What is a MAC Address?
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer. It is a 12-digit hexadecimal number that is used to identify devices on a local area network (LAN). Every device that can connect to a network, such as a computer, smartphone, or router, has its own MAC address.
The MAC address is hard-coded into the network interface card at the time of manufacturing and cannot be changed. It serves as a permanent and globally unique identifier for the device. The MAC address consists of two parts: the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and the device-specific identifier.
The OUI contains the manufacturer’s unique identification number, which is assigned by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). This ensures that no two manufacturers have the same OUI. The device-specific identifier is assigned by the manufacturer and is unique to each device they produce.
The MAC address is essential for communication on a LAN. When devices on a network need to send data to another device, they use the MAC address to identify the intended recipient. It acts as a physical address, similar to how a street address identifies a building.
It is important to note that the MAC address operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model, which is responsible for transferring data between neighboring network devices. This is different from an IP address, which is used at the Network Layer to identify devices on a wider network.
How MAC Address Filtering Works
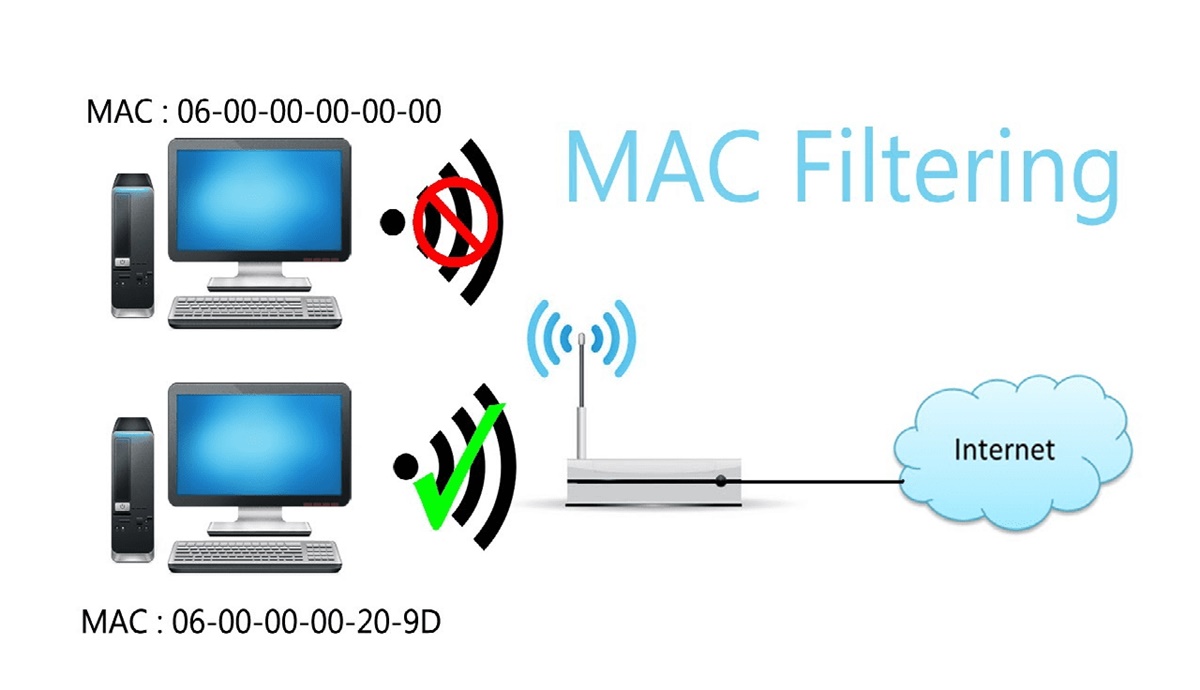
MAC address filtering is a security feature implemented in routers and access points to control network access. It allows the network administrator to specify which devices are allowed to connect to the network based on their MAC addresses. When MAC address filtering is enabled, the router will only allow devices with authorized MAC addresses to connect to the network, while blocking all other devices.
Here’s how MAC address filtering works:
- The network administrator configures the router to enable MAC address filtering.
- A list of authorized MAC addresses is created in the router’s settings. This list includes the MAC addresses of all devices that are allowed to connect to the network.
- When a device attempts to connect to the network, the router checks its MAC address against the list of authorized addresses.
- If the MAC address matches an entry in the list, the device is granted access to the network.
- If the MAC address is not found in the list, the device is denied access and unable to connect to the network.
It’s important to note that MAC address filtering operates at the local network level and does not provide protection against unauthorized access from external networks. It is primarily used to control access within a home or office network where physical access to the router is restricted.
While MAC address filtering can be an effective security measure, it is important to understand its limitations. MAC addresses can be spoofed or easily changed, so it is not foolproof against determined attackers. Additionally, managing a large number of MAC addresses can be cumbersome, especially in environments with frequently changing devices or guest access.
Despite its limitations, MAC address filtering can be a useful additional layer of security for network administrators who want to exert more control over their network. By allowing only authorized devices to connect, it can help prevent unauthorized access and mitigate some security risks.
