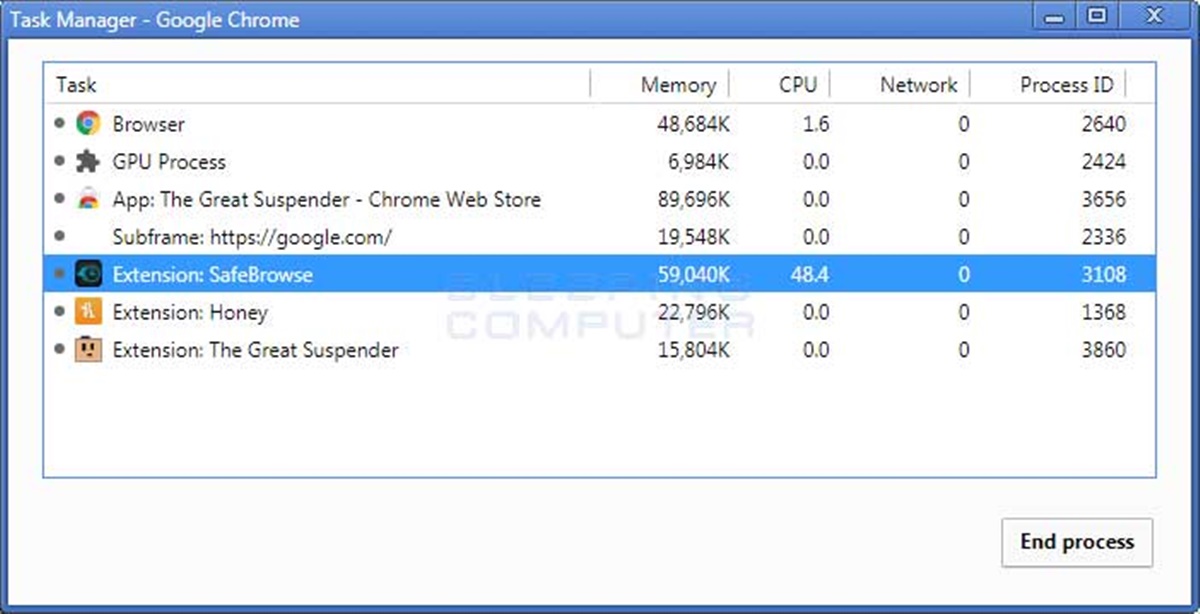
What is the Google Chrome Task Manager?
The Google Chrome Task Manager is a powerful tool that allows users to monitor and manage the various processes, memory usage, CPU usage, network usage, and extensions within the Google Chrome browser. It provides valuable insights into the performance and resource allocation of different tabs, extensions, and plugins in Chrome, helping users optimize their browsing experience and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Think of the Chrome Task Manager as a built-in task manager for your browser. It allows you to see what’s happening behind the scenes and gives you the ability to take control of your browsing environment. Whether you’re experiencing slowdowns, freezing tabs, or excessive memory usage, the Task Manager can provide the information you need to diagnose and resolve these problems.
One of the key benefits of using the Chrome Task Manager is its accessibility. You can easily access it with just a few clicks, making it a convenient and efficient tool for managing the performance of your browser.
The Task Manager shows you a comprehensive list of all the open tabs, extensions, and plugins, along with their corresponding resource usage. By monitoring this information, you can identify any processes that are consuming too much memory or CPU, and take appropriate action to optimize performance.
Additionally, the Task Manager can help you identify and troubleshoot issues that may be caused by specific tabs or extensions. If you notice a particular tab or extension causing excessive resource usage or slowdowns, you have the option to end that process directly from the Task Manager, allowing you to regain control and continue browsing smoothly.
Overall, the Google Chrome Task Manager is a valuable tool that empowers users to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot their browsing experience. Its intuitive interface and accessibility make it an indispensable resource for anyone looking to enhance the performance and efficiency of their Chrome browser.
How to Access the Task Manager in Google Chrome
Accessing the Task Manager in Google Chrome is a straightforward process that can be done in a few simple steps. Here’s how:
- Open Google Chrome: Launch the Google Chrome browser on your computer. Ensure that it is up to date for optimal performance.
