Understanding Hidden Networks
Hidden networks, also known as stealth networks or invisible networks, are wireless networks that intentionally hide their existence from public view. Unlike regular networks that broadcast their network name or Service Set Identifier (SSID), hidden networks operate by disabling the SSID broadcast feature.
When a device wants to connect to a regular network, it scans for available networks and displays a list of SSIDs. However, in the case of a hidden network, the SSID is not broadcasted, making it invisible to casual users.
Hidden networks can be set up using various devices such as routers or access points, and they require the user to manually enter the network name and password to connect.
So why would someone want to hide their network? One common reason is to add an additional layer of security. By making the network invisible, it reduces the chances of unauthorized users from attempting to connect. It adds an extra level of obscurity that may deter potential hackers.
Another reason for using a hidden network is for organizations or individuals who want to limit access to their network to only trusted individuals. By keeping the network hidden, they have more control over who can connect to it.
However, it’s important to note that although hidden networks provide an extra layer of security, they are not foolproof. Skilled hackers can still discover hidden networks through various techniques, such as sniffing network traffic or using specialized tools.
Setting up a hidden network is relatively simple. You need to access the settings of your router or access point and disable the SSID broadcast feature. After that, you can manually enter the network name and password on devices that you want to connect to the hidden network.
It’s worth mentioning that hiding your network does come with drawbacks. One major drawback is the inconvenience it can cause for legitimate users. Since the SSID is not broadcasted, users need to manually enter the network details every time they want to connect to the hidden network. This can be cumbersome, especially for guests or when connecting multiple devices.
How Hidden Networks Differ from Regular Networks
Hidden networks differ from regular networks in the way they operate and the level of visibility they provide to users. Here are some key differences:
- SSID Broadcast: Regular networks broadcast their network name or SSID, allowing devices to easily identify and join them. In contrast, hidden networks disable the SSID broadcast feature, making them invisible to casual users.
- Manual Network Connection: To connect to a regular network, users can simply select the network from the list of available options and enter the password. However, hidden networks require users to manually enter the network name and password, as they do not appear in the list of available networks.
- Visibility: Regular networks are visible to anyone within range, including potential attackers. Hidden networks, on the other hand, are not visible to casual users, making it less likely for unauthorized individuals to discover and attempt to connect to them.
- Network Discoverability: While regular networks are easily discoverable through scanning, hidden networks require users to know the exact network name and manually enter it to connect. This adds an extra layer of obscurity to the network.
- Security Measures: Hidden networks are often used as an additional security measure to protect against unauthorized access. However, it’s important to note that while hiding the SSID adds an extra layer of security, it should not be the only security measure in place, as skilled hackers can still find hidden networks using specialized tools and techniques.
Despite these differences, hidden networks and regular networks share the same underlying technology and can offer similar features, such as encryption and password protection. The main distinction lies in the level of visibility and accessibility they provide to users.
It’s important to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of hidden networks before deciding to use them. While they can provide an additional layer of security, they also come with drawbacks such as the need for manual network connection and inconvenience for legitimate users.
Reasons for Using a Hidden Network
There are several reasons why individuals and organizations may choose to use a hidden network. Here are the most common motives:
- Enhanced Security: One of the primary reasons for using a hidden network is to add an extra layer of security. By hiding the network’s SSID, the network becomes less visible to potential attackers. This can deter casual hackers from attempting to connect to the network and make it harder for them to identify its existence.
- Controlled Access: Hidden networks are often utilized by organizations or individuals who want to restrict access to their networks only to trusted individuals. By hiding the network, they can maintain better control over who can connect to it and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Privacy: Some users value their privacy and prefer not to have their network visible to everyone. Hiding the network can provide a sense of privacy and minimize the chances of strangers attempting to connect.
- Information Protection: Companies that handle sensitive information may opt for hidden networks to protect their data. By reducing the visibility of the network, they decrease the likelihood of potential breaches and data theft.
- Network Congestion: In areas with high network congestion, using a hidden network can be advantageous. By reducing the visibility of the network, it minimizes the number of devices attempting to connect and can potentially improve network performance and speed.
It’s important, however, to understand that while hidden networks can provide additional security benefits, they are not foolproof. Determined attackers can still discover hidden networks using specialized tools and techniques. Therefore, it’s essential to combine the use of a hidden network with other security measures, such as strong encryption and regularly updating passwords.
Ultimately, the decision to use a hidden network should be based on the specific needs and preferences of the user or organization. It is essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages, evaluate the level of security required, and consider the impact on user convenience before opting for a hidden network.
