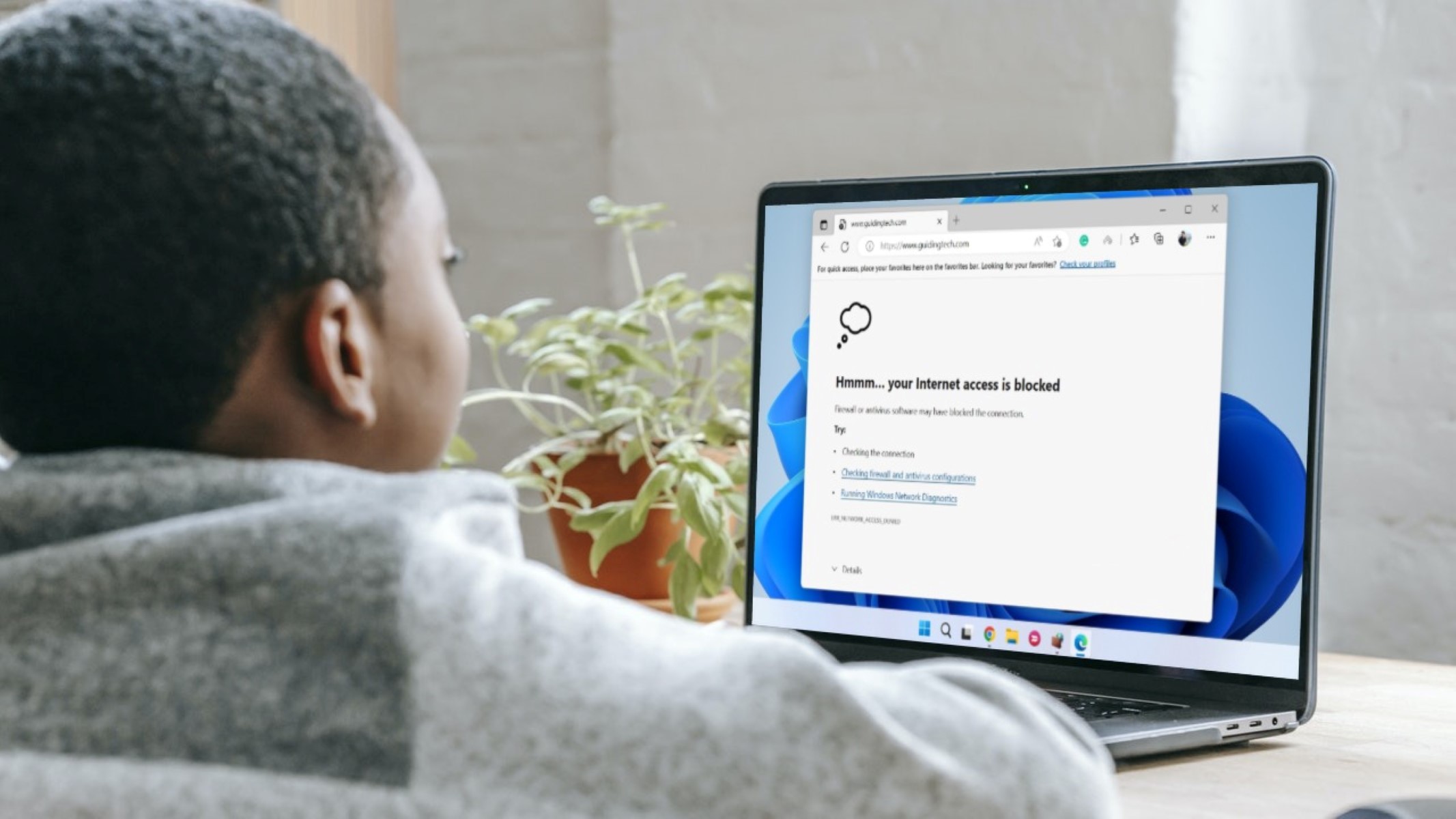
Symptoms of a Blocked Firewall
A firewall is a crucial security measure that acts as a barrier between your computer network and the vast expanse of the internet. It helps protect your system from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. However, there may be instances when your firewall mistakenly blocks legitimate traffic, causing connectivity issues. Recognizing the signs of a blocked firewall can help you identify and resolve these issues effectively.
Here are some symptoms that indicate your firewall could be blocking something:
- Connection Timeout: If you find that certain websites or online services are taking an unusually long time to load, it could be an indicator that your firewall is blocking the necessary connections.
