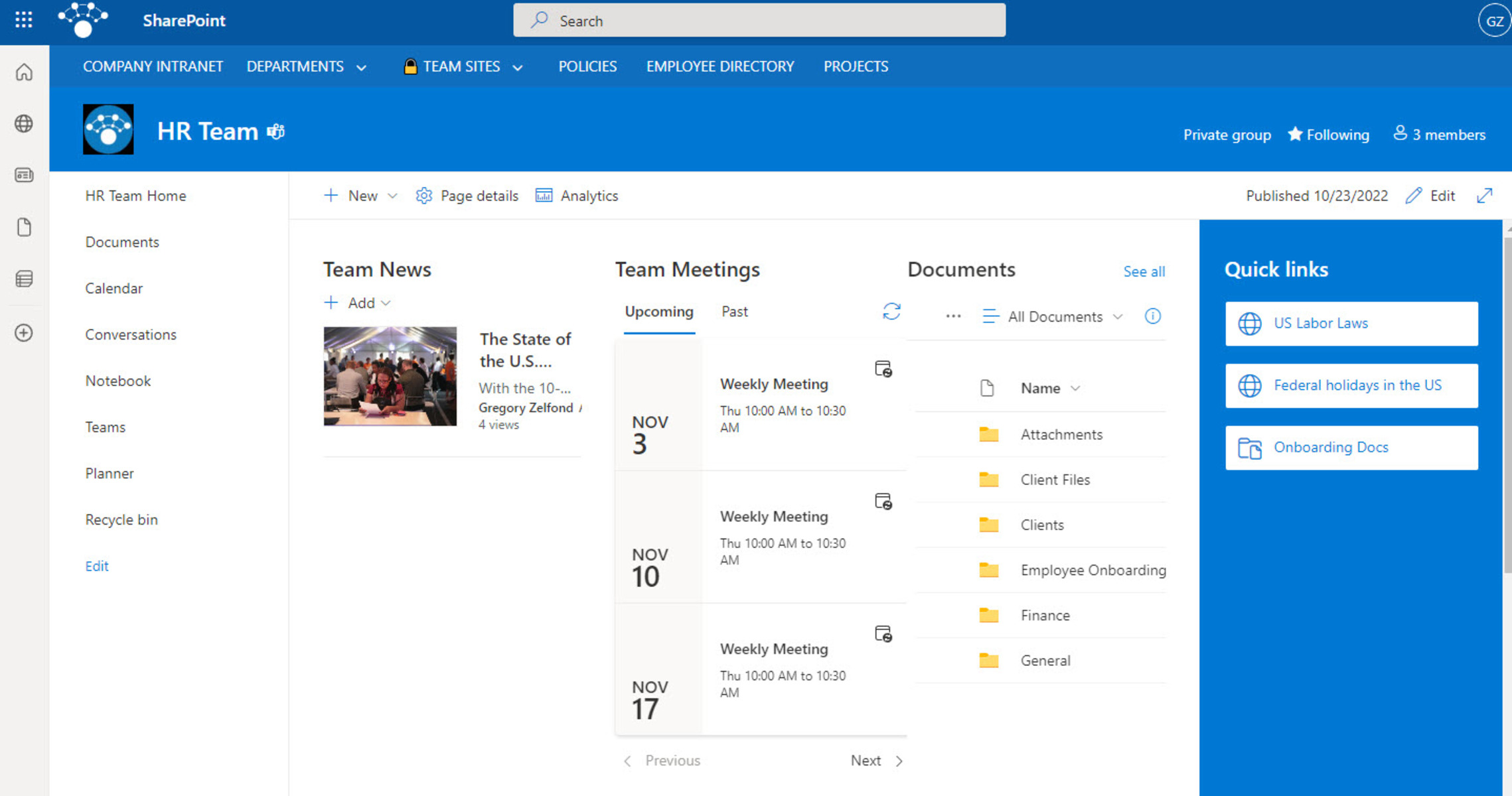
What is SharePoint?
SharePoint is a widely-used web-based collaboration and content management platform developed by Microsoft. It provides organizations with a centralized and secure environment for sharing, organizing, and managing information, as well as facilitating collaboration and communication among team members.
At its core, SharePoint is designed to enhance productivity and streamline business processes by enabling efficient information sharing and collaboration within a company and with external stakeholders. It serves as a central hub for accessing and managing documents, projects, workflows, and other relevant data, empowering teams to work together seamlessly and achieve their goals.
SharePoint offers a versatile array of features that make it suitable for various use cases across industries. It serves as a customizable platform that can adapt to the unique needs of different organizations and teams, allowing them to tailor their SharePoint sites and applications to fit their specific requirements.
With SharePoint, users can create and manage websites, intranets, portals, and extranets, making it an essential tool for internal communication, document management, project collaboration, and knowledge sharing. It integrates with other Microsoft solutions, such as Microsoft Office, Outlook, and Teams, providing a comprehensive suite of productivity tools.
SharePoint enables users to store and organize documents in a hierarchical structure, facilitating easy access and version control. It supports various file types, preserves metadata, and allows for document co-authoring and simultaneous editing.
In addition, SharePoint offers robust security features to protect sensitive information and control access permissions. It provides options for managing user roles and permissions, implementing data loss prevention measures, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Overall, SharePoint is a powerful and versatile platform that empowers organizations to enhance collaboration, streamline document management, and improve productivity. Whether used as an intranet solution, a document repository, or a collaboration tool, SharePoint provides a scalable and customizable platform that can meet the diverse needs of modern businesses.
History of SharePoint
The history of SharePoint dates back to the early 2000s when Microsoft recognized the need for a platform that could address the growing challenges of collaboration and document management in enterprises. The first version of SharePoint, SharePoint Portal Server 2001, was released in 2001 as a document management and search solution.
Over the years, SharePoint underwent significant advancements and iterations. SharePoint 2003 introduced improved collaboration features, such as document versioning, discussions, and surveys. With the release of SharePoint 2007, Microsoft introduced a more robust and integrated platform, offering enhanced document management, content publishing, and search capabilities.
