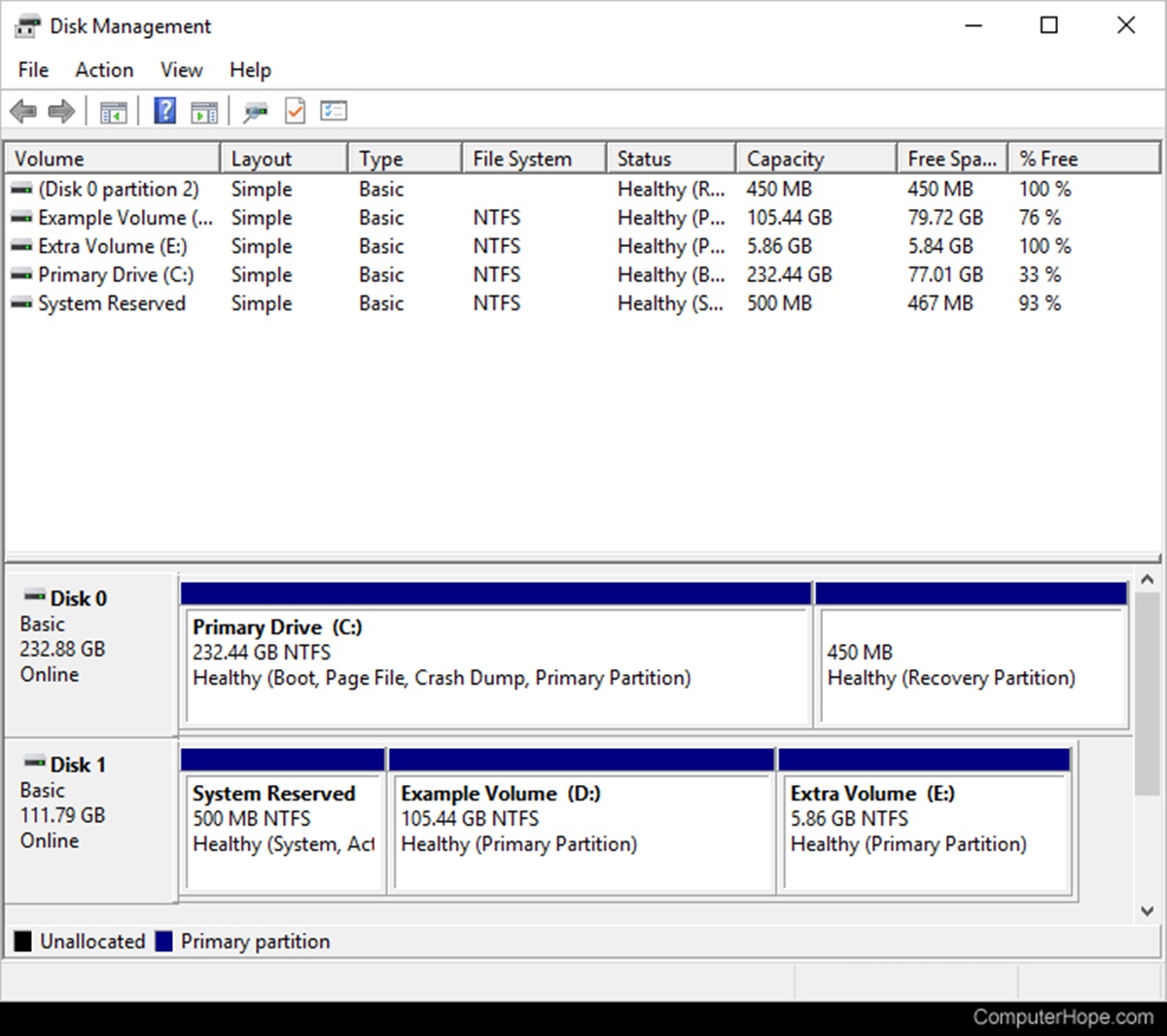
Disk Management Overview
Disk Management is a crucial utility tool in the Windows operating system that helps users manage and control their computer’s hard disk partitions and volumes. It provides a user-friendly interface to perform various tasks, such as creating, deleting, and resizing partitions, as well as formatting and assigning drive letters to volumes. This powerful tool is essential for organizing and optimizing your computer’s storage space efficiently. In this article, we will explore the key functionalities of Disk Management and understand how it can benefit you.
