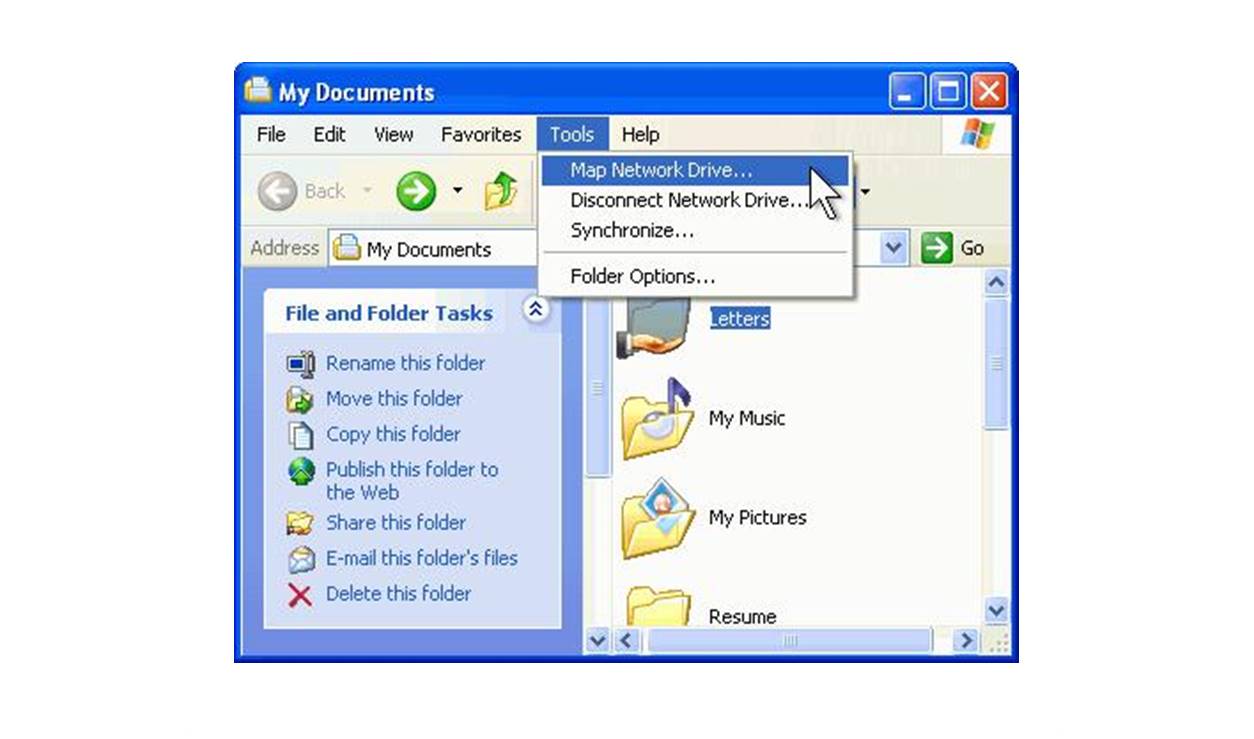
What is a Network Drive?
A network drive is a storage device or a shared folder on a remote server that is accessed over a computer network. It allows users to have easy and centralized access to files and folders stored on a server or another computer on the network. Think of it as a virtual drive that provides a seamless connection between your local computer and the remote server.
Unlike a local drive that is physically connected to your computer, a network drive exists on a separate machine. It can be located in the same building or even in a different country, as long as it is connected to the same network. Network drives are commonly used in business environments where multiple users need to collaborate and share files.
The advantage of using a network drive is that it allows for centralized data storage and sharing. Instead of each individual user having their own set of files stored locally, files are stored on the network drive, making them easily accessible to authorized users. This not only improves efficiency but also simplifies data management and backup procedures.
Network drives can be accessed by authorized users either through a wired or wireless connection, depending on the network infrastructure. Once connected, users can browse, open, modify, and save files on the network drive, just as they would on a local drive.
