Why Email Encryption is Important
Email has become an integral part of our communication, whether it’s for personal or professional purposes. We rely on email to send sensitive information such as financial data, confidential documents, and personal conversations. However, with the increasing prevalence of cybercrime and data breaches, it has become essential to safeguard our email communication with encryption.
Email encryption is the process of encoding the content of an email message to protect it from unauthorized access. It ensures that only the intended recipient can read the email by making the message unreadable to anyone else who may intercept it. Here are a few reasons why email encryption is crucial in today’s digital world:
- Privacy: With email encryption, you can maintain the privacy of your conversations, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the content of the email. This is particularly important when communicating sensitive information such as personal details or financial data.
- Security: Encryption adds an extra layer of security to your email, making it more difficult for hackers and cybercriminals to intercept and decipher the message. It helps protect your data from unauthorized access and potential misuse.
- Compliance: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, have specific regulations regarding the protection of sensitive information. Encrypting emails helps organizations meet these compliance requirements and avoids potential penalties or legal consequences.
- Trust: When you encrypt your emails, it demonstrates to your recipients that you take the security of your communication seriously. It builds trust, especially when sharing confidential information or engaging in business transactions.
- Preventing Data Breaches: By encrypting emails, you reduce the risk of a data breach. Even if an unauthorized person gains access to your email account or intercepts the email in transit, they won’t be able to decipher the encrypted content, thus minimizing the potential damage.
Setting Up a Secure Connection in Gmail
Ensuring a secure connection is the first step towards email encryption in Gmail. By enabling secure connections, you can protect your email communication from being intercepted or tampered with by unauthorized individuals. Follow these steps to set up a secure connection in Gmail:
- Enable HTTPS: Open the Gmail settings by clicking on the gear icon in the top right corner of the Gmail interface. Select “Settings” and navigate to the “General” tab. Scroll down to the “Browser Connection” section and make sure that the option “Always use HTTPS” is checked. This ensures that your connection to Gmail is encrypted throughout your entire session.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your Gmail account. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to provide a second authentication factor, such as a unique code sent to your phone, in addition to your password. To enable 2FA, go to your Google Account settings and navigate to the “Security” section. Choose the 2FA option and follow the instructions to set it up.
- Keep Gmail App and Operating System Updated: It is crucial to keep your Gmail app and operating system up to date. Regular updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities and protect against potential threats. Make sure to enable automatic updates to ensure that you have the latest security features and fixes.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Choose a strong and unique password for your Gmail account. Avoid using easily guessable passwords and consider using a password manager to help generate and store complex passwords securely.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Exercise caution when clicking on links or downloading attachments from emails. Phishing attacks are one of the most common methods used to gain unauthorized access to email accounts. Always verify the sender’s email address and double-check the legitimacy of any suspicious email before taking any action.
By implementing these steps, you can significantly enhance the security of your Gmail account and establish a secure connection for your email communication.
Step-by-step Guide to Encrypting Emails in Gmail
Gmail provides built-in encryption features that allow you to easily encrypt your emails and protect them from unauthorized access. Follow these step-by-step instructions to encrypt your emails in Gmail:
- Compose a New Email: Start by clicking on the “Compose” button in Gmail to create a new email message.
- Compose your Email: Write your email as usual, adding the subject line and the content of the email.
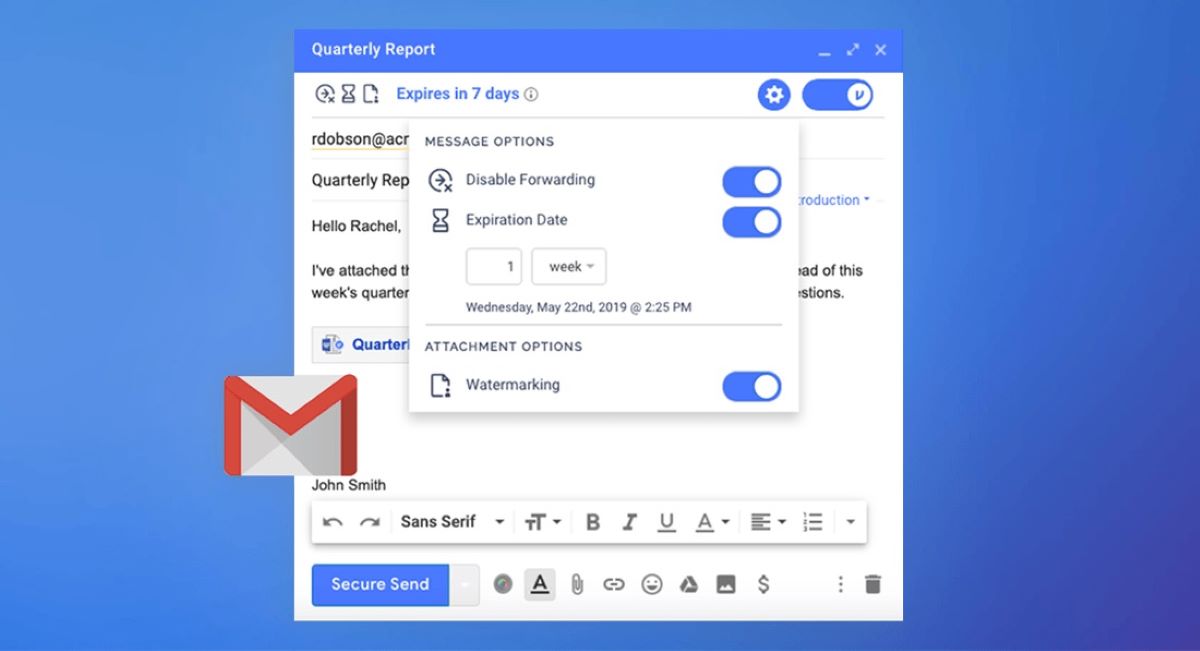
- Enable Confidential Mode: In the bottom toolbar of the compose window, you will find a padlock icon with a clock. This represents “Confidential Mode.” Click on it to enable this feature.
