Overview
Sideloading refers to the process of installing and running applications on a device from a source other than an official app store. While the term is most commonly associated with the installation of applications on smartphones and tablets, it can also be applied to other devices like smart TVs, streaming devices, and even gaming consoles.
In contrast to traditional app installations, which are done through official app stores like Google Play Store or Apple App Store, sideloading allows users to bypass these curated platforms and directly install apps from third-party sources. This can be done by downloading the app file (APK for Android, IPA for iOS) from a website, email attachment, or any other means, and then manually installing it on the device.
Sideloading offers several benefits, such as the ability to access apps that are not available on official app stores, testing pre-release or beta versions of apps, and customizing devices with apps that have been modified or customized by developers or users. However, it also comes with certain risks, including the potential for installing malicious apps that could compromise the device’s security or privacy.
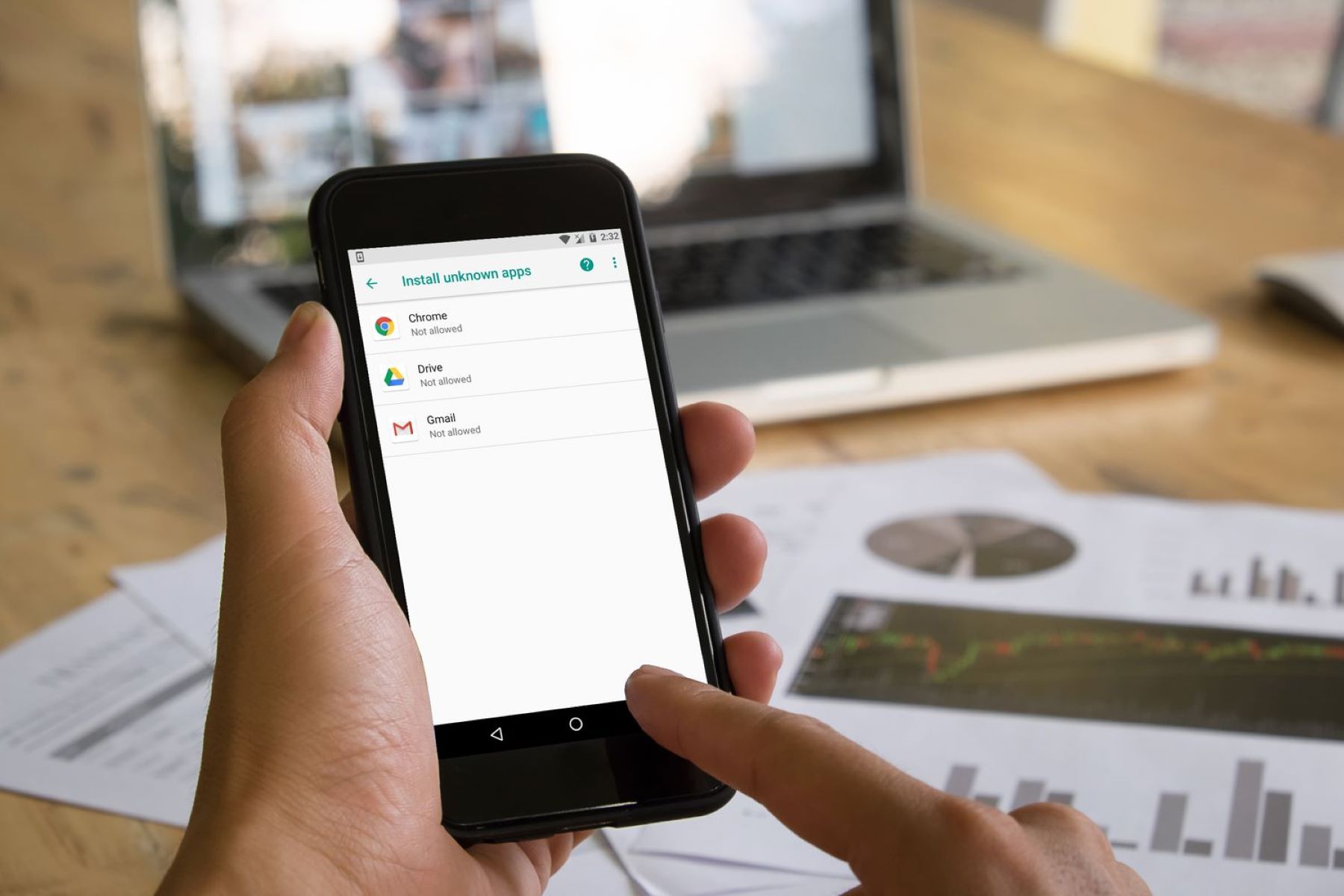
To enable sideloading, users need to adjust the settings on their devices to allow installation from unknown sources. The process varies depending on the device and operating system, but it usually involves navigating to the device settings, accessing the security or developer options, and toggling the “Unknown Sources” or “Install Unknown Apps” setting.
