but keep in mind that this method is not as secure as others, as data can still be recovered with specialized software.
2. Command Prompt: Another option is to use the Command Prompt to wipe your hard drive. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and use the “diskpart” command to access the DiskPart tool. From there, you can select and clean the desired hard drive, ensuring that the data is removed. Remember to exercise caution and double-check the drive you are working on to avoid accidentally wiping the wrong drive.
3. Third-Party Software: There is a wide range of third-party software available that offers more advanced and secure wiping options. Examples include DBAN (Darik’s Boot and Nuke), which can be downloaded and booted from a USB or CD/DVD, or software like CCleaner and Eraser. These programs overwrite the data on your hard drive multiple times, making it extremely difficult or virtually impossible to recover the original data.
4. Physical Destruction: If you require the highest level of security and have no intention of reusing the drive, physically destroying it is the most effective method. This involves drilling or shredding the hard drive to render it completely unreadable and irretrievable.
Before proceeding with any method, it is crucial to back up your important files and data to ensure nothing is lost during the wiping process. Also, remember that wiping a hard drive is irreversible, so double-check and confirm your decision before proceeding.
Keep in mind that the level of security and data erasure provided by each method may vary. Consider your specific requirements and the sensitivity of the data you’re dealing with when selecting the most appropriate method for wiping your hard drive on a Windows OS.
Wiping a Hard Drive on Mac OS
If you’re using a Mac operating system and need to wipe your hard drive for security or privacy reasons, there are several methods you can employ. Here are some effective ways to wipe your hard drive on a Mac OS:
1. Built-in Disk Utility: Mac OS provides a built-in utility called Disk Utility, which can be used to erase and format hard drives. To access Disk Utility, go to the “Applications” folder, then “Utilities,” and open “Disk Utility.” From there, select the hard drive you want to wipe, click on the “Erase” tab, and choose the appropriate format. By selecting the “Security Options” button, you can adjust the level of data wiping by choosing the number of passes to overwrite the data.
2. macOS Recovery Mode: Another method for wiping a hard drive on a Mac OS is through macOS Recovery Mode. Restart your Mac and hold down the “Command + R” keys until the Apple Logo or a spinning globe appears. Select “Disk Utility” from the macOS Utilities window and follow the same steps as mentioned in the previous method.
3. Third-Party Software: There are also third-party software options available for wiping a hard drive on a Mac. Programs like CCleaner and Drive Genius offer additional features and flexibility for securely erasing your data. These tools often provide multiple wiping algorithms and advanced options to ensure the data cannot be recovered.
4. Secure Empty Trash: If you want to focus on wiping specific files rather than the entire hard drive, you can use the “Secure Empty Trash” feature. This securely empties the Trash and ensures that the deleted files cannot be recovered easily.
Before proceeding with any method, it is essential to back up your important files and data to ensure nothing is lost during the wiping process. Additionally, make sure you have selected the correct hard drive to avoid accidentally wiping the wrong drive.
Consider the sensitivity of your data and the level of security you require when choosing the most suitable method for wiping your hard drive on a Mac OS. Ensure that you understand the implications of wiping a hard drive, as the process is often irreversible.
Wiping a Hard Drive on Linux OS
If you’re using a Linux operating system and need to wipe your hard drive for security or privacy reasons, there are several methods you can utilize. Here are some effective ways to wipe your hard drive on a Linux OS:
1. dd Command: The dd command in Linux is a powerful tool for data copying and conversion. It can also be used for wiping a hard drive. By running a specific command with appropriate options, you can overwrite the entire hard drive with random data, making it extremely difficult to recover the original information. However, be cautious when using the dd command, as incorrect usage can lead to data loss on unintended drives.
2. shred Command: The shred command is another tool available in Linux for securely wiping a hard drive. It overwrites files or entire devices with random data, making the original data unrecoverable. The shred command allows you to specify the number of iterations for overwriting, providing flexibility in data wiping.
3. DBAN (Darik’s Boot and Nuke): DBAN is a popular third-party software that allows you to wipe your hard drive on Linux. It provides a user-friendly interface and offers multiple data wiping algorithms to choose from. DBAN can be booted from a USB or CD/DVD, allowing you to wipe the hard drive without booting into the Linux OS directly.
4. ATA Secure Erase: ATA Secure Erase is a hardware-based method that utilizes the built-in secure erase feature supported by many modern hard drives. This method sends a command to the hard drive, instructing it to erase all data securely. The process is quick and effective, ensuring that the data is not recoverable.
Before proceeding with any method, it’s crucial to back up your important files and data to ensure nothing is lost during the wiping process. Additionally, exercise caution and double-check that you have selected the correct hard drive to avoid accidentally wiping the wrong one.
Consider the sensitivity of your data and the desired level of security when choosing the most suitable method for wiping your hard drive on a Linux OS. Ensure that you understand the implications of wiping a hard drive, as the process is often irreversible.
Using Third-Party Software to Wipe Your Hard Drive
When it comes to wiping your hard drive, using third-party software can provide enhanced security and flexibility compared to built-in utilities. These software options offer more advanced features and algorithms to ensure the complete and secure erasure of your data. Here are some benefits and considerations of using third-party software to wipe your hard drive:
Enhanced Data Wiping: Third-party software often utilizes advanced algorithms to overwrite the data on your hard drive multiple times. This process ensures that the original data becomes virtually unrecoverable, providing a higher level of security compared to basic formatting or deletion methods.
Multiple Wiping Methods: Third-party software generally offers multiple wiping methods or algorithms to choose from. These methods vary in the number of passes used to overwrite the data, providing flexibility based on your security needs and time constraints.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Most third-party software for wiping hard drives is designed with user-friendly interfaces, making it easier for individuals without technical expertise to use the software effectively. These interfaces often provide step-by-step instructions and intuitive tools for a smoother user experience.
