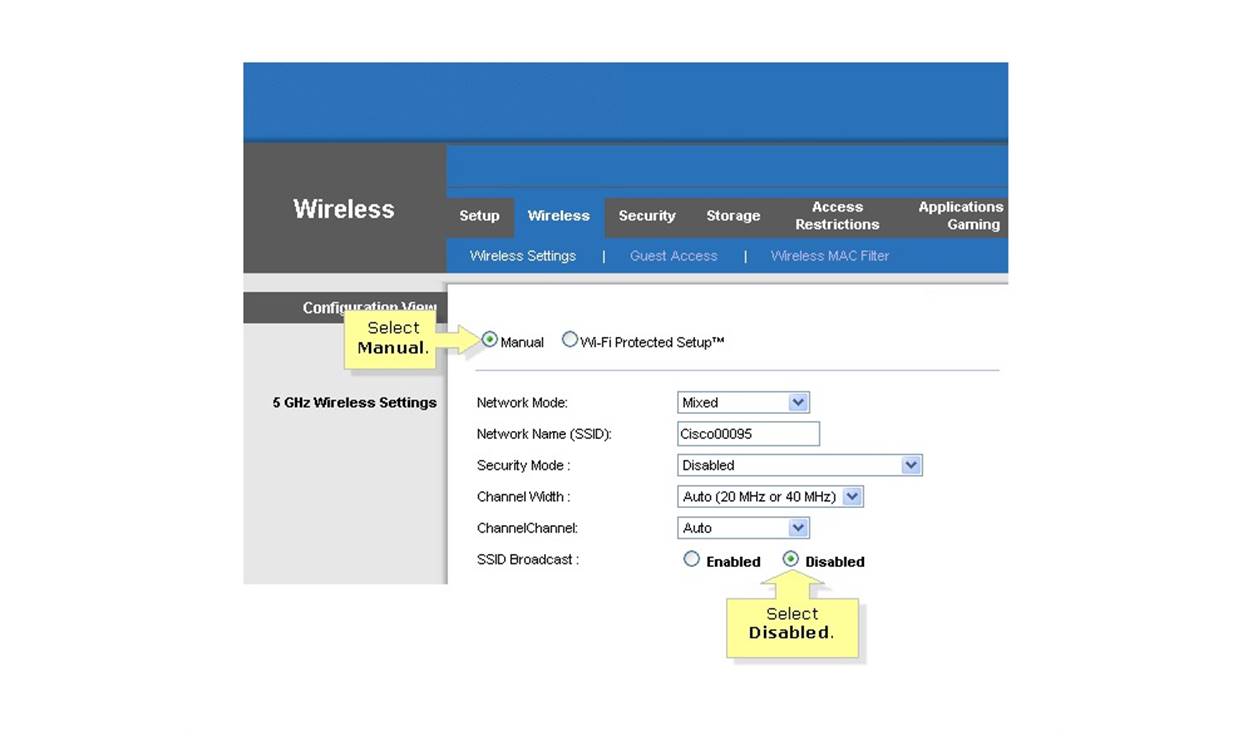
What is SSID Broadcasting?
SSID broadcasting, also known as Service Set Identifier broadcasting, is a feature of wireless networks that is enabled by default on most routers and access points. It involves the transmission of the network’s name, or SSID, over the airwaves, allowing devices to detect and connect to the network.
The SSID is essentially the name of the wireless network that appears when users scan for available Wi-Fi connections. It helps users identify and connect to their desired network, especially when multiple networks are present in the vicinity. By broadcasting the SSID, the network administrator makes it easier for devices to discover and join the network.
When SSID broadcasting is enabled, the network’s name is periodically sent out in beacon frames by the router or access point. These beacon frames are like radio signals that devices listen for when searching for available networks. Once a device detects a beacon frame with a matching SSID, it can connect to the network with the appropriate credentials.
However, there is an ongoing debate about whether it is beneficial or advisable to disable SSID broadcasting. Some argue that disabling SSID broadcasting can enhance network security and provide additional protection against unauthorized access. Others believe that the drawbacks of disabling SSID broadcasting outweigh any potential benefits.