It’s important to note that access to a network drive is subject to user permissions and security settings. Administrators can define who has read-only access, who can modify files, and who has full control. This ensures that sensitive information remains secure, as only authorized personnel can access and alter the files.
Network drives can be a valuable tool for individuals and organizations alike, providing a convenient and secure way to store and share files across a network. Whether you need to collaborate with colleagues, share important documents, or simply have remote access to your files, mapping a network drive can greatly simplify and streamline your workflow.
Why Map a Network Drive?
Mapping a network drive offers several advantages and benefits for individuals and organizations. Here are some of the key reasons why you should consider mapping a network drive:
- Easy Access: By mapping a network drive, you can have seamless and convenient access to files and folders stored on a remote server. Instead of having to navigate through multiple folders or remember lengthy file paths, you can simply access the network drive as if it were a local drive on your computer.
- Centralized Storage: Mapping a network drive allows for centralized storage of files and documents. This means that instead of each user having their own copies of files scattered across different devices, all files can be stored in one central location, making it easier to manage, update, and back up data.
- Improved Collaboration: Sharing files and collaborating with team members becomes much more efficient when using a network drive. By mapping a network drive, team members can access and work on the same files simultaneously, eliminating the need to constantly transfer files back and forth or use unreliable file-sharing methods.
- Enhanced Data Security: Network drives offer better data security compared to storing files locally on individual computers. With a network drive, administrators can implement access controls, user permissions, and data encryption to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Mapping a network drive allows for greater flexibility and mobility, as you can access your files from any computer connected to the network. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers or those who frequently switch between different devices.
- Streamlined File Management: With a mapped network drive, file management becomes more streamlined and organized. You can easily create new folders, move files, and update documents directly on the network drive, ensuring that everyone has access to the most up-to-date versions of files.
Whether you are an individual seeking better file organization or part of a team collaborating on projects, mapping a network drive is a practical solution that can enhance productivity, streamline workflows, and improve data management and security.
Prerequisites for Mapping a Network Drive
Before you can map a network drive, there are a few prerequisites that you need to ensure are in place. These prerequisites ensure a smooth and successful mapping process. Here are the key prerequisites to keep in mind:
- Network Connection: You must have a functioning network connection to the server or computer hosting the network drive. Make sure that you are connected to the network either through a wired Ethernet connection or a wireless connection.
- Permission to Access: Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to access the network drive. Without the appropriate permissions, you may not be able to map the drive or access its contents. Contact your system administrator to verify your access rights.
- Server Name or IP Address: You will need to know the server name or IP address of the computer hosting the network drive. This information is essential for mapping the drive successfully. If you are unsure about the server details, contact your system administrator for assistance.
- Shared Folder: Confirm that the shared folder on the server or computer hosting the network drive is set up and accessible. The shared folder should contain the files that you want to access and work with through the mapped network drive.
- Username and Password: Depending on the network configuration, you may need to provide a username and password to access the network drive. Ensure that you have the correct credentials to authenticate yourself when mapping the drive.
- Firewall and Antivirus Settings: Check your firewall and antivirus settings to ensure that they do not block or interfere with the mapping process. Adjust the settings if necessary, keeping in mind the security implications.
By ensuring that these prerequisites are met, you can proceed with confidence to map the network drive successfully. If you encounter any issues during the mapping process, double-check these prerequisites and seek assistance from your system administrator if needed.
Steps to Map a Network Drive
Mapping a network drive is a straightforward process that can be done in a few simple steps. Follow these steps to successfully map a network drive:
- Open File Explorer: Start by opening File Explorer on your Windows computer. You can do this by clicking on the File Explorer icon in the taskbar or by pressing the Windows key and E simultaneously.
- Select “This PC”: In the left-hand navigation pane of File Explorer, locate and select “This PC.” This will display a list of available drives on your computer.
- Click on “Map Network Drive“: At the top of the File Explorer window, click on the “Map network drive” button. This will open the “Map Network Drive” wizard.
- Select a Drive Letter: In the “Map Network Drive” wizard, select a drive letter from the dropdown menu. This letter will be used to identify the network drive on your computer.
