Overview of Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode in Windows operating systems that allows users to start their computer with only essential system services, drivers, and programs. It is designed to help troubleshoot and fix issues that may be causing your computer to malfunction. When you enter Safe Mode, Windows loads a minimal set of drivers and startup programs, preventing non-essential software from running. This allows you to identify and resolve problems that may be caused by incompatible drivers, malware, or problematic software installations.
In Safe Mode, you will notice that the graphical user interface (GUI) looks different compared to normal mode. The screen resolution is typically lower, and certain visual effects and features may be disabled. This is because Safe Mode prioritizes functionality over aesthetics, focusing on the core components necessary for your computer to function properly.
By starting Windows in Safe Mode, you can troubleshoot a wide range of issues, such as software conflicts, driver problems, and even malware infections. It provides a clean, controlled environment where you can isolate and diagnose problems without interference from third-party software.
Safe Mode is particularly useful when your computer is experiencing frequent crashes, freezes, or errors during startup. It allows you to access important system tools and utilities, as well as perform tasks like uninstalling problematic software or updating drivers.
It’s important to note that when in Safe Mode, some functionalities, such as network connectivity and audio, may be disabled. This is because certain services and drivers necessary for these features to work are not loaded in Safe Mode. However, these features will be available again once you restart your computer in normal mode.
Overall, Safe Mode is a powerful troubleshooting tool that can help you identify and resolve issues that may be preventing your computer from functioning properly. Whether you’re dealing with software conflicts, driver problems, or malware infections, starting Windows in Safe Mode provides a safe and controlled environment to diagnose and fix these issues.
Why Start Windows in Safe Mode?
There are several reasons why you may need to start Windows in Safe Mode. It is often the go-to solution when your computer is experiencing issues that prevent it from starting up or functioning normally. Here are some common scenarios where starting Windows in Safe Mode can be beneficial:
1. Troubleshooting Startup Issues: If your computer is stuck in a continuous startup loop, Safe Mode provides a way to break that cycle. It allows you to start your computer with minimal drivers and programs, making it easier to identify the source of the problem and resolve it. Whether it’s a faulty driver, a recently installed program, or a malware infection, Safe Mode provides the necessary environment for troubleshooting.
2. Removing Problematic Software: Sometimes, a recently installed program or driver can cause your computer to crash or behave erratically. By starting Windows in Safe Mode, you can uninstall or disable the problematic software that is causing the issue. This can help restore your computer’s stability and functionality.
3. Fixing Driver Conflicts: Conflicting drivers can lead to various problems, such as blue screen errors or hardware malfunctions. In Safe Mode, you can identify and resolve driver conflicts by selectively disabling or updating drivers. This helps ensure that your hardware components are working harmoniously with the rest of your system.
4. Removing Malware Infections: If you suspect that your computer is infected with malware, starting in Safe Mode is recommended. In this mode, many types of malware are unable to run, making it easier to detect and remove them. By running a thorough scan with reliable antivirus software, you can effectively eradicate any malicious programs that may be causing harm to your system.
5. Accessing Windows System Tools: Safe Mode provides access to important Windows system tools and utilities, such as System Restore, Device Manager, and Event Viewer. These tools can help diagnose and repair various issues that you may encounter on your computer. When in Safe Mode, these tools can be especially useful as they operate in a simplified environment, free from potential interference caused by third-party software.
Overall, starting Windows in Safe Mode offers a controlled and minimalistic environment to troubleshoot and resolve system issues. Whether you’re dealing with startup problems, software conflicts, driver issues, or malware infections, Safe Mode provides a valuable toolset to help you get your computer up and running smoothly again.
Ways to Start Windows in Safe Mode
There are several methods to start Windows in Safe Mode, depending on your specific situation and the version of Windows you are using. Here are four commonly used methods:
Method 1: Using the Shift + Restart Option: This method is applicable to Windows 10 and Windows 8.1. Press and hold the Shift key on your keyboard, then click on the “Restart” option in the Start Menu or the Power Menu. This will restart your computer and bring up the Advanced Startup Options menu. From there, you can access the Safe Mode options.