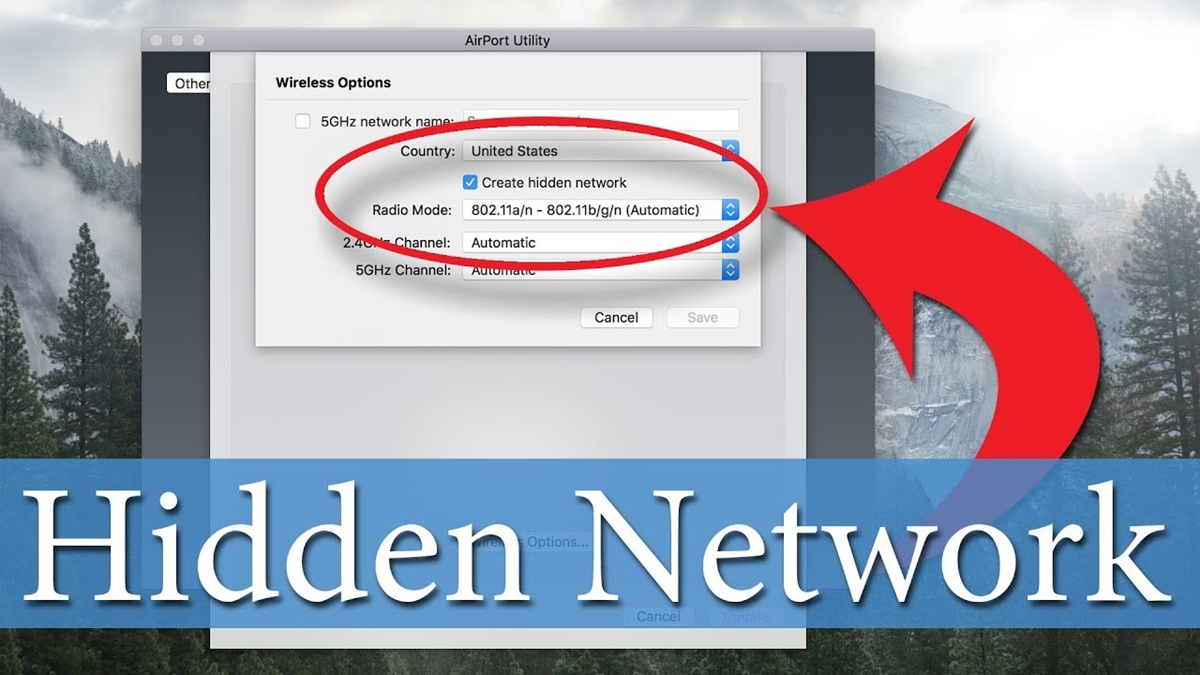
How to Set Up a Hidden Network
Setting up a hidden network is a relatively straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
- Access Router Settings: To configure a hidden network, you need to access the settings of your wireless router. Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address (usually found on the back or bottom of the router) into the address bar. Press Enter to access the router settings page.
- Login to Router: You will be prompted to enter a username and password to log into the router. This information is usually provided with the router documentation. Enter the credentials and click on the log-in button.
- Navigate to Wireless Settings: Once logged in, navigate to the wireless settings section of the router’s admin interface. The location of this setting may vary depending on the router model and firmware.
- Disable SSID Broadcast: Look for the option to disable the SSID broadcast or enable the “hidden network” feature. This setting is often found under the wireless network settings or advanced wireless settings.
- Enter Network Name (SSID): Manually enter the name you want to use for your hidden network in the designated field. Choose a unique name that is not easily guessable but still memorable to you.
- Configure Security Settings: Set up the desired security encryption protocols, such as WPA2-PSK (preferred for its stronger security) or WPA3, and enter a strong password to protect your network. Avoid using common or easily guessable passwords.
- Save and Apply Settings: Once you have configured the necessary settings, click on the “Save” or “Apply” button to save your changes. Your router will then apply the new settings, and your network will become hidden.
It’s important to note that once the network is hidden, devices will no longer automatically detect it in the list of available networks. To connect to the hidden network, users will need to manually enter the network name (SSID) and password on their devices.
Remember to make a note of the network name and password for future reference. Additionally, in case you need to make any changes or troubleshoot network issues, you will need to access the router settings again using the same steps mentioned above.
By following these steps, you can successfully set up a hidden network and add an extra layer of security to your wireless network.
Pros and Cons of Hidden Networks
Hidden networks, also known as stealth networks or invisible networks, have both advantages and disadvantages. It’s important to consider these pros and cons before deciding to implement a hidden network.
Pros of Hidden Networks:
- Enhanced Security: Hiding the network’s SSID adds an extra layer of security by making it less visible to potential attackers. This can deter casual hackers and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Controlled Access: Hidden networks allow organizations or individuals to have more control over who can connect to their network. By keeping the network invisible, they can restrict access to trusted individuals only, reducing the risk of unauthorized users.