Benefits of Disabling SSID Broadcasting
While the decision to disable SSID broadcasting may vary depending on individual needs and preferences, there are several potential benefits associated with this practice. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
Enhanced Network Security
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you are effectively making your network invisible to casual observers and potential attackers. Since the network’s name is not broadcasted, it becomes less visible to unauthorized devices trying to connect to Wi-Fi networks in the area. This can act as an additional layer of security, as it adds an extra obstacle for attackers attempting to gain access to your network.
Protection against Unauthorized Access
When SSID broadcasting is disabled, users must manually enter the network’s name to connect. This means that even if someone manages to capture your Wi-Fi signal, they would not be able to identify your network without prior knowledge. This reduces the risk of unauthorized users attempting to gain access to your network, as they would need to know the exact SSID to connect.
Reduction in Network Congestion
SSID broadcasting can contribute to network congestion in areas with multiple Wi-Fi networks. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, devices constantly scan for available networks, leading to increased traffic and higher levels of interference. By disabling SSID broadcasting, you effectively reduce the number of devices scanning for your network, resulting in decreased congestion and potentially improved network performance.
Concealing Network Presence
Disabling SSID broadcasting can be useful in situations where network privacy is a priority. If you do not want your network to be easily detected by passersby or neighboring devices, disabling SSID broadcasting helps keep your network hidden. This is particularly beneficial in crowded environments or areas where you want to maintain a low profile.
These benefits highlight some of the reasons why individuals may choose to disable SSID broadcasting. However, it’s important to consider the potential drawbacks and limitations associated with this practice, which we will explore in the next section.
Enhanced Network Security
One of the primary benefits of disabling SSID broadcasting is the enhanced network security it provides. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, your network’s name becomes visible to anyone scanning for available Wi-Fi networks. This can make it an easy target for attackers attempting to gain unauthorized access.
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you effectively hide your network from casual observers and potential intruders. Since the network name is not broadcasted, it becomes more difficult for unauthorized devices to detect and target your network. This can serve as an extra layer of security, as it adds an additional step for attackers trying to break into your network.
Furthermore, disabling SSID broadcasting can deter less tech-savvy individuals from attempting to connect to your network. Without the network name being readily visible, it becomes less likely that someone passing by or in the vicinity of your network will try to connect to it.
Another security advantage of disabling SSID broadcasting is the reduction in the number of detectable networks in the area. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, nearby devices continuously scan for available networks, and this can lead to increased network congestion. By disabling SSID broadcasting, you contribute to reducing the overall network traffic, making it less appealing for potential attackers to target your network due to the decreased number of visible networks.
It’s important to note that disabling SSID broadcasting alone is not sufficient to guarantee absolute network security. Other security measures, such as implementing strong encryption, using secure passwords, and enabling network authentication protocols, should also be in place to strengthen network security.
Lastly, while disabling SSID broadcasting may provide enhanced security, it is worth mentioning that determined attackers can still employ advanced techniques to identify hidden networks. They can use network sniffing tools or exploit vulnerabilities in the Wi-Fi protocols to discover hidden SSIDs. Therefore, disabling SSID broadcasting should be complemented with other security measures to create a more robust and secure network environment.
Protection against Unauthorized Access
Disabling SSID broadcasting offers a significant benefit when it comes to protecting your wireless network against unauthorized access. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, your network’s name is visible to anyone in the vicinity, making it an easy target for potential intruders.
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you effectively hide your network from casual observers and deter opportunistic individuals from attempting to connect to it. When the network name is not readily visible, unauthorized devices will need prior knowledge of the exact SSID to connect, making it more challenging for them to gain access to your network.
While disabling SSID broadcasting can act as a deterrent, it is important to remember that it is not a foolproof security measure. Unauthorized users who are determined and skilled may still attempt to gain access to your network using other methods, such as utilizing Wi-Fi cracking tools or employing brute-force attacks.
To provide an additional layer of security against unauthorized access, it is crucial to implement other security measures alongside disabling SSID broadcasting. These measures may include:
- Using strong and unique passwords for your Wi-Fi network
- Enabling network encryption protocols like WPA2 or WPA3
- Implementing MAC address filtering to allow only authorized devices
- Regularly updating your router’s firmware to fix any known vulnerabilities
By combining these security measures with disabling SSID broadcasting, you can create a more secure network environment and make it significantly more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to your wireless network.
It’s worth noting that disabling SSID broadcasting may present some challenges when connecting new devices to your network. You will need to manually enter the network name (SSID) when setting up new devices, which can be more inconvenient compared to devices automatically detecting and connecting to a broadcasted network. However, this inconvenience can be mitigated by saving the network credentials on your devices once the initial setup is complete.