- Set Expiration and Passcode (optional): You have the option to set an expiration date for the email, after which the recipient won’t be able to access it. Additionally, you can choose to add an SMS passcode that the recipient will need to enter to open the email.
- Add Recipients: Enter the email addresses of the recipients in the “To” field. You can also add recipients in the “Cc” or “Bcc” fields if needed.
- Provide Additional Security (optional): You can choose to require the recipient to verify their identity through a passcode sent to their email or by entering their Google account password, adding an extra layer of security.
- Add Attachments (if needed): If you have any attachments to include in the email, click on the paperclip icon in the compose window to attach files.
- Review and Send: Double-check your email content, recipients, and security settings. Once you are satisfied, click the “Send” button to send the encrypted email.
After you send the email, the recipient will receive a notification regarding the confidential email. They will be able to view the email content by following the steps provided in the email and, if applicable, entering any required passcodes.
By following these step-by-step instructions, you can easily encrypt your emails in Gmail and add an extra layer of protection to your sensitive information.
Using the Confidential Mode Feature in Gmail
Gmail’s Confidential mode feature offers an additional level of email security by allowing you to send sensitive information with restricted access. With this feature, you have control over how recipients can interact with your email, such as preventing them from forwarding, printing, or downloading the email content. Here’s how to use the Confidential mode feature in Gmail:
- Compose a New Email: Begin by clicking on the “Compose” button in Gmail to create a new email message.
- Enable Confidential Mode: In the bottom toolbar of the compose window, click on the padlock icon with a clock to enable Confidential mode.
- Set Expiration and Passcode (optional): Optionally, you can set an expiration date for the email after which the recipient won’t be able to access it. You can also choose to add an SMS passcode that the recipient will need to enter to open the email.
- Add Recipients: Enter the email addresses of the recipients in the “To” field. You can also add recipients in the “Cc” or “Bcc” fields if needed.
- Choose Access Options: Select the desired access options for the email. You can choose to prevent recipients from forwarding, copying, downloading, or printing the email content.
- Add Attachments (if needed): Attach any files you want to include with the email by clicking on the paperclip icon in the compose window.
- Review and Send: Double-check the email content, recipients, and access options. Once everything is in order, click the “Send” button to send the email.
When the recipient receives the email, they will see a notification indicating that the email has been sent in Confidential mode. They will be able to open and read the email, but depending on the access options you selected, they may not be able to forward, print, download, or copy the content.
Note that even though Confidential mode adds an extra layer of security, it does not guarantee complete protection, as recipients may still capture screenshots or take photos of the email content. Therefore, it’s essential to exercise caution and discretion when using this feature for sensitive information.
By utilizing the Confidential mode feature in Gmail, you can ensure that your sensitive emails remain confidential and prevent unauthorized sharing or distribution of your content.
Encrypting Attachments in Gmail
Encrypting email attachments is just as important as encrypting the content of the email itself. By encrypting attachments, you add an extra layer of security to the files you share, ensuring that only the intended recipients can access and open them. Gmail provides several methods for encrypting attachments. Here’s how to encrypt attachments in Gmail:
- Compress and Encrypt: One of the simplest ways to encrypt attachments is by compressing them into a password-protected ZIP file. Right-click on the file(s) or folder you want to attach, select “Compress,” and choose the ZIP format. Then, set a strong password for the ZIP file, ensuring that only the recipient knows the password necessary to extract the files.
- Third-Party Encryption Tools: You can also make use of third-party encryption tools to secure your attachments before sending them via Gmail. These tools offer additional security features such as advanced encryption algorithms and secure key exchange. Encrypt your files using the desired encryption tool, and then attach the encrypted files to your Gmail email.
- File Encryption Software: If you frequently send sensitive attachments via email, consider using file encryption software. These programs allow you to encrypt individual files or folders on your computer, adding an extra layer of protection to your attachments. You can then attach the encrypted files to your Gmail email as usual.
When sending the encrypted attachments in Gmail, ensure that you provide the necessary instructions to the recipient on how to decrypt and access the files securely. This may include sharing the password for ZIP files or providing information on the encryption software used.
