Understanding Network Connection Speed
Network connection speed refers to the rate at which data travels between your device and the internet. Understanding the dynamics behind connection speed is essential for troubleshooting connectivity issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring a smooth online experience.
Several factors contribute to the overall speed of your network connection. Bandwidth is one such factor, referring to the capacity of your internet connection to transmit data. Bandwidth is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps), with higher values indicating faster speeds.
Latency is another crucial element affecting network speed. It refers to the time it takes for data packets to travel from your device to a remote server and back. Lower latency values are desirable, as they signify shorter delays in data transmission.
Additionally, network congestion can impact connection speed. If many users are simultaneously accessing the network, it can result in slower speeds for everyone due to increased competition for available bandwidth.
It’s important to note that network connection speed can vary depending on the type of connection you have. For instance, a wired Ethernet connection typically offers faster and more stable speeds compared to a wireless Wi-Fi connection. However, advancements in Wi-Fi technology have narrowed the gap and now provide reliable speeds for most common online activities.
To determine your current network connection speed, various speed testing methods are available. These methods allow you to measure the upload and download speeds of your connection, as well as assess factors like latency and packet loss.
Additionally, certain terms are commonly associated with network connection speed tests. Upload speed refers to the rate at which data is sent from your device to the internet, while download speed indicates the rate at which data is received by your device. Ping is another term often encountered, representing the time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to a server and back.
By understanding the fundamental aspects of network connection speed and familiarizing yourself with relevant terminologies, you can effectively evaluate and troubleshoot connectivity issues. The subsequent sections will explore various methods you can employ to test your network connection speed and interpret the results.
Why Test Network Connection Speed?
Testing your network connection speed is crucial for several reasons. Whether you are a casual internet user or rely heavily on a stable and fast connection for your work, understanding the performance of your network is essential. Here are a few key reasons why you should regularly test your network connection speed:
- Identify Performance Issues: By testing your network connection speed, you can quickly identify any performance issues. If you notice slower-than-usual speeds, you can investigate further and address any potential bottlenecks that may be affecting your internet experience.
- Troubleshoot Connectivity Problems: Testing the speed of your connection can help troubleshoot connectivity problems. If you are experiencing frequent disconnects or intermittent slowdowns, running a speed test can provide valuable insights into the stability and consistency of your network.
- Compare Actual Speeds with Advertised Speeds: Internet service providers often advertise their connection speeds, promising fast and reliable performance. By conducting regular speed tests, you can compare the actual speeds you are experiencing with the advertised speeds. If there is a significant discrepancy, you can reach out to your provider to address the issue.
- Optimize Streaming and Downloading: Testing your network connection speed is particularly useful if you frequently stream movies, play online games, or download large files. Knowing your connection speed can help you select appropriate streaming quality settings, ensure smooth gameplay, and estimate the time required for downloads.
- Monitor Network Performance over Time: Regularly testing your network connection speed allows you to monitor its performance over time. By keeping track of your speed test results, you can identify patterns, fluctuations, or any degradation in your network performance. This information can be valuable when troubleshooting issues with your internet service provider.
Testing your network connection speed serves as an important diagnostic tool to ensure you are getting the most out of your internet service. It empowers you with the knowledge of your network’s performance, allowing you to take appropriate actions to address any issues that may arise. Now that you understand the significance of testing your network connection speed, let’s explore the different methods available for conducting these tests.
Factors that Affect Network Connection Speed
Network connection speed can be influenced by various factors, both external and internal. Understanding these factors can help you troubleshoot and optimize your network performance. Here are some key factors that can affect your network connection speed:
- Bandwidth: The available bandwidth is a significant factor in determining your network connection speed. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over your internet connection in a given time. If you have a higher bandwidth, you will generally experience faster connection speeds.
- Network Congestion: When multiple devices are connected to the same network and using it simultaneously, it can lead to network congestion. This congestion can cause a decrease in network connection speed for all devices connected to the network.
- Distance from the Server: The physical distance between your device and the server you are connecting to can impact your network connection speed. If the server is located far away, the data packets need to travel a longer distance, leading to increased latency and potentially slower speeds.
- Network Type: The type of network connection you are using can also affect your connection speed. Wired connections, such as Ethernet, generally offer faster and more stable speeds compared to wireless connections, such as Wi-Fi. Additionally, newer generations of Wi-Fi technology, like Wi-Fi 6, provide faster speeds and better performance compared to older standards.