There are also different methods for sideloading apps, depending on the device and operating system. Some common methods include using file manager apps, connecting the device to a computer and transferring the app file, or using specialized sideloading tools or software.
It’s important to note that sideloading should be done with caution. Users should only download apps from trusted sources and verify their authenticity before installing them. Additionally, users should keep their devices and apps updated to mitigate any security risks associated with sideloaded apps.
In summary, sideloading provides a way to install apps on devices from sources other than official app stores. It offers flexibility and customization options, but also carries certain risks. By understanding how to enable sideloading and following best practices, users can safely explore and enjoy the benefits of sideloaded apps.
Definition of Sideloading
Sideloading is the process of installing and running applications on a device from a source other than an official app store. It allows users to download and install apps directly onto their devices, bypassing the need to go through the curated platforms like Google Play Store, Apple App Store, or other similar marketplaces.
The term “sideloading” often refers to the installation of applications on smartphones and tablets, but it can also extend to other devices such as smart TVs, streaming devices, and gaming consoles. It provides users with the opportunity to explore a wider range of apps and access content that may not be available through official channels.
Sideloading is typically done by obtaining the app file, which is usually in the form of an APK (Android Package Kit) for Android devices or an IPA (iOS App Store Package) for iOS devices. These app files can be acquired from various sources, including websites, email attachments, or file-sharing platforms. Once downloaded, the app file can be manually installed on the device.
The ability to sideload apps expands the possibilities for users by allowing them to access apps that have not been approved or are not available on official app stores. This includes beta versions of apps, apps that have been removed from app stores, or apps that offer unique functionalities and features that may not fit within the guidelines of official platforms.
However, it’s worth noting that sideloading introduces certain risks. Since apps installed through sideloading bypass the security checks of the official app stores, there is a higher chance of encountering malicious or counterfeit apps. These apps may compromise the device’s security, privacy, or even functionality.
To safeguard against potential risks, users should exercise caution when sideloading apps. They should only download apps from trusted sources and verify the authenticity of the app and its source before installation. Additionally, keeping the device’s operating system and installed apps up to date can help mitigate any security vulnerabilities.
In summary, sideloading refers to the process of installing applications on a device from sources other than official app stores. It provides users with the flexibility to explore a wider variety of apps but also raises security concerns. By understanding the risks and taking necessary precautions, users can safely leverage the benefits of sideloading to enhance their device’s functionality and access unique app experiences.
Benefits of Sideloading
Sideloading offers several benefits that enhance the app installation experience beyond what official app stores provide. By allowing users to install apps from sources other than official channels, sideloading opens up new possibilities and customization options for device owners. Here are some of the key benefits of sideloading:
1. Access to Unofficial Apps:
Sideloading enables users to access apps that may not be available on official app stores. This includes apps that have been removed or rejected from the app stores due to policy violations or other reasons. Users can explore a wider range of applications and discover hidden gems that may not have gained recognition through official channels.
2. Beta Testing and Pre-release Versions:
Sideloading allows users to participate in beta testing programs and try out pre-release versions of apps. Users get a chance to provide valuable feedback and help shape the development of their favorite apps. This gives them a sense of involvement and the opportunity to experience new features or improvements before they are officially released.