Method 2: Using the System Configuration Tool: This method works for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Type “msconfig” and hit Enter. In the System Configuration window, go to the “Boot” tab and check the “Safe boot” option. Choose the type of Safe Mode you want to start in (Minimal, Network, or Alternate shell) and click OK. Restart your computer, and it will boot into Safe Mode.
Method 3: Using the Startup Settings Menu: This method is ideal for Windows 10 and Windows 8.1. Go to the Start Menu and click on the Power button. While holding the Shift key, click on “Restart.” After your computer restarts, you will see the Startup Settings menu. Press the corresponding number key or function key to select the desired Safe Mode option.
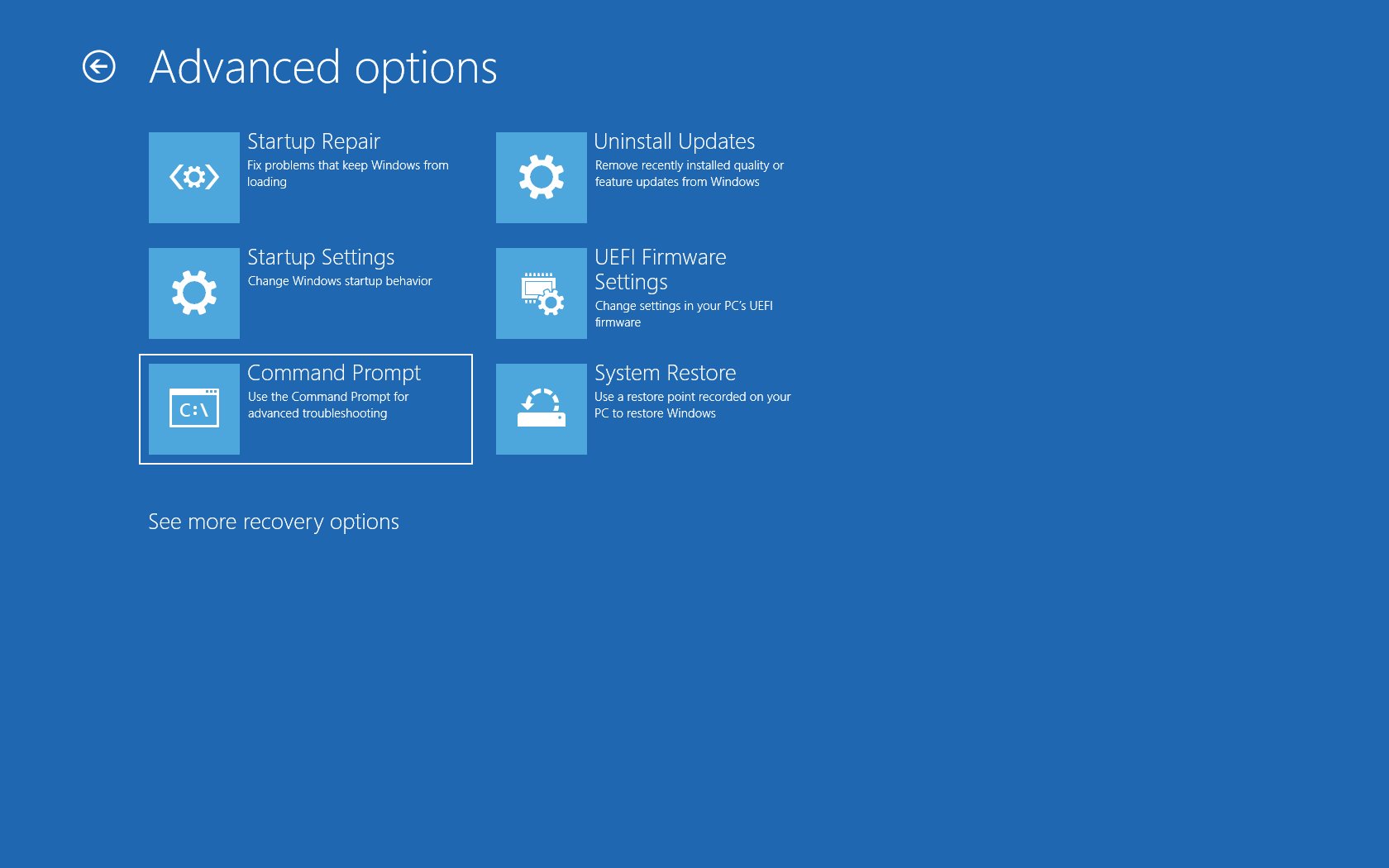
Method 4: Using the Windows Recovery Environment: This method is useful when you are unable to boot into Windows normally. Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive, and boot your computer from it. Select your language preferences and click “Next.” On the next screen, click on “Repair your computer.” In the Windows Recovery Environment, select “Troubleshoot” and then “Advanced options.” From there, you can access the Advanced Startup Options and choose Safe Mode.