- Network Equipment: The quality and capabilities of your network equipment, including routers and modems, can impact your network connection speed. Outdated or improperly configured equipment may limit the speed and performance of your network.
- Interference: Interference from nearby electronic devices, such as other Wi-Fi networks, cordless phones, or microwaves, can disrupt the wireless signals and degrade your connection speed. It is essential to minimize sources of interference to ensure optimal network performance.
- Network Provider: Your internet service provider (ISP) plays a significant role in determining your network connection speed. Different ISPs offer varying speeds and quality of service. If you are consistently experiencing slow speeds, it might be worth considering a different ISP or contacting your current provider for assistance.
By considering these factors, you can gain insights into why your network connection speed may be slower than expected. Addressing these factors, such as optimizing network equipment, managing network congestion, or choosing a better network provider, can help improve your overall network performance. Now that we have discussed the factors that can affect network connection speed, let’s explore common terms associated with network speed testing.
Common Network Connection Speed Terms
When it comes to network connection speed testing, there are several terms you should be familiar with to understand the results. Here are some common network connection speed terms you may come across:
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over your internet connection in a given time. It is typically measured in terms of megabits per second (Mbps) and determines how quickly data can be downloaded or uploaded.
- Download Speed: Download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device. It is usually expressed in Mbps and represents how quickly you can access and retrieve data.
- Upload Speed: Upload speed signifies the rate at which data is sent from your device to the internet. It is measured in Mbps and is crucial for activities like uploading files, sending emails, or video conferencing.
- Latency: Latency, also known as ping, represents the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a remote server and back. It is usually measured in milliseconds (ms) and impacts the responsiveness and real-time interaction of applications.
- Ping Test: A ping test measures the network’s response time by sending a small data packet from your device to a server and assessing the time taken for the server to respond. It helps evaluate network latency and stability.
- Ping Loss: Ping loss refers to the failure to receive a response from the server during a ping test. A high ping loss percentage can indicate network instability or congestion.
- Jitter: Jitter refers to the variation in latency over time. It measures the inconsistency in the response time of data packets and can affect the smoothness of real-time communication, such as VoIP calls or video streaming.
Understanding these terms will allow you to interpret the results of network connection speed tests accurately. By taking into account factors like download and upload speeds, latency, ping tests, and jitter, you can assess the overall performance and stability of your network connection. Now that we are familiar with these terms, let’s explore the different methods you can employ to test your network connection speed.
Network Speed Testing Methods
When it comes to testing your network speed, there are several methods available that can provide valuable insights into the performance of your connection. Here are some common network speed testing methods:
- Method 1: Using Online Speed Testing Tools: Online speed testing tools are widely accessible and provide a convenient way to measure your network speed. These tools typically require you to visit a website and initiate the test by clicking a button. They will then analyze your download and upload speeds, as well as latency and other metrics.
- Method 2: Using Command Line Tools: For more advanced users, command line tools offer a powerful way to test network speed. Tools like ‘ping’, ‘traceroute’, and ‘iperf’ can provide detailed information about network latency, packet loss, and bandwidth utilization.
- Method 3: Using Speed Testing Apps: There are various speed testing apps available for smartphones and tablets, allowing you to test your network connection speed on the go. These apps often provide a user-friendly interface and display detailed results for download and upload speeds, as well as latency and other relevant metrics.
- Method 4: Testing Connection Speed with File Downloads: Downloading files of known sizes can also be used as a method to test your network connection speed. By timing how long it takes to download a large file, you can estimate your download speed. This method may not provide as detailed information as specialized speed testing tools but can serve as a quick and straightforward test.
- Method 5: Conducting Ping Tests: Ping tests, as mentioned earlier, can help evaluate network latency and stability. By using tools like the ‘ping’ command or online ping test websites, you can measure the response time between your device and a target server, allowing you to assess the quality of your network connection.
- Method 6: Testing Network Speed with Browser Extensions: Certain browser extensions, such as Speedtest by Ookla or Fast.com, offer convenient options to quickly test your network speed from within your web browser. These extensions often display results for download and upload speeds, as well as latency, with just a click of a button.
Using one or more of these network speed testing methods can provide you with a comprehensive assessment of your connection’s performance. It is recommended to perform multiple tests at different times of the day to account for any variations in network usage that may impact speed. With the test results in hand, you can better understand your network’s capabilities and make informed decisions about optimizing its performance.