- Specify the Folder: Now, you need to specify the folder or network address that you want to map as a network drive. You can do this by either typing the path directly or clicking on the “Browse” button to locate the shared folder.
- Choose Reconnect at Sign-in (optional): If you want the network drive to be mapped every time you sign in to your computer, check the box that says “Reconnect at sign-in.” This will ensure that the network drive is automatically mapped on system startup.
- Click “Finish”: Once you have specified the drive letter and folder, click the “Finish” button. Windows will attempt to connect to the network drive using the provided information.
- Enter Credentials (if required): If prompted, enter the username and password associated with the network drive. This step is necessary if the network drive requires authentication.
- Access the Mapped Network Drive: After successfully mapping the network drive, it will appear in the File Explorer under “This PC.” You can now access and work with the files and folders on the network drive as if they were stored locally on your computer.
Following these steps allows you to map a network drive on your Windows computer, providing you with seamless access to shared files and folders on the network. If you encounter any difficulties during the mapping process, double-check your network connection, permissions, and server settings, or consult your system administrator for assistance.
Option 1: Mapping a Network Drive Using Windows Explorer
Windows Explorer provides a simple and straightforward method to map a network drive. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open Windows Explorer: Begin by opening Windows Explorer on your Windows computer. You can do this by clicking on the File Explorer icon in the taskbar or by pressing the Windows key and E simultaneously.
- Go to “This PC”: In the left-hand navigation pane of Windows Explorer, find and select “This PC.” This will display a list of drives on your computer.
- Click on “Map network drive”: At the top of the Windows Explorer window, click on the “Map network drive” button. It appears in the toolbar with an icon resembling a folder and a plus sign.
- Choose a Drive Letter: In the “Map Network Drive” window, select a drive letter from the dropdown menu. This letter will serve as the identifier for the network drive on your computer.
- Specify the Folder: Now, enter the path of the network folder you want to map. You can either enter it manually (e.g., \\servername\sharedfolder) or click on the “Browse” button to locate the folder on the network.
- Check “Reconnect at sign-in” (optional): If you want the network drive to be mapped automatically every time you sign in to your computer, check the box that says “Reconnect at sign-in.”
- Click “Finish”: Once you have chosen the drive letter and specified the folder, click the “Finish” button. Windows will attempt to connect to the network drive using the provided information.
- Enter Credentials (if required): If prompted, enter the username and password required to access the network drive. This step is necessary if the network drive requires authentication.
- Access the Mapped Network Drive: After successfully mapping the network drive, it will appear in Windows Explorer under “This PC.” You can now access and work with the files and folders on the network drive just like any other local drive on your computer.
Mapping a network drive using Windows Explorer is a quick and efficient method that allows you to access shared files and folders on the network with ease. Remember to provide the correct credentials and ensure that you have the necessary permissions to access the network drive.
Option 2: Mapping a Network Drive Using the Map Network Drive Wizard
In addition to using Windows Explorer, Windows provides a convenient map network drive wizard to assist in the process. Follow these steps to map a network drive using the Map Network Drive wizard:
- Open the Map Network Drive Wizard: Start by opening the Map Network Drive wizard. You can do this by right-clicking on the “This PC” icon on your desktop or in File Explorer, and then selecting “Map network drive” from the context menu.
- Choose a Drive Letter: In the Map Network Drive dialog box, select a drive letter from the dropdown menu. This letter will serve as the identifier for the network drive on your computer.
- Specify the Folder: Enter the network path or browse to the folder you want to map as a network drive. You can enter the path manually (e.g., \\servername\sharedfolder) or click on the “Browse” button to locate the folder on the network.
- Check “Reconnect at sign-in” (optional): If you want the network drive to be mapped automatically every time you sign in to your computer, check the box that says “Reconnect at sign-in.”
- Click “Finish”: Once you have chosen the drive letter and specified the folder, click the “Finish” button. Windows will attempt to connect to the network drive using the provided information.
- Enter Credentials (if required): If prompted, provide the username and password required to access the network drive. This step is necessary if the network drive requires authentication.