3. Customization and Modification:
Sideloading provides users with the ability to customize and modify their devices by installing apps with tweaked functionality or modified interfaces. This gives users the freedom to personalize their device experience and tailor it to their specific needs. For example, users can sideload apps that offer advanced customization options, alternative launchers, or unique system utilities.
4. App Availability in Restricted Regions:
Some apps may be restricted or geo-blocked in certain regions due to licensing or regulatory reasons. Sideloading allows users to bypass these restrictions and install apps that are otherwise not accessible in their location. This can be particularly useful for users who want to access region-specific content or services.
5. Offline Installation:
Sideloading eliminates the need for an active internet connection during the installation process. Users can download app files from a trusted source and manually install them on their device, even in situations where internet connectivity is limited or unavailable. This can be beneficial for users in remote areas or those with limited data plans.
While sideloading offers these benefits, users should exercise caution and verify the authenticity and safety of the app files they are installing. They should only download apps from trusted sources to minimize the risk of malware or other security threats.
Risks of Sideloading
Although sideloading offers a range of benefits, it is not without its risks. By installing apps from sources other than official app stores, users expose themselves to certain security and privacy vulnerabilities. Here are some of the key risks associated with sideloading:
1. Malicious Apps:
One of the most significant risks of sideloading is the potential for installing malicious apps on your device. Unlike apps from official app stores, which go through rigorous security checks, sideloaded apps bypass these safeguards. Malicious apps can compromise the security of your device, steal personal information, or even control your device without your consent.
2. Modified and Counterfeit Apps:
Sideloading opens the door to installing modified or counterfeit versions of popular apps. These apps may contain hidden malware, adware, or collect sensitive information without your knowledge. It’s crucial to verify the authenticity of the app and the source before installing sideloaded apps to protect yourself from such risks.
3. Lack of Updates and Support:
Sideloaded apps may not receive regular updates or support from the original developers. Official app stores provide a centralized platform for developers to push updates, bug fixes, and security patches to their apps. When sideloading, it is the responsibility of the user to manually update the apps, increasing the chances of using outdated and vulnerable versions.
4. Compatibility Issues:
Sideloading apps may result in compatibility issues with your device’s operating system or hardware. Since sideloaded apps are not vetted for compatibility by the official app store, they may not function optimally or may be prone to crashes and other software glitches. This can negatively impact the user experience and device performance.
5. Legal Consequences:
Depending on your jurisdiction and the purpose of sideloading, there may be legal ramifications. Some apps and content may be subject to copyright protection or licensing restrictions, and sideloading them without authorization can infringe upon those rights. It is important to familiarize yourself with the laws and regulations in your region regarding sideloading to avoid any legal consequences.
To mitigate the risks associated with sideloading, it is essential to exercise caution and follow best practices. Only download apps from trusted sources, research user reviews and ratings, and scan apps with reputable security software before installation. Regularly update your device’s operating system and installed apps to patch any security vulnerabilities that may arise.
In summary, sideloading introduces risks such as malicious apps, modified versions, lack of updates, compatibility issues, and potential legal consequences. It is crucial to weigh these risks against the benefits and take appropriate measures to safeguard your device and personal data when sideloading apps.
Common Applications that Support Sideloading
Sideloading is a versatile method that can be applied to various devices and operating systems. While the availability of sideloading may vary depending on the platform, there are several popular applications that support sideloading. Here are some common examples:
1. Kodi:
Kodi is a popular media center application that allows users to manage and stream their media content. It supports sideloading on devices like smart TVs, streaming devices, and even smartphones. With sideloaded add-ons, users can enhance Kodi’s functionality by accessing additional streaming sources, customizing the user interface, and adding advanced features.
2. VLC Media Player:
VLC Media Player is a versatile multimedia player that supports sideloading on Android devices. It allows users to play various audio and video formats, and by sideloading additional codecs, users can ensure compatibility with a wide range of file types. Additionally, VLC Media Player offers customization options and advanced settings that can be accessed through sideloading.
