Why Do You Need to Log In to a Modem?
Logging in to your modem is an essential step in managing and configuring your internet connection. By accessing the modem’s settings, you gain control over various aspects of your network and ensure optimal performance. Here are some key reasons why you need to log in to your modem:
- Network Security: Logging in allows you to customize security settings, such as changing the default username and password, creating a strong Wi-Fi password, and enabling encryption protocols like WPA2. This helps protect your network from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
- Network Configuration: Through the modem’s configuration interface, you can modify network settings like SSID (network name), channel selection, and IP address assignment. Adjusting these settings can help optimize Wi-Fi coverage, reduce interference, and ensure a stable connection.
- Connection Troubleshooting: Accessing the modem’s interface provides valuable diagnostic tools for identifying and resolving network issues. You can view connection status, signal quality, and error logs, allowing you to troubleshoot problems and improve performance.
- Bandwidth Management: Additionally, logging in allows you to manage network bandwidth usage. You can prioritize certain devices or applications over others, set up QoS (Quality of Service) rules, and create guest networks with restricted access. This helps allocate resources and ensures a smooth online experience.
- Firmware Updates: Some modems require periodic firmware updates to enhance features, security, and compatibility. Logging in enables you to check for available updates and apply them when needed, ensuring your modem is up to date and functioning optimally.
Overall, logging in to your modem empowers you to take control of your network, customize configurations, and enhance security and performance. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the login process and regularly access the modem interface to ensure a reliable and secure internet connection.
Finding the Default IP Address of Your Modem
To log in to your modem, you need to know its default IP address. This address is a set of numbers that serves as the location for accessing the modem’s configuration interface. Here are some methods to find the default IP address of your modem:
- Check the Documentation: The easiest way to find the default IP address is to refer to the documentation provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Look for a user manual or a setup guide that mentions the default IP address of the modem.
- Check the Modem Label: If you can’t find the documentation, look for a label on the modem itself. Most modems have a label on the bottom or back that displays important information, including the default IP address, username, and password. Look for keywords like “Gateway” or “Default IP.”
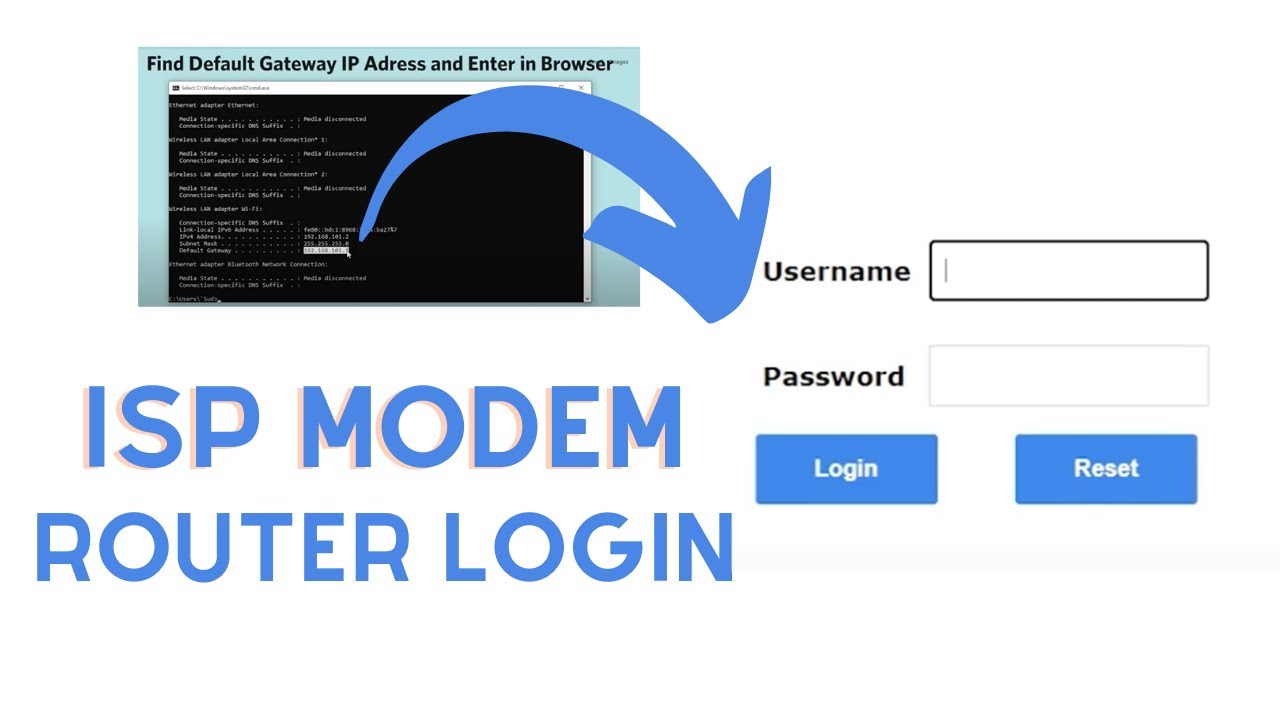
- Use Command Prompt (Windows): If you’re using a Windows computer, you can use the Command Prompt utility to find the default IP address. Open the Command Prompt by pressing Windows + R, typing “cmd,” and hitting Enter. Then, type “ipconfig” and press Enter. Look for the “Default Gateway” under the Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter section. The value listed here is the default IP address of your modem.
- Use Terminal (MacOS/Linux): For MacOS or Linux users, open Terminal and enter the command “ifconfig” or “ip route show.” Look for the “Default Gateway” or “default via” line, which displays the default IP address of your modem.
