What is BIOS and why it matters?
BIOS, short for Basic Input/Output System, is a fundamental component of a computer system that is responsible for initializing hardware, performing diagnostic tests, and loading the operating system. It is stored in a firmware chip on the motherboard and acts as a bridge between the hardware components and the operating system.
BIOS may seem like a technical aspect that only computer enthusiasts need to be concerned about, but it plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a computer. It is responsible for controlling the basic operations of the system, including the keyboard, mouse, storage devices, and other peripheral devices.
One of the key functions of BIOS is to determine the boot order or boot sequence of the computer. The boot order specifies the order in which the computer searches for a bootable device from which to load the operating system. This could be from the hard drive, CD/DVD drive, USB drive, or network. The boot order determines which device gets priority during the boot process, and it can have a significant impact on the system’s startup time and overall performance.
Why does the boot order matter? Well, imagine a scenario where the computer is set to boot from a USB drive first, but there is no bootable USB connected. In this case, the computer would waste time searching for a bootable USB that doesn’t exist, resulting in a longer startup time. By setting the correct boot order, you can ensure that the computer boots from the desired device and avoids unnecessary delays.
Moreover, the boot order is essential when troubleshooting issues with the operating system. For example, if you suspect that the operating system is corrupted, you may need to boot from a recovery CD or USB to perform system repairs. Without the ability to change the boot order, you may not be able to access the necessary tools to fix the problem.
How to access the BIOS settings?
Accessing the BIOS settings is a relatively straightforward process, although the exact steps may vary depending on the computer’s manufacturer and model. Here are some common methods to access the BIOS settings:
- Restart your computer: Start by restarting your computer. During the boot process, you will typically see a message that prompts you to press a specific key to enter the BIOS settings. This key is usually displayed briefly, and it can vary but commonly it is the Del, F2, or F10 key.
- Check your computer manual: If you’re unsure which key to press, refer to your computer’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions on accessing the BIOS settings. They often provide detailed information on the key to press and the BIOS interface.
- Use the Windows 10 settings: If you’re using Windows 10, you can also access the BIOS settings from within the operating system. Go to the Start menu, click on “Settings,” then select “Update & Security.” From there, choose “Recovery,” and under the “Advanced startup” section, click on “Restart now.” This will restart your computer and bring up a menu where you can select “Troubleshoot,” then “Advanced options,” and finally “UEFI Firmware Settings” to enter the BIOS.
- Try other key combinations: In some cases, different computer models may require different key combinations to access the BIOS settings. Some common alternatives include Esc, F1, F12, or even Ctrl+Alt+Esc. If the previously mentioned keys don’t work, try searching online for your specific computer model to find the correct key combination.
Once you’ve successfully entered the BIOS settings, you’ll be presented with a graphical interface or text-based menu. Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate through the various options and settings. Be cautious when making changes in the BIOS settings, as modifications to critical settings can affect the system’s stability and functionality.
Remember to save your changes before exiting the BIOS settings. Most BIOS interfaces provide an option to save and exit, typically labeled “Save and Exit” or something similar. Upon exiting, your computer will restart with the new BIOS settings applied.
Understanding the boot order in BIOS
The boot order in BIOS refers to the sequence in which a computer searches for a bootable device to load the operating system. It is essential to understand how the boot order works, as it directly affects the startup process and determines which device takes priority.
When you power on your computer, the BIOS performs a series of tests and checks to ensure that all hardware components are functioning correctly. Once the diagnostics are complete, the BIOS begins searching for a bootable device based on the specified boot order.
The boot order typically consists of a list of different devices that the computer can boot from, such as the hard drive, CD/DVD drive, USB drive, or network. The BIOS will start with the first device on the list and check if it contains a bootable operating system. If it doesn’t, it moves on to the next device, and so on until a bootable device is found.
It’s important to note that the boot order can be customized and adjusted according to your preferences. By default, most systems are set to boot from the hard drive as the primary device, as that is where the operating system is usually installed.
Changing the boot order can be useful in various situations. For example, if you want to install a new operating system from a CD or USB drive, you would need to set the boot order to prioritize the CD/DVD drive or USB drive. This ensures that the computer looks for a bootable operating system on those devices first.
Another scenario where the boot order becomes significant is when dealing with multiple operating systems installed on different drives. By modifying the boot order, you can select which operating system to boot into by default.
Understanding the boot order can also help troubleshoot issues related to the startup process. For instance, if your computer is not booting properly, you can check the boot order to ensure that the correct device is set as the primary boot option. Incorrect boot order settings can lead to boot failures or delays.
Overall, comprehending the boot order in BIOS is essential for managing the startup process effectively and ensuring that the computer boots from the desired device. It provides flexibility and control over your system’s boot process and enables you to make necessary adjustments based on your specific requirements.