- Privacy: Users who value their privacy may opt for a hidden network to minimize the chances of strangers attempting to connect. By making the network invisible, they can maintain a greater level of privacy.
- Reduced Network Congestion: In densely populated areas where regular networks may experience high congestion, using a hidden network can reduce the number of devices attempting to connect. This can potentially improve network performance and speed.
Cons of Hidden Networks:
- Inconvenience: Connecting to a hidden network requires manual entry of the network details (name and password) on each device. This can be cumbersome, especially for guests or when connecting multiple devices to the network.
- Compatibility Issues: Some older or less common devices may have difficulty detecting and connecting to hidden networks, as they rely on the automatic discovery of SSIDs. This can limit device compatibility and cause connectivity issues.
- False Sense of Security: While hiding the SSID adds an extra layer of security, it should not be the only security measure in place. Skilled hackers can still discover hidden networks through specialized tools and techniques. It’s important to combine the use of hidden networks with other security measures like strong encryption and regularly updating passwords.
- Troubleshooting Challenges: Debugging and resolving network issues on hidden networks can be more challenging due to the lack of visibility. It may require accessing the router settings again or manually entering network details on devices for troubleshooting purposes.
Considering the above pros and cons is crucial to make an informed decision about whether to implement a hidden network. It’s important to find the right balance between security and convenience, taking into account the specific needs and preferences of the users or organization.
Common Misconceptions about Hidden Networks
Hidden networks, also known as stealth networks or invisible networks, are often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions associated with hidden networks:
1. Hidden Networks Provide Absolute Security:
One common misconception is that hiding the network’s SSID provides complete security. While it adds an extra layer of obscurity, skilled attackers can still discover hidden networks using specialized tools and techniques. It’s important to combine hidden networks with other security measures to ensure robust protection.
2. Hidden Networks are Difficult to Set Up:
Some believe that setting up a hidden network is complex and time-consuming. In reality, the process is relatively straightforward. Accessing the router settings and disabling the SSID broadcast typically involves a few simple steps.
3. Hidden Networks Prevent All Unauthorized Access:
Another misconception is that a hidden network will prevent all unauthorized access. While it can deter casual hackers, determined attackers can still discover hidden networks and attempt to gain access. Strong encryption, regular password updates, and other security measures are crucial to enhance network security.
4. Hidden Networks are Incompatible with Devices:
Some believe that hidden networks are incompatible with certain devices or operating systems. While older or less common devices may have difficulty detecting hidden networks, most modern devices are capable of connecting to hidden networks without issues.
5. Hidden Networks are the Only Security Measure Needed:
Some users assume that hiding the network’s SSID is sufficient as the sole security measure. It’s important to emphasize that a hidden network should not be relied upon as the sole means of security. Additional measures such as strong encryption, firewall protection, and regular software updates are essential to maintain network security.
6. Hidden Networks always Improve Network Performance:
It is sometimes believed that hidden networks automatically provide better network performance and speed. While they can potentially reduce network congestion in densely populated areas, it’s not a guaranteed solution for network performance issues. Other factors such as bandwidth, interference, and router configurations also contribute to network performance.
Understanding these common misconceptions is important to make informed decisions about utilizing hidden networks. By debunking these misconceptions and implementing appropriate security measures, users can enhance the security and privacy of their networks.
Security Risks and Concerns with Hidden Networks
While hidden networks can provide an additional layer of security, they also come with their own set of risks and concerns. It’s important to understand these potential issues and take appropriate precautions to mitigate them. Here are some security risks and concerns associated with hidden networks:
1. Limited Security through Obscurity:
One of the main security risks with hidden networks is solely relying on the hidden SSID as a security measure. While it adds an extra layer of obscurity, skilled attackers can still discover the network through techniques such as sniffing network traffic or using specialized software tools. Thus, it’s crucial to implement other security measures, such as strong encryption and authentication protocols.
2. Password Security:
Using a hidden network does not exempt users from ensuring strong password security. Weak or easily guessable passwords can still be compromised, granting unauthorized access to the network. It’s essential to use strong, unique passwords and regularly update them to prevent unauthorized entry.
3. Lack of Network Monitoring:
Hidden networks can pose challenges in terms of network monitoring and detection of potential security breaches. With the SSID broadcast disabled, it becomes harder to detect and identify unauthorized access attempts or suspicious network activity. Implementing network monitoring tools and regularly reviewing access logs can help mitigate this concern.
4. Compatibility Issues:
Although most modern devices are compatible with hidden networks, older or less common devices may encounter difficulties in detecting and connecting to these networks. This can create compatibility issues and potentially lead to network vulnerabilities if alternative connection methods are used or outdated security protocols are employed. Therefore, it’s important to ensure device compatibility and consider security measures for all connected devices.