- Use IP Scanner Software: Alternatively, you can use third-party IP scanner software to discover the IP address of your modem. These tools scan your network and identify connected devices, including the modem. Some popular IP scanner software is Angry IP Scanner, Advanced IP Scanner, and Fing.
Once you have determined the default IP address of your modem, you are ready to log in and access its configuration interface. Simply enter the IP address into your web browser’s address bar and press Enter. This will take you to the login page where you can enter the default username and password provided by your ISP.
Finding the default IP address is an important first step in logging in to your modem and gaining access to its settings. Keep in mind that some modems may have a different IP address if the default one has been changed. In such cases, you may need to consult your ISP or refer to alternative methods to find the current IP address.
Connecting to the Modem’s Network
Before you can access the configuration interface of your modem, you need to ensure that your device is connected to the modem’s network. Most modems provide both wired and wireless connectivity options, allowing you to choose the method that suits your needs. Here’s how you can connect to your modem’s network:
- Wired Connection: To establish a wired connection, use an Ethernet cable to connect your device (such as a computer or laptop) to one of the Ethernet ports on the modem. Ensure that the cable is securely plugged into both the device and the modem. This direct connection provides a stable and reliable network connection.
- Wireless Connection: To connect wirelessly, make sure that your device has Wi-Fi capability. Open the Wi-Fi settings on your device and search for available networks. Locate your modem’s network name (SSID) in the list of available networks. Select your modem’s network and enter the password when prompted. Once successfully connected, your device will join the modem’s wireless network.
It’s important to note that the default Wi-Fi password is often printed on the modem label or provided in the documentation. If you choose to connect wirelessly, ensure that you enter the correct password to establish a secure connection.
If you’re unable to connect to the modem’s network, here are some troubleshooting steps to follow:
- Restart your modem and device to ensure a fresh connection attempt.
- Double-check that the Ethernet cable is firmly connected or that you’ve entered the correct Wi-Fi password.
- Move closer to the modem to ensure a strong Wi-Fi signal.
- Check if other devices can connect to the modem’s network to rule out any network connectivity issues.
- If all else fails, consult your ISP for further assistance or troubleshoot using the modem’s documentation.
By establishing a successful connection to your modem’s network, you are now ready to proceed to log in to the modem’s configuration interface and access its settings.
Opening a Web Browser and Entering the IP Address
Once you have connected your device to the modem’s network, you can proceed to open a web browser and enter the default IP address of the modem to access its configuration interface. Follow these steps to log in to your modem:
- Open your preferred web browser on your device. You can use popular browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, or Safari.
