Why Reset Network Settings on Mac?
Resetting network settings on your Mac can be a useful troubleshooting step in some situations. Network issues can occur for various reasons, such as incorrect configurations, conflicts between different network settings, or software glitches. Resetting the network settings helps to eliminate these potential problems and allows your Mac to establish a fresh network connection.
Here are some reasons why you may want to consider resetting your network settings:
- Resolve Connectivity Issues: If you are experiencing frequent disconnections, slow internet speed, or difficulties connecting to certain networks, resetting the network settings can help resolve these issues. It clears any conflicting or corrupt network configurations that may be causing the problems.
- Fix DNS Issues: DNS (Domain Name System) is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. If you are having trouble accessing websites or your browser is displaying DNS-related errors, resetting the network settings can help reset the DNS cache and resolve these issues.
- Clear Proxy and VPN Settings: If you have previously configured proxy or VPN settings on your Mac, you may encounter problems when trying to connect to different networks. Resetting the network settings clears these configurations, allowing you to establish new connections without any conflicts.
- Resolve Software Conflicts: Some software installations or updates can inadvertently modify network settings, leading to connectivity problems. By resetting the network settings, you can undo any changes made by software and start with a clean slate.
- Prepare for Network Configuration Changes: If you are planning to make significant changes to your network setup, such as installing a new router or changing your internet service provider, resetting the network settings can help ensure that your Mac is ready to adapt to the new configuration.
Overall, resetting network settings can be a useful troubleshooting step to address various network-related issues on your Mac. It provides a fresh start and helps to eliminate any potential conflicts or configuration errors that may be affecting your network connectivity. However, it is important to note that resetting network settings will remove any saved Wi-Fi passwords and custom network configurations, so make sure to back up any important settings before proceeding with the reset.
Step 1: Backup Your Network Settings
Before you proceed with resetting the network settings on your Mac, it is important to back up any important network configurations and settings. This will help you easily restore your previous settings if needed. Follow these steps to backup your network settings:
- Document your current network configurations: Take note of your current Wi-Fi network name, password, and any other network settings that you have customized. This will ensure that you can easily reconfigure your network settings after the reset.
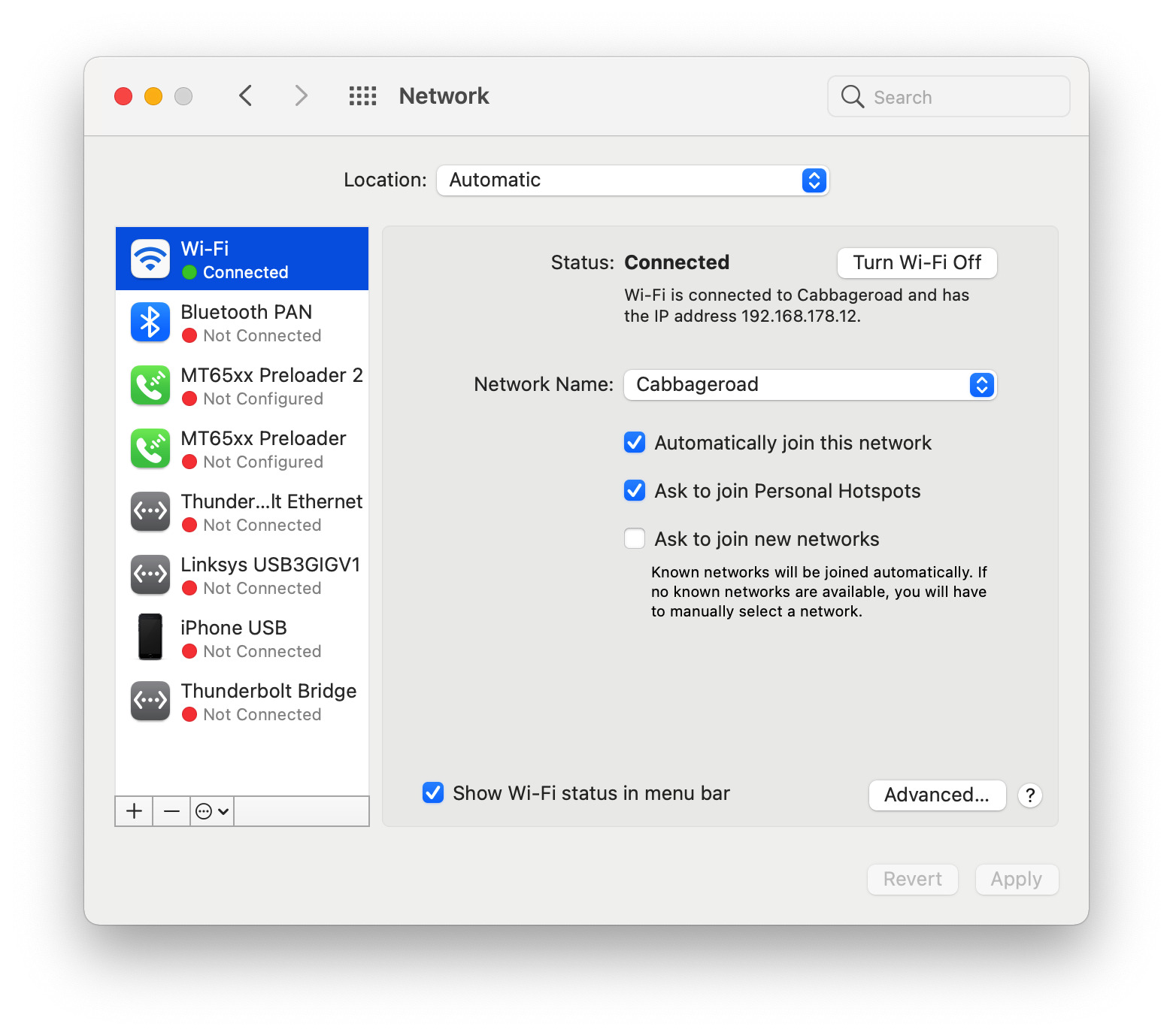
- Export Preferred Networks: Mac stores a list of preferred Wi-Fi networks that you have connected to in the past. It is a good idea to export this list as a backup. To do this, go to the “Network” section of “System Preferences” and click on the “Wi-Fi” tab. Then, click on the “Advanced” button and select the “Wi-Fi” tab. Finally, click on the “Export…” button and save the file in a safe location.
- Save any custom network configurations: If you have manually configured any network settings, such as DNS servers or proxy configurations, make sure to note down the details so that you can easily recreate them after the reset.
- Backup Network-related files: Some network settings are stored in specific files on your Mac. Navigate to the following directory and make a copy of the files for backup:
/Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/
Make sure to save these files in a separate location.
- Consider taking screenshots: If you have customized any advanced network settings, consider taking screenshots of the configurations for reference later. This can include settings like IPv6 configurations or custom network locations.
By backing up your network settings, you can ensure that you have a copy of all the important configurations, preferences, and files related to your network connections. This will help you restore your previous settings quickly and easily after resetting the network on your Mac.
Step 2: Disable Wi-Fi and Ethernet
Before proceeding with resetting the network settings on your Mac, it is important to disable both Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections. This will ensure that your Mac is not actively connected to any networks during the reset process. Follow these steps to disable Wi-Fi and Ethernet:
- Disable Wi-Fi: Click on the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar at the top-right corner of your screen. From the drop-down menu, select “Turn Wi-Fi Off.” This will disable the Wi-Fi connection on your Mac.
- Disable Ethernet: If you have an Ethernet connection, unplug the Ethernet cable from your Mac to disconnect it from the network. By doing this, you are disabling the Ethernet connection temporarily.