In 2010, SharePoint 2010 was released, bringing a wide range of improvements and new features. This version introduced social features, such as blogs and wikis, allowing for better knowledge sharing and collaboration. SharePoint 2010 also offered enhanced search capabilities, workflow management, and business intelligence integration.
The next major release came in 2013 with SharePoint 2013, which focused on improving the user experience and introducing new features for mobile and cloud integration. This version introduced a responsive design, making SharePoint more accessible on various devices. It also introduced the SharePoint App Model, enabling developers to build and deploy custom applications on SharePoint.
SharePoint continued to evolve with the release of SharePoint 2016. This version emphasized hybrid deployments, allowing organizations to leverage both on-premises and cloud-based capabilities. SharePoint 2016 also introduced improved user experience, enhanced mobile support, and tighter integration with Microsoft Office 365.
The latest iteration of SharePoint is SharePoint 2019, released in 2018. SharePoint 2019 focuses on modernizing the platform and improving user experience. It offers improved integration with Office 365, including seamless synchronization with OneDrive for Business and enhanced hybrid capabilities.
In addition to the on-premises versions, Microsoft developed SharePoint Online as part of the Office 365 suite. SharePoint Online is a cloud-based service that provides organizations with all the capabilities of SharePoint without the need for maintaining infrastructure. SharePoint Online is continually updated and offers the latest features and enhancements.
The evolution of SharePoint reflects Microsoft’s commitment to addressing the changing needs of organizations and providing a powerful platform for collaboration, content management, and productivity. With each iteration, SharePoint continues to add new features and capabilities, empowering businesses to work more efficiently and effectively.
SharePoint Versions
SharePoint has evolved over the years, with each version offering new features and enhancements to improve collaboration and content management. Here are some of the key versions of SharePoint:
- SharePoint 2001: Also known as SharePoint Portal Server 2001, this was the first version of SharePoint released by Microsoft. It primarily focused on document management and search functionalities.
- SharePoint 2003: SharePoint 2003 introduced enhanced collaboration features, such as document versioning, discussions, and surveys. It also included improved search capabilities and customizable portal sites.
- SharePoint 2007: With SharePoint 2007, Microsoft introduced a more integrated and robust platform. It offered improved document management, content publishing, and search functionalities. SharePoint 2007 also introduced workflows and introduced web parts for easy customization.
- SharePoint 2010: SharePoint 2010 brought significant advancements in collaboration and social features. It introduced blogs, wikis, and enhanced document co-authoring. This version also included improvements in search, business intelligence, and web content management.
- SharePoint 2013: SharePoint 2013 focused on enhancing the user experience and providing better mobile support. It introduced responsive design to make SharePoint accessible on various devices. SharePoint 2013 also introduced the SharePoint App Model, allowing developers to create and deploy custom applications.
- SharePoint 2016: SharePoint 2016 emphasized hybrid deployments, allowing organizations to leverage both on-premises and cloud capabilities. It included improvements in user experience, mobile support, and tighter integration with Office 365 services.
- SharePoint 2019: Released in 2018, SharePoint 2019 focuses on modernizing the platform and improving user experience. It offers improved integration with Office 365, including seamless synchronization with OneDrive for Business. SharePoint 2019 also provides enhanced hybrid capabilities.
In addition to these on-premises versions, Microsoft introduced SharePoint Online as a part of the Office 365 suite. SharePoint Online is a cloud-based service that provides organizations with the latest features and capabilities without the need for managing the underlying infrastructure. SharePoint Online receives regular updates and enhancements from Microsoft.
Each version of SharePoint has brought new features and improvements to meet the evolving needs of organizations. Users can choose the SharePoint version that best suits their requirements, whether it’s an on-premises deployment or a cloud-based solution like SharePoint Online.
Features of SharePoint
SharePoint offers a wide range of features that empower organizations to collaborate, manage documents, and streamline business processes. Here are some of the key features of SharePoint:
- Document Management: SharePoint provides a robust document management system, allowing users to create, store, organize, and share documents in a secure and centralized location. It supports version control, document checkout/check-in, and metadata tagging.
- Collaboration: SharePoint facilitates collaboration and teamwork by providing tools for team sites, calendars, task management, discussion boards, and social features. It enables users to work together on documents, co-author in real-time, and utilize workflows for seamless collaboration.
- Search Capabilities: SharePoint includes powerful search functionality that allows users to quickly find and retrieve information from within SharePoint sites. It supports keyword searches, metadata-based filtering, and customizable search result displays.
- Workflows: SharePoint offers a workflow engine that enables organizations to automate business processes and streamline approvals. Users can design and customize workflows to automate tasks, notifications, and document approvals, improving productivity and reducing manual effort.
- Business Intelligence Integration: SharePoint integrates with Microsoft Power BI, enabling users to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations to gain insights from their data. Organizations can utilize SharePoint’s business intelligence features to analyze data and make informed decisions.
- Content Management: SharePoint provides content management capabilities, allowing organizations to create and manage web pages, intranet sites, and portals. It includes features like content publishing, branding, site templates, and document retention policies to ensure consistent and effective content management.
- Integration with Microsoft Office: SharePoint seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Office applications, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. Users can work with SharePoint documents directly from Office applications and collaborate more efficiently.
- Social Features: SharePoint includes social features like blogs, wikis, discussion boards, and social profiles. These features promote knowledge sharing, encourage collaboration, and enhance internal communication within the organization.
- Security and Permissions: SharePoint offers robust security features, allowing organizations to control access to sensitive information. It supports granular permissions, user authentication, data loss prevention, and information rights management to ensure data security and compliance.
These are just some of the many features that make SharePoint a versatile and powerful platform. Organizations can leverage these features to improve collaboration, streamline document management, automate workflows, and make data-driven decisions, ultimately improving productivity and driving business success.