One of the primary features of Disk Management is disk partitioning. With this tool, you can create multiple partitions on your hard disk, allowing you to logically separate and organize your data. This is especially useful if you have one large drive and want to keep your system files separate from personal files or create a dedicated partition for a specific operating system.
In addition to partitioning, Disk Management enables you to format the newly created partitions or existing volumes. Formatting a partition prepares it for storing data by creating a file system, such as NTFS or FAT32. This process erases all existing data on the partition, so be sure to back up any important files before proceeding.
Another essential function of Disk Management is assigning drive letters to volumes. Drive letters are used to identify each volume in your system and provide easy access to them. By assigning a drive letter, you can navigate through your computer’s file system and access the desired volume through the Windows Explorer interface or command prompt.
Creating new simple volumes is another useful feature available in Disk Management. It allows you to combine unallocated space or free space from different drives into a single volume. This is ideal for expanding storage capacity or creating a new partition when you have limited disk space left.
If you have an existing volume that needs more space, Disk Management allows you to extend it by utilizing the available unallocated space on the same disk. This eliminates the need to back up and recreate the volume, saving time and effort.
On the other hand, if you have excess free space on a volume, you can shrink it using the Shrink Volume option. This feature is handy when you want to create additional partitions or allocate free space for other purposes.
Disk Management also offers the option to delete volumes. This feature is useful if you no longer need a particular partition or want to repurpose the space it occupies.
Furthermore, Disk Management allows you to change drive letters of existing volumes. This can be helpful when you want to reassign letters to match your preferred naming convention or resolve conflicts between multiple drives.
Lastly, Disk Management provides the option to convert a disk from basic to dynamic or vice versa. Dynamic disks offer advanced features such as spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID. Converting a disk type gives you access to these advanced functionalities to meet specific storage requirements.
In summary, Disk Management is a vital tool for managing your computer’s hard disk partitions and volumes. It offers a range of features, including partitioning, formatting, assigning drive letters, creating new volumes, extending existing volumes, shrinking volumes, deleting volumes, changing drive letters, and converting disk types. With its user-friendly interface and powerful capabilities, Disk Management empowers you to efficiently utilize and organize your computer’s storage space.
Disk Partitioning
Disk partitioning is a fundamental function of Disk Management that allows users to divide a hard disk into multiple logical sections known as partitions. This process helps organize and optimize your storage space, making it easier to manage and access your data.
When you first install a hard disk or initialize it, you are typically left with one large partition that spans the entire disk. However, it is often beneficial to divide this space into smaller partitions for various reasons.
One of the main advantages of disk partitioning is the ability to segregate different types of data. For example, you can create separate partitions for your operating system and programs, personal files and documents, multimedia content, or even a dedicated partition for backup purposes. This separation helps in isolating critical files and ensures that if one partition becomes corrupted or needs formatting, the data on other partitions remains intact.
Disk partitioning also allows you to install multiple operating systems on the same computer. With multiple partitions, you can set up a dual-boot configuration, enabling you to switch between different operating systems such as Windows and Linux. Each operating system will have its dedicated partition to store its files and programs, preventing conflicts and providing a smoother user experience.
In addition to improving data organization and multi-boot capabilities, disk partitioning can also enhance system performance. By separating the operating system and program files from user data, disk access for each partition becomes more efficient. This can result in faster file access and improved overall system responsiveness.
When partitioning a disk, it is important to consider the size and allocation of each partition. Windows provides a logical unit called “drive letters” to identify and access each partition. You can assign a unique drive letter (such as C:, D:, E:, etc.) to each partition, making it easy to navigate and access specific data. It is recommended to reserve a sufficient amount of space for each partition, considering the type of data it will store and future expansion needs.
It is worth noting that disk partitioning is not a reversible process, and resizing or modifying partitions after data has been stored on them can be complex and risky. Therefore, it is essential to plan and allocate partitions appropriately during the initial setup or when adding a new hard disk to your system.
Overall, disk partitioning is a powerful feature of Disk Management that offers flexibility, organization, data protection, and improved system performance. By dividing a hard disk into multiple partitions, you can efficiently manage your data, create multi-boot configurations, and optimize your computer’s storage space. Consider utilizing disk partitioning to enhance your system’s functionality and organization to meet your specific needs.