It’s worth noting that the steps for accessing Safe Mode may vary slightly depending on the version of Windows you are using. If one method doesn’t work, you can try another until you successfully enter Safe Mode. Once you are in Safe Mode, you can troubleshoot and resolve the issues causing problems on your computer.
Method 1: Using the Shift + Restart Option
This method allows you to start Windows in Safe Mode by utilizing the Shift + Restart option. It is a quick and convenient way to access the Advanced Startup Options menu in Windows 10 and Windows 8.1. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Begin by navigating to the Start Menu or the Power Menu. Hold down the Shift key on your keyboard while clicking on the “Restart” option. This combination will prompt your computer to restart.
Step 2: After your computer restarts, you will be presented with a menu called “Choose an option” screen. From this screen, select “Troubleshoot.”
Step 3: In the Troubleshoot menu, click on “Advanced options.” This will lead you to another menu where you can access additional recovery options.
Step 4: Locate and click on the “Startup Settings” option. This will bring up a screen displaying various startup settings for your computer.
Step 5: To start Windows in Safe Mode, press the corresponding number key or function key associated with the Safe Mode option you wish to use. The available options may include Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, or Safe Mode with Command Prompt. For example, pressing the 4 or the F4 key will start your computer in Safe Mode.
Step 6: Once you have selected the desired Safe Mode option, your computer will reboot and start in Safe Mode. You will notice that the desktop, visuals, and functionality appear different than in normal mode. This is because Safe Mode restricts the loading of non-essential components, prioritizing system stability and troubleshooting capability.
Using the Shift + Restart option to start Windows in Safe Mode is particularly useful when you need to access Safe Mode quickly, without going through additional settings or menus. It provides a straightforward method to troubleshoot and fix issues on your computer, ensuring a more stable and controlled environment for troubleshooting and diagnosing problems.
Remember that when you are done troubleshooting in Safe Mode, you can exit by restarting your computer and allowing it to boot normally. This will bring your computer back to its regular startup configuration.
Method 2: Using the System Configuration Tool
The System Configuration tool is a built-in utility in Windows that allows you to configure various system settings, including the ability to start Windows in Safe Mode. This method works for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, and Windows Vista. Here’s how to use the System Configuration tool to start Windows in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
Step 2: Type “msconfig” into the Run dialog box and hit Enter. This will open the System Configuration window.
Step 3: In the System Configuration window, navigate to the “Boot” tab.
Step 4: Under the Boot options section, check the box next to “Safe boot.” This enables the Safe Mode option for your next system startup.
Step 5: You can choose between three types of Safe Mode: “Minimal,” “Network,” or “Alternate shell.” Select the option that best suits your needs. The “Minimal” option loads only the essential drivers and services, while the “Network” option additionally enables network connectivity. The “Alternate shell” option starts Safe Mode with the Command Prompt.
Step 6: After selecting the desired Safe Mode option, click on the “Apply” button and then “OK” to save the changes.
Step 7: You will be prompted to restart your computer to apply the changes. Click on “Restart” to restart your computer and start in Safe Mode.