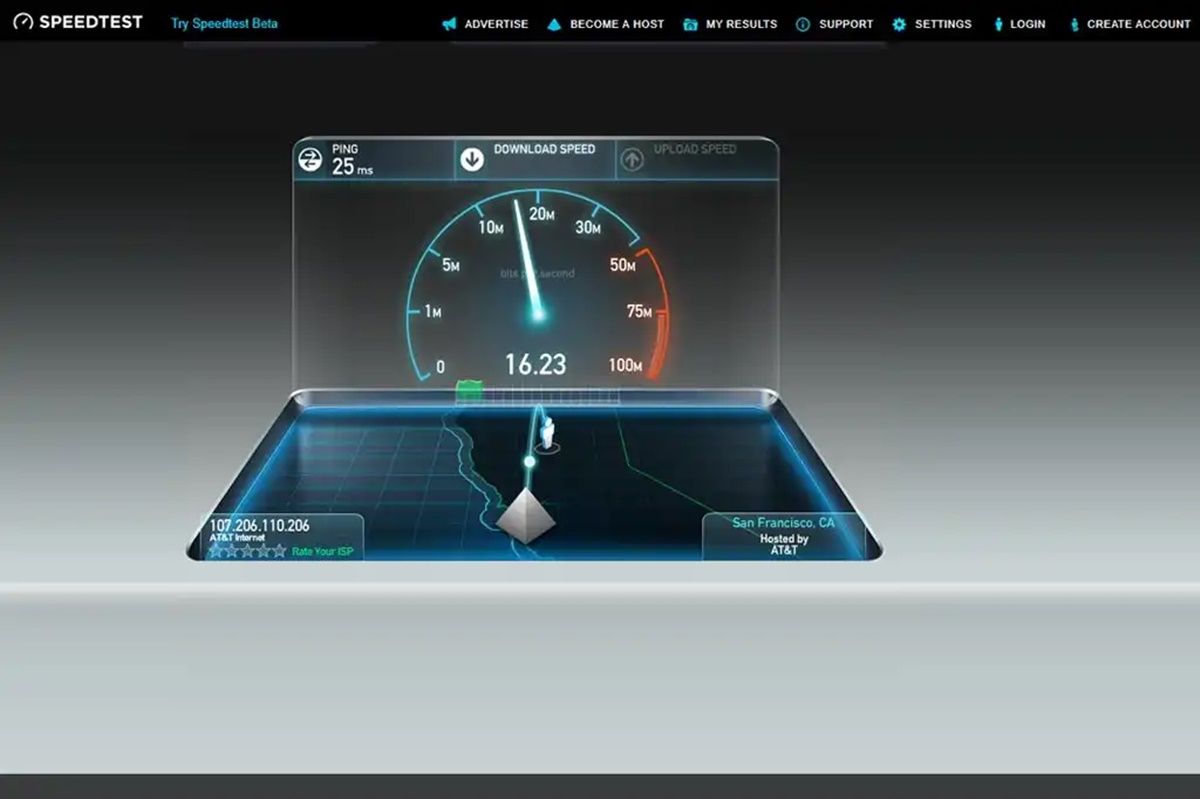
Method 1: Using Online Speed Testing Tools
One of the most common and convenient methods to test your network speed is by using online speed testing tools. These tools are easily accessible through various websites and offer a user-friendly interface to measure your network connection speed. Here’s how you can use online speed testing tools:
- Open a web browser on your device and search for “online speed test” or “internet speed test” in your preferred search engine.
- Choose a reputable and reliable speed testing website from the search results. Popular options include Ookla Speedtest, Fast.com, and Google’s internet speed test.
- Once you’ve selected a website, click on the “Start” or “Begin Test” button to initiate the speed test.
- The speed testing tool will then measure your download speed, upload speed, and ping latency. These results are typically presented in a clear and easy-to-read format.
- After the test is complete, the speed testing tool will display your network connection speed results. These results will include your download speed, upload speed, and ping latency, usually measured in Mbps or milliseconds.
- Take note of the results, as they will provide you with an understanding of your current network connection performance.
Online speed testing tools are beneficial as they provide quick and accurate measurements of your network connection speed. They also offer additional information such as your IP address and the server location used for the speed test, which can be useful for troubleshooting purposes.
When using online speed testing tools, it’s important to keep in mind that the results may vary based on factors like network congestion, your device’s hardware capabilities, and the performance of the speed testing server. For more accurate results, try performing multiple tests at different times of the day and compare the average values.
Using online speed testing tools allows you to easily monitor and track changes in your network connection speed over time. It is recommended to conduct regular speed tests to ensure that you are getting the internet speeds you are paying for and to identify any potential issues with your network connection.