SharePoint Components
SharePoint is comprised of various components that work together to provide a comprehensive collaboration and content management platform. Here are the main components of SharePoint:
- Sites: SharePoint Sites serve as the building blocks of the platform. Sites can be created for teams, projects, departments, or any other organizational structure. Each site has its own set of functionalities, including document libraries, lists, calendars, and workflows.
- Document Libraries: Document Libraries are where files and documents are stored within SharePoint. They provide features for organizing, versioning, and securing documents. Users can create folders, upload files, and collaborate on documents within the document libraries.
- Lists: SharePoint Lists are flexible data structures that can store various types of information, such as tasks, announcements, contacts, or custom data. Lists can be customized with columns, views, and workflows to suit specific business needs.
- Pages: Pages are web pages within SharePoint sites that can be customized to display content dynamically. They can contain text, images, web parts, and links to provide informative and interactive experiences.
- Web Parts: Web Parts are reusable components that can be added to SharePoint pages to display specific content or functionality. Web Parts can include calendars, document libraries, task lists, news feeds, and more. They allow users to customize their SharePoint experience and access relevant information easily.
- Metadata: Metadata refers to additional information associated with documents or items within SharePoint. It helps in classifying and organizing content. Custom metadata can be defined based on business requirements to enhance the search and organization of information.
- Workflows: Workflows in SharePoint automate business processes and tasks. They allow users to create, review, and approve documents and other items. Workflows can be customized using SharePoint Designer or Microsoft Power Automate (formerly known as Microsoft Flow) to match specific business processes.
- Security and Permissions: SharePoint ensures security and control of the data by providing granular permissions. Administrators can assign different levels of access to users or groups, controlling who can view, edit, or delete specific content.
- Search: SharePoint incorporates a powerful search engine that enables users to find information quickly. The search functionality provides powerful filtering and refinement options, ensuring that users can locate relevant content within SharePoint sites.
These components, working together, create a comprehensive and customizable platform that empowers organizations to collaborate, manage content, automate processes, and improve productivity. SharePoint’s modular architecture allows businesses to tailor the platform to their specific needs and provides a foundation for efficient collaboration and information management.
SharePoint Deployment Options
SharePoint offers flexible deployment options to meet the varying needs of organizations. Depending on their requirements, businesses can choose from the following deployment options:
- SharePoint Online: SharePoint Online is a cloud-based service provided as part of the Office 365 suite. Organizations can subscribe to SharePoint Online and access it through a web browser. With SharePoint Online, Microsoft takes care of infrastructure management, updates, and maintenance, allowing businesses to focus on their core activities.
- SharePoint On-Premises: SharePoint On-Premises refers to deploying and maintaining SharePoint servers within an organization’s own infrastructure. With this option, businesses have full control over the hardware, configuration, and customization of their SharePoint environment. On-Premises deployment is suitable for organizations with specific security or compliance requirements or those who prefer to manage their own infrastructure.
- Hybrid Deployment: Hybrid deployment is a combination of SharePoint Online and SharePoint On-Premises. It allows businesses to leverage the benefits of both cloud-based and on-premises deployments. Organizations can integrate their on-premises SharePoint environment with SharePoint Online, enabling seamless collaboration and data synchronization between the two environments. Hybrid deployment is beneficial for organizations looking to migrate gradually to the cloud or maintain certain data on-premises while taking advantage of cloud features.
The choice of deployment option depends on multiple factors, including the organization’s size, resources, security requirements, scalability requirements, and budget. Here are some considerations for each deployment option:
- SharePoint Online: SharePoint Online is a cost-effective option, as it eliminates the need for upfront hardware and infrastructure investment. It provides automatic updates and scalability, allowing businesses to easily scale their SharePoint environment as their needs grow. SharePoint Online is suitable for organizations seeking a cloud-based solution with minimal IT management responsibilities.
- SharePoint On-Premises: SharePoint On-Premises offers maximum control and customization capabilities. It is suitable for organizations with stringent security requirements or those that require full control over their SharePoint environment. On-Premises deployment allows businesses to leverage their existing infrastructure and integrate SharePoint with other on-premises systems.
- Hybrid Deployment: Hybrid deployment offers the best of both worlds by combining the flexibility of SharePoint Online with the control of SharePoint On-Premises. It allows organizations to gradually move to the cloud while preserving certain data on-premises. Hybrid deployment is suitable for businesses with specific compliance or data sovereignty requirements.
It’s important for businesses to carefully assess their needs, consider factors such as security, scalability, budget, and industry regulations, and choose the deployment option that best aligns with their goals and requirements.
SharePoint Online vs SharePoint On-Premises
When considering SharePoint deployment, organizations often have a choice between SharePoint Online and SharePoint On-Premises. Understanding the differences and benefits of each option is crucial in making an informed decision. Here’s a comparison between SharePoint Online and SharePoint On-Premises:
SharePoint Online:
SharePoint Online is a cloud-based service provided as part of the Office 365 suite. It offers several advantages:
- Scalability and Maintenance: SharePoint Online allows organizations to scale their SharePoint environment effortlessly. Microsoft handles the infrastructure and servers, ensuring reliable performance and availability. Updates and maintenance tasks, such as patches and security fixes, are automatically applied by Microsoft.
- Cost: SharePoint Online eliminates the upfront costs associated with purchasing and managing infrastructure. Organizations pay a subscription fee based on the number of users, making it a cost-effective option for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Collaboration Anywhere, Anytime: SharePoint Online enables teams to collaborate seamlessly from anywhere with an internet connection. Users can access, edit, and share documents in real-time, promoting productivity and flexibility.
- Integration with Office 365: SharePoint Online seamlessly integrates with other Office 365 applications, such as Word, Excel, and Teams. This integration enhances productivity and allows for a seamless user experience across different tools.
- Automatic Updates: Microsoft regularly updates SharePoint Online, delivering new features, security enhancements, and performance improvements without any additional effort from the organization.