3. Amazon Appstore:
While the Amazon Appstore is an official app marketplace, it also allows users to sideload apps onto their Android devices. This approach expands the selection of available apps beyond what is offered through the Amazon Appstore itself. Users can download APK files from trusted sources and install them manually on their devices.
4. F-Droid:
F-Droid is an alternative app store for Android devices that focuses on open-source applications. It allows users to sideload apps that may not be available on other app stores due to restrictions or different licensing models. F-Droid hosts a wide array of apps that promote privacy, customization, and open-source development.
5. Cydia:
Cydia is an application specifically designed for jailbroken iOS devices. Jailbreaking allows users to bypass Apple’s restrictions and gain root access to their devices. Cydia acts as an alternative app store, enabling users to sideload apps that are not available through official channels, as well as customize their device’s appearance and behavior.
6. APKMirror:
APKMirror is a trusted website that hosts APK files for Android apps. It allows users to sideload apps onto their devices by providing a repository of safe and verified app files. APKMirror offers a wide range of apps, including popular ones, and users can download the APK files and manually install them on their devices.
It’s important to note that while these applications support sideloading, users should exercise caution and only download apps from trusted sources. Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the sideloaded apps is crucial to mitigate the risk of installing malicious or modified applications.
In summary, there are various applications that support sideloading on different platforms. Whether it is media center applications like Kodi and VLC, alternative app stores like Amazon Appstore and F-Droid, or specific tools like Cydia for jailbroken iOS devices, sideloading offers users the flexibility to customize their devices and access a wider range of apps.
How to Enable Sideloading on Different Devices
Enabling sideloading on different devices involves adjusting specific settings to allow the installation of apps from sources other than official app stores. While the exact process may vary depending on the device and operating system, here are general instructions on how to enable sideloading on different devices:
1. Android Devices:
On Android devices, sideloading is typically allowed by default. However, to ensure it is enabled, follow these steps:
– Go to “Settings” on your device.
– Navigate to “Security” or “Privacy” (this may vary depending on the device).
– Look for the “Unknown Sources” or “Install Unknown Apps” option.
– Toggle the switch to enable sideloading from unknown sources.
– A warning message may appear, alerting you to the potential risks associated with sideloading. Confirm your choice to proceed.
2. iOS Devices (Jailbroken):
For iOS devices that have been jailbroken, enabling sideloading can be done through the Cydia app. Follow these steps:
– Open the Cydia app on your jailbroken device.
– Search for and install the “AppSync” or “AppCake” package.
– Once installed, you will be able to sideload IPA files using a file manager or other methods.
3. Amazon Fire Devices:
Amazon Fire devices, including Fire tablets and Fire TV devices, have a unique setting to enable sideloading. Here’s how:
– Go to “Settings” on your Fire device.
– Select “Device” or “My Fire TV.”
– Scroll down and choose “Developer options.”
– Look for the “Apps from Unknown Sources” option and toggle the switch to enable sideloading.
4. Windows PC:
PCs running Windows allow sideloading of applications by default. However, you should still exercise caution when installing apps from unknown sources to avoid potential security risks.
5. macOS:
On macOS, sideloading is not a default setting, but it can be enabled using the Terminal app. Here’s how:
– Open the Terminal app on your Mac.
– Enter the following command: `sudo spctl –master-enable`.
– Press Enter and provide your admin password when prompted.
– Restart your Mac to enable sideloading.
It’s important to note that sideloading may not be available on all devices or operating systems. Some devices or platforms, such as iOS devices without jailbreaking, may have restrictions in place to prevent sideloading. Additionally, enabling sideloading may void warranty or violate terms of service for certain devices or software.
Before enabling sideloading, ensure you understand the risks involved and only download apps from trusted sources to minimize the potential for malware or compromised security.
How to Sideload Apps Using Different Methods
Sideloading apps onto devices can be done through various methods, depending on the device and operating system. Here are different ways to sideload apps:
1. File Manager Apps:
Many devices come with a built-in file manager app that allows users to navigate through their device’s internal storage or external SD card. To sideload apps using a file manager:
– Download the APK (Android) or IPA (iOS) file of the app you want to sideload.