Disk Formatting
Disk formatting is a crucial process in Disk Management that prepares a partition or volume on your hard disk to store data. When you format a disk, it sets up the file system structure, allocating the necessary space and creating the directory structure for organizing files and folders.
One of the primary reasons for formatting a disk is to ensure compatibility with the operating system. Different file systems, such as NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT, are used by Windows to manage data on storage devices. By formatting a partition with the appropriate file system, you ensure smooth data transfer, file access, and compatibility with the operating system.
Formatting a disk also wipes out all existing data on the partition, making it useful when you want to start fresh or when you encounter disk errors or data corruption. It is essential to note that formatting a partition erases all data permanently, so it is crucial to backup any important files before proceeding.
Another scenario where disk formatting is necessary is when you want to switch from one file system to another. For example, if you have been using FAT32 and want to take advantage of the advanced features offered by NTFS, formatting the partition with NTFS is required. However, keep in mind that formatting a partition erases all data, so be sure to back up your files before proceeding.
Disk formatting also plays a vital role when you want to repurpose a partition or install a new operating system. In these scenarios, formatting the partition ensures that it is in the correct format for the intended use, whether it is for installing an operating system or creating a dedicated workspace for specific types of files.
To format a disk using Disk Management, you can simply right-click on the partition or volume and select the “Format” option. This will open a dialog box where you can choose the file system, allocation unit size, volume label, and perform a quick or full format. Quick format only erases the file system structure, while full format thoroughly scans the disk for bad sectors and takes more time to complete.
It is important to note that formatting a disk is a one-way process, and the data on the partition cannot be easily recovered once the formatting is complete. Therefore, it is crucial to double-check and ensure that you have the necessary backups in place before proceeding with the formatting process.
In summary, disk formatting is an essential process in Disk Management to prepare a partition or volume on your hard disk for storing data. It sets up the file system structure, erases existing data, and ensures compatibility with the operating system. Whether you want to start fresh, switch to a different file system, or repurpose a partition, formatting allows you to create a clean and organized space for your files and applications. Be sure to back up your data before performing the formatting process to avoid any loss of important files.
Assigning Drive Letters
Assigning drive letters is a crucial task in Disk Management that allows you to identify and access different partitions, volumes, and external storage devices connected to your computer. Each partition or volume is assigned a unique drive letter, such as C:, D:, E:, and so on, making it easier to navigate and access specific data.
When a new hard disk or external storage device is connected to your computer, and it has partitions or volumes that are not yet assigned a drive letter, Disk Management automatically assigns an available drive letter to them. However, you can also manually assign or change drive letters to suit your preferences or resolve conflicts between multiple drives.
To assign a drive letter, you can open Disk Management, right-click on the partition or volume, and select the “Change Drive Letter and Paths” option. This will open a dialog box where you can choose an available drive letter or assign a specific letter to the selected partition or volume.
Assigning drive letters has several benefits. Firstly, it provides an easy way to access and navigate through your computer’s file system. By associating a drive letter with a partition or volume, you can simply open Windows Explorer, select the corresponding drive letter, and access the files and folders within that partition.
Secondly, assigning drive letters helps in organizing your data and making it more accessible. You can assign specific drive letters to partitions based on their contents or purpose. For example, you can assign the letter C: to the partition containing the operating system, D: to the partition storing your personal files, and E: to the partition for multimedia content. This logical arrangement simplifies file management and improves overall productivity.
In cases where you have multiple partitions or volumes on the same physical disk, assigning drive letters allows you to differentiate and access each partition individually. This is particularly useful when setting up dual-boot configurations, where each operating system requires its dedicated partition with a unique drive letter.
Additionally, assigning drive letters helps in troubleshooting and resolving issues related to drive recognition. If a certain partition or external storage device is not appearing in Windows Explorer or is not accessible, checking and changing the assigned drive letter can help in resolving the problem.
It is worth noting that drive letters are assigned on a per-computer basis. This means that if you connect the same external storage device to a different computer, it might be assigned a different drive letter. Therefore, when transferring data or working with external storage devices, it is important to be mindful of the assigned drive letters to ensure smooth access to the data.
In summary, assigning drive letters is an essential task in Disk Management that allows you to identify and access partitions, volumes, and external storage devices. It simplifies file management, improves accessibility, and helps in troubleshooting drive recognition issues. Whether you are organizing your computer’s internal drives or working with external storage, assigning drive letters gives you the convenience and control to navigate and access specific data with ease.