SharePoint On-Premises:
SharePoint On-Premises refers to deploying and maintaining SharePoint servers within an organization’s own infrastructure. This option offers the following benefits:
- Control and Customization: SharePoint On-Premises provides complete control over the SharePoint environment. Organizations can customize the platform extensively, tailor it to specific needs, and integrate it with other on-premises systems.
- Data Security and Compliance: With SharePoint On-Premises, organizations have direct control over data security and compliance measures. This is advantageous for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare, finance, or government sectors.
- Connectivity to On-Premises Systems: SharePoint On-Premises allows integration with on-premises applications and systems that may not be suitable for the cloud environment. This enables seamless workflow integration and data exchange between different systems.
- Network Performance: SharePoint On-Premises can offer faster performance as the infrastructure is located within the organization’s own network. This can be beneficial for organizations that require quick response times for large files or complex operations.
- Offline Access: SharePoint On-Premises allows users to access and work on documents even without an internet connection. This can be useful in environments with limited or intermittent internet access.
Ultimately, the choice between SharePoint Online and SharePoint On-Premises depends on organizational needs, budget, compliance requirements, and scalability considerations. It’s important to evaluate the specific goals and constraints of the organization to make the right decision for SharePoint deployment.
Common Uses of SharePoint
SharePoint is a versatile platform that can be utilized in various ways across different industries. Here are some common uses of SharePoint:
- Document Management: SharePoint excels as a document management system. It provides a centralized location for creating, storing, organizing, and sharing documents. Users can apply metadata, version control, and access controls to ensure efficient document management and collaboration.
- Collaboration and Communication: SharePoint facilitates collaboration and communication within teams and across departments. It provides tools for team sites, discussion boards, calendars, and task lists, enabling teams to work together on projects, share knowledge, and coordinate tasks.
- Intranets and Portals: SharePoint is commonly used to build intranets and portals, serving as a central hub for internal communication, corporate news, and resources. Organizations can create custom intranet sites that house important information, policies, and announcements, fostering effective communication and engagement.
- Workflow Automation: SharePoint offers workflow capabilities, allowing organizations to automate business processes and approvals. Workflows can be created and customized to streamline tasks and improve efficiency. This automation reduces manual effort, saves time, and ensures consistent and standardized processes.
- Business Intelligence: SharePoint integrates with Microsoft Power BI to provide powerful business intelligence capabilities. It allows organizations to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations that offer insights into business data. SharePoint’s integration with Power BI enables data-driven decision-making and enhances business performance.
- Content Management: SharePoint serves as a content management system, enabling organizations to create and manage web pages, documents, and media content. It provides features for content publishing, branding, versioning, and approval workflows, ensuring consistent and effective content management.
- Knowledge Management: SharePoint facilitates knowledge sharing and management within organizations. It allows users to capture, store, organize, and search for information, making it easily accessible to employees. SharePoint’s collaborative features and search capabilities enable efficient knowledge sharing and retrieval.
- Project Management: SharePoint can be used for project management, providing tools for task tracking, document sharing, collaboration, and timelines. It allows project teams to coordinate efforts, manage tasks, and track progress, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
These are just a few examples of how SharePoint can be utilized. The flexibility and customization options of SharePoint make it a valuable tool for organizations in various industries, enabling efficient collaboration, content management, workflow automation, and knowledge sharing.
SharePoint for Document Management
SharePoint is widely recognized for its robust document management capabilities, making it an ideal platform for organizations to effectively manage their documents. Here’s how SharePoint facilitates efficient document management:
Centralized Document Repository: SharePoint provides a centralized location for storing and organizing documents, eliminating the need for scattered file shares or individual employee drives. Users can create document libraries and folders within SharePoint sites, allowing for easy access and efficient management of files.
Version Control and History: SharePoint ensures version control by allowing users to check-out and check-in documents. It keeps a record of document versions, preventing accidental overwriting or loss of important information. Users can easily revert to previous versions if needed and view the revision history.
Metadata and Tagging: SharePoint enables users to assign metadata to documents, such as document types, categories, tags, or custom attributes. This metadata helps in efficient search, filtering, and organizing of documents based on specific criteria, improving document discoverability and retrieval.
Collaborative Editing and Co-Authoring: SharePoint allows multiple users to collaborate on the same document simultaneously. Users can edit documents directly within SharePoint using familiar Microsoft Office applications, such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Co-authoring capabilities ensure real-time collaboration and reduce the need for email attachments and manual document merging.
Document Workflow: SharePoint’s workflow capabilities enable the automation of document-centric business processes. Organizations can create approval workflows, ensuring proper review and authorization of documents before finalization or publication. Workflows can be customized based on specific business requirements.
Document Search and Discovery: SharePoint offers robust search functionality, allowing users to quickly search and discover documents within SharePoint sites. Users can search by keywords, metadata, or other document attributes, refining search results to find the most relevant documents. Additionally, search results can be customized and tailored to specific user roles and permissions.
Document Security and Permissions: SharePoint provides granular control over document access and permissions. Organizations can assign unique permissions to specific documents or document libraries, ensuring that sensitive information is accessed only by authorized individuals. SharePoint also integrates with Active Directory, enabling seamless user authentication and access management.
Document Retention and Compliance: SharePoint allows organizations to enforce document retention and compliance policies. This ensures that documents are retained for the required duration and disposed of according to regulatory guidelines. Organizations can set up information management policies to automate document retention and disposal processes.
Document Alerts and Notifications: SharePoint enables users to set up alerts and notifications to stay informed about changes or updates to specific documents or document libraries. Users can receive email notifications when documents are added, modified, or deleted, ensuring they are up-to-date with the latest document versions and changes.
With its comprehensive document management capabilities, SharePoint serves as a powerful platform for organizations to efficiently organize, collaborate, secure, and manage their documents. By utilizing SharePoint for document management, organizations can streamline document-related processes, improve productivity, and enhance the overall efficiency of their operations.