– Open the file manager app on your device.
– Navigate to the location where the app file is saved.
– Tap on the app file to start the installation process.
2. USB Connection:
Some devices allow sideloading apps by connecting them to a computer via USB. Follow these steps:
– Download the app file on your computer.
– Connect your device to the computer using a USB cable.
– Transfer the app file from the computer to your device’s internal storage or SD card.
– Disconnect your device from the computer.
– Use a file manager app on your device to locate the app file and initiate the installation process.
3. Sideloading Tools or Software:
Depending on the device and platform, specific sideloading tools or software may be available to simplify the process. For example:
– Android devices can use tools like ADB (Android Debug Bridge) or platforms like Android Studio to sideload apps. These tools require connecting the device to a computer and running specific commands to install the app.
– iOS devices that are jailbroken can utilize tools like Cydia Impactor or AltStore to sideload IPA files onto the device.
– Some platforms, like Smart TVs or streaming devices, may have their own software or developer modes that allow sideloading of apps.
It’s important to note that the specific steps and requirements for each method may differ based on the device and operating system. Additionally, certain devices or platforms may have additional security measures in place that restrict or monitor sideloading.
Before sideloading apps, ensure that the app files come from trusted sources. Verify the authenticity of the app and exercise caution to mitigate the risk of installing malicious or modified applications.
Also, keep in mind that sideloading may void warranties or violate terms of service for certain devices or software. Make sure to familiarize yourself with any applicable policies before proceeding with sideloading.
By following the appropriate method for your device and ensuring the safety of the app files, you can successfully sideload apps and expand the functionality of your device beyond the limitations of official app stores.
Best Practices for Sideloading
Sideloading apps can offer a range of benefits, but it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure a safe and secure experience. Here are some recommended practices for sideloading:
1. Download Apps from Trusted Sources:
Only download app files (APK for Android, IPA for iOS) from trusted sources. Stick to reputable websites, official developer websites, or well-known app repositories. Be cautious of downloading from unfamiliar sources, as they may distribute altered or malicious apps.
2. Verify App Authenticity:
Before sideloading an app, verify its authenticity. Check the app’s publisher, reviews, and ratings to ensure it is a legitimate and reputable application. Be wary of apps that claim to be a modified version of popular apps, as these may contain malware or other security risks.
3. Keep Software and Apps Updated:
Regularly update your device’s operating system and installed apps. Developers often release updates to fix security vulnerabilities and bugs. By keeping your software and apps up to date, you reduce the risk of a security breach that could be exploited through sideloaded apps.
4. Use Security Software:
Install and regularly update reputable security software on your device. Antivirus and anti-malware applications can scan sideloaded apps for any potential threats, offering an additional layer of protection against malicious apps.
5. Understand App Permissions:
Pay attention to the permissions that an app requests during installation. Some apps may request access to an excessive amount of information or device functions that are not necessary for their functionality. Be cautious of granting permissions that seem unnecessary or excessive.
6. Backup Data:
Before sideloading any apps, ensure you have a backup of your device’s data. This includes important files, contacts, and any other information that you wouldn’t want to lose. In the event that something goes wrong during the sideloading process, having a backup will help prevent data loss.
7. Research Sideloading Methods:
Familiarize yourself with the specific methods and tools required for sideloading on your particular device and operating system. Understand the risks involved and follow appropriate steps when sideloading to ensure a smooth and secure installation.
8. Be Cautious with Rooted or Jailbroken Devices:
If your device is rooted (Android) or jailbroken (iOS), exercise caution when sideloading apps. These devices have more flexibility but also carry increased security risks. Only sideload apps from trusted sources and be mindful of the potential for unauthorized access or modification.
By following these best practices, you can reduce the risks associated with sideloading and enjoy the benefits of exploring a wider range of apps outside of official app stores.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Sideloading
While sideloading apps can offer great flexibility, it can sometimes come with its own set of challenges. Here are some common issues that users may encounter when sideloading and troubleshooting tips to address them:
1. App Installation Errors:
If you encounter errors while installing a sideloaded app, try the following troubleshooting steps:
– Verify that the app file is not corrupted or incomplete by re-downloading it from a trusted source.