Now that you are familiar with using online speed testing tools, let’s explore other methods that can help you evaluate the performance of your network connection.
Method 2: Using Command Line Tools
For more advanced users or those who prefer a command-line interface, using command line tools offers a powerful method to test network connection speed. Command line tools provide detailed information about network latency, packet loss, and bandwidth utilization. Here’s how you can use command line tools to test your network speed:
- Open the command line interface on your operating system. On Windows, you can use the Command Prompt or PowerShell. On macOS and Linux, you can use the Terminal.
- Choose the appropriate command line tool based on your specific needs. Here are a few commonly used ones:
- Ping: The ‘ping’ command is commonly used to measure network latency. By pinging a remote server or website, you can determine the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from your device to the server and back. For example, typing ‘ping www.example.com’ and pressing Enter will initiate the ping test.
- Traceroute: The ‘traceroute’ command helps identify the network path taken by data packets from your device to a remote server or website. It shows the routers or nodes that the packets pass through, which can help identify any network hops or delays. To use this command, type ‘traceroute www.example.com’ and press Enter.
- Iperf: The ‘iperf’ command is a powerful tool for measuring network bandwidth. It allows you to conduct performance tests by simulating network traffic between your device and a server. It provides detailed information about the throughput and bandwidth utilization. To use this command, you’ll need a server running the iperf software. Type ‘iperf -c server_ip_address’ and press Enter.
- Once you enter the command, the tool will initiate the test and provide you with real-time information about the network speed, latency, and packet loss.
- Take note of the results displayed in the command line interface, including the latency in milliseconds and any other relevant information.
Using command line tools can provide more detailed and specific measurements of your network connection speed and performance. They offer advanced capabilities and options for conducting various tests, such as latency, network path tracing, and bandwidth utilization.
However, it’s important to note that using command line tools requires a certain level of technical proficiency, and the results may not be as user-friendly as those provided by graphical tools. Additionally, it’s recommended to perform multiple tests and compare the results for more accurate measurements.
Command line tools provide a flexible and comprehensive way to assess your network connection speed and diagnose any potential issues. They are particularly useful for advanced users, network administrators, or individuals seeking more in-depth analysis of their network performance.
Now that you are familiar with using command line tools, let’s explore other methods to test network connection speed that are accessible through various apps and extensions.
Method 3: Using Speed Testing Apps
Another convenient method to test your network connection speed is by using speed testing apps. These apps are available for smartphones and tablets, allowing you to measure your network speed on the go. Speed testing apps typically offer a user-friendly interface and provide detailed results for download and upload speeds, as well as latency and other relevant metrics. Here’s how you can use speed testing apps:
- Open the app store on your mobile device (such as the App Store for iOS or Google Play Store for Android).
- Search for “speed test” or “network speed test” in the app store’s search bar.
- Choose a well-rated and reputable speed testing app from the search results. Popular options include Speedtest by Ookla, Fast.com, and Meteor Speed Test.
- Download and install the app on your device.
- Open the speed testing app, and you will usually be greeted with a simple and intuitive interface.
- Tap the “Run Test” or similar button to initiate the speed test.
- The app will then measure your download speed, upload speed, and ping latency.
- After the test completes, the app will display the results, providing you with detailed information about your network connection speed, including download and upload speeds in Mbps and latency in milliseconds.
- Take note of the results and any other relevant information provided by the app.
Speed testing apps offer the advantage of being specifically designed for mobile devices and provide a convenient option to test your network speed on the go. They often offer additional features such as historical results and comparisons with other users in your area.
These apps are user-friendly and provide quick and accurate measurements of your network connection speed. However, it’s important to note that results may vary based on factors like network congestion and your device’s hardware capabilities.
By using speed testing apps, you can easily monitor and track changes in your network connection speed over time. Regularly performing speed tests can help identify any issues with your network connection and ensure that you are receiving the internet speeds you are paying for.
Now that you are familiar with using speed testing apps, let’s explore another method that involves testing network speed through file downloads.
Method 4: Testing Connection Speed with File Downloads
An alternative method to test your network connection speed is by using file downloads of known sizes. This method provides a quick and straightforward way to estimate your download speed. Here’s how you can test your connection speed with file downloads:
- Choose a large file for download, preferably from a reputable source. Some websites offer files specifically designed for speed testing purposes.
- Start a timer or take note of the current time.
- Initiate the file download by clicking on the download link or button.
- Monitor the progress of the download. Once the download is complete, stop the timer or take note of the time it took to download the file.