Advantages of MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering offers several advantages when it comes to securing a network. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Enhanced Access Control: MAC address filtering provides an additional layer of access control by only allowing devices with authorized MAC addresses to connect to the network. This helps prevent unauthorized access and can be particularly useful in environments where network security is a top priority.
- Prevention of Unauthorized Devices: By explicitly specifying which devices are allowed to connect to the network, MAC address filtering prevents unauthorized devices from gaining access. This can help protect against potential security breaches and ensure that only trusted devices can join the network.
- Protection against Network Attacks: MAC address filtering can be effective in mitigating certain types of network attacks, such as MAC address spoofing. By allowing only legitimate MAC addresses to connect, it reduces the risk of attackers impersonating authorized devices and gaining unauthorized access to the network.
- Simplicity in Deployment: Implementing MAC address filtering is relatively easy and does not require any additional software or complex configurations. Most routers and access points have built-in support for MAC address filtering, making it a straightforward security measure to implement.
- Reduced Network Congestion: By limiting network access to only authorized devices, MAC address filtering can help reduce network congestion. This can be particularly beneficial in larger networks where the available bandwidth needs to be optimized for essential devices and users.
While MAC address filtering provides these advantages, it is important to note that it is not a comprehensive solution for network security. It should be used in conjunction with other security measures, such as strong encryption, regular software updates, and strong passwords, to ensure a robust and secure network.
Overall, MAC address filtering can be an effective security measure for controlling network access and preventing unauthorized devices from connecting. It offers enhanced access control, protection against certain network attacks, and simplicity in deployment, making it a valuable tool for network administrators seeking to strengthen their network security protocols.
Disadvantages of MAC Address Filtering
While MAC address filtering can be a useful security measure, it also has some limitations and disadvantages that should be taken into consideration:
- MAC Address Spoofing: MAC addresses can be easily spoofed or changed by attackers. This means that a determined individual could impersonate an authorized MAC address and bypass the filtering mechanism, gaining unauthorized access to the network.
- Management Challenges: Managing a large number of MAC addresses can be cumbersome and time-consuming. In environments with frequently changing devices or guest access, constantly updating the list of authorized MAC addresses can become a burden for network administrators.
- Inconvenience for Legitimate Users: MAC address filtering can be inconvenient for legitimate users who are allowed to connect to the network. If their device’s MAC address is not added to the authorized list or is accidentally removed, they will be denied network access until the issue is resolved, causing frustration and disruption.
- Interference with Device Replacement: MAC address filtering can pose challenges when replacing or upgrading devices on the network. If a new device is introduced that has a different MAC address, its address must be added to the authorized list before it can connect to the network. This can lead to delays and issues during device upgrades or replacements.
- Limited Protection: MAC address filtering only provides protection at the local network level. It does not protect against attacks originating from external networks, such as the internet. Additional security measures, such as firewalls and encryption, are necessary to secure the network against external threats.
It’s important to consider these disadvantages and evaluate whether MAC address filtering is the appropriate security measure for your specific network environment. While it can offer some level of control and protection, it should be used in conjunction with other security measures to create a comprehensive and robust network security strategy.
Setting Up MAC Address Filtering on a Router
Setting up MAC address filtering on a router involves a series of steps to enable the feature and configure the list of authorized MAC addresses. Here’s a general guide to help you set up MAC address filtering:
- Access the router’s administration interface by typing the router’s IP address into a web browser. You may need to enter a username and password to log in.
- Navigate to the MAC address filtering section of the router’s settings. This location may vary depending on the router model and firmware.
- Enable MAC address filtering by selecting the appropriate option or checkbox.
- Create a list of authorized MAC addresses by entering each address individually or importing a file containing the addresses.
- Specify the filtering mode, which determines whether the router allows or denies access to devices on the authorized list.
- Save the changes and apply the settings to activate MAC address filtering.
- Test the configuration by attempting to connect a device to the network. The router should either grant or deny access based on the MAC address being recognized on the authorized list.
It’s important to consult the router’s user manual or the manufacturer’s website for specific instructions on setting up MAC address filtering, as the steps may vary depending on the router model. Additionally, some routers offer additional features, such as time-based filtering or the ability to create groups of MAC addresses with different access permissions.
Remember to regularly review and update the list of authorized MAC addresses as devices may change or be replaced over time. Keeping the list up to date ensures that only approved devices can connect to the network and helps maintain the effectiveness of the MAC address filtering feature.
Managing MAC Address Filtering
Managing MAC address filtering involves ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of the filtering feature. Here are some important aspects to consider when managing MAC address filtering:
- Regularly Review Authenticated Devices: Periodically review the list of authorized MAC addresses to ensure that it is up to date. Remove any devices that are no longer in use or have been replaced. Additionally, add any new devices that require network access.
