Why is Understanding the Date and Time in Email Headers Important?
The date and time information in email headers play a crucial role in various aspects of email communication. Whether you are a business professional, an email marketer, or an everyday user, understanding the timestamps in email headers is essential. Here are a few reasons why it is important to grasp this information:
- Email Tracking and Analytics: By analyzing the timestamps in email headers, you can gain valuable insights into your email campaigns’ performance. You can see when your emails were opened, how quickly recipients responded, and the overall engagement levels. This information helps you optimize your email strategies and improve your communication with clients and customers.
- Organizing and Prioritizing: When you receive a flood of emails every day, being able to determine the time and date when an email was sent can help you organize your inbox effectively. By knowing the order in which emails were received, you can prioritize your responses and manage your time more efficiently.
- Dealing with Time-Sensitive Matters: In certain professions, such as legal or financial services, timely response to emails is crucial. Understanding the date and time in email headers allows you to assess the urgency of an email and respond promptly. This is especially important when dealing with deadlines, time-sensitive requests, and urgent matters that require immediate attention.
- Collaboration and Communication: When working in a global or remote team, understanding time zones is essential to ensure effective collaboration. Email headers provide information about the time the email was sent, which helps synchronize communication across different time zones. It allows team members to know when a message was sent and plan their responses accordingly.
In summary, understanding the date and time information in email headers is crucial for email tracking, efficient organization of your inbox, prioritizing responses, responding to time-sensitive matters, and facilitating collaboration in a global or remote work environment. By paying attention to these timestamps, you can improve your email communication and ensure timely and effective responses.
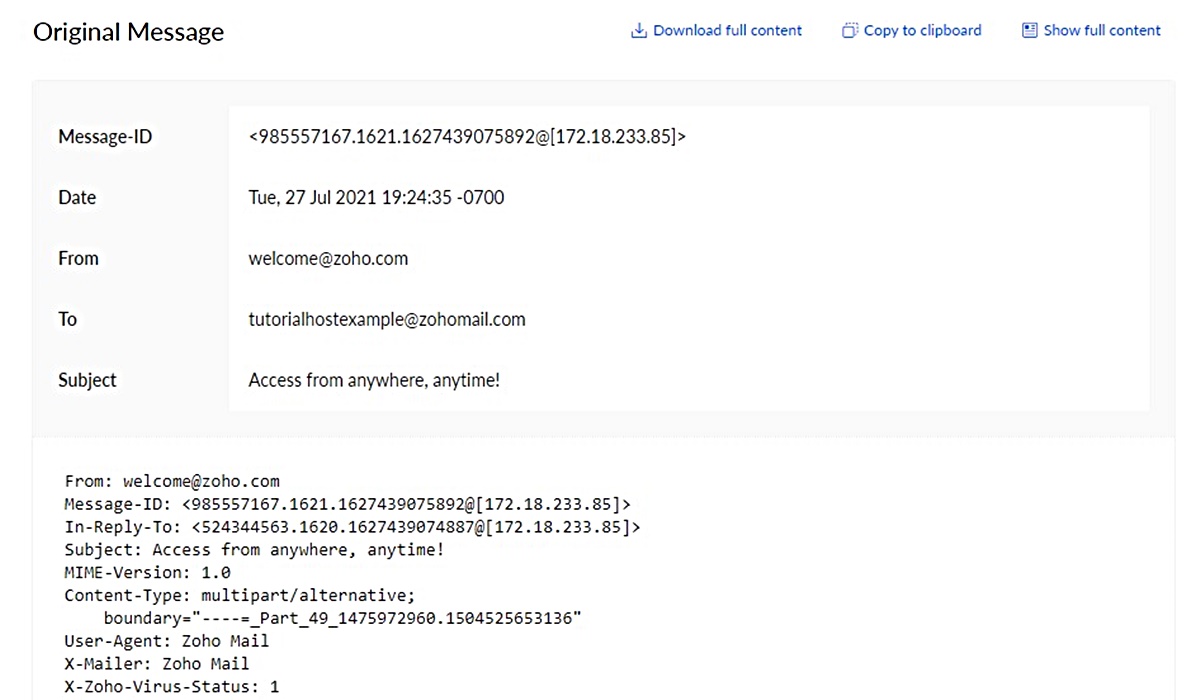
Anatomy of an Email Header
Email headers contain valuable information about the origin, path, and content of an email. They are like the “envelope” of an email, containing details about the sender, recipient, subject, and other important metadata. Understanding the different components of an email header can help you gain insights into the journey of an email and its authenticity. Here are the key elements of an email header:
- From: This field displays the email address of the sender. It indicates who initiated the email communication.
- To: This field shows the email address of the recipient or recipients. It indicates who the email is intended for.
- Date: The date field indicates the date and time when the email was sent. It provides a chronological reference for the email communication.
- Subject: The subject field displays the brief summary of the email’s content. It gives recipients a glimpse into the purpose or topic of the email.
- Reply-To: The reply-to field specifies the email address to which replies should be sent. It may differ from the from field, allowing for more precise email routing.
