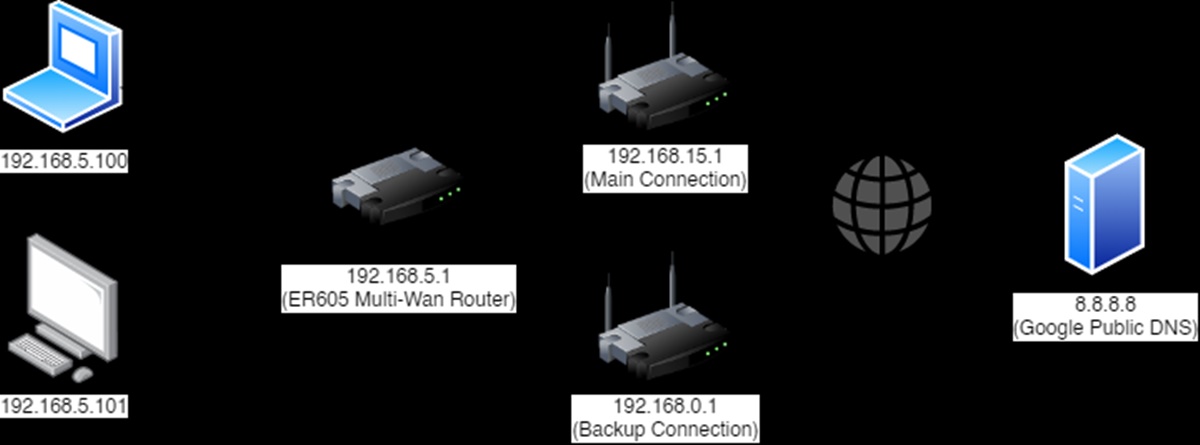
Benefits of Using Two Internet Connections for One Home Network
Having a reliable and fast internet connection is crucial in today’s digital age. It enables us to stream movies, connect with friends and family, work remotely, and stay updated with the latest news and trends. However, as our reliance on the internet continues to grow, so does the need for a stable and uninterrupted connection.
One solution to address this issue is to have two internet connections for your home network. This setup offers several benefits that can greatly enhance your online experience:
1. Increased Reliability: With two internet connections, you are less likely to experience downtime. If one connection fails, the other one can seamlessly take over, ensuring that you remain connected to the internet. This is especially beneficial for individuals who rely on the internet for their work or need to have a constant connection for streaming or gaming.
2. Improved Bandwidth: By combining two internet connections, you can significantly increase your available bandwidth. This means faster download and upload speeds, smoother video streaming, and improved overall performance. It allows multiple devices to simultaneously connect to the internet without experiencing a decrease in speed or performance.
3. Load Balancing: With two internet connections, you have the option to distribute the network traffic evenly between the two connections using load balancing. This ensures that each connection is utilized efficiently and optimizes the performance of your home network. Load balancing also prevents overloading a single connection, which can result in slower speeds or dropped connections.
4. Seamless Failover: In the event that one internet connection fails, having a second connection enables seamless failover, ensuring uninterrupted internet connectivity. Your network will automatically switch to the backup connection, allowing you to continue your online activities without any disruption.
5. Enhanced Security: Having two internet connections can enhance the security of your home network. You can allocate specific devices or tasks to each connection, segregating sensitive activities from regular browsing. This helps to minimize the risk of a single point of failure and provides an additional layer of protection against cyber threats.
6. Greater Flexibility: Two internet connections offer greater flexibility when it comes to internet service providers (ISPs). You can choose different ISPs for each connection, benefiting from competitive pricing, better coverage, or specific features offered by each provider. This allows you to customize your home network setup based on your specific needs and preferences.
How to Get Two Internet Connections for Your Home Network
Setting up two internet connections for your home network may seem like a complex process, but with the right approach, it can be achieved smoothly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Determine Your Internet Needs: Assess your internet requirements to understand the type and speed of connections you need. Consider factors such as the number of devices in your home, the nature of your online activities, and the desired level of reliability and performance.
2. Research ISPs: Research different internet service providers (ISPs) in your area to find the options available to you. Compare factors such as pricing, speed, customer reviews, and reliability to choose the ISPs that best suit your needs.