- Divide the file size (in megabytes, for example) by the time taken to download (in seconds) to calculate your download speed in megabits per second (Mbps).
- For example, if you downloaded a 100 MB file and it took 10 seconds to download, your download speed would be 100 MB / 10 seconds = 10 Mbps.
- Take note of the calculated download speed.
Testing connection speed with file downloads is a simple and practical way to estimate your download speed. However, unlike specialized speed testing tools, this method does not provide detailed information about upload speed, latency, or other network metrics.
It’s important to note that the download speed calculated through this method may not be entirely accurate due to various factors, such as server limitations, network congestion, or fluctuations in your internet connection. For more precise measurements, it is recommended to use dedicated speed testing tools or apps.
Despite its limitations, this method can still give you a rough estimate of your download speed and help identify significant discrepancies between the advertised speed and the actual speed you are experiencing. It can also be useful for a quick and basic speed check when alternative speed testing methods are not readily accessible.
Now that you are familiar with testing connection speed with file downloads, let’s explore another method that involves conducting ping tests to evaluate network performance.
Method 5: Conducting Ping Tests
Ping tests are a valuable method to evaluate network performance and assess the quality of your network connection. Ping tests measure the response time between your device and a target server or website, providing insights into network latency and stability. Here’s how you can conduct ping tests:
- Open the command line interface on your computer or device. On Windows, you can use the Command Prompt or PowerShell. On macOS and Linux, you can use the Terminal.
- Type ‘ping’ followed by the target server or website address. For example, ‘ping www.example.com’.
- Press Enter to initiate the ping test.
- The ping test will send small data packets from your device to the target server or website.
- The test results will show the response time for each packet, typically displayed in milliseconds (ms).
- The ping test will continue until you manually stop it by pressing Ctrl+C (Windows) or Command+C (macOS).
- Take note of the average response time, as well as any significant fluctuations or packet loss observed during the test.
Ping tests provide insights into the latency or delay experienced between your device and the target server. Lower response times indicate a more responsive and stable network connection.
It’s important to note that ping tests primarily measure network latency and may not provide a comprehensive assessment of overall network speed. However, they are effective in evaluating the quality of your network connection, especially for activities that require real-time interaction, such as online gaming or video conferencing.
When conducting ping tests, it’s recommended to perform tests to various servers or websites to obtain a holistic view of your network connection’s performance. Comparing the average response times between different targets can help identify potential issues with specific servers or network paths.
By regularly conducting ping tests, you can monitor changes in network latency over time and identify any persistent issues that may affect your internet experience. This method provides a quick and easy way to evaluate the stability and responsiveness of your network connection.
Now that you are familiar with conducting ping tests, let’s explore another method that involves testing network speed using browser extensions.
Method 6: Testing Network Speed with Browser Extensions
Another convenient method to test your network speed is by using browser extensions. These extensions provide a seamless way to measure your network connection speed directly from within your web browser. They offer various features and provide detailed results for download and upload speeds, as well as latency and other relevant metrics. Here’s how you can test your network speed with browser extensions:
- Open your web browser (such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge).
- Access the browser’s extension or add-on store.
- Search for “network speed test” or similar keywords in the store’s search bar.
- Choose a reputable speed testing extension that suits your browser and preferences. Some popular options include Speedtest by Ookla extension or Fast.com extension.
- Click on the “Install” or “Add to Chrome/Firefox” button to install the extension.
- Once installed, the extension should appear on the browser’s toolbar or extensions menu.
- Click on the extension icon to open the speed testing tool.
- Click on the “Start Test” or similar button to initiate the speed test.
- The extension will measure your download speed, upload speed, and ping latency.
- After the test completes, the extension will display the results in a clear and easy-to-read format.
- Take note of the results, including download and upload speeds in Mbps and latency in milliseconds.
Browser extensions offer a quick and convenient way to test your network speed without leaving your web browser. They provide real-time measurements and often offer additional features such as historical results and comparisons with global averages.
It’s important to note that different browser extensions may have slight variations in their features and presentation of results. However, the core functionality remains the same: evaluating your network connection speed directly from your browser.
Using browser extensions allows you to easily monitor your network speed while browsing the web. You can quickly assess the performance of your network connection and identify any significant fluctuations or issues that may impact your internet experience.
Now that you are familiar with testing network speed using browser extensions, you have a variety of tools and methods to choose from to evaluate your network connection speed effectively.