Overall, while disabling SSID broadcasting is not a foolproof security measure, it can provide added protection against unauthorized access to your wireless network when combined with other security measures.
Reduction in Network Congestion
Disabling SSID broadcasting can have a positive impact on reducing network congestion in areas with multiple Wi-Fi networks. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, devices in the vicinity continuously scan for available networks, contributing to increased network traffic and potential interference.
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you effectively reduce the number of devices scanning for your network. This can lead to a decrease in network congestion and improved overall network performance.
In densely populated areas, such as apartment buildings or office complexes, there can be a significant number of Wi-Fi networks operating simultaneously. Each network’s beacon frames, containing the SSID information, contribute to the overall network overhead. By disabling SSID broadcasting on your network, you help reduce this overhead and minimize the interference caused by overlapping signals from other nearby networks.
Reducing network congestion not only improves performance but also enhances the stability and reliability of your Wi-Fi connection. When networks are congested, it can lead to slower data transfer rates, increased latency, and a higher likelihood of connection drops or disruptions. Disabling SSID broadcasting can help mitigate these issues and create a smoother and more reliable network experience.
It’s important to note that the reduction in network congestion achieved by disabling SSID broadcasting may not have a significant impact in all scenarios. The extent of the improvement depends on various factors, including the density of Wi-Fi networks in the area, the number of connected devices, and the overall network setup.
Furthermore, while disabling SSID broadcasting can reduce network congestion to some extent, other factors like signal strength, channel selection, and interference from non-Wi-Fi devices also play a role in overall network performance. It’s recommended to optimize these aspects, in addition to disabling SSID broadcasting, for optimal network efficiency.
Overall, disabling SSID broadcasting can contribute to a reduction in network congestion and improve network performance, particularly in areas with multiple overlapping Wi-Fi networks. However, it’s important to consider the specific network environment and other factors that can affect network performance when evaluating the potential benefits of disabling SSID broadcasting.
Concealing Network Presence
Disabling SSID broadcasting can provide the benefit of concealing your network’s presence from passersby and neighboring devices. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, your network’s name is visible to anyone scanning for available Wi-Fi networks, potentially making it a target for unwanted attention or unauthorized access.
By disabling SSID broadcasting, you effectively make your network invisible to casual observers. Without the network name being readily visible, it becomes significantly more challenging for others to detect and target your network. This can be particularly useful in crowded environments or areas where you want to maintain a low profile.
Concealing your network’s presence through the disabling of SSID broadcasting can help protect your privacy and minimize the risk of unwanted visitors attempting to connect to your Wi-Fi network. It acts as an extra layer of defense by making it less likely for individuals in the vicinity to even be aware of your network’s existence.
This concealment can be especially advantageous in scenarios where you have specific authorized devices that you want to connect to your network. By disabling SSID broadcasting, only those with prior knowledge of the network name can connect, offering an added level of control over network access.
While concealing your network’s presence via disabling SSID broadcasting offers a degree of protection, it’s important to note that determined attackers or experienced hackers can still employ sophisticated techniques to detect hidden networks. They may use network sniffing tools or exploit vulnerabilities to uncover your network’s SSID.
Therefore, to maintain a more secure network environment, it’s crucial to combine SSID broadcasting disablement with other security measures. Implementing strong encryption, using secure passwords, regularly updating your router’s firmware, and enabling other authentication protocols can further enhance network security alongside the concealed SSID.
Lastly, as an additional consideration, concealing your network’s presence through SSID broadcasting disablement may introduce some challenges when connecting new devices to your network. Manually entering the network name (SSID) may be required during the initial setup, which could be more cumbersome compared to devices automatically detecting and connecting to a broadcasted network. However, this inconvenience can be mitigated by saving the network credentials on the devices once the initial setup is complete.
Drawbacks of Disabling SSID Broadcasting
While disabling SSID broadcasting can offer certain benefits, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and limitations associated with this practice. Let’s explore some of the downsides of disabling SSID broadcasting:
Difficulty in Connecting to Network
One of the main drawbacks of disabling SSID broadcasting is the inconvenience it can cause when connecting new devices to your network. Without the network name being broadcasted, you will need to manually enter the SSID on each device during the initial setup. This can be time-consuming and may require more technical know-how, particularly for less tech-savvy individuals.