3. Check Availability: Contact the ISPs you are interested in and verify if their services are available in your area. Inquire about the availability of specific connection types, such as cable, DSL, fiber, or satellite, and determine if they can offer multiple connections to your home.
4. Sign Up for Services: Once you have selected the ISPs, sign up for their services. Provide them with the necessary information, such as your address and contact details, and schedule the installation appointments for each connection.
5. Install the Equipment: Follow the instructions provided by the ISPs to install the necessary equipment, such as modems and routers, for each internet connection. Make sure to connect and configure the devices properly to ensure smooth connectivity.
6. Configure Your Network: To utilize two internet connections effectively, you need to configure your home network accordingly. This can involve setting up load balancing or failover mechanisms, as well as managing devices and network settings. Consult the user manuals or contact the ISPs for guidance on configuring your specific setup.
7. Test and Troubleshoot: After the installation and configuration, test both internet connections to ensure they are functioning properly. Check the speeds, stability, and performance of each connection. If you encounter any issues, consult the ISPs’ support teams for troubleshooting assistance.
8. Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor the performance of both internet connections and address any issues promptly. Keep an eye out for any changes in speeds or inconsistencies in the network. Stay updated with firmware updates for your network equipment and make necessary adjustments as required.
By following these steps, you can successfully set up two internet connections for your home network. Enjoy the benefits of increased reliability, improved bandwidth, and enhanced security that come with having multiple connections.
Setting Up Your Home Network to Utilize Two Internet Connections
Once you have acquired two internet connections for your home network, it’s important to properly configure your network to maximize their benefits. Here are the key steps to setting up your home network to utilize two internet connections:
1. Identify Your Network Equipment: Take stock of your existing network equipment, including routers, switches, and modems. Determine if your current devices can support the dual internet connection setup or if you need to purchase additional equipment.
2. Connect the Modems: Connect each modem to its respective internet service provider’s (ISP) network. Follow the instructions provided by the ISP or refer to the modem’s user manual for the correct configuration.
3. Connect the Routers: Connect each modem to a separate router. In a dual internet connection setup, you will have two routers, each connected to its corresponding modem. Use Ethernet cables to connect the routers to the modems.
4. Configure IP Addresses: Assign unique IP addresses to each router. This helps differentiate the two connections and ensures proper communication between devices and the internet.
5. Enable Load Balancing or Failover: Decide whether you want to implement load balancing or failover for your dual internet connection setup.
Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes the network traffic evenly across both connections, optimizing the use of available bandwidth. This can be helpful when you have multiple devices accessing the internet simultaneously. Consult the manuals of your routers or seek the assistance of an IT professional to configure load balancing.
Failover: Failover ensures continuous internet connectivity in case one connection fails. It automatically switches the network traffic to the backup connection. This setup is ideal if you prioritize uninterrupted internet access. Configure failover settings in your routers according to the instructions provided by the manufacturers.
6. Configure Network Settings: Access the administration panel of each router to configure network settings specific to each connection. This includes setting up SSIDs (network names), passwords, and security settings. It is advisable to use different network names and passwords for each router to avoid confusion and enhance security.
7. Connect Devices: Connect your devices to the appropriate router based on their intended usage or priorities. For example, you may connect devices that require higher bandwidth or low latency to one router, while connecting other devices to the second router for regular internet usage.
8. Test and Monitor: Test the functionality of both internet connections and monitor their performance. Measure the speeds, stability, and overall performance of each connection to ensure they are functioning properly. Make any necessary adjustments to settings or equipment if you encounter any issues.
By following these steps, you can effectively set up your home network to utilize two internet connections. Enjoy the benefits of increased reliability, improved bandwidth, and optimized performance for all your connected devices.
Load Balancing vs. Failover: Which Approach is Right for Your Home Network?
When setting up a home network with two internet connections, you have the option to choose between load balancing and failover. Both approaches offer distinct benefits, so it’s important to understand the differences and determine which one is right for your specific needs.