How to Interpret Network Speed Test Results
Interpreting network speed test results is crucial to understand the performance of your network connection. Whether you have used online speed testing tools, command line tools, speed testing apps, or other methods, here are some key factors to consider when interpreting network speed test results:
- Download Speed: The download speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from the internet to your device. A higher download speed ensures faster loading times for websites, smoother streaming, and quicker file downloads.
- Upload Speed: The upload speed indicates the rate at which data is sent from your device to the internet. It is crucial for activities such as uploading files, sending emails, or participating in video conferences. Higher upload speeds enable faster sharing of files and smoother video calls.
- Latency (Ping): Latency, also known as ping, measures the delay or response time for data packets to travel between your device and a remote server. Lower latency values indicate a more responsive network connection, important for real-time communication applications like gaming and video conferencing.
- Consistency: Consistency in network speed is essential for a smooth and reliable internet experience. Analyze if there are any significant fluctuations or inconsistencies in the speed test results. Consistently low speeds or high variability may indicate network connectivity issues or congestion.
- Expected vs. Advertised Speeds: Compare your speed test results with the advertised speeds provided by your internet service provider (ISP). If your actual speeds are consistently lower than the advertised speeds, it might be necessary to contact your ISP to address any potential issues or consider upgrading your plan.
- Upload-Download Discrepancy: Notice the ratio between your upload and download speeds. Ideally, the upload speed should be a reasonable fraction of the download speed. If the discrepancy is significant, it may indicate limitations in your plan or potential issues with your network connection.
- Comparison with Global or Local Averages: Some speed testing tools provide comparisons with global or local averages, allowing you to see how your speeds compare to others in your region. This can give you a better understanding of how your network speed ranks and whether it falls within the expected range.
- Benchmarking: Consider using speed test results as benchmarks for future comparisons. Run speed tests periodically and compare the results to monitor any changes and identify trends in your network performance.
Keep in mind that network speed test results are influenced by various factors, such as network congestion, server location, and the type of internet connection. It is recommended to perform multiple tests at different times of the day to account for any variations in network usage that may impact speed.
By interpreting network speed test results and considering these factors, you can gain valuable insights into the performance of your network connection. This information can guide you in optimizing your network setup, troubleshooting connectivity issues, or making informed decisions about your internet service provider.
Now that you know how to interpret network speed test results, let’s explore some tips to improve your network connection speed.
Tips to Improve Network Connection Speed
If you are experiencing slow network connection speeds, there are several steps you can take to potentially improve your internet performance. Consider implementing the following tips to optimize your network connection speed:
- Restart Your Router: Sometimes, the simplest solution is the most effective. Restarting your router can help resolve temporary glitches and improve the overall performance of your network connection.
- Check Your Network Equipment: Ensure that your network equipment, such as your router and modem, are up to date and functioning properly. Outdated or faulty equipment can hinder network speed and stability.
- Optimize Router Placement: Position your router in a central location and away from potential sources of interference, such as walls, appliances, or other electronic devices. This can minimize signal degradation and improve Wi-Fi coverage.
- Secure Your Network: Implement security measures, such as enabling password protection and encrypting your Wi-Fi network, to prevent unauthorized access. Unsecured networks can be exploited, leading to reduced speeds and compromised network performance.
- Manage Network Congestion: If you notice slow speeds during peak usage times, consider scheduling bandwidth-intensive activities for off-peak hours. Additionally, prioritizing important tasks and applications can help allocate bandwidth more efficiently.
- Update Firmware and Software: Regularly update the firmware of your router and ensure that your devices have the latest software updates. Updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes that can positively impact network speed.
- Use Wired Connections: If possible, utilize a wired Ethernet connection instead of relying solely on Wi-Fi. Wired connections typically offer faster and more stable speeds, especially for bandwidth-intensive activities.
- Remove Network Interference: If you’re using Wi-Fi, adjust your wireless channel settings to minimize interference from other nearby networks. Additionally, keep cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and other electronics away from your router to reduce signal interference.
- Consider Network Upgrade: If you consistently experience slow speeds and none of the above solutions improve your situation, it may be worth considering upgrading your internet plan or switching to a different internet service provider that offers higher speeds and better performance in your area.
Implementing these tips can help optimize your network connection speed and improve your overall internet experience. However, it’s important to keep in mind that network speeds can vary based on external factors and your internet service provider’s capabilities.
Regularly testing your network connection speed and implementing these optimization techniques can ensure that you are getting the most out of your internet service and enjoying fast and reliable connectivity.
Now that you have some valuable tips to improve your network connection speed, you can take the necessary steps to enhance your internet experience.