What is Safe Mode?
Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in Windows that allows you to start your computer with minimal drivers and services. It is designed to help troubleshoot and fix various software and hardware issues that may be preventing your computer from starting properly in normal mode.
When you start your computer in Safe Mode, only essential system files and drivers are loaded. This means that third-party software, such as antivirus programs or startup applications, are not loaded, making it easier to isolate and resolve issues.
Safe Mode provides a basic, stripped-down version of Windows, with limited functionality but increased stability. It can be a useful tool when troubleshooting problems such as malware infections, driver conflicts, or issues with recently installed software or updates.
In Safe Mode, you have the ability to uninstall problematic software, update drivers, run antivirus scans, or perform system restore operations. By starting your computer in this mode, you can often identify and resolve issues that may be causing your computer to crash or exhibit abnormal behavior.
Overall, Safe Mode is an essential tool in every Windows user’s troubleshooting arsenal. It is a reliable way to diagnose and fix software and hardware issues by providing a stable environment with minimal interference from third-party applications and services.
Why would you need to start Windows in Safe Mode?
There are several reasons why you might need to start Windows in Safe Mode. Let’s explore some common situations where Safe Mode can be helpful:
- Troubleshooting software issues: If your computer is experiencing frequent crashes, freezes, or error messages, starting Windows in Safe Mode can help you determine if the problem is caused by a third-party software application. By disabling these applications in Safe Mode, you can isolate the issue and take necessary steps to fix it.
- Removing malware: If your computer is infected with malware or viruses, starting in Safe Mode can prevent the malicious software from loading and running. This allows you to perform a thorough scan with your antivirus software and remove any detected threats without interference.
- Fixing driver conflicts: In certain cases, incompatible or outdated drivers can cause issues with your computer’s hardware. By starting Windows in Safe Mode, you can disable problematic drivers and subsequently update or reinstall them to resolve conflicts and ensure proper functionality.
- Undoing recent changes: Whether it’s a new application, a driver update, or a system configuration change, sometimes changes made to your computer can cause problems. By starting in Safe Mode, you can effectively roll back these changes, restore previous settings, and undo any updates that may be causing issues.
- Diagnostic purposes: Safe Mode provides a clean and stable environment that allows you to perform various diagnostic tasks. For example, if you suspect that a hardware component is failing, starting in Safe Mode can help you determine if the issue persists without the interference of other software or services.
Starting Windows in Safe Mode gives you a controlled environment where you can troubleshoot and resolve various software and hardware issues. It provides a safe and stable platform to diagnose problems, remove malware, fix driver conflicts, and undo recent changes. By utilizing Safe Mode, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve issues with your Windows computer.
How to access MSConfig?
MSConfig, short for Microsoft System Configuration, is a powerful tool in Windows that allows you to manage system startup, services, and boot options. It is a useful tool for troubleshooting and optimizing your computer’s performance. Here’s how you can access MSConfig:
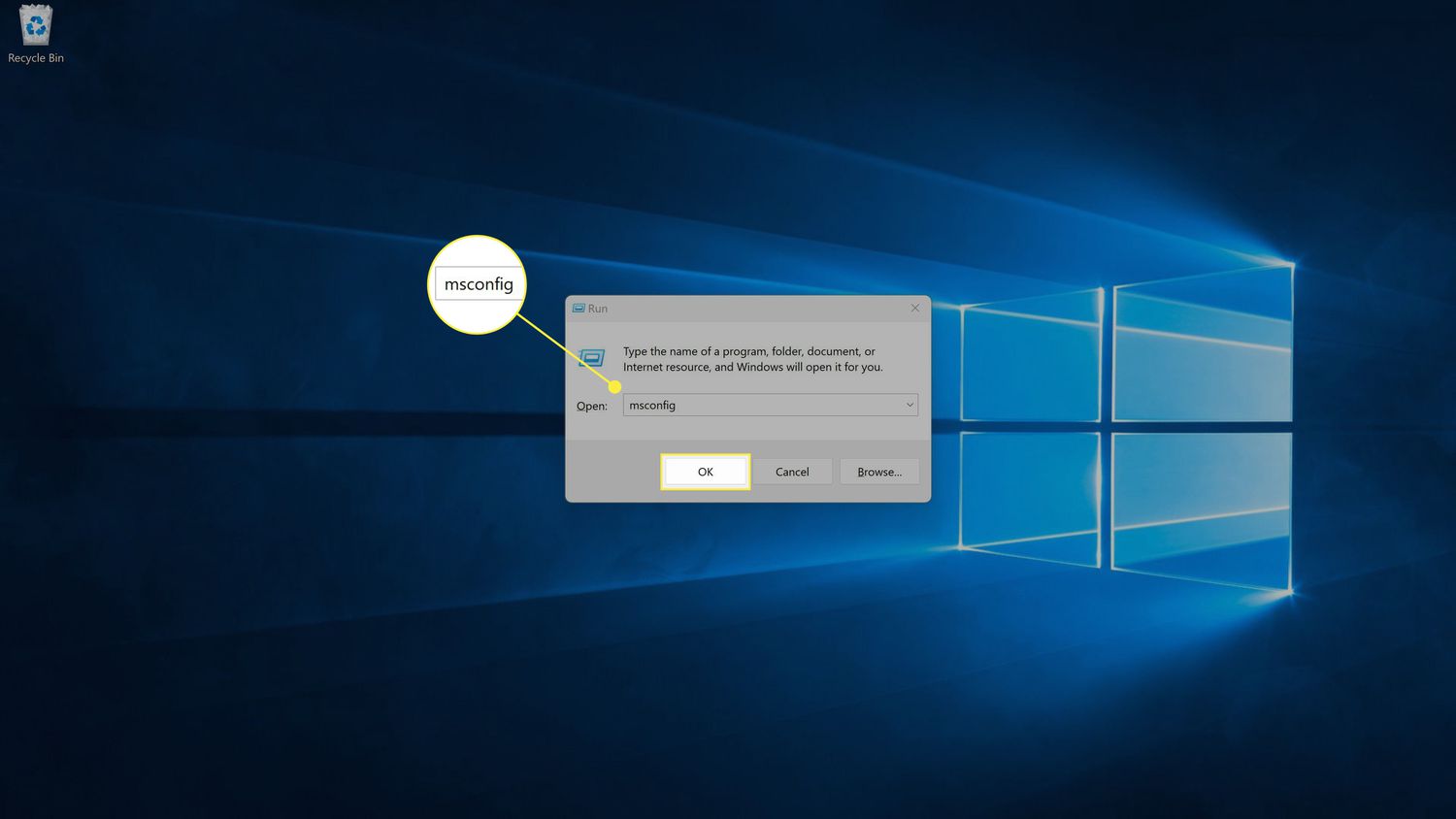
- Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type “msconfig” (without quotes) in the text box and press Enter. This will open the System Configuration window.
- In the System Configuration window, you will see several tabs: General, Boot, Services, Startup, and Tools. Each tab provides different options for managing your system’s configuration.
- To access advanced boot options, click on the Boot tab. Here, you can enable options such as Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, and Safe Mode with Command Prompt. You can also modify the timeout settings for booting into Safe Mode.