5. Inconvenience and Guest Access:
Hidden networks can be inconvenient for guests or visitors who need temporary access to the network. Since the network name is not visible in the list of available networks, these users will require manual entry of the network name and password. Providing temporary access or offering a separate guest network can help minimize this inconvenience and ensure the security of the main network.
6. Complexity of Network Setup:
Setting up a hidden network requires adjusting specific settings in the router’s admin interface. This process can be intimidating for casual users who are not familiar with network configurations. It’s crucial to follow step-by-step guidelines or seek professional assistance during setup to avoid any misconfigurations that could compromise network security.
By acknowledging and addressing these security risks and concerns, users can maximize the benefits of hidden networks while ensuring the overall security and privacy of their wireless networks.
Tips for Securing a Hidden Network
While hidden networks can provide an additional layer of security, it’s important to implement proper security measures to ensure the network remains protected. Here are some important tips for securing a hidden network:
1. Strong Encryption:
Ensure that your hidden network is encrypted using strong encryption protocols such as WPA2-PSK or WPA3. This helps protect the transmitted data from being intercepted by unauthorized users.
2. Unique and Complex Password:
Choose a strong and unique password for your hidden network. Avoid using dictionary words or easily guessable phrases. Create a password that combines lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters for maximum security.
3. Regularly Update Password:
Regularly update your network password to prevent unauthorized access. It’s recommended to change the password at least every few months or if you suspect a security breach.
4. Use MAC Address Filtering:
Implement MAC address filtering as an additional layer of security. This feature allows you to specify which devices are allowed to connect to the network based on their unique MAC addresses.
5. Disable Remote Management:
Disable remote management access to your router’s settings if it’s not necessary. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing and modifying your network settings from outside your home or organization.
6. Regularly Update Router Firmware:
Keep your router firmware up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Manufacturers often release firmware updates to address security vulnerabilities and improve network security.
7. Enable Network Logging:
Enable network logging on your router to monitor any suspicious activity or attempts to access your hidden network. Regularly review the logs to detect any potential security breaches.
8. Separate Guest Network:
If you need to provide network access to guests or visitors, consider setting up a separate guest network with its own SSID and password. This helps ensure that guests do not have access to your main hidden network.
9. Educate Users:
Educate all users on the importance of network security and proper network usage practices. Remind them to avoid connecting to unknown or untrusted networks and emphasize the need to protect their devices with strong passwords and security software.
10. Regular Security Audits:
Perform regular security audits of your network to identify any vulnerabilities or weaknesses. This can involve conducting penetration testing or hiring a professional to assess the overall security of your hidden network.
By following these tips, you can enhance the security of your hidden network and minimize the risk of unauthorized access or potential security breaches.
Detecting and Joining a Hidden Network
Detecting and joining a hidden network requires some additional steps compared to connecting to a regular network. Here’s a guide on how to detect and join a hidden network:
1. Manual Network Search:
On your device, navigate to the Wi-Fi settings and look for the option to manually search for networks. This option may be named differently depending on the operating system and device.
2. Enter Network Details:
In the manual network search, you’ll need to enter the network name (SSID) of the hidden network. This information is typically provided by the network administrator or can be found in the router settings. Double-check the spelling and case sensitivity of the network name.
3. Select Security Settings:
Choose the security settings that match the hidden network you’re trying to connect to. This is usually WPA2-PSK or WPA3, depending on the network configuration. Enter the corresponding password for the network.
4. Connect to the Hidden Network:
Once you have entered the network details and security settings, select the “Connect” or “Join” button to attempt to connect to the hidden network.
5. Confirmation and Authentication:
In some cases, your device may require additional authentication, such as entering a username or accepting a certificate, depending on the network settings. Follow the prompts and provide the necessary information to complete the connection process.
6. Wait for Successful Connection:
Your device will attempt to connect to the hidden network using the provided details. Wait for a moment to allow the connection process to complete. If successful, you will be connected to the hidden network.
7. Saving Network Details:
After successfully connecting to the hidden network, you may have the option to save the network details on your device for future automatic connection. This saves you from manually entering the network details each time you want to connect.
8. Troubleshooting Connection Issues:
If you encounter any issues connecting to the hidden network, double-check the network name (SSID) and password to ensure they are correct. Additionally, consider checking the network signal strength or contacting the network administrator for assistance.
It’s important to note that the process of detecting and joining a hidden network may vary slightly depending on the device and operating system being used. Refer to the specific device’s documentation or online resources for detailed instructions.
By following these steps, you can successfully detect and join a hidden network on your device and enjoy the added security and privacy it provides.