- Document Authorized MAC Addresses: Keep a record of the MAC addresses of authorized devices along with their associated users or purposes. This documentation can help in managing and troubleshooting network connectivity issues and make it easier to update the filtering settings when needed.
- Consider Grouping MAC Addresses: Some routers allow the creation of MAC address groups with different access permissions. This can help in managing different categories of devices, such as employees, guests, or IoT devices, with varying levels of network access freedom.
- Monitor Network Activity: Regularly monitor network activity and check for any unauthorized devices attempting to connect to the network. Analyzing logs and using network monitoring tools can help identify any potential security breaches or misuse of network resources.
- Implement Other Security Measures: MAC address filtering should be used in conjunction with other security measures, such as strong passwords, network encryption, and firewall protection. This multi-layered approach enhances the overall security of the network.
- Educate Users: Provide guidance and education to network users on the importance of network security and the purpose of MAC address filtering. Teach them to report any suspicious activities or unauthorized devices to the IT department to help detect and address potential security threats.
By proactively managing MAC address filtering, you can ensure that only authorized devices have network access, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or security breaches. Regularly reviewing and updating the list of authorized MAC addresses, monitoring network activity, and implementing additional security measures are essential for maintaining a secure and well-functioning network.
Common Issues with MAC Address Filtering
While MAC address filtering can be a valuable network security measure, it can also encounter some common issues that may affect its effectiveness. Understanding these challenges can help in troubleshooting and resolving any problems that may arise. Here are some common issues to be aware of:
- MAC Address Spoofing: As MAC addresses can be easily spoofed or changed, determined attackers can impersonate authorized MAC addresses and bypass the filtering mechanism. This can result in unauthorized access to the network, compromising its security.
- Maintenance and Updates: Managing a large number of MAC addresses can be a challenge, especially in dynamic environments with frequently changing devices. Keeping the list of authorized MAC addresses up to date requires regular maintenance and prompt updates when devices are added or removed from the network.
- Compatibility Issues: Some devices may not properly support MAC address filtering or may have limitations in their firmware or network stack. These compatibility issues can lead to connectivity problems or inconsistent filtering behavior.
- Complexity in Large Networks: MAC address filtering might become complex and unwieldy in larger networks with a vast number of authorized devices. Maintaining and managing the MAC address list can be time-consuming and may require additional resources.
- Impact on Guest Access: MAC address filtering can hinder guest access to the network. Adding and removing MAC addresses for guest devices can be inconvenient and might require manual intervention, impacting the user experience for visitors or clients.
- Increased Support Efforts: When MAC address filtering is in place, troubleshooting network connectivity issues can be more challenging. Network administrators may need to provide additional support to users who experience difficulties connecting their devices to the network.
- Dependence on Hardware MAC Addresses: MAC address filtering relies on the unique and unchangeable hardware MAC addresses of devices. However, certain devices, such as virtual machines or network adapters with MAC address spoofing capabilities, might have mutable MAC addresses, which can bypass the filtering.
Despite these common issues, MAC address filtering can still be a valuable security measure when used in conjunction with other network security practices. Regular monitoring, timely updates, and implementing additional security measures can help mitigate these challenges and enhance the overall effectiveness of MAC address filtering.
Alternatives to MAC Address Filtering
While MAC address filtering can provide a level of network security, there are alternative methods and technologies that can be used either in conjunction with or as alternatives to MAC address filtering. These alternatives can address some of the limitations and challenges associated with MAC address filtering. Here are a few commonly used alternatives:
- Network Segmentation: Instead of relying solely on MAC address filtering, network segmentation divides the network into separate subnets or VLANs. This helps isolate different sections of the network and restrict access based on IP addresses or other criteria. Network segmentation enhances security by controlling and limiting network traffic flow.
- Port Security: Port security restricts network access based on the physical Ethernet port to which a device is connected. It allows network administrators to define which MAC addresses are allowed to connect to specific ports, preventing unauthorized devices from accessing the network through those ports.
- 802.1X Authentication: 802.1X is an authentication protocol that provides port-based access control. It requires users or devices to authenticate themselves before gaining network access. This authentication can be based on usernames, passwords, or digital certificates, providing an additional layer of security and granularity in controlling network access.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS solutions monitor network traffic for suspicious or malicious activities. They can detect and block unauthorized access attempts, identify potential threats, and provide real-time security alerts. IDS/IPS can help safeguard the network against both internal and external threats.
- Firewalls: Firewalls are network security devices that control and filter incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules. They can be set up to block or allow access based on IP addresses, protocols, ports, or applications. Firewalls provide a strong defense against unauthorized access and can be more flexible than MAC address filtering.
These alternative methods and technologies offer diverse approaches to network security, each with its own strengths and considerations. Depending on the specific network environment and security requirements, a combination of these alternatives can be employed to provide a more comprehensive and robust network security solution.
It is recommended to carefully evaluate the network’s needs, consider the limitations and strengths of each alternative, and seek professional advice if necessary when deciding on the most suitable approach for securing the network.