- If you want to manage startup programs, click on the Startup tab. Here, you will see a list of programs that start when your computer boots up. You can disable unnecessary programs to improve startup time or troubleshoot any issues caused by specific applications.
- If you need to modify services running on your system, click on the Services tab. To make it easier to identify services, you can check the “Hide all Microsoft services” option to only show third-party services. You can disable or enable services as needed.
- The Tools tab provides access to various Windows tools, such as Event Viewer, Task Manager, and System Restore. You can quickly launch these tools from within MSConfig.
Accessing MSConfig gives you the ability to control and manage various aspects of your Windows system configuration. It is a valuable tool for troubleshooting and optimizing your computer’s performance, allowing you to enable Safe Mode, manage startup programs, modify services, and access essential Windows tools.
Using MSConfig to start Windows in Safe Mode
MSConfig provides a straightforward way to start Windows in Safe Mode. Here’s how you can use MSConfig to access Safe Mode:
- Open the System Configuration window by pressing the Windows key + R on your keyboard, then typing “msconfig” (without quotes) in the Run dialog box and pressing Enter.
- In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Boot” tab.
- Under the “Boot options” section, check the box next to “Safe boot”. You can choose one of three options: Minimal, Alternate shell, or Network.
- Minimal: Selecting this option will start Windows in Safe Mode with only the essential drivers and services loaded. It is recommended to choose this option if you are not sure which option to select.
- Alternate shell: This option starts Windows in Safe Mode with the Command Prompt as the interface. It is useful if you need to perform advanced troubleshooting or run specific commands.
- Network: Choosing this option will start Windows in Safe Mode with networking support, allowing you to connect to the internet and other network resources.
- Optional: If you want to set the amount of time your computer waits before booting into Safe Mode, you can modify the “Timeout” value.
- Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
- When prompted, click “Restart” to reboot your computer and start Windows in Safe Mode.
Once your computer restarts, it will boot into Safe Mode according to the option you selected in MSConfig. You can then proceed to troubleshoot any issues or perform the necessary tasks in a safe and controlled environment.
Remember that when you’re finished in Safe Mode, you should return to MSConfig and uncheck the “Safe boot” option to start Windows normally the next time you restart your computer.
Restarting Windows in Normal Mode
After troubleshooting or performing tasks in Safe Mode, you may need to restart Windows in normal mode to return to the standard operating state. Here’s how you can restart your computer in normal mode:
- Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type “msconfig” (without quotes) in the text box and press Enter. This will open the System Configuration window.
- In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Boot” tab.
- Under the “Boot options” section, ensure that the “Safe boot” option is unchecked. This will indicate that Windows will start in normal mode.
- Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
- When prompted, click “Restart” to reboot your computer and start Windows in normal mode.
Once your computer restarts, it will boot into normal mode, which means all drivers, services, and startup programs will be loaded as usual. You can now use your computer in its standard operating state.
If you encounter any issues after restarting in normal mode, it might be worth revisiting Safe Mode to further investigate the cause or to perform additional troubleshooting steps.
Remember that starting your computer in Safe Mode is a helpful tool for diagnosing and resolving issues, but it is not intended to be used as a permanent mode of operation. Normal mode allows you to utilize the full functionality of your system and is the recommended mode for everyday use.