- Access the Chrome Menu: Click on the three-dot icon located at the top-right corner of the browser window. This will open a drop-down menu.
- Select the Task Manager Option: From the drop-down menu, hover over the “More tools” option, and another sub-menu will open. Click on “Task Manager” from the available options. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to directly access the Task Manager.
- Navigate the Task Manager: After clicking on the Task Manager option, a new window will open, displaying all the active tabs, extensions, and plugins running in your Google Chrome browser. The Task Manager interface consists of several columns providing information about the process name, memory usage, CPU usage, and network usage.
- Sort and Organize: To better organize the information and identify the processes consuming the most resources, click on the column headers. For example, clicking on the “Memory” header will reorder the list based on memory usage, helping you quickly pinpoint any memory-intensive processes.
- End Processes: To free up system resources or resolve performance issues, you have the option to end a specific process. Select the process you want to close and click on the “End Process” button at the bottom right of the Task Manager window. Ensure that you only terminate processes you are familiar with to prevent unintended consequences.
That’s it! You have successfully accessed the Task Manager in Google Chrome. It’s a handy tool to keep tabs on resource-intensive processes and address any performance issues that may arise during your browsing sessions.
Understanding the Task Manager Interface
The Task Manager interface in Google Chrome provides valuable insights into the performance and resource allocation of the various processes, tabs, extensions, and plugins running in your browser. Understanding the key elements of the Task Manager interface will enable you to make informed decisions and optimize your browsing experience. Here’s a breakdown of the different components:
- Process Name: This column displays the names of the processes, including the active tabs, extensions, and plugins in your Chrome browser. Each process is listed separately, allowing you to identify and monitor them individually.
- Memory: The memory column shows the amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) that each process is utilizing. By keeping an eye on memory usage, you can identify any processes that are consuming a significant amount of memory and troubleshoot accordingly.
- CPU: The CPU column displays the amount of CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources being utilized by each process. This helps identify processes that may be causing high CPU usage and potentially impacting the overall performance of your browser.
- Network: The network column indicates the network bandwidth being used by each process. It provides insights into processes that may be heavily reliant on data transfer, such as streaming videos or downloading files. Monitoring network usage can help identify processes that are consuming excessive bandwidth.
- Process ID: The process ID column displays the unique identifier assigned to each process. This can be useful when referring to a specific process for troubleshooting purposes.
By closely monitoring the Task Manager interface, you can identify any processes that are consuming excessive resources, causing performance issues, or even potential security risks. It allows you to have a granular view of the different components within Chrome, empowering you to make informed decisions to optimize your browsing experience.
Monitoring and Killing Processes in the Task Manager
The Task Manager in Google Chrome not only allows you to monitor the various processes running in your browser but also gives you the ability to terminate or “kill” specific processes. This can be particularly useful when dealing with unresponsive tabs or addressing performance issues. Here’s how you can monitor and kill processes using the Task Manager:
- Open the Task Manager: Access the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Monitor Process Performance: In the Task Manager window, you will see a list of active processes, including tabs, extensions, and plugins. Keep an eye on the columns displaying memory usage, CPU usage, and network usage to identify any resource-intensive processes or those causing performance issues.
- Identify Unresponsive Tabs: If you notice a tab that is unresponsive or causing your browser to freeze, look for the corresponding process in the Task Manager. The “Memory” and “CPU” columns can help you identify the tab that is consuming excessive resources.
- Kill a Process: To terminate a specific process, select it from the Task Manager list and click on the “End Process” button at the bottom-right corner of the window. A confirmation dialog will appear, asking you to confirm the action. Click “End Process” to terminate the selected process. Be aware that ending a process may close the associated tab or halt the extension or plugin.
- Close Unresponsive Tabs: If a tab is unresponsive, you can choose to close it directly from the Task Manager. Select the unresponsive tab’s process in the Task Manager and click on the “End Process” button. This will close the unresponsive tab and free up system resources.
