Reasons to Indent in Word
Indentation is a crucial formatting technique that can greatly improve the readability and organization of text in Microsoft Word. By creating consistent indentations, you can enhance the structure of your documents and make them more visually appealing. Here are several reasons why indentation is important:
- Improved Readability: Indentation helps to visually separate paragraphs and sections, making it easier for readers to navigate through your document. It allows them to quickly identify the start of a new paragraph, which aids in comprehension and understanding.
- Enhanced Clarity: By indenting the first line of each paragraph, you can clearly indicate the beginning of a new thought or idea. This helps to organize your content and prevent it from appearing as a single block of text, which can be overwhelming and confusing for readers.
- Professional Appearance: Proper indentation adds a professional touch to your documents. It shows that you have put effort into formatting and structuring your content, making it more visually appealing and engaging to the reader.
- Consistency: Indenting your paragraphs ensures consistency throughout your document. It provides a uniform structure that makes it easier for readers to follow along and understand the flow of your content.
- Highlighting Key Points: Indentation can be used to draw attention to specific sections or key points within your document. By indenting these sections, you can create a visual hierarchy that guides the reader’s focus and highlights important information.
Overall, proper indentation in Microsoft Word is essential for creating well-structured, visually pleasing, and easily readable documents. It improves the overall user experience and helps convey your ideas more effectively. So, take the time to master the art of indentation and make your documents stand out!
How to Indent Using the Tab Key
One of the simplest and most commonly used methods to indent in Microsoft Word is by utilizing the Tab key on your keyboard. It allows you to create consistent and uniform indentations throughout your document. Here’s how you can use the Tab key to indent:
- Place your cursor at the beginning of the paragraph you wish to indent.
- Press the Tab key on your keyboard. This will move the entire paragraph to the right, creating an indentation.
- If you want to increase the indent further, press the Tab key multiple times.
- To reduce the indent, press the Shift + Tab keys together.
- To apply the same indentation to multiple paragraphs, first, select all the paragraphs you want to indent. Then, press the Tab key to indent them simultaneously.
Using the Tab key for indentation is quick and easy, but it may not always be the best option, especially if you need precise and consistent indentations throughout your document. In such cases, it’s recommended to use the built-in indentation options available in Microsoft Word.
Remember, employing the Tab key is a straightforward way to indent paragraphs, but depending on your specific formatting needs, you may need to explore other indentation methods.
Using the Increase Indent and Decrease Indent Buttons
Microsoft Word provides dedicated buttons to quickly increase or decrease the indentation of paragraphs. These buttons offer a convenient and reliable way to achieve consistent indentations throughout your document. Here’s how you can use the “Increase Indent” and “Decrease Indent” buttons:
- Select the paragraph or paragraphs you want to indent.
- Locate the “Increase Indent” and “Decrease Indent” buttons in the toolbar. These buttons typically appear as right-facing and left-facing triangles with horizontal lines next to them.
- To increase the indent, click on the “Increase Indent” button. This will move the selected paragraph(s) to the right, creating a larger indentation.
- To decrease the indent, click on the “Decrease Indent” button. This will move the selected paragraph(s) back to the left, reducing the indentation.
- If you want to apply the same indentation to multiple paragraphs, first, select all the paragraphs you wish to indent. Then, click on the “Increase Indent” or “Decrease Indent” button to adjust their indentations simultaneously.
The “Increase Indent” and “Decrease Indent” buttons provide a hassle-free way to adjust paragraph indentations. They are especially useful when you need consistent indentations across different sections of your document or want to modify existing indentations quickly.
By using these buttons, you can easily achieve well-structured and visually appealing documents without the need for manual adjustments or relying solely on the Tab key for indentation.
Indenting First Line of Paragraphs with the Ruler
Microsoft Word offers a powerful feature called the ruler, which allows you to precisely adjust the indentation of paragraphs, including the first line. This method is particularly useful if you want to create a hanging indent or customize the indentation for specific paragraphs. Here’s how you can indent the first line of paragraphs using the ruler:
- Select the paragraph or paragraphs you want to indent.