– Clear the cache and data of the app you are using to install the sideloaded app (e.g., the file manager app).
– Restart your device, then attempt to install the app again.
– Check if your device has sufficient storage space available for the sideloaded app.
2. App Crashes or Freezes:
If a sideloaded app crashes or freezes, consider the following steps:
– Restart your device to clear any temporary issues.
– Update both the operating system and the app to the latest versions available.
– Check if the app is compatible with your device and operating system version.
– Uninstall and reinstall the app to ensure a fresh installation that may resolve any conflicts or corrupt files.
3. Compatibility Issues:
Some sideloaded apps may not be compatible with your device’s hardware or software. If you experience compatibility issues, try the following:
– Verify that your device meets the minimum system requirements specified by the app.
– Consult user forums or developer documentation to see if there are any known compatibility issues with your specific device model.
– Try installing an older or different version of the app, as newer releases may introduce changes that affect compatibility.
4. Security and Privacy Concerns:
Sideloading apps from unknown or untrusted sources may expose your device to security and privacy risks. Here’s how to address these concerns:
– Only install apps from trusted sources, such as reputable websites or official developer repositories.
– Use security software or antivirus apps to scan sideloaded apps for potential threats.
– Review and manage the permissions granted to each app to ensure they align with your privacy preferences.
5. Unwanted Modifications or Behavior:
If a sideloaded app modifies your device’s settings or behaves unexpectedly, consider these troubleshooting steps:
– Uninstall the problematic app and confirm if the unwanted behavior ceases.
– Report the issue to the app’s developer or seek guidance from online forums or support communities.
– Consider factory resetting your device if the issues persist, as this will remove all sideloaded apps and configurations.
Remember, sideloading apps come with certain risks, so it’s vital to stay vigilant and cautious. When encountering issues, investigate and follow the appropriate troubleshooting steps for your specific device and operating system. If needed, seek assistance from the app’s developers or online communities to troubleshoot more complex or unique issues.
Is Sideloading Legal?
The legality of sideloading apps can vary depending on factors such as the device, operating system, and jurisdiction. While sideloading itself is generally legal, there are certain considerations to keep in mind:
1. Android:
Android is an open-source operating system that allows sideloading of apps by default. Google, the company behind Android, permits users to install apps from sources other than the official Google Play Store. However, it is important to note that some apps may violate copyright or licensing agreements if downloaded and used without proper authorization.
2. iOS:
On iOS devices, sideloading is restricted unless the device is jailbroken. Apple, the company behind iOS, maintains strict control over app distribution through the App Store. By default, iOS devices only allow installation of apps from the App Store. Sideloading apps onto non-jailbroken iOS devices may violate the terms of service and warranty agreements.
3. Regional Laws and Regulations:
The legality of sideloading can also vary by jurisdiction. Some countries have certain laws or regulations that restrict or prohibit the installation of apps from sources other than official app stores. It is important to familiarize oneself with the local laws and regulations regarding sideloading to avoid any legal consequences.
4. Copyright and Intellectual Property:
Sideloading apps that infringe upon copyright or intellectual property rights can be deemed illegal. Downloading apps that are protected under copyright without proper authorization from the copyright holder may result in legal consequences.
5. App Developers’ Terms of Service:
App developers may have specific terms of service that prohibit sideloading or using their apps outside of official app stores. It is crucial to review and adhere to the terms and conditions set forth by app developers to avoid any legal implications.
It is essential for users to understand and respect the legal boundaries associated with sideloading. While sideloading itself may not be illegal, the means by which sideloaded apps are obtained or used can potentially breach copyright, licensing agreements, or other legal restrictions. Users should exercise caution, conduct proper research, and comply with applicable laws and regulations to ensure a legal and safe sideloading experience.
It is advisable to consult with legal professionals or seek guidance from authorized sources to fully understand the legal implications of sideloading in your specific jurisdiction.