Disabling Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections ensures that your Mac is not connected to any networks while you reset the network settings. This is an important step to prevent any interference or conflicts as you proceed with the reset process.
Step 3: Reset Network Settings
Once you have backed up your network settings and disabled Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections, you can proceed with resetting the network settings on your Mac. Follow these steps to reset the network settings:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Network”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Network” icon. This will open the Network settings panel.
- Unlock the Network settings: At the bottom-left corner of the Network panel, click on the lock icon and enter your administrator password to unlock the settings. This will give you the necessary permissions to make changes.
- Select and remove network interfaces: In the left-hand sidebar, select each network interface (such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet) that you want to reset. Then, click on the “-” button at the bottom of the sidebar to remove the selected interface. Repeat this step for all interfaces that you want to reset.
- Remove DNS configurations: Click on the “DNS” tab and remove any DNS server addresses that are listed. To do this, select each address and click on the “-” button to remove it.
- Apply the changes: Once you have removed all the network interfaces and DNS server addresses, click on the “Apply” button at the bottom-right corner of the Network panel. This will apply the changes and reset the network settings on your Mac.
- Close System Preferences: After the changes have been applied, close the System Preferences window. Your network settings have now been reset.
By following these steps, you have successfully reset the network settings on your Mac. This removes any custom configurations, network interfaces, and DNS server addresses, allowing your Mac to start fresh with network connections.
Step 4: Re-enable Wi-Fi and Ethernet
After resetting the network settings on your Mac, you need to re-enable both Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections. Follow these steps to re-enable Wi-Fi and Ethernet:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Network”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Network” icon. This will open the Network settings panel.
- Unlock the Network settings: If the settings are locked, click on the lock icon at the bottom-left corner of the panel and enter your administrator password to unlock the settings.
- Add network interfaces: In the left-hand sidebar, click on the “+” button at the bottom of the sidebar to add a new network interface.
- Select Wi-Fi or Ethernet: In the pop-up window, select either “Wi-Fi” or “Ethernet” as per your preference and click on the “Create” button.
- Configure Wi-Fi or Ethernet settings: Depending on your connection type, you may need to enter the network name, password, or any other required details. Fill in the necessary information and click on the “Apply” button to save the settings.
- Repeat for other interfaces: If you have multiple network interfaces, repeat steps 4-6 for each interface you want to re-enable.
Once you have re-enabled Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections and configured the necessary settings, your Mac will be ready to connect to networks again. Proceed to the next step to reconnect to Wi-Fi networks.
Step 5: Reconnect to Wi-Fi Networks
After re-enabling Wi-Fi on your Mac, it’s time to reconnect to your preferred Wi-Fi networks. Follow these steps to reconnect to Wi-Fi networks:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Network”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Network” icon. This will open the Network settings panel.
- Choose Wi-Fi: In the left-hand sidebar, select the Wi-Fi interface.
- Enable Wi-Fi: If the Wi-Fi status is currently off, click on the checkbox next to “Wi-Fi” to enable it.
- Select a network: Click on the “Network Name” dropdown menu and select your preferred Wi-Fi network from the list of available networks.
- Enter password (if required): If the Wi-Fi network is password-protected, enter the network password in the “Password” field. Make sure to enter the correct password to establish a successful connection.
- Toggle “Remember this network”: If you want your Mac to automatically connect to this network in the future, make sure to check the “Remember this network” option.
- Click “Connect”: Once you have entered the required information, click on the “Connect” button to connect to the Wi-Fi network.
Repeat these steps for all the Wi-Fi networks you want to connect to. Your Mac will save the Wi-Fi network information, allowing it to automatically connect to these networks in the future when they are in range.
By reconnecting to Wi-Fi networks, you can regain internet access and enjoy seamless connectivity on your Mac. Proceed to the next step to reconfigure your personal hotspot settings (if applicable).