- Unresponsive Applications: When you attempt to use specific applications or services, and they appear to freeze or become unresponsive, it is worth checking if your firewall is interfering with their functionality.
- Errors and Warning Messages: Pay attention to any error messages or warning pop-ups that you encounter while trying to access certain websites or services. These messages can provide valuable information about blocked connections.
- Partial Access: Sometimes, you might find that you can access certain features or sections of a website or service, but not others. This partial access indicates that certain connections are being blocked by your firewall.
- Failed Downloads: If you frequently experience failed downloads or interrupted file transfers, it could be a sign that your firewall is blocking the necessary connections for successful data transfer.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to investigate whether your firewall is the culprit. While these signs do not necessarily confirm a blocked firewall, they provide a starting point for further investigation. In the following sections, we will explore various methods to determine if your firewall is blocking something and how to troubleshoot and resolve these issues.
Checking Firewall Logs
Firewall logs are an invaluable resource for determining if your firewall is blocking specific connections or traffic. They provide a detailed record of the activities and events that your firewall has encountered. By analyzing these logs, you can gain insights into any potential blocks and take appropriate actions.
Follow these steps to check your firewall logs:
- Access Firewall Settings: Open your firewall management interface or software. This can typically be done by accessing your network settings or system preferences.
- Locate Log Files: Look for a section or tab labeled “Logs” or “Logging” within your firewall settings. In this section, you should be able to find the log files containing relevant information.
- Analyze the Logs: Open the log file(s) and carefully examine the entries. Look for any entries that indicate blocked connections or denied traffic. These entries will typically include the source and destination IP addresses, ports, and the reason for the block.
- Filter and Sort: Depending on your firewall software, you may have options to filter and sort the logs to narrow down your search. You can filter by time, IP address, or specific events to find the relevant entries more efficiently.
- Investigate Blocked Entries: Focus on the blocked entries in the log file to identify patterns or recurring blocks. Take note of the IP addresses, ports, and protocols involved in the blocked connections.
By reviewing the firewall logs, you can determine if certain connections are being blocked and gain insights into the potential causes. This information will be valuable when you proceed to troubleshoot and resolve firewall-related issues.
Using Network Troubleshooting Tools
When you suspect that your firewall might be blocking something, network troubleshooting tools can be immensely helpful in identifying and diagnosing the issue. These tools provide in-depth analysis of network connections, helping you pinpoint any blocks caused by the firewall. Here are some commonly used network troubleshooting tools:
- Ping: The ping command is a simple yet powerful tool used to test the connectivity between two devices. By sending ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets to the target device, you can determine if the device is reachable and measure the round-trip time. If you receive a “Request Timeout” or “Destination Host Unreachable” response, it could indicate that your firewall is blocking the connection.
- Traceroute: Traceroute helps you trace the path that packets take from your device to a target destination. It shows the IP addresses of each network hop along the way, allowing you to identify potential bottlenecks or blocks. If you notice a sudden halt or excessive delays at a particular hop, it could indicate a firewall block.
- Port Scanner: Port scanners are used to identify open ports on a target device. If your firewall is blocking a specific port, a port scanner can help you determine its status. By scanning the target device’s ports, you can identify which ports are accessible and which ones are blocked.
- Packet Sniffer: Packet sniffers capture and analyze network traffic on a particular interface. They allow you to examine the content of packets, including the source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports. By monitoring the traffic, you can identify any blocks or anomalies caused by the firewall.
These tools, among others, can provide valuable insights into the behavior of your network connections and help identify if your firewall is blocking something. By leveraging network troubleshooting tools, you can gather the necessary information to further investigate and resolve firewall-related issues.
Checking Network Activity and Port Scans
Another effective way to determine if your firewall is blocking something is to monitor the network activity and perform port scans. By examining the traffic and analyzing the availability of specific ports, you can identify any potential blocks imposed by the firewall. Here’s how you can check network activity and perform port scans:
- Network Monitoring Tools: Utilize network monitoring tools to observe the incoming and outgoing traffic on your network. These tools provide real-time insights into the connections being established and can help identify any patterns or blocks.
- Firewall Logs: As mentioned earlier, reviewing firewall logs can provide valuable information about blocked connections. Look for entries related to specific IP addresses or ports that indicate potential blocks by the firewall.
- Port Scanning Tools: Perform port scans using specialized tools to identify open and closed ports on your network. This can help ascertain if specific ports are being blocked by the firewall. Note that port scanning should only be performed on networks that you have explicit permission to test.