- Restart Chrome if Necessary: In some cases, terminating a process may not resolve the issue. If you continue to experience performance problems, consider restarting the Chrome browser. This can help refresh the browser environment and resolve any lingering issues.
Regularly monitoring and managing processes in the Task Manager can help optimize your browsing experience, improve performance, and address any issues that may arise while using Google Chrome.
Identifying and Managing Memory and CPU Usage
Memory and CPU resources play a crucial role in the performance of your browser. The Task Manager in Google Chrome provides valuable insights into the memory and CPU usage of different processes, helping you identify and manage resource-intensive tasks. Here’s how you can effectively monitor and optimize memory and CPU usage:
- Open the Task Manager: Access the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Monitor Memory Usage: In the Task Manager, look at the “Memory” column to identify processes that are utilizing a significant amount of memory. Higher memory usage can lead to sluggish performance. Sort the processes by memory usage to prioritize resource-heavy tasks.
- Identify CPU Intensive Processes: Review the “CPU” column to identify processes that are consuming excessive CPU resources. These processes can cause your browser to slow down or become unresponsive. Sorting the processes by CPU usage will help you identify the most resource-intensive tasks.
- Mitigate High Memory and CPU Usage: Once you have identified memory or CPU-intensive processes, you can take several steps to manage and optimize their usage:
- Close Unnecessary Tabs: If you have multiple tabs open, close the ones you’re not using to reduce memory usage.
- Disable/Remove Extensions: Extensions can consume significant resources. Consider disabling or removing unnecessary or resource-intensive extensions to free up memory and CPU.
- Update Chrome and Extensions: Keeping Chrome and extensions up to date ensures optimal performance and can address memory and CPU usage issues caused by outdated software.
- Manage Background Processes: Some extensions or plugins may continue running in the background even when you’re not actively using them. Check the Task Manager to see if any background processes are consuming resources and consider disabling or removing them if they are not essential.
- Reduce Content and Plugin Usage: Content-heavy websites, such as media-rich pages or pages with excessive animations, can strain both memory and CPU. Limiting your usage of such content or enabling “click to play” for plugins like Flash can reduce resource usage.
By monitoring and managing memory and CPU usage effectively, you can optimize the performance of your browser, prevent slowdowns, and ensure a smoother browsing experience.
Analyzing Network Usage and Resources
The Task Manager in Google Chrome provides a valuable feature that allows you to analyze network usage and resources. By monitoring the network column in the Task Manager, you can gain insights into the bandwidth consumption of different processes, helping you optimize your browsing experience. Here’s how you can effectively analyze network usage:
- Open the Task Manager: Access the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Monitor Network Usage: In the Task Manager, observe the “Network” column to identify processes that are utilizing significant network bandwidth. Higher network usage can lead to slower page loads and affects the overall browsing experience.
- Identify Resource-Intensive Processes: Look for processes that consistently show high network usage. These could be streaming services, file downloads, or other activities that require substantial bandwidth.
- Optimize Network Usage: Once you have identified resource-intensive processes, you can take steps to optimize network usage:
- Pause or Limit Downloads: If you are downloading large files or streaming content, consider pausing or limiting these activities to reduce network usage and improve the performance of other tasks.
- Manage Background Processes: Some processes running in the background may be utilizing network resources unnecessarily. Use the Task Manager to identify such processes and disable or remove them if they are not essential.
- Check for Unwanted Browser Extensions: Some extensions may be consuming network bandwidth without your knowledge. Review your installed extensions and remove any that are unnecessary or resource-intensive.
- Minimize Interactive Elements: Websites with excessive animations, auto-playing videos, or content-refreshing scripts can consume significant network resources. Consider disabling or limiting such elements to reduce network usage.
- Utilize Data-Saving Features: Some browsers and extensions offer data-saving features that can compress the amount of data transferred over the network. Explore these options to reduce network usage without compromising on functionality.
By effectively analyzing network usage and managing resource-intensive processes, you can optimize the network performance of your Google Chrome browser and enjoy a faster and more efficient browsing experience.