Upon restarting, your computer will boot into Safe Mode with the selected configuration. You will notice a different appearance, with a lower screen resolution and limited functionality. This is because Safe Mode loads only the essential components, ensuring a stable environment for troubleshooting and resolving issues on your computer.
To exit Safe Mode and return to normal mode, simply follow the same steps and uncheck the “Safe boot” option in the System Configuration window. Restart your computer, and it will boot normally, loading all drivers and services as usual.
Using the System Configuration tool is a straightforward way to start Windows in Safe Mode, giving you the ability to troubleshoot and fix issues that may be impacting your computer’s performance or stability.
Method 3: Using the Startup Settings Menu
If you are using Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, you can start your computer in Safe Mode using the Startup Settings menu. This menu allows you to access various startup options, including Safe Mode. Here’s how to use the Startup Settings menu to start Windows in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Begin by clicking on the Start Menu and then the Power button. While holding down the Shift key on your keyboard, click on “Restart.” This combination of actions will initiate a restart of your computer.
Step 2: After your computer restarts, the Startup Settings menu will appear. This menu provides a range of startup options and advanced troubleshooting tools.
Step 3: To access Safe Mode, press the corresponding number key or function key on your keyboard that is associated with the Safe Mode option you want to use. The available options may include Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, or Safe Mode with Command Prompt. Typically, pressing the 4 or the F4 key will start your computer in Safe Mode.
Step 4: Once you have selected the desired Safe Mode option, your computer will reboot and start in Safe Mode. You will notice a different appearance, with a lower screen resolution and limited functionality. This is because Safe Mode loads only the essential components, ensuring a stable environment for troubleshooting and resolving issues.
In Safe Mode, you will have access to basic functionalities and tools needed to diagnose and resolve problems on your computer. It allows you to troubleshoot software conflicts, driver issues, and malware infections without interference from unnecessary third-party applications.
When you have finished troubleshooting and want to exit Safe Mode, simply restart your computer. It will boot normally, loading all drivers and services as usual.
Using the Startup Settings menu to start Windows in Safe Mode provides an efficient and relatively simple method for troubleshooting and resolving issues. It is particularly useful when you encounter startup problems or need to access Safe Mode quickly.
Method 4: Using the Windows Recovery Environment
If you are unable to start Windows normally or access the Advanced Startup Options menu, you can use the Windows Recovery Environment (RE) to start your computer in Safe Mode. This method is helpful when your computer encounters severe issues that prevent it from booting properly. Here’s how to use the Windows Recovery Environment to start Windows in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Insert your Windows installation disc or recovery drive into your computer and boot from it. You may need to change the boot order in your computer’s BIOS settings to prioritize the disc or drive.
Step 2: Select your language preferences and click “Next” to continue.
Step 3: On the next screen, click on the “Repair your computer” option. This will take you to the Windows Recovery Environment.
Step 4: In the Windows Recovery Environment, select “Troubleshoot.”
Step 5: In the Troubleshoot menu, choose “Advanced options.”
Step 6: From the Advanced options menu, select “Startup Settings.” This will bring up the Startup Settings screen.
Step 7: Click on the “Restart” button to restart your computer and access the Startup Settings menu.
Step 8: Once your computer restarts, you will see a list of startup options in the Startup Settings menu. Press the corresponding number key or function key associated with the Safe Mode option you want to use. For instance, pressing the 4 or F4 key will start your computer in Safe Mode.
Step 9: Your computer will now boot into Safe Mode. In this mode, only essential drivers and services will be loaded, providing a stable environment for troubleshooting and resolving issues.
While in Safe Mode, you can diagnose and fix problems related to software conflicts, driver issues, and malware infections without interference from unnecessary third-party programs. It provides a controlled and simplified environment to efficiently resolve issues that may be impacting your computer’s performance.
To exit Safe Mode and return to normal mode, simply restart your computer. It will boot normally, loading all drivers and services as usual.
Using the Windows Recovery Environment to start Windows in Safe Mode is a powerful method when your computer encounters severe startup problems. It allows you to access the necessary tools and options to troubleshoot and fix issues that may be preventing your computer from booting normally.