Load Balancing:
Load balancing involves distributing network traffic across both internet connections, optimizing the use of available bandwidth. Here are the key advantages of implementing load balancing:
1. Increased Performance: Load balancing allows you to utilize the combined capacity of both internet connections, providing a higher overall bandwidth. This means faster download and upload speeds, reduced buffering when streaming videos, and improved performance for multiple devices accessing the internet simultaneously.
2. Efficient Resource Utilization: By evenly distributing the network traffic, load balancing ensures that neither connection is overloaded. This prevents bottlenecks and optimizes the performance of your home network. It also helps to avoid strain on a single connection, reducing the risk of slower speeds or dropped connections.
3. Flexibility and Scalability: Load balancing allows you to easily add or remove internet connections as needed. If you require even more bandwidth in the future, you can simply add another connection and configure it to be part of the load balancing setup. This provides a highly flexible and scalable solution for your growing internet needs.
Failover:
In a failover setup, one internet connection acts as the primary connection, while the other serves as a backup. Here are the key advantages of implementing failover:
1. Continuous Internet Connectivity: With failover, if the primary connection fails for any reason, the backup connection automatically takes over, ensuring uninterrupted internet connectivity. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who require a constant and reliable internet connection, such as remote workers or individuals streaming live content.
2. Simplicity and Ease of Management: Failover is generally easier to set up and manage compared to load balancing. It requires less configuration and monitoring, as the backup connection remains dormant until the primary connection fails. This makes it a simpler solution for those who prioritize reliability over optimizing bandwidth.
3. Cost Efficiency: With failover, you typically only pay for the primary connection on a regular basis. The backup connection is only utilized when the primary connection fails. This can result in cost savings over load balancing, where you are billed for all active connections simultaneously.
Choosing the Right Approach:
The decision between load balancing and failover depends on your specific requirements and priorities. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
1. Internet Usage: Evaluate your internet usage patterns and the number of devices connected to your home network. If you have specific devices or users that require high bandwidth consistently, load balancing may be the best option. If uninterrupted connectivity is the priority, failover is a suitable choice.
2. Reliability: Assess the reliability of the internet connections available in your area. If you have two reliable connections with minimal downtime, load balancing can maximize their use. If one connection is significantly more reliable, failover ensures uninterrupted internet access when needed.
3. Budget: Consider your budget and the costs associated with multiple active connections. Load balancing involves paying for all connections simultaneously, while failover allows you to save costs when the backup connection is not in use.
Ultimately, the right approach for your home network depends on your specific needs for performance, reliability, and cost efficiency. Assess your priorities and consider the advantages of load balancing and failover to make an informed decision for your setup.
Network Configuration for Load Balancing
Load balancing is a network configuration approach that evenly distributes network traffic across multiple internet connections in order to optimize performance and bandwidth utilization. Setting up load balancing requires specific configurations to ensure seamless operation. Here are the key steps to configure your network for load balancing:
1. Network Equipment Requirements:
Ensure that your routers are compatible with load balancing. Some routers have built-in load balancing capabilities, while others may require third-party firmware or additional hardware. Confirm that your routers support the load balancing features you require.
2. Determine Balancing Method:
Decide on the load balancing method that best suits your network. Common methods include round-robin, least connections, or weighted balance. Round-robin distributes traffic evenly across the connections, least connections directs traffic to the connection with the fewest active connections, and weighted balance assigns a higher weight to connections with faster speeds or greater capacity.
3. Configure IP Address Assignment:
Assign unique IP addresses to each router and interface to ensure proper communication between devices and the internet. This helps differentiate the two connections and ensures seamless load balancing.
4. Enable Load Balancing:
Access the administration panel of each router and enable load balancing. This typically involves navigating to the load balancing settings and selecting the desired method. Consult the user manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions on enabling load balancing for your routers.
5. Set Up Session Persistence:
In situations where maintaining session persistence is important, configure session persistence settings. Session persistence ensures that a user’s connection is consistently routed through the same internet connection for the duration of their session. This can be useful for maintaining connectivity for certain applications or online services.
6. Test and Monitor:
After configuring load balancing, test the functionality of both internet connections. Monitor the performance and stability of your network to ensure that traffic is evenly distributed and that the connections are being utilized efficiently. Make any necessary adjustments to the load balancing configuration, such as modifying balancing weights or fine-tuning session persistence settings.