Incompatibility with Some Devices
Disabling SSID broadcasting can cause connectivity issues with certain devices. Some older or less advanced devices may not support manual network configuration and rely solely on automatic network scanning. These devices may not be able to detect your network if SSID broadcasting is disabled, making it impossible to connect them to your network.
Impact on Wi-Fi Performance
While the reduction in network congestion is often touted as a benefit, disabling SSID broadcasting may not always lead to noticeable improvements in Wi-Fi performance. In some cases, it may have a minimal impact on network speed and latency. Other factors such as signal strength, channel interference, and the number of connected devices play a more significant role in overall Wi-Fi performance.
Manual Configuration Requirements
Disabling SSID broadcasting requires additional manual configuration on devices that you want to connect to the network. This can be an inconvenience, especially if you have multiple devices that need to be manually configured. It adds complexity and increases the chances of errors during the process, which may result in connection issues.
It’s worth noting that while these drawbacks exist, they can be mitigated with proper planning and understanding of the network environment. For example, you can save the network credentials on your devices once they are initially configured, reducing the need for manual entry in the future.
Ultimately, the decision to disable SSID broadcasting should be based on a careful consideration of the benefits and drawbacks in relation to your specific network requirements and security concerns. It’s important to weigh the convenience and compatibility considerations against the potential security enhancements provided by disabling SSID broadcasting.
Difficulty in Connecting to Network
One of the primary drawbacks of disabling SSID broadcasting is the increased difficulty in connecting new devices to your network. When SSID broadcasting is enabled, devices are able to automatically detect and display available networks, making it easy for users to select and connect to their desired network. However, when SSID broadcasting is disabled, users must manually enter the network name (SSID) to connect to the network.
This manual configuration process can be time-consuming and may require additional technical knowledge. Users need to know the exact network name and enter it correctly on each device they wish to connect. Mistakes in entering the SSID can result in failed connection attempts, causing frustration for users.
Disabling SSID broadcasting can be particularly challenging for less tech-savvy individuals who may not be familiar with network settings or may find the process confusing. It may also be a hindrance when connecting multiple devices, as each device will need to be manually configured.
In situations where guests or temporary users need to connect to your network, disabling SSID broadcasting can present even more difficulties. Instead of simply selecting the network from a list of available networks, guests will need to be provided with the network name and instructions on how to manually connect. This can be inconvenient and time-consuming, especially when dealing with a large number of guests or limited time.
While some devices provide the option to save the network credentials once they are initially configured, allowing for easier future connections, this feature is not universally supported by all devices. Therefore, even if the network credentials are saved on one device, other devices may still require manual entry each time they attempt to connect to the network.
To mitigate the difficulty in connecting to a network with disabled SSID broadcasting, it is important to provide clear and accurate instructions to users, especially when dealing with guest connections. Consider creating a separate document or providing a FAQ section that guides users through the manual configuration process.
Incompatibility with Some Devices
Another drawback of disabling SSID broadcasting is the potential incompatibility with certain devices. While most modern devices support manual network configuration, there are still some older or less advanced devices that rely solely on automatic network scanning. These devices may not have the capability to manually enter the network name (SSID), making it impossible to connect them to a network with disabled SSID broadcasting.
Devices such as older smartphones, tablets, gaming consoles, or IoT devices may not have the option to manually configure the network settings or may have limited support for manual configuration. These devices typically rely on the automatic detection of the SSID during the Wi-Fi network selection process. As a result, they may not be able to recognize or connect to a network with disabled SSID broadcasting.
This incompatibility can be frustrating for users who encounter such devices, as it restricts their ability to connect to the network and limits their device options. It can be particularly problematic in scenarios where multiple devices of varying ages and capabilities need to connect to the network.
To overcome this limitation, one possible solution is to temporarily enable SSID broadcasting when connecting incompatible devices. By temporarily enabling SSID broadcasting, these devices will be able to automatically detect and connect to the network. Once the device is connected, SSID broadcasting can be disabled again. However, this method requires manual intervention each time a new incompatible device needs to be connected.
It’s important to note that the level of incompatibility with SSID broadcasting may vary depending on device models and firmware versions. Some devices may have workarounds or alternative methods to connect to networks with disabled SSID broadcasting. However, it is generally recommended to test the compatibility of devices with disabled SSID broadcasting before fully implementing this practice.