Step 6: Reconfigure Personal Hotspot (if applicable)
If you previously used the Personal Hotspot feature on your Mac, you will need to reconfigure it after resetting the network settings. Follow these steps to reconfigure your Personal Hotspot:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Sharing”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Sharing” icon. This will open the Sharing settings panel.
- Enable Personal Hotspot: In the left-hand sidebar, check the box next to “Internet Sharing” to enable it.
- Configure Personal Hotspot: Click on the “Internet Sharing” option in the sidebar and select the type of connection you want to share from the “Share your connection from” dropdown menu. This can be Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or other available options.
- Set up Wi-Fi hotspot: If you want to share your internet connection via Wi-Fi, click on the “Wi-Fi Options” button. Enter a network name, password, and other desired settings for your Wi-Fi hotspot. Make sure to choose a secure password to protect your hotspot.
- Toggle “Internet Sharing”: Once you have configured your Personal Hotspot settings, check the box next to “Internet Sharing” to activate it.
- Connect to Personal Hotspot: On your other devices, search for available Wi-Fi networks and select the network name you configured for your Personal Hotspot. Enter the password when prompted to establish a connection.
Reconfiguring your Personal Hotspot allows you to share your Mac’s internet connection with other devices, providing them with internet access through your Mac. Make sure to secure your hotspot with a strong password to prevent unauthorized access.
Now that you have reconfigured your Personal Hotspot (if applicable), you can proceed to the next step to reset network locations on your Mac.
Step 7: Resetting Network Locations
Resetting network locations on your Mac can be beneficial if you have multiple network configurations or if you frequently switch between different networks. It allows you to start afresh and organize your network settings. Follow these steps to reset network locations:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Network”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Network” icon. This will open the Network settings panel.
- Unlock the Network settings: If the settings are locked, click on the lock icon at the bottom-left corner of the panel and enter your administrator password to unlock the settings.
- Select “Location”: In the left-hand sidebar, click on the “Location” dropdown menu and select “Edit Locations…”
- Create a new location: Click on the “+” button at the bottom-left corner of the window to create a new network location.
- Provide a name: Enter a memorable name for your new network location, such as “Default” or “Reset.” This name will help you identify and select the location in the future.
- Save the new location: Click on the “Done” button to save the new network location.
- Select the new location: In the “Location” dropdown menu, select the new network location you just created.
By resetting network locations, you can organize your network settings and focus on specific network configurations. This can be useful if you frequently switch between different networks or troubleshoot connection issues specific to certain locations.
With network locations reset, you have a fresh start and can easily manage your network settings based on your current requirements. Proceed to the next step to check the network settings on your Mac.
Step 8: Check the Network Settings
After resetting the network settings on your Mac, it is important to verify that everything is configured correctly and functioning as expected. Follow these steps to check the network settings:
- Open “System Preferences”: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select “Network”: In the System Preferences window, click on the “Network” icon. This will open the Network settings panel.
- Review network interfaces: In the left-hand sidebar, check if the network interfaces you need (such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet) are present. If any interfaces are missing, click on the “+” button at the bottom-left corner to add them.
- Check network status: Ensure that the network status for each interface displays “Connected” or “On”. If not, click on the interface and check the settings, including the network name and password, to ensure they are correct.
- Verify network configurations: Review any customized configurations, such as DNS settings or proxy configurations, to ensure they are accurate. Make any necessary adjustments or additions if required.
- Test network connectivity: Open a web browser or any other network-dependent application to test the connection. Visit a few websites or perform any network-related tasks to ensure that the internet connection is stable and functioning properly.
- Reconnect devices (if applicable): If you were sharing your internet connection via Personal Hotspot, reconnect your other devices and ensure that they can successfully connect to your Mac’s hotspot.
By checking the network settings thoroughly, you can confirm that the network configurations are accurate and that your Mac is connected to the desired networks. This step allows you to identify and resolve any potential issues that may have arisen during the reset process.
If everything is working correctly and you have successfully established a stable network connection, you can consider the network settings on your Mac to be back in optimal condition.