Troubleshooting Safe Mode Startup Issues
While Safe Mode is a valuable tool for troubleshooting and resolving computer issues, you may occasionally encounter problems when trying to start Windows in Safe Mode. Here are a few common issues with their respective solutions:
Issue 1: Inability to Start in Safe Mode: If you are having difficulty entering Safe Mode using any of the methods mentioned earlier, try restarting your computer and repeating the steps. Make sure to follow the instructions carefully and press the correct keys when accessing the Safe Mode options.
Solution: In some cases, the timing of pressing the keys can be crucial. Try pressing the required keys repeatedly or at different intervals until you can successfully access Safe Mode. If the issue persists, consider seeking assistance from a technical expert.
Issue 2: Continuous Looping or Restarting: If your computer continuously restarts or gets stuck in a loop when trying to enter Safe Mode, it could be due to a corrupted system file or incompatible hardware.
Solution: To resolve this issue, start by booting into the Windows Recovery Environment and running the Startup Repair tool. This tool can automatically detect and correct problems that may be causing the continuous loop or restart. If the issue persists, try removing recently installed hardware or performing a system restore to a previous stable state.
Issue 3: Safe Mode Hangs or Freezes: Sometimes, Safe Mode may hang or freeze during the startup process due to problematic drivers, software, or malware infections.
Solution: To troubleshoot this issue, start by booting into Safe Mode with Networking. This enables network connectivity and allows you to update or reinstall drivers that may be causing the freeze. Additionally, perform a thorough scan for malware using reliable antivirus software. If the issue persists, try uninstalling recently installed programs or driver updates that may be causing the freeze.
Issue 4: Limited Functionality: In Safe Mode, certain functionalities such as network connectivity and audio may be disabled.
Solution: This is normal behavior in Safe Mode, as only essential services are loaded for troubleshooting purposes. When you exit Safe Mode and restart your computer in normal mode, these functionalities will be restored.
Remember, Safe Mode is primarily a diagnostic mode intended for troubleshooting and resolving issues. If you are unable to resolve the problem or encounter persistent errors, it may be necessary to seek professional help or contact your computer manufacturer for further assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions about Safe Mode
Here are some frequently asked questions about Safe Mode and their answers:
Q: Can I access the internet in Safe Mode?
A: By default, network connectivity is disabled in Safe Mode. However, if you need internet access in Safe Mode, you can choose the “Safe Mode with Networking” option. This enables network functionality, allowing you to connect to the internet and perform tasks that require online access, such as downloading updates or running online antivirus scans.
Q: Will my files be affected in Safe Mode?
A: Safe Mode does not delete or modify your personal files. It only loads essential system services and drivers, allowing you to troubleshoot and resolve issues. Your data will remain intact, and once you restart the computer in normal mode, all files will be accessible.
Q: Can I install or uninstall software in Safe Mode?
A: It is generally not recommended to install or uninstall software in Safe Mode. Safe Mode is primarily used for troubleshooting and fixing issues, rather than making changes to the system. Some installation or uninstallation processes may not work correctly in Safe Mode, and certain software installation options may be restricted.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode for regular computer use?
A: Safe Mode is not intended for regular computer use. It is a diagnostic mode with limited functionality and lower screen resolution. While in Safe Mode, some features, such as audio and visual effects, may be disabled. It is designed specifically for troubleshooting and resolving issues on your computer.
Q: How do I exit Safe Mode?
A: To exit Safe Mode, simply restart your computer. Upon restarting, your computer will boot in normal mode, loading all drivers and services as usual.
Q: Can I run antivirus scans in Safe Mode?
A: Yes, you can run antivirus scans in Safe Mode. In fact, it is often recommended to scan your computer for malware while in Safe Mode as certain types of malware may be inactive or easier to detect in this mode. Make sure you have an up-to-date antivirus program and run a full system scan for comprehensive protection.
Remember that Safe Mode is a powerful tool for troubleshooting and resolving computer issues. If you encounter persistent problems or are unsure about specific actions to take in Safe Mode, it is always a good idea to consult a professional or the official support resources provided by your operating system.