7. Consider additional Load Balancing Techniques:
Depending on your network’s needs and capabilities, you may need to implement additional load balancing techniques. This can include protocol-based load balancing, where traffic is routed based on the type of protocol or application being used, or load balancing based on specific ports or port ranges.
Configuring your network for load balancing requires careful consideration of your network equipment, balancing methods, IP address assignment, and session persistence settings. With proper configuration, load balancing can greatly enhance your network’s performance, improve bandwidth utilization, and provide a seamless and reliable internet experience for all connected devices.
Network Configuration for Failover
Failover is a network configuration approach that ensures uninterrupted internet connectivity by automatically switching to a backup internet connection when the primary connection fails. Setting up failover requires specific configurations to ensure a seamless transition. Here are the key steps to configure your network for failover:
1. Network Equipment Requirements:
Ensure that your routers are compatible with failover configurations. Some routers have built-in failover capabilities, while others may require third-party firmware or additional hardware. Confirm that your routers support the necessary failover features.
2. Identify Primary and Backup Connections:
Determine which connection will serve as the primary and which will act as the backup. Typically, the primary connection will be the one with the higher speed, reliability, or other desired characteristics. The backup connection should have similar specifications with sufficient bandwidth to handle your network’s needs.
3. Configure IP Address Assignment:
Assign unique IP addresses to each router and interface to ensure proper communication between devices and the internet. This helps differentiate the two connections and ensures a seamless failover process.
4. Enable Failover:
Access the administration panel of each router and enable failover functionality. This typically involves navigating to the failover settings and configuring the backup connection as a failover option. Consult the user manual or manufacturer’s website for specific instructions on enabling failover for your routers.
5. Set Up Monitoring and Detection:
Configure monitoring and detection settings to recognize when the primary connection fails. This typically involves setting up a monitoring method, such as pinging a particular IP address or monitoring the link state, to determine the availability of the primary connection. When a failure is detected, the failover mechanism will automatically trigger the switch to the backup connection.
6. Test and Monitor:
After configuring failover, thoroughly test the functionality of both internet connections. Monitor the network to ensure that the failover process is functioning as expected and that the backup connection seamlessly takes over when the primary connection fails. Make any necessary adjustments to the failover configuration or monitoring settings to ensure a smooth transition.
7. Consider Automatic Restoration:
To minimize downtime and restore the primary connection once it becomes available again, consider configuring an automatic restoration process. This ensures that the network automatically switches back to the primary connection once it is restored, providing a seamless failover experience for users.
By configuring your network for failover, you can ensure uninterrupted internet connectivity in the event of a primary connection failure. With proper configuration and monitoring, failover provides a reliable and seamless backup solution for maintaining connectivity for critical online activities.
Utilizing Two Internet Connections for Increased Bandwidth
When you have two internet connections for your home network, you can combine them to effectively increase your available bandwidth. This allows for faster download and upload speeds, smoother streaming, and improved performance for all connected devices. Here are the key benefits and strategies for utilizing two internet connections to maximize your bandwidth:
1. Load Balancing:
One approach to utilizing two internet connections is load balancing. Load balancing evenly distributes network traffic across both connections, effectively utilizing the combined capacity of both connections. This allows for optimal bandwidth usage, resulting in increased overall bandwidth and improved performance for your home network.
2. Multiple Devices:
With two internet connections, you can connect multiple devices to each connection, distributing the load across both connections. This ensures that each device has sufficient bandwidth and reduces congestion on a single connection, leading to smoother and faster internet speeds for all devices.
3. Streaming and Downloading:
Streaming and downloading activities often require significant bandwidth. By utilizing two internet connections, you can dedicate one connection specifically for streaming and downloading purposes. This ensures uninterrupted streaming, reduces buffering, and allows for faster downloads while preserving bandwidth on the other connection for general internet usage.
4. Network Segmentation:
Segmenting your network can be a useful strategy to effectively utilize two internet connections. For example, you can assign specific devices or types of activities to each connection. For instance, you can allocate gaming consoles or devices requiring low latency to one connection, while assigning regular web browsing and email to the other.