- Firewall Configuration: Examine the firewall configuration to ensure that the necessary ports are open and accessible. Compare the configured rules with the required ports for the services you want to access. If any ports are being blocked in the firewall configuration, adjust the rules accordingly.
- Test Remote Connections: If you suspect that a remote service or server is being blocked by your firewall, attempt to establish a connection from a different network or device. By testing connections from external networks, you can determine if the issue lies with your firewall blocking the connection.
By checking network activity and performing port scans, you can gather valuable information to determine if your firewall is blocking something. Keep in mind that making changes to your firewall configuration should be done with caution and in accordance with security best practices.
Analyzing Blocked Connections and Traffic
When your firewall blocks connections, it is crucial to analyze the blocked connections and traffic to identify the root cause and take appropriate action. By examining the blocked connections, you can gain insights into the patterns, IP addresses, and protocols involved in the blocks. Here’s how you can analyze blocked connections and traffic:
- Firewall Logs: Review the firewall logs to identify entries related to blocked connections. Look for information such as source IP addresses, destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols involved in the blocked connections. This data can help you understand the specific connections being blocked and the reasons behind the blocks.
- Traffic Analysis Tools: Utilize traffic analysis tools to gain a deeper understanding of the blocked connections and network traffic. These tools can provide comprehensive insights into the traffic patterns, protocols, and anomalies. By analyzing the blocked connections alongside the overall network traffic, you can identify any potential trends or recurring blocks.
- IP Reputation Services: Use IP reputation services to determine if any of the blocked connections are originating from IP addresses with a reputation for malicious activity. These services can help you assess the level of threat posed by the connections and determine if the blocks are justified.
- Packet Analysis: If necessary, perform packet analysis to examine the content of the blocked packets. This can help identify any suspicious or unauthorized activity that might be triggering the blocks. Packet analysis tools allow you to inspect the packet headers, payload, and associated metadata.
- Correlate with Security Events: Compare the blocked connections with any security events or alerts that your network or security systems have detected. This correlation can provide additional context and help determine if the blocks are in response to malicious activity or a misconfiguration.
By thoroughly analyzing the blocked connections and traffic, you can gain a clearer understanding of the underlying causes and take appropriate steps to resolve the blocking issues. Remember to follow security best practices and consult with network security professionals if needed.
Analyzing Firewall Configuration and Rules
When troubleshooting a blocked firewall, it is crucial to thoroughly analyze the firewall configuration and rules to determine if there are any misconfigurations or rule conflicts causing the blocks. By reviewing and understanding the firewall’s configuration, you can identify potential issues and make the necessary adjustments to resolve the blocks. Here’s how you can analyze the firewall configuration and rules:
- Review Rule Order: Examine the order of the firewall rules to ensure that they are prioritized correctly. Rules are typically evaluated from top to bottom, and the first rule that matches the connection criteria is applied. Check if there are any conflicting rules that might be causing the blocks. Consider reordering the rules if necessary.
- Check Rule Actions: Make sure that the actions specified in the firewall rules are appropriate. Some rules may have actions like “Block” or “Deny” explicitly defined. Verify that these actions align with your intended traffic policies. It is also essential to review any rules with ambiguous or overly permissive actions that can inadvertently allow or block traffic.
- Verify IP and Port Specifications: Double-check the IP addresses, ports, and protocols specified in the firewall rules. Ensure that the rules accurately reflect the services or connections you wish to allow or block. A simple typo or incorrect value can lead to unexpected blocks or allow unintended traffic.
- Consider Rule Overlapping: Look for overlapping rules that might conflict with each other. If there are conflicting rules with similar or contradicting criteria, it can result in unpredictable blocking behavior. Resolve any rule conflicts by either merging or redefining the rules to maintain consistency.
- Assess Logging and Notifications: Review the firewall’s logging and notification settings. Ensure that logs are capturing relevant information about blocked connections and traffic. Configure notifications so that you are alerted when blocks occur, allowing for prompt investigation and resolution.
- Consult Documentation and Best Practices: Refer to the firewall’s documentation and industry best practices to ensure that the configuration aligns with recommended guidelines. Firewall vendors often provide specific recommendations and guidelines for optimal configuration. Following these guidelines can help mitigate common configuration pitfalls that lead to blocking issues.
By closely analyzing the firewall configuration and rules, you can identify any misconfigurations, conflicts, or oversights that may be causing the blocks. Make necessary adjustments to the configuration to align it with your intended network requirements and security policies.