Creating New Simple Volumes
Creating new simple volumes is a useful feature in Disk Management that allows you to combine unallocated space or free space from different drives into a single volume. This process helps to efficiently utilize available disk space and create larger storage areas for storing data or installing applications.
When you add a new hard disk to your computer or delete a partition, you may end up with unallocated space. Unallocated space is unused disk space that is not assigned to any partition or volume. By creating a new simple volume, you can convert this unallocated space into a usable partition or volume.
To create a new simple volume, open Disk Management, right-click on the unallocated space, and select the “New Simple Volume” option. This will start the New Simple Volume Wizard, guiding you through the process of creating a new volume.
During the wizard, you can specify the size of the new volume by entering the volume size or using the default maximum available size. You can also assign a drive letter or mount the volume to an empty folder on an existing drive. Assigning a meaningful drive letter or mount point can help you easily identify and access the new volume.
You can also choose the file system for the new volume, such as NTFS, FAT32, or exFAT. NTFS is the recommended file system for Windows operating systems, as it offers advanced features like file and folder permissions, encryption, and compression. FAT32 and exFAT are more suitable for compatibility with other devices and older versions of Windows.
The option to perform a quick format or enable file and folder compression is available during the volume creation process. Quick format erases the existing data structures on the volume without scanning for bad sectors, offering a faster format process. Enabling file and folder compression allows for saving disk space by compressing files and folders on the volume, but it may impact performance.
Creating new simple volumes provides several advantages. It allows you to utilize unused disk space efficiently, creating larger storage areas for storing data, installing applications, or even creating dedicated partitions for specific purposes. It also helps in better file organization, as you can have all your data on one easily accessible volume instead of spread across multiple smaller partitions.
However, it is important to note that the creation of new simple volumes does not provide data redundancy. If one volume fails, data stored on that volume may be lost. Therefore, it is recommended to regularly back up your important files to prevent data loss.
In summary, creating new simple volumes in Disk Management enables you to convert unallocated space into usable partitions or volumes. By combining free space from different drives, you can efficiently utilize disk space and create larger storage areas for data and applications. Assigning drive letters, choosing the file system, and specifying volume size are all part of the volume creation process. Keep in mind the importance of data backup, as creating new simple volumes does not provide data redundancy. By using this feature, you can optimize your disk space and enhance your computer’s storage capabilities.
Extending Existing Volumes
Extending existing volumes is a valuable feature in Disk Management that allows you to increase the size of a partition or volume by utilizing available unallocated space on the same disk. This functionality enables you to address storage needs and expand the capacity of a volume without the need to back up and recreate it.
Extending a volume is especially useful when you have insufficient disk space and need to accommodate growing data. By extending an existing volume, you can add more storage capacity without the hassle of moving or deleting existing files.
To extend an existing volume, open Disk Management, right-click on the volume you want to extend, and select the “Extend Volume” option. This will open a wizard that will guide you through the process of extending the volume.
One important requirement for extending a volume is that there must be unallocated space available on the same disk. The unallocated space must be contiguous, meaning it should be located right after the volume you want to extend. If there is no contiguous unallocated space available, you may need to shrink or delete adjacent volumes to create the necessary space.
During the extension process, you can select the amount of unallocated space you want to add to the existing volume. You can also choose to allocate the maximum available space. The wizard will dynamically display the new size of the volume, allowing you to verify the changes before proceeding.
It is important to note that extending a volume is only possible on dynamic disks or basic disks with the NTFS file system. If your disk is not already a dynamic disk, you may need to convert it before extending a volume. Additionally, the extension process will only work if the volume you are extending has enough free space in its file system structure to accommodate the extension.
Extending existing volumes can provide several benefits. It allows you to overcome space limitations and add more storage capacity to accommodate growing data. This is particularly useful when the existing volume is reaching its capacity and deleting or moving files is not a feasible option. By extending the volume, you can continue to use the same drive letter and maintain the file structure, ensuring compatibility with your applications and user preferences.
It is important to exercise caution when extending volumes, as any interruption or failure during the process could result in data loss. It is highly recommended to backup your important files and data before extending a volume to mitigate the risk.