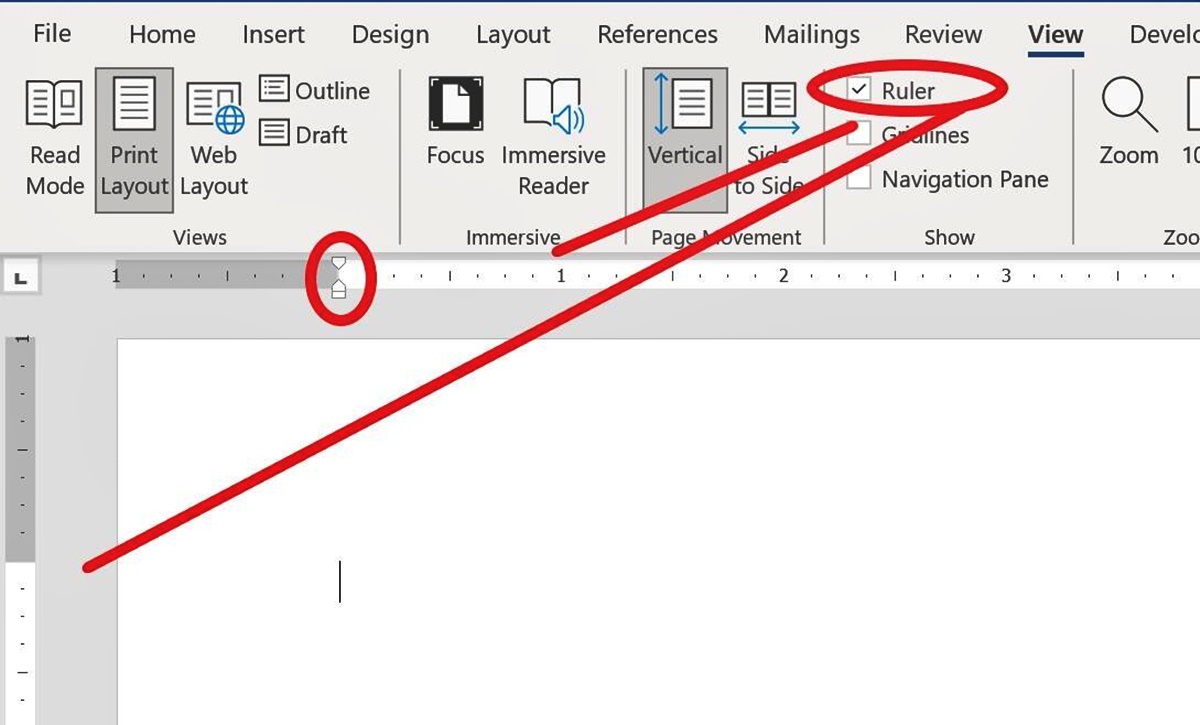
- Go to the “View” tab in the Word ribbon and check the “Ruler” option. This will display the ruler at the top of your document.
- Locate the margin marker on the left side of the ruler. It is represented by a small square-shaped icon.
- Click and drag the margin marker to the right to increase the indentation of the first line of the selected paragraph(s). You can adjust it to your desired position.
- If you want to apply a hanging indent, where the first line is slightly pushed back and the subsequent lines are indented further, adjust the “First-line indent” marker on the ruler. It is represented by a small upside-down triangle below the margin marker.
- You can also adjust the “Left indent” marker to change the overall indentation of the entire paragraph, including the first line.
Using the ruler in Microsoft Word provides precise control over paragraph indentation, giving you the flexibility to customize the appearance of your document. It allows for greater consistency and visual appeal, especially when dealing with different types of paragraphs or specific formatting requirements.
Experiment with the ruler feature to create unique and professional-looking indentations that enhance the structure and readability of your document.
Using the Hanging Indent Feature
The hanging indent feature in Microsoft Word is a valuable tool for creating consistent and visually appealing indentations. It is particularly useful when working with reference lists, bibliographies, or any content where you want the first line to be flush with the left margin while indenting the subsequent lines. Here’s how you can use the hanging indent feature:
- Select the paragraph or paragraphs you want to apply the hanging indent to.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group. This will open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Indentation” section of the dialog box, find the “Special” dropdown menu.