Using the Task Manager to Identify and Troubleshoot Tab or Extension Issues
The Task Manager in Google Chrome is a powerful tool that can be instrumental in identifying and troubleshooting issues related to tabs or extensions. By closely monitoring the Task Manager and utilizing its features, you can gain valuable insights into problematic processes and take appropriate action. Here’s how you can effectively use the Task Manager for troubleshooting:
- Open the Task Manager: Access the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Identify Problematic Tabs: Look for tabs that exhibit high CPU or memory usage. These tabs may be causing your browser to slow down or become unresponsive. Sort the processes in the Task Manager by CPU or memory usage to identify the problematic tabs.
- End Problematic Tabs: Once you have identified the problematic tab, select its corresponding process in the Task Manager and click on the “End Process” button. This will close the problematic tab and free up system resources.
- Disable Problematic Extensions: If a specific extension is causing issues, you can identify it in the Task Manager. Select the process related to the extension and click on the “End Process” button to disable it temporarily. This will allow you to determine if the extension is the root cause of the problem.
- Monitor System Performance: After closing problematic tabs or disabling extensions, monitor the Task Manager to ensure that CPU and memory usage have decreased. This will help you determine if the troubleshooting steps were successful in alleviating the issue.
- Re-enable and Update Extensions: If you have identified a specific extension causing issues, consider updating it to the latest version. If the issue persists, you may need to remove the extension entirely and find an alternative or updated version.
- Test in Incognito Mode: If you are still experiencing issues, try browsing in Incognito mode, which disables all extensions by default. If the problem does not occur in Incognito mode, it is likely that one of your installed extensions is causing the issue.
- Reset Chrome Settings: If the above steps do not resolve the problem, you may need to reset your Chrome settings to their default state. This can help eliminate any conflicting settings that may be causing the issue.
By utilizing the Task Manager to identify and troubleshoot tab or extension issues, you can quickly pinpoint problematic processes, improve browser performance, and enjoy a smoother browsing experience.
Managing Chrome Extensions and Plugins in the Task Manager
The Task Manager in Google Chrome not only provides insights into the performance of your browser’s tabs but also allows you to manage your installed extensions and plugins. By leveraging the Task Manager’s functionality, you can easily identify and take action on extensions and plugins that may be causing issues or consuming excessive resources. Here’s how you can manage your Chrome extensions and plugins using the Task Manager:
- Open the Task Manager: Launch the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Identify Extensions and Plugins: In the Task Manager window, you will see a list of running processes, including tabs, extensions, and plugins. Look for processes related to your installed extensions and plugins.
- Assess Resource Usage: Review the columns displaying memory usage, CPU usage, and network usage to assess the impact of each extension or plugin on your browser’s performance. Higher resource usage may indicate that certain extensions or plugins are consuming excessive resources.
- Take Action: If you identify an extension or plugin that is causing issues or consuming excessive resources, you have a few options to manage them:
- End Process: Select the process associated with the extension or plugin in the Task Manager and click on the “End Process” button. This will stop the extension or plugin, freeing up system resources.
- Disable or Remove: If you frequently encounter problems with a specific extension or plugin, consider disabling or removing it. To disable an extension, go to the Extensions page in Chrome’s settings and uncheck the “Enabled” box. To remove an extension, click on the three-dot icon on the extension’s tile and select “Remove from Chrome.”
- Update Extensions: Outdated extensions can sometimes cause compatibility issues or performance problems. To update an extension, go to the Extensions page in Chrome’s settings and click on the “Update” button next to the extension.
- Manage Extension Permissions: Some extensions may have access to personal information or certain features of your browser. If you are concerned about privacy or prefer to limit an extension’s access, you can review and modify its permissions in Chrome’s settings.
By effectively managing your Chrome extensions and plugins using the Task Manager, you can optimize your browser’s performance, resolve issues caused by problematic extensions or plugins, and create a browsing experience tailored to your needs.
Adjusting Task Manager Preferences and Settings
The Task Manager in Google Chrome offers flexibility and customization options that allow you to adjust its preferences and settings according to your needs. By exploring these settings, you can optimize the Task Manager’s functionality and tailor it to your preferences. Here’s how you can adjust the Task Manager preferences and settings:
- Open the Task Manager: Launch the Task Manager by clicking on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the Chrome browser window, selecting “More tools,” and then clicking on “Task Manager.” Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut “Shift + Esc” to open it directly.