Firewall Testing and Simulation Tools
When troubleshooting a blocked firewall, utilizing firewall testing and simulation tools can be extremely beneficial. These tools allow you to test and evaluate the effectiveness of your firewall configuration by simulating various network scenarios. By using these tools, you can identify any potential vulnerabilities, rule conflicts, or misconfigurations that may be causing the blocks. Here are some popular firewall testing and simulation tools:
- Firewalk: Firewalk is a penetration testing tool that helps in determining the effectiveness of firewall rules. It sends specially crafted packets through the firewall, attempting to reach specific destinations. By analyzing the responses, Firewalk can identify allowed and blocked ports, helping to validate and refine firewall rules.
- PacketFence: PacketFence is an open-source network access control (NAC) system that includes a firewall testing feature. It allows you to simulate attacks on your network by emulating the behavior of different types of network traffic. This can help uncover any gaps or weaknesses in your firewall configuration.
- GNS3: GNS3 is a network simulation platform that enables you to create virtual network topologies and test various network scenarios. With GNS3, you can set up virtual firewalls and simulate traffic to assess the effectiveness of your firewall rules and configurations.
- NMap: NMap, along with its graphical interface Zenmap, is a powerful network scanning and mapping tool. It can be used to discover available hosts, open ports, and determine if your firewall is correctly configured to allow or block specific connections.
- iptables-sim: iptables-sim is a simulator for Linux’s netfilter firewall framework. It allows you to test and verify firewall rules without modifying the actual firewall configuration. By running simulations, you can assess how your firewall will behave under different network scenarios.
By utilizing firewall testing and simulation tools, you can evaluate the resilience and effectiveness of your firewall configuration. These tools enable you to discover potential vulnerabilities, optimize rule settings, and ensure that your firewall is adequately protecting your network while allowing legitimate traffic to pass through.
Troubleshooting Firewall Issues
When faced with firewall issues, it is essential to follow a systematic approach to identify and resolve the problems. Troubleshooting firewall issues can help restore normal network connectivity and ensure the proper functioning of your security measures. Here are some steps to help you troubleshoot firewall issues:
- Identify the Symptoms: Begin by gathering information about the symptoms you are experiencing. Determine specific connections or services that are being blocked or causing issues. This will help you narrow down the possible causes.
- Check Network Configuration: Verify that your network devices, such as routers and switches, are properly configured and functioning correctly. Ensure that there are no conflicting settings or misconfigurations that could be contributing to firewall issues.
- Review Firewall Logs: Examine the firewall logs to identify any blocked connections or traffic. Look for patterns, IP addresses, ports, and protocols involved in the blocks. Analyze the log entries and search for any recurring issues or anomalies.
- Inspect Firewall Configuration: Review the firewall configuration and rules to ensure they align with your network requirements. Check for any misconfigurations, conflicting rules, or ambiguity that could be causing the blocks. Make necessary adjustments to ensure the configuration is accurate and up-to-date.
- Perform Network Tests: Use network troubleshooting tools to perform tests like pinging, tracerouting, or port scanning to identify if specific connections are being blocked by the firewall. This will help pinpoint the source of the problem and determine whether the firewall is causing the issue.
- Consult Documentation and Vendor Support: Refer to the firewall’s documentation and vendor support resources for guidance. They may provide troubleshooting guides or offer assistance in resolving specific issues. Utilize their expertise and take advantage of any available patches or updates.
- Consider Firewall Testing Tools: Employ firewall testing and simulation tools to evaluate the effectiveness of your firewall configuration. These tools can help identify vulnerabilities, rule conflicts, or misconfigurations that may need to be addressed. Use their insights to optimize and refine your firewall settings.
- Implement Firewall Best Practices: Ensure that your firewall follows best practices for security and configuration. This includes keeping up-to-date with firmware updates, using strong passwords, and regularly reviewing and updating firewall rules to align with evolving security threats.
- Document Changes and Resolutions: Document any changes made to the firewall configuration and the resolutions applied to resolve the issues. This documentation will serve as a reference for future troubleshooting and can be helpful for maintaining an accurate and secure firewall setup.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively identify and resolve firewall issues. Be thorough in your examination, and consult with network security professionals or the firewall vendor if needed for more complex problems.
Common Causes of Firewall Blocks
Firewall blocks can occur due to various reasons, ranging from misconfigurations to security threats. Understanding the common causes of firewall blocks can help you identify and resolve these issues promptly. Here are some typical causes of firewall blocks:
- Incorrect Firewall Configuration: Misconfigured firewall rules or settings can unintentionally block legitimate traffic. This might occur due to human error or lack of understanding of the network requirements. Review the firewall configuration to ensure that it accurately reflects your intended network traffic policies.