In summary, extending existing volumes in Disk Management allows you to increase the size of a partition or volume by utilizing unallocated space on the same disk. It provides a convenient way to address storage needs and expand the capacity of a volume without the need to back up and recreate it. By following the process outlined in Disk Management, you can extend volumes efficiently and effectively manage your disk space to accommodate growing data demands.
Shrink Volume
The “Shrink Volume” feature in Disk Management allows you to reduce the size of a partition or volume, creating unallocated space on the same disk. Shrink Volume is useful when you have excess free space on a partition or when you want to create additional partitions for specific purposes without formatting the entire disk.
When you shrink a volume, Disk Management analyzes the amount of space that can be safely reduced from the partition based on the location of the data. It then creates unallocated space that becomes available for other uses, such as creating new partitions or expanding existing volumes.
To shrink a volume, open Disk Management, right-click on the partition you want to shrink, and select the “Shrink Volume” option. This will initiate a scan to determine the maximum amount of space that can be safely removed from the partition. You then have the option to enter the amount of space you want to shrink or use the maximum available space recommended by Disk Management.
It is essential to note that the amount of space you can shrink a volume by may be limited by factors such as the file system, the location of unmovable files, and the presence of volume snapshots. In some cases, you may need to perform disk defragmentation or disable volume shadow copies to create more available space for shrinking.
The Shrink Volume feature has several benefits. It allows you to reclaim unused disk space and make it available for other purposes, such as creating new partitions or resizing existing volumes. By resizing the partition, you can improve disk management and optimize storage space utilization, preventing wasted disk space and ensuring efficient data storage.
One common use case for shrinking a volume is to create space for dual-boot configurations or installing multiple operating systems on the same disk. By shrinking an existing partition, you can create unallocated space that can be used to install another operating system or create a separate partition for data specific to the second operating system.
It is important to understand that shrinking a volume is a disk-intensive operation that may take some time to complete, especially if there is a large amount of data stored on the partition. Also, shrinking a volume can result in fragmentation within the remaining space, affecting disk performance. Therefore, regular disk maintenance, such as defragmentation or optimizing file placement, is recommended after shrinking a volume.
Lastly, it is crucial to back up your important files before shrinking a volume. While shrinking a volume is generally considered safe, unexpected issues or interruptions during the process could potentially result in data loss. It is always better to be prepared and have a backup available to mitigate any risks.
In summary, the Shrink Volume feature in Disk Management allows you to reduce the size of a partition or volume, creating unallocated space on the same disk. It provides flexibility in managing disk space and enables you to reclaim unused space for other purposes without formatting the entire disk. By understanding the implications and following the recommended steps, you can efficiently shrink volumes and optimize your disk management to better suit your specific needs.
Deleting Volume
The “Deleting Volume” feature in Disk Management allows you to remove a partition or volume from your hard disk. Deleting a volume permanently erases all data stored on that volume, so it is crucial to back up any important files before proceeding with the deletion process.
To delete a volume, open Disk Management, right-click on the volume you want to delete, and select the “Delete Volume” option. A warning message will appear, informing you that the deletion process will erase all data on the volume. Once you confirm the deletion, Disk Management will remove the volume, and the allocated space will become unallocated, available for other uses.
Deleting a volume is useful in several scenarios. One common use case is when you no longer need a particular partition and want to repurpose the space it occupies. For example, if you have created a separate partition for a specific operating system but no longer require that operating system, deleting the corresponding volume can free up valuable disk space that can be allocated for other tasks.
Another scenario where deleting a volume is necessary is when you want to combine multiple partitions or volumes into a single partition. By deleting the separate volumes, you can create unallocated space and then use it to extend or create a new, larger partition using Disk Management’s “Extend Volume” or “New Simple Volume” features.
It is important to note that the deletion of a volume is irreversible and will result in the permanent loss of all data stored on that volume. Therefore, it is crucial to back up any important files beforehand and ensure you have copies of any data that you do not wish to lose. Additionally, exercise caution when deleting volumes to avoid accidentally deleting an incorrect volume, as the process cannot be undone.
After deleting a volume, it is recommended to check your disk and perform disk cleanup to remove any leftover data or remnants from the deleted volume. This will help in optimizing the performance and organization of your disk space.
In summary, deleting a volume in Disk Management allows you to permanently remove a partition or volume from your hard disk. This feature is useful when you want to repurpose disk space, combine multiple partitions, or remove unnecessary partitions. However, it is important to remember that deleting a volume results in the permanent loss of all data stored on it, so it is crucial to back up your important files before proceeding with the deletion process.