SharePoint for Collaboration
SharePoint is widely recognized as a powerful collaboration platform, enabling teams and organizations to work together seamlessly. Here’s how SharePoint enhances collaboration:
Team Sites: SharePoint provides dedicated team sites where teams can collaborate on projects, share documents, and communicate effectively. Team sites serve as a central location where members can access important project-related information, including tasks, calendars, announcements, and discussions.
Document Sharing and Co-Authoring: SharePoint enables teams to easily share and collaborate on documents. Multiple team members can work on the same document simultaneously, with real-time updates and changes automatically synced. This eliminates the need for version confusion and enables efficient collaboration.
Discussion Boards and Communication: SharePoint includes discussion boards and communication tools that facilitate team communication and knowledge sharing. Team members can engage in discussions, ask questions, share ideas, and provide feedback, fostering effective collaboration and enhancing teamwork.
Task Management and Workflows: SharePoint offers built-in task management capabilities and the ability to create workflows. Teams can assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress within SharePoint. Workflows can automate the routing of tasks, approvals, and notifications, streamlining collaborative processes and improving efficiency.
Calendars and Scheduling: SharePoint’s integrated calendars enable teams to manage and coordinate schedules effectively. Team members can schedule meetings, share calendars, and view availability, making it easier to plan and organize team activities.
Access Control and Permissions: SharePoint provides granular access control, allowing teams to define specific permissions for different users or groups. This ensures that team members have appropriate access to documents, information, and features, while maintaining the necessary security and confidentiality of sensitive data.
Social Features and Collaboration: SharePoint offers social features such as blogs, wikis, and social profiles. These features encourage knowledge sharing, brainstorming, and community-building within teams and across the organization. Team members can contribute to wikis, write blogs to share insights, and connect with colleagues through social profiles.
Integration with Microsoft 365: SharePoint seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft 365 applications, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Teams. This integration enables teams to collaborate on documents, conduct virtual meetings, and communicate in real-time, creating a cohesive and efficient collaborative environment.
Mobile Access and Offline Sync: SharePoint provides mobile access, allowing teams to collaborate and access documents from anywhere, using their smartphones or tablets. SharePoint also offers offline sync capabilities, enabling users to work on documents even without an internet connection and sync changes once they are back online.
By utilizing SharePoint for collaboration, teams can streamline communication, enhance knowledge sharing, improve project management, and foster a culture of collaboration. With its extensive features and integration capabilities, SharePoint empowers organizations to work together effectively and achieve their shared goals.
SharePoint for Intranets and Portals
SharePoint is a popular choice for building and managing intranets and portals within organizations. With its robust features and customizable nature, SharePoint offers several advantages for creating effective intranets and portals:
Centralized Information Hub: SharePoint serves as a centralized information hub, providing a single point of access for employees to find important company resources, documents, policies, and news. Intranets built on SharePoint help promote internal communication and create a unified digital workplace.
Document Management and Collaboration: SharePoint’s document management capabilities make it easy to organize and share important documents throughout the organization. Intranets built with SharePoint allow employees to collaborate on documents, track changes, and ensure that everyone has access to the latest versions.
Customizable Design and Branding: SharePoint provides extensive customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the design and branding of their intranets to align with their corporate identity. Custom themes, logos, and color schemes can be applied to create a cohesive and branded intranet experience.
Employee Directory and Profiles: SharePoint enables the creation of employee directories and user profiles, making it easy for employees to find and connect with their colleagues. User profiles can contain information like job title, contact details, skills, and expertise, promoting visibility and collaboration among employees.
News and Announcements: SharePoint intranets can feature news sections or announcement boards that keep employees informed about company updates, events, policies, and other relevant information. This helps to improve internal communication and ensure that employees are up-to-date with important news.
Task Management and Workflows: SharePoint’s task management and workflow capabilities enhance intranets by allowing teams to assign tasks, track progress, and automate processes. Workflows can streamline document reviews, approvals, and other business processes, improving productivity and ensuring smooth operations.
Integration with Office 365 Apps: SharePoint seamlessly integrates with other Office 365 apps, such as Outlook, Teams, and Planner. This integration enables employees to access emails, schedule meetings, participate in team chats, and manage tasks directly from the intranet, creating an integrated and efficient digital workspace.
Information Sharing and Knowledge Management: SharePoint intranets facilitate knowledge sharing through features like wikis, forums, and blogs. Employees can contribute their insights, share best practices, and seek information, fostering a culture of learning and collaboration within the organization.
Employee Self-Service: SharePoint intranets can include self-service functionalities, such as HR portals, where employees can access and manage their benefits, request time off, update personal information, and find answers to commonly asked questions. This improves efficiency, reduces administrative overhead, and empowers employees.
Overall, SharePoint provides a comprehensive platform for building powerful and customizable intranets and portals. By utilizing SharePoint for intranets, organizations can create centralized hubs that enhance internal communication, improve knowledge sharing, streamline workflows, and provide employees with easy access to the resources they need to be productive and engaged.
SharePoint for Workflow Automation
SharePoint offers robust workflow automation capabilities, enabling organizations to automate and streamline their business processes. Here’s how SharePoint facilitates workflow automation:
Visual Workflow Designer: SharePoint provides a visual workflow designer that allows users to design and create workflows without the need for coding. Through an intuitive interface, users can define the sequence of actions, conditions, and approvals required for each workflow.
Pre-built Templates: SharePoint offers a collection of pre-built workflow templates, covering common business scenarios. These templates act as starting points for creating customized workflows, saving time and effort. Users can modify the templates to suit their specific requirements.
Automation of Business Processes: SharePoint workflows enable the automation of business processes, reducing manual effort and ensuring consistent and standardized operations. Workflows can automate tasks like document review and approval, onboarding processes, leave requests, purchase requisitions, and more.
Integration with SharePoint Features: SharePoint workflows integrate seamlessly with other SharePoint features, such as document libraries, lists, and calendars. This integration allows workflows to trigger actions based on document changes, list item updates, or specific events, improving process efficiency.