- Resizing the Task Manager Window: Once the Task Manager is open, you can resize the window by clicking on the bottom-right corner and dragging it to the desired dimensions. This allows you to view more processes at once or expand the window for better visibility.
- Sorting and Organizing Columns: By clicking on any of the column headers, such as “Process,” “Memory,” “CPU,” or “Network,” you can sort the processes based on that column’s values. This helps you prioritize resource-intensive tasks and easily identify the processes that require attention.
- Fine-Tuning Displayed Columns: Right-click on any column header to customize the visible columns in the Task Manager. You can choose to show or hide columns such as “Process ID” or “GPU Memory,” based on your monitoring requirements.
- Refreshing Task Manager Data: If you want real-time updates on process performance, click on the refresh button (circular arrow) at the top-left corner of the Task Manager window. This will update the displayed data, allowing you to monitor the latest information.
- Viewing Task Manager in Expanded View: By clicking on the upward-facing arrow icon at the bottom-right corner of the Task Manager window, you can switch to the expanded view. This provides more details about each process, such as memory allocation breakdown and JavaScript memory usage.
- Understanding Task Manager Multiselect: Hold down the “Shift” or “Ctrl” key on your keyboard while selecting multiple processes to enable multiselect mode in the Task Manager. This allows you to end or perform actions on multiple processes simultaneously.
By adjusting the preferences and settings of the Task Manager, you can enhance its functionality, customize the displayed information, and make the most out of its features for efficient monitoring and management of processes in Google Chrome.
Best Practices for Using the Google Chrome Task Manager
The Google Chrome Task Manager is a powerful tool that can help you monitor, manage, and troubleshoot processes within your browser. By following some best practices, you can make the most out of the Task Manager and optimize your browsing experience. Here are some best practices for using the Google Chrome Task Manager:
- Regularly Monitor Performance: Make it a habit to check the Task Manager regularly to monitor the performance of your browser. By keeping an eye on resource usage, you can identify any processes that might be causing slowdowns or consuming excessive memory or CPU.
- Identify Problematic Processes: Look for processes that consistently show high resource usage or cause browser instability. These could indicate problematic tabs, extensions, or plugins. Identifying and addressing these issues will help improve your overall browsing experience.
- End Unresponsive Tabs or Processes: If you encounter an unresponsive tab or a process causing issues, use the Task Manager to end the process associated with it. This will help free up system resources and restore your browser’s functionality.
- Disable or Remove Unnecessary Extensions: Extensions can consume memory and CPU resources. Disable or remove any extensions that you no longer use or those that are causing performance issues.
- Keep Chrome and Extensions Updated: Regularly update your Chrome browser and extensions to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with the latest features and security patches. Outdated software can often lead to performance problems or conflicts with other processes.
- Manage Background Processes: Some extensions or tabs continue to run in the background even when not in use, consuming resources. Use the Task Manager to identify and manage such background processes, disabling or removing them if necessary.
- Monitor Network Resources: Keep an eye on the network usage of different processes. Excessive network consumption can impact browsing speed and overall performance. Take action, such as limiting downloads or disabling unnecessary content, to optimize network resources.
- Take Note of Unusual Behavior: If you observe any processes or activities that seem suspicious or unfamiliar, investigate further. It could be a sign of malware or unwanted extensions. Use the Task Manager to identify and address such issues promptly.
- Be Selective with Extensions: Install extensions from reliable sources and be cautious about granting excessive permissions. Too many extensions can impact browser performance and increase the risk of conflicts or security vulnerabilities.
- Restart Chrome as Needed: If you experience persistent issues or notice a significant decrease in performance, try restarting your Chrome browser. This can help refresh the browser environment and resolve any temporary issues.
By following these best practices, you can effectively utilize the Google Chrome Task Manager to optimize your browser’s performance, enhance security, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise during your browsing sessions.