Changing Drive Letter
The ability to change drive letters in Disk Management allows you to modify the assigned letter of a partition or volume on your computer. This feature is useful for reorganizing your drives, resolving naming conflicts between different partitions, or simply personalizing the drive letters to your preference.
To change a drive letter, open Disk Management, right-click on the partition or volume for which you want to modify the drive letter, and select the “Change Drive Letter and Paths” option. In the dialog box that appears, click on the “Change” button. From there, you can select a different drive letter from the available options or even remove the drive letter entirely.
Changing drive letters offers several benefits. Firstly, it allows you to personalize the drive letters to match your preferred naming convention or organization system. By assigning meaningful letters, such as “D” for documents or “P” for pictures, you can easily identify and locate specific partitions or volumes within your computer’s file system.
Secondly, changing drive letters can help resolve conflicts that may arise when multiple partitions or external storage devices have the same drive letter assigned. This conflict can occur when you connect a new device that automatically receives a previously assigned drive letter. By changing the drive letter of one of the conflicting partitions or devices, you can ensure that each partition or device is uniquely identified and accessible.
Moreover, changing drive letters allows you to maintain consistent drive letter assignments when using external storage devices, such as USB drives or external hard drives. If you often connect and disconnect these devices, changing the drive letter ensures that each device consistently receives the same letter when connected, making it easier to access your data and maintain the organization across different sessions.
It is important to note that changing the drive letter does not affect the data stored on the partition or volume. The drive letter is simply an identifier used to access the data. However, it is still prudent to create backups of important files before making any changes, as unexpected issues or interruptions during the process could potentially lead to data loss.
One thing to consider when changing drive letters is the impact it may have on software or applications that rely on the previous drive letter. It is recommended to review any software or applications that use specific drive letters and update their configurations accordingly after changing drive letters.
In summary, changing drive letters in Disk Management provides flexibility and personalization in managing your computer’s partitions and volumes. It allows you to assign meaningful letters, resolve conflicts, and maintain consistent drive letter assignments for external storage devices. As with any changes to your disk configuration, it is essential to take precautions and back up your data before making any modifications to drive letters.
Converting Disk Type
The “Converting Disk Type” feature in Disk Management allows you to change the type of a disk from basic to dynamic, or vice versa. Each disk type has distinct characteristics and offers different functionalities, making it useful to convert disk types to suit specific storage requirements.
To convert a disk type, open Disk Management, right-click on the disk you want to convert, and select the “Convert to Dynamic Disk” or “Convert to Basic Disk” option, depending on the type you wish to convert to. A warning message will appear, informing you of the potential consequences of converting the disk. Once you confirm the change, Disk Management will initiate the conversion process.
Converting a disk from basic to dynamic provides extra features and flexibility for disk management. Dynamic disks support advanced functionalities such as creating spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks). These features allow you to combine multiple disks into a single logical volume, improve performance through data striping, or achieve data redundancy through mirroring or RAID configurations.
On the other hand, converting a dynamic disk back to basic removes these advanced functionalities, returning the disk to its original basic configuration. This can be useful if you no longer require the advanced features of dynamic disks or if you want to simplify your disk management and ensure compatibility with older operating systems or hardware that do not support dynamic disks.
It is important to note that converting a disk type is a non-reversible process and can result in data loss. Therefore, it is crucial to back up all important data before converting a disk to ensure you have a copy of your files in case of any unforeseen issues during the conversion process.
When converting a basic disk to dynamic, keep in mind that dynamic disks are not supported by all operating systems. Ensure that your current operating system supports dynamic disks before proceeding with the conversion. Additionally, converting a disk with system or boot partitions to dynamic can render the disk unbootable, so exercise caution and consult the documentation or seek expert guidance if needed.
It is worth mentioning that basic disks are more commonly used and offer compatibility with a wider range of systems and devices. They are generally recommended for basic storage needs and situations where complex disk management features are not required.
In summary, converting disk types in Disk Management allows you to change the configuration of a disk from basic to dynamic or vice versa. Converting to dynamic disks provides advanced storage features such as spanned volumes, striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and RAID. Converting back to basic disks simplifies disk management and ensures compatibility with older systems. However, it is crucial to back up your data before proceeding with disk conversions, as it is a non-reversible process and can result in potential data loss.