- Select “Hanging” from the options. This will apply the hanging indent style to the selected paragraph(s).
- Use the “By” field to specify the amount of indentation you want for the hanging lines. You can enter a specific measurement or use the up and down arrows to adjust it.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the hanging indent to the selected paragraph(s).
The hanging indent feature is a great way to create clean and professional-looking documents, especially when dealing with references or long lists that require indentation. It ensures that subsequent lines are aligned neatly and consistently, making it easier for readers to scan through the content.
Experiment with the hanging indent feature to enhance the readability and visual appeal of your documents. Whether you’re creating a bibliography, an outline, or any other content that requires indentation, the hanging indent feature in Microsoft Word can help you achieve the desired formatting effortlessly.
Modifying Indentation Spacing
In Microsoft Word, you have the flexibility to adjust the spacing of your indentations to meet your specific formatting needs. Whether you want to increase or decrease the amount of space between the left margin and the start of your paragraphs, Word provides various options to modify the indentation spacing. Here’s how you can do it:
- Select the paragraph or paragraphs you want to modify the indentation spacing for.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group. This will open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Indentation” section of the dialog box, find the “Special” dropdown menu.
- Select “First line” or “Hanging” from the options, depending on the type of indentation you want to modify.
- Use the “By” field to specify the desired amount of spacing for the indentation. You can enter a specific measurement or use the up and down arrows to adjust it. Positive values increase the space, while negative values decrease it.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the modified indentation spacing to the selected paragraph(s).
By modifying the indentation spacing, you can achieve a variety of formatting effects. Increasing the spacing can help to visually separate paragraphs, making your document easier to read. On the other hand, decreasing the spacing can save space and create a compact layout.
Experiment with different indentation spacing options to find the balance that best suits your document’s overall design and readability. Keep in mind that you can always adjust the indentation spacing for individual paragraphs or apply changes to the entire document, depending on your specific needs.
Applying Different Indents to Different Sections
In Microsoft Word, you have the flexibility to apply different indentation styles to different sections of your document. This feature allows you to create visually distinct sections, such as block quotes, citations, or captions, that require specific indentations. Here’s how you can apply different indents to different sections:
- Select the section or paragraph you want to apply a different indent to.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group. This will open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Indentation” section of the dialog box, customize the indentation settings according to your preference. You can adjust the left indent, right indent, first-line indent, and hanging indent.
- If you want to create a new style for the selected section, click on the “Format” button located in the bottom-left corner of the “Paragraph” dialog box. Choose “Define New Style” and specify a name for the style.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the different indent to the selected section or paragraph.
- To apply the same indentation to other sections or paragraphs, repeat the process for each section or use the “Apply Styles” feature to quickly apply the newly created style.
Applying different indents to different sections allows you to create a visually appealing and well-structured document. It helps to highlight specific parts of your content and improves the overall readability and understanding of your document.
Experiment with different indentation styles and apply them strategically to different sections of your document to enhance the organization and visual hierarchy of your content.
Using Tabs to Create Columns
Microsoft Word offers a powerful feature that allows you to create columns of text within your document using tabs. This can be especially useful for designing newsletters, brochures, or other types of documents that require multiple columns. Here’s how you can use tabs to create columns:
- Select the text or paragraph you want to format into columns.
- Go to the “Page Layout” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Page Setup” group.
- Click on the “Columns” dropdown menu, and choose the number of columns you desire.
- If you want to create custom column widths, click on “More Columns” at the bottom of the dropdown menu. In the “Columns” dialog box, you can specify the number of columns and set individual widths for each column if desired.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the columns to the selected text or paragraph.
- Now, when you type or insert content within the selected area, it will automatically flow into the specified number of columns.
- If you need to adjust the column layout at any point, repeat the steps above to modify the column settings.
Using tabs to create columns can help you structure your content in a visually appealing way. Whether you’re designing a newsletter with multiple sections or dividing text into columns for easier reading, this feature provides a flexible and efficient solution.