Conditional Logic and Branching: SharePoint workflows support conditional logic, allowing different actions to be taken based on specific conditions. Branching in workflows enables different paths to be followed based on certain criteria, ensuring that processes are customized and appropriate actions are taken.
Approval Workflows: SharePoint workflows include built-in approval processes, enabling organizations to set up multi-level, hierarchical approval chains. Workflows can route items or documents to the appropriate individuals or groups for review and approval, ensuring compliance and reducing bottlenecks.
Task Assignment and Notifications: SharePoint workflows can assign tasks to individuals or groups, along with due dates and reminders. Task notifications can be sent via email or within SharePoint itself, keeping participants informed about pending tasks and requests.
Data Integration and Manipulation: SharePoint workflows can interact with external systems, web services, and databases, allowing for data integration and manipulation. This capability enables workflows to pull or push data from/to other systems, enhancing process automation and data synchronization.
Error Handling and Escalation: SharePoint workflows include error handling and escalation mechanisms, allowing organizations to define actions to be taken in case of errors or delays. For instance, if a task is not completed within a specific timeframe, the workflow can escalate the task to a higher-level approver or send notifications for resolution.
Reporting and Analytics: SharePoint workflows provide reporting capabilities, allowing organizations to monitor and analyze the performance of their automated processes. Organizations can track workflow status, monitor process bottlenecks, and identify areas for improvement through SharePoint’s reporting features.
By leveraging SharePoint for workflow automation, organizations can optimize their business processes, reduce manual errors, improve efficiency, and ensure compliance. SharePoint’s intuitive workflow designer, pre-built templates, and integration capabilities make it a powerful platform for automating and streamlining various business processes.
SharePoint for Business Intelligence
SharePoint serves as a robust platform for business intelligence (BI), providing organizations with the tools they need to analyze data, gain insights, and make informed decisions. Here’s how SharePoint supports business intelligence:
Data Integration and Consolidation: SharePoint enables the integration and consolidation of data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and external systems. This data can be centrally stored and managed within SharePoint, providing a unified view of business information.
Interactive Dashboards and Reports: SharePoint allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports using its built-in BI capabilities or by integrating with Microsoft Power BI. These dashboards provide visual representations of key metrics, trends, and analysis, enabling stakeholders to quickly understand and interpret data.
Data Visualization: SharePoint offers a range of visualization options, including charts, graphs, and maps, to present data in a visually appealing and meaningful way. These visualizations enhance data comprehension and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
Ad Hoc Analysis: SharePoint empowers users to perform ad hoc analysis by providing self-service BI capabilities. Users can explore, filter, and slice data to uncover insights and patterns without the need for IT or BI expertise.
Data Refresh and Scheduled Updates: SharePoint allows for the automatic refresh and scheduled updates of data within dashboards and reports. This ensures that data is always up-to-date and provides real-time insights into business performance.
Collaboration and Data Sharing: SharePoint facilitates collaboration and data sharing among team members and stakeholders. Users can collaborate on dashboards, reports, and analysis, enabling cross-functional teams to work together, share insights, and collectively drive business performance.
Data Security and Permissions: SharePoint applies robust security measures to protect sensitive information and ensure data integrity. Organizations can define granular permissions, restricting access to specific data and dashboards based on user roles and responsibilities.
Workflow Integration: SharePoint integrates with SharePoint workflows, allowing organizations to automate and streamline data-driven processes. For example, workflows can be used to automate data refreshes, trigger notifications based on specific data conditions, or initiate approval processes based on data insights.
Mobile Access and Collaboration: SharePoint provides mobile access to BI dashboards and reports, empowering users to access and view critical data from anywhere, at any time. The mobile-friendly interface ensures a consistent user experience across different devices, enabling collaboration and informed decision-making on the go.
Advanced Analytics: SharePoint integrates with advanced analytics tools, such as Microsoft Power BI and Microsoft Azure Machine Learning, to perform advanced data analysis and predictive modeling. These tools extend the capabilities of SharePoint, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights and make data-driven forecasts.
By leveraging SharePoint for business intelligence, organizations can transform their raw data into actionable insights. SharePoint’s data integration, visualization, collaboration, and security capabilities facilitate data-driven decision-making, empower teams, and drive business performance.
SharePoint for Content Management
SharePoint is widely regarded as a robust content management platform, offering organizations the tools to effectively create, organize, and manage their content. Here’s how SharePoint supports content management:
Centralized Content Repository: SharePoint provides a centralized location for storing and organizing content, eliminating the need for scattered file shares or individual employee drives. Users can create document libraries, lists, and pages within SharePoint sites, allowing for easy access and efficient management of content.
Document Versioning and Control: SharePoint ensures version control by allowing users to check-out and check-in documents. This helps maintain a record of document versions, preventing accidental overwriting or loss of important information. Users can easily revert to previous versions if needed and view the revision history.
Metadata and Tagging: SharePoint enables users to assign metadata to documents, such as document types, categories, or custom attributes. This metadata enhances search, filtering, and organization of content based on specific criteria, improving discoverability and retrieval.
Content Collaboration and Co-Authoring: SharePoint allows multiple users to collaborate on the same document simultaneously. Users can edit documents directly within SharePoint using familiar Microsoft Office applications, such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Co-authoring capabilities ensure real-time collaboration and enhance productivity.
Document Workflow Automation: SharePoint’s workflow capabilities enable the automation of document-centric business processes. Organizations can create and customize workflows to automate tasks such as document review, approval, and publication, streamlining content management and ensuring consistent processes.
Enterprise Search: SharePoint incorporates a powerful search engine that allows users to quickly search and discover content within SharePoint sites. Users can search by keywords, metadata, or other document attributes, refining search results to find the most relevant content. Additionally, search results can be customized and tailored to specific user roles and permissions.
Content Syndication and Publishing: SharePoint supports content syndication, enabling organizations to publish and distribute content to multiple sites or platforms. Content published in one location can be automatically updated across various sites, ensuring consistency and reducing duplication of efforts.