Step-by-step guide to change the boot order in BIOS
Changing the boot order in BIOS is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to modify the boot sequence and prioritize the desired bootable device:
- Restart your computer: Start by restarting your computer and wait for the manufacturer’s logo or initial screen to appear. Typically, you will see a message indicating which key to press to enter the BIOS settings.
- Enter the BIOS settings: Press the indicated key (such as Del, F2, or F10) to access the BIOS settings. Different computer models may have different keys, so refer to your computer’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions.
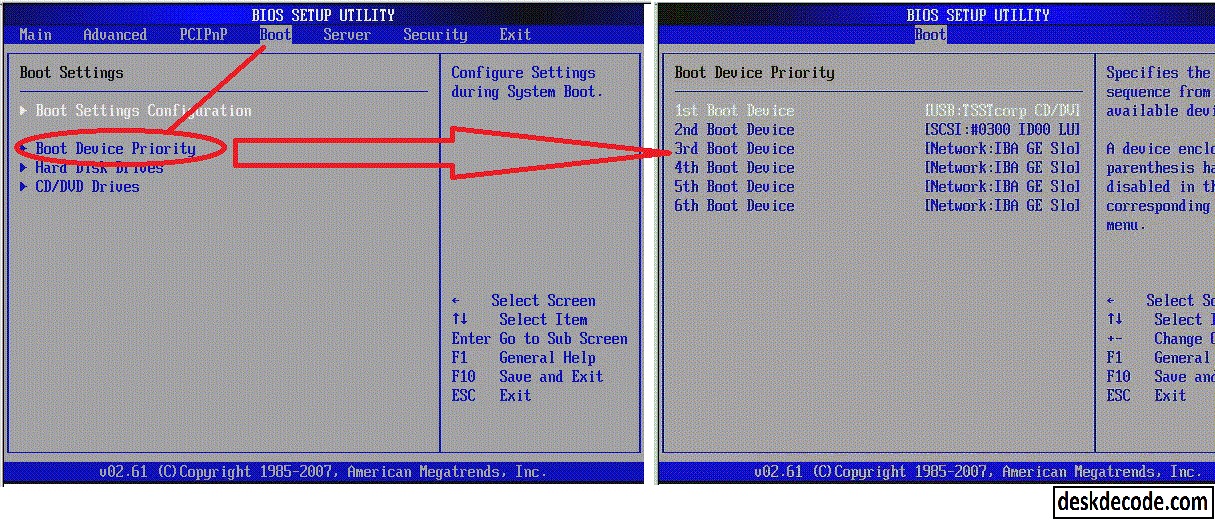
- Navigate to the boot settings: Once you’re in the BIOS settings, use the arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate to the “Boot” or “Boot Order” section. The exact name may vary depending on the BIOS version and manufacturer.
- Adjust the boot order: In the boot settings, you will see a list of bootable devices such as the hard drive, CD/DVD drive, USB drive, or network. Use the arrow keys to highlight the device you want to set as the primary boot option.
- Move the selected device up or down: To change the boot order, you need to move the selected device up or down the list. Some BIOS interfaces allow you to do this by pressing the “+” or “-” keys, while others may use different keys like PgUp or PgDn. Refer to the on-screen instructions or the manual for your specific BIOS.
- Save changes and exit: Once you’ve adjusted the boot order according to your preferences, save the changes by selecting the appropriate option. This is usually labeled as “Save and Exit” or something similar. Confirm your selection, and the computer will restart with the modified boot order.
It’s important to note that the steps mentioned above are general guidelines. The BIOS interface and options may differ slightly depending on your computer’s manufacturer and model. For specific instructions on changing the boot order in your BIOS, refer to the user manual or the manufacturer’s website.
Remember, making changes in the BIOS settings should be done with caution. Incorrect settings can cause boot failures or other system issues. If you’re unsure about any changes, it’s advisable to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek assistance from a professional.
Tips for troubleshooting boot order issues
Encountering boot order issues can be frustrating, but don’t worry. Here are some useful tips to help you troubleshoot and resolve common boot order problems:
- Check the boot order: Double-check the boot order settings in the BIOS to ensure that the correct device is set as the primary boot option. Sometimes, incorrect or changed settings can cause the computer to not boot from the desired device.
- Disconnect unnecessary devices: If you have multiple external devices connected to your computer, such as USB drives or external hard drives, try disconnecting them and booting the system. Sometimes, conflicts between devices can result in boot order issues. Disconnecting unnecessary devices can help narrow down the problem.
- Verify bootable media: If you’re trying to boot from a specific device, such as a USB drive or a CD/DVD, make sure that the media is bootable and properly connected. Faulty or corrupted bootable media can prevent the system from booting correctly.
- Reset the BIOS settings: If you’ve made changes to the BIOS settings and are experiencing boot problems, try resetting the BIOS settings to their default values. This can help eliminate any incorrect configurations that may be causing the issue.