Experiment with different column layouts and widths to optimize the presentation of your content. Keep in mind that you can apply column formatting to specific sections or even just a few paragraphs within your document, allowing for versatile and customizable column design.
Adjusting Tab Stops and Alignment
Microsoft Word allows you to customize the tab stops and alignment to precisely control the placement of text within your document. Tab stops are markers that define where the text aligns when you press the Tab key. By adjusting the tab stops and alignment settings, you can create professional-looking documents with consistent and precise indentations. Here’s how you can adjust tab stops and alignment:
- Place your cursor in the paragraph where you want to adjust the tab stops and alignment.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group. This will open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Tabs” section of the dialog box, you can see the current tab stops and alignment settings.
- To adjust an existing tab stop, select it from the list, and modify its position or alignment using the available options.
- To add a new tab stop, enter the desired position in the “Tab stop position” field, and choose the desired alignment from the options (left, center, right, decimal, or bar).
- Click the “Set” button to apply the changes to the selected tab stop or click the “Clear” button to remove a tab stop.
- If you want to apply the same tab stops and alignment to other paragraphs, use the “Apply to” dropdown menu to choose the desired scope (selected text, current paragraph, or whole document).
- Click the “OK” button to apply the adjusted tab stops and alignment to the selected paragraph(s).
By adjusting the tab stops and alignment in Microsoft Word, you have precise control over the placement of text within your document. This feature is especially useful when creating tables, aligning numbers, or formatting lists with hanging indents.
Take the time to experiment with different tab stop positions and alignments to achieve the desired layout and organization of your content.
Creating Custom Tab Stops
Microsoft Word allows you to create custom tab stops at specific positions within your document. Custom tab stops offer greater flexibility and control when it comes to aligning text or creating unique formatting effects. Here’s how you can create custom tab stops:
- Place your cursor in the paragraph where you want to add a custom tab stop.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group. This will open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Tabs” section of the dialog box, enter the desired position for your custom tab stop in the “Tab stop position” field.
- Choose the desired alignment for the custom tab stop from the options (left, center, right, decimal, or bar).
- Click the “Set” button to add the custom tab stop.
- If you want to add multiple custom tab stops, repeat steps 4-6 for each additional tab stop.
- Remove any unwanted custom tab stops by selecting them from the list and clicking the “Clear” button.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the custom tab stops to the selected paragraph(s).
Creating custom tab stops allows you to align text precisely at specific positions within your document. This can be useful for aligning numbers in tables, creating formatted lists, or adding unique formatting effects to your content.
Experiment with different custom tab stop positions and alignments to achieve the desired formatting and layout for your document. Take advantage of this feature to create professional-looking documents with precision and style.
Understanding the Tab Leader Feature
The tab leader feature in Microsoft Word is a powerful tool that allows you to add visual cues and improve the readability of documents containing lists, tables, or other structured information. Tab leaders are used to create a line of dots, dashes, or other characters that connect tab stops. Understanding how to utilize the tab leader feature can enhance the presentation and organization of your content. Here’s what you need to know:
- Place your cursor at the beginning of the line where you want to add a tab leader.
- Go to the “Home” tab in the Word ribbon and locate the “Paragraph” group.
- Click on the small arrow icon in the bottom-right corner of the “Paragraph” group to open the “Paragraph” dialog box.
- In the “Tabs” section of the dialog box, select the desired tab stop position where you want to insert the tab leader.
- Choose the type of tab leader you want to use, such as dots, dashes, or other characters, from the “Leader” dropdown menu.
- Click the “Set” button to apply the tab leader to the selected tab stop.
- Repeat steps 4-6 for any other tab stops where you want to add tab leaders.
- Click the “OK” button to apply the tab leaders to the selected paragraph(s).
The tab leader feature can greatly improve the readability and organization of your documents. It helps to visually connect related information, making it easier for readers to follow and understand lists, tables, or other structured content.
Experiment with different tab leader styles and placements to find the most suitable option for your specific document. Tab leaders can be used to add a professional touch and improve the overall appearance of your work.