Considering the potential incompatibility with some devices, it’s crucial to weigh the benefits of disabling SSID broadcasting against the limitations it may pose. If you have a significant number of older or less advanced devices that rely on automatic network scanning, disabling SSID broadcasting may not be the most suitable option.
Impact on Wi-Fi Performance
Disabling SSID broadcasting may have an impact on the performance of your Wi-Fi network, although the extent of this impact can vary depending on various factors. While the reduction in network congestion is often cited as a benefit, it may not always lead to noticeable improvements in Wi-Fi performance.
SSID broadcasting is a fundamental feature of Wi-Fi networks that allows devices to automatically detect and connect to available networks. When SSID broadcasting is disabled, devices are no longer able to passively scan and display your network in the list of available networks. Instead, users must manually enter the network name (SSID) to connect to the network.
One potential impact on Wi-Fi performance is the increased complexity of connecting devices. The manual entry of the SSID on each device can introduce a higher probability of user error, leading to failed connection attempts or prolonged setup times. This can be particularly problematic when connecting new devices or having guests connect to your network.
Furthermore, disabling SSID broadcasting may impact the efficiency of devices’ automatic network scanning process. Without the broadcasted SSID, devices no longer receive periodic beacon frames containing network information, making it more time-consuming for them to detect and connect to your network. This can result in slower connection times and a less seamless user experience.
It’s important to note that the impact on Wi-Fi performance may also depend on other factors such as signal strength, channel interference, and the number of connected devices. Disabling SSID broadcasting does not directly address these performance factors, and their optimization remains crucial for optimal network performance.
However, in scenarios where there are multiple Wi-Fi networks in close proximity, disabling SSID broadcasting may have a positive effect on reducing network congestion. By making your network less visible, you can potentially decrease the number of devices actively scanning for available networks, leading to reduced interference and improved performance in these specific situations.
Ultimately, the impact on Wi-Fi performance due to disabling SSID broadcasting can vary depending on the specific network environment and configuration. It’s important to consider the potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as perform thorough testing and monitoring of network performance, to determine if disabling SSID broadcasting is the right choice for your particular situation.
Manual Configuration Requirements
When SSID broadcasting is disabled, manual configuration becomes necessary for devices to connect to the Wi-Fi network. While this practice offers certain benefits, it also introduces additional requirements and considerations that can impact user experience. Here are some key points to consider regarding manual configuration:
Manual Entry of Network Credentials
With SSID broadcasting disabled, users need to manually enter the network name (SSID) and other network credentials, such as the password, on each device they want to connect to the network. This manual entry can be time-consuming, especially when connecting multiple devices or when setting up new devices that are not already configured.
Potential for User Error
Manual configuration increases the likelihood of user error during the network setup process. Users may mistype the SSID or password, resulting in failed connection attempts or authentication errors. This can lead to frustration and additional troubleshooting steps to ensure the correct entry of network credentials.
Complexity for Less Tech-Savvy Users
Disabling SSID broadcasting and relying on manual configuration can be more challenging for less tech-savvy users who may not be familiar with network settings or troubleshooting processes. They may require additional guidance and support during the setup process, which can add complexity to the overall user experience.
Guest Network Configuration
Configuring guest networks can be more challenging when SSID broadcasting is disabled. Guests will need to be provided with the network name (SSID) and security credentials in advance, as they will not be able to discover the network through automatic scanning. Communication and coordination become essential to ensure a smooth and hassle-free guest network setup.
Long-Term Device Connectivity
While the initial manual configuration is required for each device, subsequent connections can be easier as devices can remember the network credentials. Once a device is connected to the network, it can save the network information for future use. However, if the network name or password changes, all devices will need to be reconfigured manually.
As with any manual configuration process, it’s important to provide clear instructions and support to users, especially for those who may be less familiar with network settings and troubleshooting. Documenting the necessary steps and providing ongoing assistance can help simplify the manual configuration process and minimize user frustration.
Considering the additional requirements and potential complexities introduced by manual configuration, it’s important to weigh the benefits of disabling SSID broadcasting against the impact it may have on user convenience and experience. Thoroughly assessing the specific network environment and user requirements will help determine if manual configuration is feasible and suitable for your particular situation.