Support for Different Operating Systems: Third-party software is available for Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems, ensuring compatibility regardless of your preferred platform. This versatility allows you to choose the software that best suits your needs, regardless of the operating system you’re using.
Additional Features: In addition to data wiping, third-party software may offer additional features such as disk diagnostics, partition management, and recovery options. These features can be valuable for maintaining and optimizing your hard drive’s performance.
When selecting third-party software to wipe your hard drive, it’s essential to research and choose from reputable sources. Look for software that has positive reviews, regular updates, and a good track record of customer satisfaction. Additionally, ensure that the software is compatible with your operating system and offers the specific features and wiping methods you require.
Remember to back up your important files and data before using any third-party software to wipe your hard drive. This precaution helps ensure that no critical data is lost during the wiping process. Take the time to set up a secure and reliable backup system before proceeding.
By using trusted third-party software, you can have peace of mind knowing that your hard drive will be securely wiped, making your data virtually irretrievable and protecting your privacy and security.
Tips for Securely Wiping Your Hard Drive
When it comes to securely wiping your hard drive, following best practices is essential to ensure that your data is completely and irreversibly erased. Here are some valuable tips to help you securely wipe your hard drive:
1. Back Up Your Data: Before initiating the wiping process, it is crucial to back up any important data you want to preserve. This ensures that you don’t lose any important files during the wipe and provides a safety net in case you need to access the data again in the future.
2. Select the Right Method: Choose a wiping method that meets your specific needs for security and data erasure. Consider using specialized software designed for secure data wiping, as these tools offer advanced algorithms and multiple passes to thoroughly overwrite the data on your hard drive.
3. Verify the Wiping Process: After wiping your hard drive, it is essential to verify that the process was successful. Use a data recovery tool to scan the drive and ensure that no remnants of the original data can be recovered. This step provides peace of mind and confirms the effectiveness of the wiping process.
4. Consider Physical Destruction: For maximum security, physical destruction of the hard drive is the most foolproof method. This involves physically damaging the drive, rendering it unreadable and unrecoverable. It is crucial to follow proper disposal protocols and ensure that the damaged hard drive is disposed of responsibly.
5. Multiple Wiping Passes: If you are using software-based wiping methods, consider performing multiple passes to overwrite the data on your hard drive. Multiple passes enhance data security by making it exponentially more challenging to recover any remnants of the original data. Refer to the software’s documentation for recommendations on the number of passes for optimal data erasure.
6. Encrypting Your Data: Before wiping your hard drive, consider encrypting your data. Encryption secures your files and makes them unreadable without the proper decryption key. This extra layer of security ensures that even if remnants of the data are recoverable, they will be useless without the encryption key.
7. Take Precautions When Donating or Selling: If you plan to donate or sell your hard drive, securely wiping your data becomes even more critical. Ensure that you wipe the hard drive thoroughly and consider using specialized software or services that provide certification of data erasure. This certification can offer peace of mind to the new owner that their data will not be compromised.
By following these tips, you can ensure a secure and thorough wipe of your hard drive, protecting your privacy and preventing the possibility of data breaches. It is important to familiarize yourself with the available wiping methods, choose the most suitable method for your needs, and take the necessary precautions to safeguard your data throughout the process.
What to Do After Wiping Your Hard Drive
After successfully wiping your hard drive, there are several important steps to take to ensure a smooth transition and maintain data security. Here are some key actions to consider after wiping your hard drive:
1. Dispose of the Hard Drive Responsibly: If you don’t plan to reuse the hard drive, it’s crucial to dispose of it responsibly. Hard drives may contain sensitive information, and improper disposal could pose a risk. Research local recycling or electronic waste disposal programs that can ensure the hard drive is properly recycled or destroyed.
2. Install a Fresh Operating System: After wiping your hard drive, it’s time to install a fresh operating system. This step ensures that you have a clean and optimized system to work with. Follow the installation instructions provided by the operating system manufacturer for a seamless installation process.
3. Update System and Software: After installing the operating system, ensure that you update it to the latest version. This helps improve security and compatibility. Additionally, update any software applications or drivers to ensure that you have the most up-to-date versions and patches.
4. Install Antivirus and Security Software: Protect your newly wiped hard drive by installing reputable antivirus and security software. This provides an additional layer of protection against potential threats, ensuring the safety of your data and system.
5. Restore Backed-Up Data: If you have backed up your data before wiping the hard drive, now is the time to restore it. Carefully copy the backed-up files and data to their appropriate locations on the newly installed operating system. Verify that all important files and documents are intact and accessible.
6. Set Up Data Backup Routine: Establish a regular backup routine to prevent any future data loss. This can be done through external hard drives, cloud storage services, or network backups. Regular backups ensure that you have copies of important files and minimize the risk of data loss due to hardware or software issues.
7. Secure Your System: Take steps to secure your newly wiped hard drive and system. Set strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and consider using encryption methods to protect your sensitive data. Regularly update your security software and be cautious while browsing the internet or downloading files.
8. Maintain Good Data Hygiene: After wiping your hard drive, develop a habit of good data hygiene. This includes regularly organizing and decluttering files, avoiding unnecessary downloads, and being mindful of the websites you visit and the emails you open. By practicing good data hygiene, you can reduce the risk of future data loss or security breaches.
By following these steps, you can ensure a secure and smooth transition after wiping your hard drive. Taking the necessary precautions and maintaining data security practices will help protect your information and maintain the integrity of your newly wiped system.