5. Prioritizing Bandwidth:
If certain devices or applications require more bandwidth, you can prioritize their access to one connection. This can be achieved through Quality of Service (QoS) settings in your routers, which give priority to specific devices or applications based on your preferences. Prioritizing bandwidth ensures a smooth and uninterrupted online experience for activities that require higher speeds.
6. Network Monitoring and Management:
It is important to regularly monitor and manage your network to ensure effective utilization of both internet connections. This includes monitoring bandwidth usage and performance, and making adjustments as needed. You may need to fine-tune load balancing settings or prioritize bandwidth based on changing needs or usage patterns.
7. Intelligent Network Switching:
To further optimize your network’s bandwidth utilization, you can implement intelligent network switching. This involves automatically routing specific types of traffic or applications through the connection that offers the best performance for that particular activity. For example, you can route video conferencing traffic through the connection with the lowest latency, ensuring clear and uninterrupted communication.
By effectively utilizing two internet connections, whether through load balancing, network segmentation, or intelligent network switching, you can maximize your available bandwidth and enhance the overall internet experience for your home network. Enjoy faster speeds, smoother streaming, and improved performance across all your connected devices.
Ensuring a Smooth Transition between Internet Connections
When utilizing two internet connections for your home network, ensuring a seamless transition between the connections is crucial to maintaining a reliable and uninterrupted internet experience. Here are some key considerations to ensure a smooth transition between internet connections:
1. Failover Configuration:
If you have implemented a failover setup, configure the failover mechanism to automatically detect and switch to the backup connection when the primary connection fails. This ensures minimal disruption to your internet connectivity and a smooth transition for all connected devices.
2. Monitoring Tools:
Utilize network monitoring tools to keep an eye on the performance and status of both internet connections. By proactively monitoring the connections, you can quickly identify any issues or fluctuations in performance and take appropriate actions to rectify them before they affect your internet experience.
3. Connection Speed and Latency:
Ensure that both internet connections offer similar speeds and latency characteristics. Having significant disparities in these aspects can lead to issues during the transition between connections. Ideally, aim for two connections that are as closely matched as possible to minimize any disruptions during the transition.
4. Equipment Reliability:
Use reliable and high-quality network equipment, including routers, modems, and cables. Faulty or unreliable equipment can lead to frequent disconnections or delays during the transition process. Regularly update the firmware of your network equipment to ensure compatibility and optimum performance.
5. Network Configuration:
Properly configure your network settings to facilitate smooth transitions between internet connections. Ensure that your routers are correctly set up for failover or load balancing, depending on your desired setup. Additionally, configure settings such as IP address allocation, gateway assignment, and DNS settings to ensure seamless switching between the connections.
6. Network Testing and Optimization:
Regularly test and optimize your network to identify and address any potential bottlenecks or performance issues. Conduct speed tests, assess bandwidth usage, and monitor network traffic to ensure that the transition between connections does not introduce any unnecessary delays or disruptions.
7. Redundancy:
Consider implementing redundancies in your network setup to further enhance reliability. For example, you can have multiple routers or network switches, each configured to handle a specific connection. This redundancy can ensure continuous network connectivity even if one of the network devices encounters an issue.
By implementing these measures, you can ensure a smooth and uninterrupted transition between internet connections. This will provide a seamless internet experience for your home network, minimizing any disruptions or downtime that may occur during the switch from one connection to another.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Dual Internet Connections
While utilizing dual internet connections for your home network can enhance reliability and performance, it is not uncommon to encounter certain issues. Here are some common problems that may arise with dual internet connections and troubleshooting steps to help you resolve them:
1. Unequal Bandwidth Distribution:
If you notice that one internet connection is consistently receiving more traffic than the other, it may indicate an issue with load balancing. Check your load balancing settings and ensure that the distribution method is configured correctly. Adjust the weights or parameters as necessary to evenly distribute the traffic between the two connections.
2. Unstable Connections or Dropped Packets:
If you experience frequent disconnections or encounter dropped packets, it can be due to a variety of factors. Check the physical connections of your routers, modems, and cables. Verify that all connections are secure and properly seated. If the issue persists, contact your internet service providers (ISPs) to determine if there are any known issues with their networks.