Content Permissions and Security: SharePoint provides granular control over content access and permissions. Organizations can assign unique permissions to specific documents or document libraries, ensuring that sensitive information is accessed only by authorized individuals. SharePoint also integrates with Active Directory for seamless user authentication and access management.
Document Retention and Compliance: SharePoint allows organizations to enforce document retention and compliance policies. This ensures that documents are retained for the required duration and disposed of according to regulatory guidelines. Organizations can set up information management policies to automate document retention and disposal processes.
Content Publishing and Approval: SharePoint supports the publishing and approval of content, ensuring that only approved content is published to the organization’s public-facing sites or shared with external stakeholders. Content approval workflows enable efficient review, approval, and scheduling of content publication.
By leveraging SharePoint for content management, organizations can streamline their content-related processes, improve collaboration, enhance access and discoverability, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. SharePoint’s comprehensive content management capabilities provide organizations with the tools they need to effectively manage their content throughout its lifecycle.
SharePoint Integration with Other Microsoft Products
SharePoint offers seamless integration with various other Microsoft products, providing a comprehensive and integrated suite of productivity tools for organizations. Here’s how SharePoint integrates with other Microsoft products:
Microsoft Office: SharePoint integrates tightly with Microsoft Office applications, such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. Users can edit and collaborate on documents directly within SharePoint using familiar Office tools. SharePoint libraries can be synchronized with OneDrive for Business, allowing for easy offline access and automatic document synchronization.
Microsoft Teams: SharePoint integration with Microsoft Teams allows users to access SharePoint sites, document libraries, and lists directly within the Teams interface. Team members can collaboratively work on documents, access files, and share content from SharePoint without leaving the Teams application.
Microsoft Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow): SharePoint integrates with Power Automate, a cloud-based service that allows users to create automated workflows across multiple applications and services. SharePoint workflows can be triggered or connected to external systems, creating seamless and automated processes that span various platforms.
Microsoft Power BI: SharePoint can integrate with Power BI, a business intelligence and data analytics tool. Users can embed Power BI reports and dashboards directly into SharePoint pages, providing real-time data visualizations and insights within the SharePoint environment.
Microsoft Azure: SharePoint can be integrated with Microsoft Azure, a cloud computing platform, to extend its capabilities and leverage Azure services. Organizations can use Azure services to enhance SharePoint scalability, security, and performance, or build custom applications that interact with SharePoint.
Microsoft Exchange: SharePoint and Microsoft Exchange integrate to improve collaboration and communication. SharePoint calendars can be synchronized with Exchange calendars, ensuring that events and meetings are managed and displayed consistently across both platforms.
Microsoft OneNote: SharePoint integrates with Microsoft OneNote, an application for note-taking and information management. Users can create and store OneNote notebooks within SharePoint, allowing for easy access and collaboration on shared notebooks within the SharePoint environment.
Microsoft Yammer: SharePoint can be integrated with Yammer, a social networking and collaboration platform. This integration enables users to embed Yammer feeds and conversations within SharePoint pages, enhancing social collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Microsoft Dynamics 365: SharePoint integration with Microsoft Dynamics 365 enables organizations to store and manage documents related to customer relationships, sales, and projects. SharePoint libraries can be linked to Dynamics 365 entities, ensuring that relevant documents are accessible within the context of customer interactions and business processes.
Microsoft Azure Active Directory: SharePoint integrates with Azure Active Directory, providing a seamless single sign-on experience for users. This integration allows for centralized user authentication, access management, and synchronization of user information across various Microsoft services.
By integrating with other Microsoft products, SharePoint provides organizations with a unified and cohesive digital workplace, allowing users to seamlessly collaborate, access content, and leverage the advantages of multiple Microsoft tools within a single platform. This integration enhances productivity, improves user experience, and enhances the overall efficiency of organizations.
SharePoint Security and Permissions
SharePoint provides robust security features to protect sensitive information and ensure that users have appropriate access to content within the platform. Here’s how SharePoint enhances security and manages permissions:
Granular Permissions: SharePoint offers granular permission settings, allowing organizations to assign specific access rights to individual users, groups, or security roles. This ensures that users can only access the content and perform actions relevant to their roles and responsibilities.
Unique Permissions: SharePoint enables unique permissions to be set at various levels, such as at the site, list/library, or item/document level. This flexibility allows for fine-grained control over access permissions, ensuring that sensitive information is accessible to authorized individuals only.
External Sharing: SharePoint allows organizations to control external sharing of content. Administrators can define the level of external sharing allowed, such as external sharing at the site level or specific permissions granted to external users. This ensures that external stakeholders can collaborate securely within established boundaries.
Active Directory Integration: SharePoint seamlessly integrates with Active Directory, enabling organizations to utilize existing user accounts for authentication and access management. This integration streamlines user provisioning, authentication, and synchronization, minimizing the administrative overhead and ensuring consistent user management.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): SharePoint offers Data Loss Prevention features, allowing organizations to define and enforce policies to protect sensitive information. DLP policies can be set to prevent unauthorized sharing or loss of sensitive data, helping organizations maintain data security and comply with regulatory requirements.
Information Rights Management (IRM): SharePoint supports Information Rights Management, providing additional layers of protection to sensitive content. IRM allows administrators to define access rights, encryption, and usage restrictions for documents, protecting data even when it’s downloaded or shared outside the SharePoint environment.
Auditing and Reporting: SharePoint includes auditing and reporting capabilities, allowing organizations to track user activities, identify potential security breaches, and monitor content usage. Audit logs provide insights into actions performed within SharePoint, aiding in compliance, security investigations, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Mobile Device Management (MDM): SharePoint integrates with Mobile Device Management solutions, enabling organizations to enforce security policies on mobile devices accessing SharePoint content. Security measures, such as device authentication, PIN locks, or remote wipe, can be applied to ensure data protection on mobile devices.