- Update BIOS firmware: Outdated BIOS firmware can sometimes cause boot order problems or compatibility issues. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available BIOS updates for your computer model. Make sure to follow the instructions carefully when updating the BIOS firmware.
- Check for hardware failures: In some cases, boot order problems may be caused by hardware failures. Run diagnostic tests to check the health of your hard drive, RAM, and other critical components. Faulty hardware can affect the boot process and prevent the system from recognizing or booting from the desired device.
- Consult the manufacturer or seek professional help: If you’ve tried the above steps and are still experiencing boot order issues, it’s advisable to contact the computer manufacturer’s support or seek assistance from a professional technician. They can provide more specific troubleshooting guidance based on your computer model and help you resolve the issue effectively.
Remember, boot order issues can have various causes, and finding the exact solution may require some trial and error. Patience and careful troubleshooting are key to resolving boot order problems and getting your computer back up and running smoothly.
Importance of maintaining the correct boot order
Maintaining the correct boot order in BIOS is crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of your computer system. Here are a few reasons why maintaining the correct boot order is important:
- Optimal startup performance: The boot order determines the sequence in which the computer searches for a bootable device. By setting the correct boot order, you can ensure that the system boots from the desired device quickly and efficiently. This helps to minimize startup time and get your computer up and running faster.
- Proper operating system loading: The boot order determines which device the computer looks for to load the operating system. If the boot order is incorrect, the system may try to load the operating system from an unavailable or non-bootable device, resulting in boot failures or delays. By maintaining the correct boot order, you can ensure that the operating system is loaded from the intended device without any issues.
- Flexibility and customization: The ability to modify the boot order provides flexibility and customization options for your computer system. You can prioritize specific devices or change the default boot device based on your requirements. For example, if you frequently utilize a USB drive for booting into different operating systems or diagnostic tools, setting the USB drive as the primary boot option allows easy access to these tools.
- Troubleshooting capabilities: Maintaining the correct boot order is essential when troubleshooting system issues. It allows you to boot from alternative devices, such as a recovery CD or USB drive, to perform system repairs or diagnostics. Without the correct boot order, you may not be able to access the necessary tools to identify and fix the problem effectively.
- Efficient multi-boot setups: If you have multiple operating systems installed on different devices, maintaining the correct boot order is crucial for efficient multi-boot setups. By selecting the appropriate boot order, you can easily switch between different operating systems during startup without any conflicts or complications.
Overall, maintaining the correct boot order is essential for optimizing the performance, stability, and functionality of your computer system. It ensures that the operating system is loaded from the desired device, minimizes startup time, and provides flexibility for customized configurations. By understanding and properly managing the boot order in BIOS, you can enhance your overall computing experience and avoid unnecessary boot-related complications.
Frequently Asked Questions about changing the boot order in BIOS
Changing the boot order in BIOS can sometimes be confusing, especially for those who are not familiar with the process. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clear up any confusion and provide further insights:
-
Why should I change the boot order in BIOS?
Changing the boot order allows you to prioritize which device the computer boots from first. This is useful when you want to boot from a specific device, such as a USB drive or CD/DVD, instead of the default boot device. It is also helpful for troubleshooting or setting up a multi-boot system.
-
What is the default boot order in BIOS?
The default boot order in BIOS usually begins with the primary hard drive. This means the computer will try to boot from the primary hard drive first. If the primary hard drive does not contain a bootable operating system, it will move on to the next device in the boot order list.
-
Which key do I press to enter the BIOS settings?
The key to enter the BIOS settings varies depending on the computer’s manufacturer and model. Common keys to access the BIOS settings include Del, F2, and F10. During the boot process, you will see a brief message indicating the correct key to press. Refer to your computer’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions.
-
Can I harm my computer by changing the boot order?
Changing the boot order itself won’t harm your computer. However, incorrect or inappropriate changes to other BIOS settings can potentially cause issues. It’s important to be cautious and only modify settings that you understand or with proper guidance to avoid unintended consequences.
-
Will changing the boot order affect my installed files and programs?
No, changing the boot order does not affect your installed files and programs. It only determines the order in which the computer searches for a bootable device. As long as the selected boot device contains a bootable operating system, your files and programs will remain intact.
-
What should I do if I accidentally change the boot order incorrectly?
If you accidentally change the boot order and encounter issues booting your computer, you can enter the BIOS settings again and restore the boot order to its previous configuration. Most BIOS interfaces offer an option to load default settings or revert to the original boot order.
-
Why don’t I see the option to change the boot order in my BIOS settings?
It’s possible that the option to change the boot order is located in a different section or labeled differently in your BIOS interface. Different computer models have varying BIOS versions and configurations. Refer to your computer’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions on accessing and modifying the boot order.
Remember, if you’re unsure about any changes in the BIOS settings or encounter difficulties, it’s always recommended to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or seek assistance from a professional technician.