- Cc (Carbon Copy) and Bcc (Blind Carbon Copy): These fields allow the sender to include additional recipients in the email. Cc recipients are visible to all other recipients, while Bcc recipients are hidden from other recipients.
- Message-ID: The message-ID field is a unique identifier assigned to each email. It helps track and refer to specific emails in threads or conversations.
- Received: The received field lists the servers through which the email passed during its delivery. It displays the IP address, date, and time of each server, helping trace the email’s route.
Understanding the different components of an email header enables you to assess the legitimacy of an email, identify any potential email spoofing or phishing attempts, and verify the source of the email. It also helps maintain transparency in email communication and assists email clients in delivering messages accurately to the intended recipients.
Date and Time Formats in Email Headers
Email headers contain timestamps that indicate the date and time when an email was sent, received, or accessed. These timestamps follow specific formats which may vary depending on the email client or server settings. Understanding the various date and time formats used in email headers is crucial for correctly interpreting and comparing timestamps. Here are some common formats you may encounter:
- DD/MM/YYYY – HH:MM:SS: This format displays the date in day/month/year format, followed by the time in hours:minutes:seconds. For example, 15/03/2022 – 09:30:45 represents March 15, 2022, at 9:30:45 AM.
- MM/DD/YYYY – HH:MM AM/PM: This format presents the date in month/day/year format, followed by the time in hours:minutes followed by either “AM” or “PM”. For example, 03/15/2022 – 09:30 AM represents March 15, 2022, at 9:30 AM.
- YYYY-MM-DD – HH:MM:SS: This format shows the date in year-month-day format, followed by the time in hours:minutes:seconds. For example, 2022-03-15 – 09:30:45 represents March 15, 2022, at 9:30:45 AM.
- Epoch Timestamp: An epoch timestamp represents the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970. It is a universal format used to standardize time representation across different systems and platforms. Epoch timestamps are often used in technical contexts and can be converted into human-readable formats using various online tools.
It is important to note that the display of date and time formats in email headers can vary based on the sender’s and recipient’s email clients or preferences. While many email clients automatically adjust the displayed time to the recipient’s local time zone, some may display timestamps in the sender’s time zone. It is crucial to take time zones into account to accurately interpret the timing of an email.
When analyzing email headers, it is also important to consider the possibility of discrepancies caused by factors such as delays in email delivery, server time variations, and differences in time zone settings. Taking these factors into account will help ensure more accurate interpretations of the timestamp information in email headers.
Common Time Zones in Email Headers
Email headers often indicate the time zone in which an email was sent, received, or accessed. Understanding common time zones mentioned in email headers is essential for accurately interpreting the timing of email communication. Here are some of the commonly encountered time zones in email headers:
- UTC (Coordinated Universal Time): UTC is a time standard used as a reference for coordinating time across different regions. It is often indicated as “+00:00” or “Z” in email headers. Email servers and some email clients use UTC as a standard for timestamp accuracy and to avoid confusion caused by different time zones.
- GMT (Greenwich Mean Time): GMT is a time zone primarily used in the United Kingdom. It is similar to UTC and is often used interchangeably. In email headers, it may be denoted as “+00:00” or “GMT”.
- EST (Eastern Standard Time): EST is the time zone observed in parts of North America. It is typically indicated as “-05:00” in email headers. When daylight saving time is in effect, it may switch to EDT (Eastern Daylight Time), which is indicated as “-04:00”.
- PST (Pacific Standard Time): PST is the time zone followed in the western part of North America, primarily along the Pacific Coast. It is typically represented as “-08:00” in email headers. During daylight saving time, it may switch to PDT (Pacific Daylight Time), indicated as “-07:00”.
- CET (Central European Time): CET is the time zone observed in central European countries. It is often indicated as “+01:00” in email headers.
- AEDT (Australian Eastern Daylight Time): AEDT is the time zone followed in eastern Australia during daylight saving time. It is typically represented as “+11:00” in email headers.
It is important to keep in mind that email headers may present time zones in different formats or use abbreviations specific to certain regions. Additionally, when communicating with individuals located in regions with different time zones, it’s crucial to understand the time difference and adjust your responses accordingly. Various online tools and converters are available to help you calculate and compare time zones accurately.
By familiarizing yourself with common time zones mentioned in email headers, you can better understand the timing of email communication and ensure effective collaboration across different regions and time zones.
Understanding Timestamps and Time Stamps in Email Headers
Timestamps and time stamps in email headers provide valuable information about the specific points in time when an email was sent, received, or accessed. They play a crucial role in analyzing the timeline of email communication and determining the sequence of events. Here’s what you need to know about understanding timestamps and time stamps in email headers:
Timestamps: Timestamps indicate the exact date and time when an email was sent or received. They provide a chronological reference that helps track the flow of email communication. Timestamps are typically displayed in various formats, such as “DD/MM/YYYY – HH:MM:SS” or “MM/DD/YYYY – HH:MM AM/PM”, depending on the email client’s settings. It is important to consider time zones when interpreting timestamps, as they may differ between the sender and recipient.