Secure File Storage: SharePoint provides secure file storage with features like encrypted transmission, encryption at rest, and secure protocols. It ensures that data remains protected during transmission and storage, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Threat Detection and Monitoring: SharePoint includes security features like threat detection, anomaly detection, and advanced monitoring. These capabilities help identify suspicious activities, detect potential security threats, and enable proactive measures to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
By leveraging SharePoint’s robust security features and permissions management, organizations can establish a secure environment for collaboration and content management. SharePoint’s flexible and customizable security measures ensure that sensitive information remains protected, while employees have the appropriate access to perform their tasks efficiently.
SharePoint Development and Customization
SharePoint provides extensive development and customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the platform to their specific needs and requirements. Here’s how SharePoint supports development and customization:
SharePoint Framework (SPFx): SharePoint Framework is a modern development model that enables developers to build responsive and personalized web parts, extensions, and solutions that can be deployed within SharePoint. SPFx allows for the creation of custom components using modern web technologies like React, Angular, and TypeScript.
Custom Web Parts and Extensions: SharePoint allows developers to create custom web parts and extensions that can be added to SharePoint pages. These customizations enhance the functionality and improve the user experience by adding specific features, integrations, or data visualizations based on organizational requirements.
Custom Workflows and Forms: SharePoint supports the creation of custom workflows and forms using tools like SharePoint Designer or Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow). These tools enable developers to design and customize workflows and forms to automate business processes and streamline data collection, validation, and approval.
Branding and User Interface Customization: SharePoint offers branding capabilities that allow organizations to customize the look and feel of SharePoint sites and pages. Organizations can create custom themes, apply custom CSS styles, and modify page layouts to match their branding guidelines and provide a consistent user interface.
Integration with Line of Business (LOB) Systems: SharePoint integrates easily with line-of-business systems, such as CRM or ERP platforms, through web services, APIs, or custom connectors. This integration enables data synchronization, information retrieval, or workflow initiation, integrating SharePoint with existing systems and improving process efficiency.
Content Type and Metadata Customization: SharePoint supports the creation of custom content types and metadata to suit specific business needs. Custom content types allow organizations to define information architecture and incorporate specific document or data management requirements, while custom metadata enhances search, filtering, and organization capabilities.
Managed Metadata and Taxonomy: SharePoint includes managed metadata and taxonomy features, allowing organizations to create and manage structured and hierarchical metadata across SharePoint sites. Managed metadata enhances content categorization, navigation, and search, resulting in improved content discoverability and retrieval.
Integration with External Data Sources: SharePoint enables integration with external data sources like databases, web services, or APIs using Business Connectivity Services (BCS) or Microsoft Power Automate. This integration allows SharePoint to display and interact with external data, providing a unified view of information across different systems.
Security and Permission Customization: SharePoint offers flexible security and permission customization options. Organizations can define custom permission levels, create custom security groups, or implement custom security trimming to control access to specific content, features, or actions within SharePoint sites.
Custom Apps and Solutions: SharePoint allows developers to create and deploy custom apps and solutions using SharePoint Add-ins, SharePoint Provider-hosted Add-ins, or SharePoint Framework extensions. These custom solutions can extend SharePoint’s capabilities, integrate with other systems, or provide specific functionality tailored to organizational requirements.
SharePoint’s development and customization options empower organizations to tailor the platform to their specific needs, ensuring a customized and optimized collaboration and content management experience. Whether it’s creating custom web parts, workflows, forms, or integrating with external systems, SharePoint provides developers with the tools necessary to enhance SharePoint’s capabilities and meet unique business requirements.
SharePoint Tips and Best Practices
As organizations implement SharePoint, following best practices can help ensure a smooth deployment and maximize the benefits of the platform. Here are some SharePoint tips and best practices:
Plan and Define Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and goals for implementing SharePoint within your organization. Identify the specific business processes, communication needs, and collaboration requirements that SharePoint will address. This will help shape your SharePoint implementation strategy.
Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders early in the planning and implementation process. Engage business units, IT teams, and end users to understand their requirements and gather feedback. Ensuring stakeholder buy-in and involvement will promote adoption and success.
Invest in Training and User Adoption: Provide comprehensive training and support to users during and after deployment. Promote user adoption by demonstrating the value and benefits of SharePoint. Encourage users to attend training sessions, participate in hands-on workshops, and provide ongoing support to address questions and concerns.
Follow Governance and Information Management: Establish governance policies and guidelines to maintain control over SharePoint usage. Establish practices for content creation, metadata management, document retention, and security. Regularly review and update governance policies to ensure compliance and optimize SharePoint usage.
Design for Scalability and Performance: Consider scalability and performance requirements during SharePoint design and architecture. Optimize site structures, configure caching, and employ good information architecture practices to ensure optimal performance as the platform grows and evolves.
Implement Data Backup and Recovery: Establish regular data backup and recovery processes to protect content and configurations. Implement a robust backup strategy, including offsite backups or cloud-based backup solutions. Regularly test the backup and recovery procedures to ensure data integrity.
Secure SharePoint Environment: Implement security best practices to protect your SharePoint environment. Utilize features such as user authentication, secure communication protocols, encryption, and intrusion detection. Regularly evaluate and update security measures to address evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Maintain a Clean and Organized Environment: Regularly review and clean up unused, outdated, or duplicative content. Use retention policies and workflows to manage content lifecycle. Encourage users to use consistent naming conventions, folders, and metadata to improve content discoverability and searchability.
Stay Updated: Keep up with SharePoint updates, patches, and feature releases. Regularly review Microsoft’s documentation and release notes for new features, bug fixes, and security updates. Stay informed about SharePoint industry trends and best practices to ensure ongoing optimization and innovation.
Leverage SharePoint Community and Resources: Engage with the SharePoint community, participate in forums and user groups, and attend conferences to learn from others’ experiences. SharePoint has a vibrant community that offers valuable insights, tips, and solutions for common challenges.
By following these tips and best practices, organizations can maximize the value of SharePoint, ensure a successful implementation, and create a well-managed and user-friendly collaboration and content management environment.