3. Slow Internet Speeds:
If you’re experiencing slower-than-expected speeds on one or both connections, conduct a speed test to measure the actual bandwidth you’re receiving. Factors such as network congestion, device limitations, or ISP throttling can impact your speeds. Consider upgrading your internet plans or contacting your ISPs to troubleshoot and address any specific issues affecting your speeds.
4. Configuration Incompatibilities:
If you’re encountering compatibility issues between your network equipment and the dual internet connections, check for firmware updates for your routers and modems. Outdated firmware can cause functionality issues and may not support the latest features required for a smooth connection. Update the firmware of your equipment and ensure that it is compatible with the dual internet setup.
5. IP Address Conflicts:
If you experience network connectivity issues or devices aren’t obtaining IP addresses correctly, there may be an IP address conflict. Ensure that each router and interface has a unique IP address assigned. Also, verify that DHCP settings are correctly configured to prevent conflicts and ensure seamless connectivity across the network.
6. DNS Resolution Problems:
If you’re having difficulty accessing websites or experiencing DNS resolution issues, try using alternative DNS servers or contact your ISPs for troubleshooting assistance. DNS issues can disrupt internet connectivity, and using reliable DNS servers can help resolve these problems.
7. Equipment or Power Failures:
In the event of equipment failures or power outages, ensure that your dual internet connections have backup power sources or surge protectors to prevent damage. Test your backup power systems regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. If an equipment failure occurs, contact the manufacturers or providers for technical support or replacements.
For persistent issues that cannot be resolved through these troubleshooting steps, consult with IT professionals, technicians, or reach out to your ISPs for further assistance. Remember that troubleshooting dual internet connection issues may involve a combination of factors, including network settings, hardware compatibility, and ISP-related problems. Patience and perseverance are key to resolving and maintaining a smooth and reliable dual internet connection setup.
Security Considerations when Using Two Internet Connections
When utilizing two internet connections for your home network, it is important to consider the security implications. Here are some key factors to consider and security measures to implement when using two internet connections:
1. Network Segmentation:
Implement network segmentation by keeping sensitive devices or tasks on a separate internet connection from regular browsing activities. This segregation helps minimize the risk of potential attacks or breaches and provides an additional layer of protection for sensitive information.
2. Firewall Configuration:
Configure your firewalls to provide adequate protection for both internet connections. Enable firewalls on routers and ensure that they are properly configured to monitor and filter network traffic. Regularly update firewall settings to adapt to emerging threats and implement intrusion prevention systems for enhanced security.
3. VPN Usage:
Utilize virtual private network (VPN) connections to encrypt your internet traffic and enhance the security of your online activities. VPNs create a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, protecting your data from potential eavesdropping or interception, particularly when accessing sensitive information or using public Wi-Fi networks.
4. Regular Firmware Updates:
Regularly update the firmware of your routers and modems to ensure that they have the latest security patches and bug fixes. Outdated firmware can contain vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Enable automatic updates or periodically check for firmware updates on the manufacturer’s website and apply them promptly.
5. Strong Passwords:
Use strong, unique passwords for your routers, modems, and any other network devices. Weak or easily guessable passwords can make it easier for unauthorized individuals to gain access to your network. Incorporate a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to create strong passwords, and avoid using common phrases or personal information.
6. Network Monitoring:
Regularly monitor your network for any suspicious or malicious activities. Implement network monitoring tools to detect unusual network traffic, unauthorized access attempts, or other suspicious behaviors. Regularly review logs and investigate any anomalies to promptly address any potential security threats.
7. Physical Security Measures:
Ensure the physical security of your network equipment by keeping routers, modems, and other devices in a secure location. Restrict physical access to your network devices to authorized individuals only. Additionally, protect your devices from power surges or outages by using surge protectors or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
8. Regular Backups:
Regularly back up your important data stored on your devices and network storage. This includes documents, photos, and any other valuable information. In the event of a security breach or network failure, having up-to-date backups ensures that you can easily recover your data and minimize potential disruptions.
By considering these security considerations and implementing the appropriate measures, you can strengthen the security of your home network when utilizing two internet connections. Safeguarding your network from potential threats and vulnerabilities is crucial in maintaining the privacy and integrity of your digital activities.