Time Stamps: Time stamps, on the other hand, refer to specific points in time within an email thread. They appear within the body of an email and indicate when a particular message or response was sent or received. Time stamps are helpful for distinguishing between the multiple interactions that may occur within an email conversation. They are typically displayed in a consistent format, such as “HH:MM:SS” or “HH:MM AM/PM”, regardless of the time zone or email client.
Understanding timestamps and time stamps in email headers helps in various scenarios. For example, when investigating the timeline of an email exchange, you can rely on timestamps to determine the order of messages and responses. Timestamps also aid in assessing the speed of email delivery or response times, which can be crucial in time-sensitive situations.
Furthermore, interpreting time stamps within the email body allows for easier tracking of specific interactions within a conversation. This is particularly useful when dealing with lengthy email threads or when referring back to previous messages during a communication exchange.
While timestamps and time stamps provide valuable information, it’s important to note that they may not always be 100% accurate. Factors like email delays, synchronization issues, and server clock discrepancies can lead to minor deviations in the displayed timestamps. However, these discrepancies are typically minimal and do not significantly affect the overall understanding of the email timeline.
By accounting for timestamps and time stamps in email headers, you can better analyze and comprehend the sequence of events in email communication. This understanding ensures smoother collaboration and communication, especially when dealing with time-sensitive matters or complex email exchanges.
Dealing with Different Time Zones in Email Headers
Email communication often involves individuals in different time zones, making it essential to consider and manage these differences when interpreting email headers. Here are some strategies for effectively dealing with different time zones in email headers:
1. Understand Time Zone Differences: Familiarize yourself with the time zones of the individuals or regions you frequently communicate with. This knowledge will help you interpret timestamps accurately and avoid confusion when scheduling meetings or responding to time-sensitive requests.
2. Adjust Your Communication: When corresponding with individuals in different time zones, be mindful of the local time of your recipients. Use phrases like “your local time” or “in your time zone” to indicate specific times or deadlines. This helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures precise communication.
3. Use Universal Time References: When discussing time-sensitive matters or scheduling events with individuals across multiple time zones, consider using Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) as a reference. UTC is a standardized time that can serve as a common frame of reference, especially when coordinating activities across different regions.
4. Include Time Zone Information: When sending emails that require time-sensitive responses or involve individuals in different time zones, consider explicitly mentioning the time zone in your communication. This helps recipients understand the context and prevents confusion regarding deadlines or meeting times.
5. Utilize Time Zone Conversion Tools: Various online tools and applications can help you convert between different time zones accurately. Utilize these tools to plan meetings, determine suitable communication timings, and avoid errors caused by manual calculations.
6. Be Flexible and Accommodating: Recognize the challenges posed by different time zones and be willing to accommodate the scheduling needs of individuals in other regions. This may involve adjusting your own availability or finding mutually convenient meeting times, thereby facilitating smoother collaboration across time zones.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively navigate the complexities of different time zones in email communication. This will enable clearer understanding, better coordination, and improved collaboration with individuals across the globe.
Tips for Reading and Analyzing Email Headers
Email headers contain vital information that can provide insights into the origin, path, and authenticity of an email. Properly reading and analyzing email headers can help you make informed decisions, identify potential issues, and ensure secure communication. Here are some tips to enhance your ability to interpret and analyze email headers effectively:
- Review the Entire Header: When analyzing an email header, make sure to examine the complete header, including all the header fields. Some important information may be hidden in the lower sections of the header, so scroll through the entire header to gather a comprehensive view.
- Focus on the “Received” Fields: The “Received” fields in the header provide a trace of the email’s journey. Analyzing these fields can help identify the servers through which the email passed, determine the route it took, and identify any potential delays or issues.
- Look for Authentication Information: Check for email authentication records, such as SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). These records help verify the authenticity of the email and ensure it hasn’t been tampered with or forged.
- Validate IP Addresses: IP addresses listed in the header can provide insights into the sender’s location, the email client used, and any intermediary servers involved in forwarding the email. Utilize IP address lookup tools to verify the legitimacy and reputation of the IP addresses involved.
- Consider Time Stamps: Pay attention to the timestamps in the header to understand when the email was sent, received, or accessed. Account for time zone differences to accurately interpret the timing of events and align them with your own records or responses.
- Check for Anomalies: Look for any unusual or suspicious elements in the header, such as unexpected servers, abrupt changes in sender IP addresses, or inconsistencies in the email’s domain. These anomalies may indicate potential phishing attempts, spoofing, or email manipulation.
- Compare Headers for Replies and Forwards: When analyzing email threads or conversations, compare the headers of replies and forwards to understand the flow of the conversation and identify any modifications or additions made to the email content.
- Seek Expert Assistance: If you encounter complex or unfamiliar components in email headers or require assistance in analyzing them, consult IT professionals or experts well-versed in email security and header analysis. They can provide valuable insights and guidance.
By following these tips, you can enhance your ability to read and analyze email headers effectively. This enables you to understand the email’s origin, detect any potential security issues, and ensure the legitimacy of the communication you receive.