- Outdated Firewall Rules: Over time, network requirements may change, and new services may be introduced. It is essential to update and revise your firewall rules accordingly. Outdated rules can block connections that should be permitted, impacting network functionality.
- Misplaced Firewall Rules: The order of firewall rules plays a crucial role in determining which rules take precedence. Placing rules in the wrong order can lead to unintended blocks or allow traffic that should be blocked. Arrange the rules properly to achieve the desired traffic control.
- Malware or Intrusions: Malicious software or unauthorized intrusions can compromise the security of your network. Firewalls are designed to block known malicious traffic, which may result in blocked connections. Regularly update your firewall’s security definitions to ensure effective protection against emerging threats.
- Insufficient Application or Protocol Support: Some Firewalls may lack support for certain applications or protocols, resulting in blocks. Verify that your firewall recognizes and allows the traffic generated by the applications and protocols used in your network. Consider using firewalls with comprehensive application and protocol support.
- Excessive Security Policies: Overly restrictive security policies can inadvertently block legitimate traffic. While stringent security measures are crucial, it is essential to strike a balance between security and network functionality. Review and refine your security policies to allow necessary connections while maintaining a secure environment.
- Traffic Surge or Denial of Service Attacks: Sudden spikes in network traffic or targeted Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can overwhelm the firewall, causing it to block legitimate connections in an attempt to protect the network. Implement measures to mitigate DoS attacks and ensure your firewall can handle high traffic volumes effectively.
- Inadequate Firewall Capacity: If the firewall appliance or hardware lacks sufficient capacity to handle the network traffic load, it may struggle to process connections efficiently. This can lead to blockages or performance issues. Evaluate your network’s traffic requirements and consider upgrading your firewall if necessary.
By recognizing the common causes of firewall blocks, you can take proactive steps to prevent and resolve such issues. Regularly reviewing and updating your firewall configuration, staying informed about emerging threats, and ensuring proper network security measures are essential to minimize firewall blocks and maintain a secure network environment.
Best Practices for Firewall Configuration
Configuring your firewall correctly is crucial to ensuring the security and optimal functionality of your network. By following best practices, you can enhance the effectiveness of your firewall and minimize the risk of unauthorized access or compromised connections. Here are some key best practices for firewall configuration:
- Implement a Defense-in-Depth Approach: A single firewall may not provide sufficient protection. Consider implementing multiple layers of security, such as using a combination of hardware and software firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to create a comprehensive defense strategy.
- Validate Default Firewall Configuration: Review and validate the default configuration of your firewall. Default settings can contain unnecessary or overly permissive rules, potentially exposing your network to risks. Modify the default configuration to align it with your specific security requirements.
- Follow the Principle of Least Privilege: Only permit the necessary traffic and access required for your network operations. Granularly define rules that allow specific traffic while blocking everything else. Regularly review and remove any unused or unnecessary rules to minimize potential security vulnerabilities.
- Regularly Update Firmware and Software: Keep your firewall firmware and software up to date with the latest patches and updates provided by the vendor. These updates often include critical security fixes and enhancements that address emerging threats.
- Utilize Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Complement your firewall with intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS). These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns or known attack signatures and can provide an additional layer of protection by blocking suspicious activities.
- Enable Logging and Regularly Review Logs: Enable firewall logging and regularly review the logs for any unusual activity or blocked connections. Logs can help you identify potential security threats and assist in troubleshooting any issues that arise.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Implement encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, to protect sensitive data transmitted across your network. Configure your firewall to allow and inspect encrypted traffic while ensuring that proper encryption standards are enforced.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication for firewall administration. Implementing these authentication measures helps prevent unauthorized access to the firewall configuration and enhances overall network security.
- Regularly Test and Update Firewall Rules: Regularly test your firewall rules to ensure they effectively control network traffic while allowing legitimate connections. Update your rules as needed to align with changes in network requirements or emerging threats.
- Train and Educate Users: Provide training and education for your network users about proper security practices and safe internet browsing. Users should be aware of potential risks, such as social engineering attacks or clicking on malicious links, which can bypass the firewall’s protection.
By following these best practices for firewall configuration, you can strengthen your network security, ensure optimal performance, and minimize the risk of unauthorized access or compromised connections. Regularly review and update your firewall configuration based on evolving security requirements and emerging threats to maintain a secure network environment.