- Access the Mapped Network Drive: After successfully mapping the network drive, it will be visible in Windows Explorer under “This PC.” You can now use it like any other local drive on your computer, accessing and manipulating files and folders with ease.
Mapping a network drive using the Map Network Drive wizard is a convenient method that simplifies the process of accessing shared files and folders on the network. Verify that you have the necessary permissions and credentials to connect to the network drive and enjoy the seamless access it provides.
Option 3: Persistent Mapping of a Network Drive
If you need to map a network drive that remains connected even after restarting your computer, you can use a persistent mapping method. By following these steps, you can ensure that the network drive is automatically mapped every time you start your computer:
- Open File Explorer: Begin by opening File Explorer on your Windows computer. You can do this by clicking on the File Explorer icon in the taskbar or by pressing the Windows key and E simultaneously.
- Go to “This PC”: In the left-hand navigation pane of File Explorer, find and select “This PC.” This will display a list of available drives on your computer.
- Click on “Map network drive”: At the top of the File Explorer window, click on the “Map network drive” button. It appears in the toolbar with an icon resembling a folder and a plus sign.
- Choose a Drive Letter: In the “Map Network Drive” window, select a drive letter from the dropdown menu. This letter will serve as the identifier for the network drive on your computer.
- Specify the Folder: Now, enter the network path or click on the “Browse” button to locate the shared folder on the network that you want to map.
- Check “Reconnect at sign-in”: To make the mapping persistent, check the box that says “Reconnect at sign-in.” This will ensure that the network drive is automatically mapped every time you start your computer.
- Click “Finish”: Once you have selected the drive letter and specified the folder, click the “Finish” button. Windows will attempt to connect to the network drive using the provided information.
- Enter Credentials (if required): If prompted, provide the username and password required to access the network drive. This step is necessary if the network drive requires authentication.
- Access the Mapped Network Drive: After successfully mapping the network drive, it will appear in File Explorer under “This PC.” You can now access and work with the files and folders on the network drive as if they were stored locally on your computer.
Mapping a network drive persistently allows for automatic reconnection to the drive, ensuring that it remains accessible even after restarting your computer. This method is particularly useful when you regularly work with files on the network drive and need uninterrupted access to them.
Troubleshooting Tips for Mapping a Network Drive
While mapping a network drive is usually a straightforward process, there are instances where you may encounter issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you overcome common problems when mapping a network drive:
- Check Network Connectivity: Ensure that your computer is properly connected to the network. Verify your Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection and make sure there are no connectivity issues preventing access to the network drive.
- Verify Server and Folder Availability: Confirm that the server hosting the network drive is accessible and running. Additionally, ensure that the shared folder is available and not experiencing any issues that may hinder mapping.
- Double-Check Network Path: Ensure that you have entered the correct network path or folder name when mapping the network drive. Typos or errors in the path may prevent successful connection.
- Confirm User Permissions: Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to access the network drive. Check with the system administrator or the owner of the network drive to verify your access rights.
- Disable Firewall or Adjust Settings: If you encounter connection problems, make sure that your firewall is not blocking access to the network drive. Temporarily disabling the firewall or adjusting its settings may resolve the issue.
- Update Network Drivers: Outdated or faulty network drivers can hinder network connectivity. Check for updates to your network drivers and install them if necessary to ensure optimal network performance.
- Clear Stored Credentials: If you are repeatedly prompted for credentials when mapping the network drive, clear any stored credentials related to the network drive. This will allow you to enter the correct credentials during the mapping process.
- Restart Your Computer: Sometimes, a simple computer restart can resolve mapping issues. Restart your computer and attempt to map the network drive again to see if the problem resolves itself.
- Seek IT Support: If you have followed the troubleshooting tips above and continue to encounter issues when mapping a network drive, it may be beneficial to seek assistance from your organization’s IT support or contact the network administrator for further troubleshooting and resolution.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can overcome common obstacles when mapping a network drive and ensure a successful connection to access and work with files and folders on the network.