- In the address bar of the web browser, enter the default IP address of your modem. The default IP address is typically in the format of “192.168.1.1” or “192.168.0.1,” but it may vary depending on the modem’s manufacturer and model. Check the modem’s documentation or label for the correct IP address.
- Press enter or click on the “Go” button, and your web browser will attempt to connect to the configured IP address of the modem.
After entering the IP address, you may need to wait for a few seconds while the browser establishes a connection with the modem’s configuration interface.
If the connection is successful, the modem’s login page will appear in your web browser. If prompted, enter the default username and password. These credentials are usually provided by your Internet Service Provider or can be found on the modem’s label or in the documentation. Note that the username and password are case-sensitive.
Once you have entered the correct login credentials, click on the “Login” or “Sign In” button to log in to the modem’s configuration interface.
If you are unable to access the configuration interface using the default IP address, there’s a possibility that the IP address has been changed. In such cases, refer to the modem’s documentation or consult your Internet Service Provider to obtain the correct IP address for accessing the configuration interface.
Now that you have successfully accessed the modem’s configuration interface, you can proceed to customize and manage your modem’s settings to optimize your network connection.
Entering the Default Username and Password
After successfully accessing the modem’s login page, you will be prompted to enter the default username and password to authenticate your access. Here’s how to enter the default login credentials to log in to the modem’s configuration interface:
- On the modem’s login page, locate the fields provided for the username and password.
- Enter the default username in the corresponding field. The default username may vary depending on the modem’s manufacturer and model. Look for the username in the modem’s documentation or on the modem’s label.
- Next, enter the default password in the password field. Like the username, the default password can also be found in the modem’s documentation or on the modem’s label.
It’s important to note that both the username and password are case-sensitive, so make sure to enter them exactly as provided, paying attention to uppercase and lowercase letters.
Once you have entered the default username and password, click on the “Login” or “Sign In” button to proceed. If the provided credentials are correct, the modem’s configuration interface will be displayed, granting you access to manage and customize your modem’s settings.
However, it is highly recommended that you change the default username and password for security reasons. Leaving the default credentials unchanged makes your network vulnerable to unauthorized access. To change your modem’s username and password, navigate to the appropriate settings within the configuration interface and follow the instructions provided.
Changing the default credentials adds an extra layer of security to your modem and ensures that only authorized users can access and modify its settings. Make sure to choose a strong and unique password that is not easily guessable or commonly used.
If you encounter any issues logging in with the default username and password, double-check that you have entered them correctly, taking note of any capitalization or spelling errors. If you continue to experience difficulties, consult your modem’s documentation or contact your Internet Service Provider for further assistance.
By successfully entering the default username and password, you gain access to the modem’s configuration interface and can begin customizing your network settings to suit your specific requirements.
Changing Your Modem’s Default Username and Password
It is highly recommended to change the default username and password of your modem after accessing the configuration interface for the first time. Changing these credentials adds an extra layer of security to your network and helps protect against unauthorized access. Here’s how you can change the default username and password:
- Log in to your modem’s configuration interface using the default username and password. Refer to the previous section on how to access the configuration interface.
- Navigate to the section or menu where you can modify the modem’s settings. This may vary depending on the modem’s manufacturer and model. Look for options like “Administration,” “Security,” or “User Management.”
- Locate the fields for the username and password and enter your desired new values. Choose a unique username and a strong password that is at least 8-10 characters long and includes a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information like your name or birthdate.
- Once you have entered the new username and password, save the changes by clicking on the “Save,” “Apply,” or “Submit” button. Some modems may require you to confirm the changes by re-entering the new credentials.
- After saving the changes, log out of the modem’s configuration interface and log back in using the newly set username and password. This step ensures that the changes have taken effect and that you can access the configuration interface with the updated credentials.
With the default username and password changed, you can rest assured that your modem is now more secure and less susceptible to unauthorized access. It is important to keep your new credentials in a safe place and avoid sharing them with others.
It is also good practice to periodically update your modem’s username and password to further enhance security. Regularly changing your credentials adds an additional layer of protection against potential security breaches.
If you forget the new username and password, you can usually perform a factory reset on your modem to restore the default settings. However, be aware that doing so will erase any custom configurations you have made, so proceed with caution.
By taking the step to change your modem’s default username and password, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your network and ensure a safer online experience for all connected devices.
Troubleshooting Login Issues
While logging in to your modem’s configuration interface is typically a straightforward process, you may encounter issues occasionally. Here are some common login issues you may face and troubleshooting steps to resolve them:
- Incorrect Username or Password: Double-check that you have entered the correct username and password. Ensure that you are using the new credentials if you have changed them from the default values.
- Case-sensitivity: Remember that usernames and passwords are case-sensitive. Make sure that you are entering uppercase and lowercase letters correctly.
- Browser Compatibility: If you are experiencing login issues, try using a different web browser to access the configuration interface. Some modems may be optimized for specific browsers, and using an alternative browser can help resolve compatibility issues.
- Clear Cache and Cookies: Clearing your web browser’s cache and cookies can resolve login problems related to outdated or conflicting data. Go to your browser’s settings or preferences and locate the option to clear cache and cookies. Once cleared, attempt to log in again.
- Power Cycle the Modem: Try power cycling your modem by unplugging it from the power source, waiting for a few seconds, and then plugging it back in. This can resolve temporary glitches or connection issues that may be affecting the login process.
- Reset Modem: If you are unable to log in even with the correct credentials, you can perform a factory reset on your modem. This will restore the modem to its default settings. Note that performing a reset will erase any custom configurations, so use this option as a last resort.
- Contact ISP or Manufacturer: If all else fails, consider reaching out to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or the modem’s manufacturer for assistance. They can provide you with specific troubleshooting steps based on your modem’s model and configuration.
It’s important to note that if you make repeated unsuccessful login attempts, some modems have security measures in place that may temporarily lock you out. This is a protective measure against unauthorized access. If you encounter this issue, wait for a few minutes and try logging in again.
Remember that each modem may have its own specific quirks or troubleshooting steps, so consult the modem’s documentation or contact the appropriate technical support for detailed guidance in troubleshooting login issues.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can overcome common login issues and regain access to your modem’s configuration interface, ensuring that you have the ability to manage and customize your network settings effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about logging in to a modem:
-
Q: What if I forget the default username and password of my modem?
A: If you forget the default login credentials of your modem, you can usually find them on the modem’s label or in the documentation provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If that’s not available, you can perform a factory reset on your modem to revert it to its default settings. Keep in mind that this will erase any custom configurations you have made. -
Q: Can I change the default IP address of my modem?
A: In most cases, you cannot change the default IP address of your modem as it is preconfigured by the manufacturer. It is recommended to consult the modem’s documentation or contact your ISP for guidance on this matter. -
Q: How can I access my modem’s configuration interface from a different location?
A: To access your modem’s configuration interface from a remote location, you typically need to enable remote management. This option is usually found in the modem’s settings. However, it is important to note that enabling remote management can pose security risks, so proceed with caution and ensure you have taken appropriate security measures. -
Q: What should I do if I am unable to access the modem’s configuration interface at all?
A: If you are unable to access the modem’s configuration interface even with the correct IP address, username, and password, ensure that your device is properly connected to the modem’s network. If the issue persists, try restarting your modem and device. If the problem continues, contact your ISP or the modem’s manufacturer for further assistance. -
Q: Can I log in to my modem using a smartphone or tablet?
A: Yes, you can log in to your modem’s configuration interface using a smartphone or tablet. Simply open a web browser on your device, enter the IP address of the modem, and proceed with the login process as you would on a computer. However, keep in mind that the interface may be optimized for desktop or laptop devices, so the user experience may vary.
If you have any additional questions or encounter specific issues while logging in to your modem, it is recommended to refer to the modem’s documentation, contact your Internet Service Provider, or reach out to the modem’s manufacturer for further assistance and guidance.