It’s important to note that while encrypting attachments adds an additional layer of security, it does not guarantee absolute protection. Recipients may still choose to forward or share the decrypted attachments with others. Therefore, it is crucial to only send attachments to trusted recipients and consider the sensitivity of the information being shared.
By taking the necessary steps to encrypt attachments in Gmail, you can protect the confidentiality and integrity of your sensitive files, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access and view them.
Understanding Encryption and Decryption Keys
Encryption and decryption keys play a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of your email communication. These keys are used in the encryption process to encode the content of an email and in the decryption process to decode the encrypted message. Here’s a basic understanding of encryption and decryption keys:
Encryption Keys: Encryption keys are used to convert readable data into an unreadable format, also known as ciphertext. When you encrypt an email, the encryption key is generated and applied to the message, scrambling the content into an encrypted form. This key is unique to each encrypted message and is required to decrypt and restore the original message’s readability.
Public Key Encryption: Public key encryption, commonly used in email encryption, involves the use of two types of encryption keys: the public key and the private key. The recipient of the encrypted email provides their public key, which is used by the sender to encrypt the email. The private key, which is kept secret by the recipient, is then used to decrypt the email.
Decryption Keys: Decryption keys are used to reverse the encryption process, converting the ciphertext back into readable data. The recipient’s private key is required to decrypt the encrypted email and restore the original content. This private key is a closely guarded secret and should not be shared with anyone.
Secure Key Exchange: When using public-key encryption, the secure exchange of encryption and decryption keys is vital. Secure mechanisms are used to ensure that the encryption key is transmitted securely from the sender to the recipient without being intercepted or tampered with. This is typically done through a process known as key exchange or key distribution.
Understanding encryption and decryption keys is essential in comprehending how email encryption works and how it protects the privacy and security of your email communication. By encrypting emails and securely exchanging encryption keys, you can ensure that only the intended recipients can access and read your sensitive information.
Options for Sending Encrypted Emails to Non-Gmail Recipients
Encrypting emails is crucial for maintaining the security and privacy of your communication. However, when it comes to sending encrypted emails to non-Gmail recipients, you may encounter some challenges. Fortunately, there are several options available to ensure the encryption of your emails reaches recipients outside the Gmail ecosystem. Here are some of the options for sending encrypted emails to non-Gmail recipients:
- Use Encryption Software: There are various third-party encryption software applications available that allow you to encrypt your emails regardless of the email service provider your recipient uses. These software applications typically offer encryption algorithms and secure key exchange mechanisms to ensure the confidentiality of your email content.
- Secure File Transfer Protocols: Instead of sending encrypted emails, you can opt to use secure file transfer protocols (SFTP) or secure file sharing services. With these methods, you encrypt the content of your email or attachments independently, and then provide the recipient with a link or access credentials to download the encrypted files securely.
- Encrypted Messaging Apps: If the recipient uses a messaging app that supports end-to-end encryption, you can send the encrypted email content as a message within the app. These apps typically use strong encryption protocols to protect the privacy and security of the messages exchanged.
- PGP/GPG Encryption: Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) encryption is a widely accepted method for sending encrypted emails. With PGP or GPG, you generate a pair of encryption keys – a public key and a private key. You can share your public key with the non-Gmail recipient, who can then use it to encrypt their email messages to you.
- Encrypted Email Providers: There are email service providers that specialize in encrypted email services. These providers offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that your emails are protected throughout the entire communication process, regardless of the recipient’s email service provider. Some examples include ProtonMail and Tutanota.
It’s important to note that when sending encrypted emails to non-Gmail recipients, you should communicate with the recipients beforehand about the encryption method and provide any additional instructions they may need to decrypt and access the encrypted content.
By utilizing these options, you can ensure that your encrypted emails reach non-Gmail recipients securely and maintain the privacy and confidentiality of your communication.
Troubleshooting Common Email Encryption Issues
Email encryption is an effective way to secure your communication, but sometimes issues may arise that prevent seamless encryption or decryption. Here are some common email encryption issues you may encounter and some troubleshooting steps to resolve them:
- Compatibility Issues: Some encryption methods may not be compatible with certain email clients or recipients’ email providers. Ensure that the encryption method you’re using is supported by both your email client and the recipient’s email provider.
- Key Exchange Problems: If you’re using public-key encryption, ensure that you have exchanged the correct public keys with the intended recipients. Verify that the recipients have imported your public key and that you have imported their public keys as well.
- Data Loss: Sometimes, email encryption can result in the loss of data or formatting, especially when using certain encryption tools or methods. Make sure to test the encryption process with small, non-sensitive sample files before encrypting and sending important emails.
- Password Issues: If you’re encrypting attachments with password protection, ensure that you use a strong, unique password and communicate the password to the recipient securely. Double-check that both you and the recipient are using the correct password to decrypt the attachments.
- Phishing and Spoofing: Be cautious of phishing attempts or spoofed emails posing as encryption-related messages. Verify the authenticity of any encryption-related emails, especially if they request sensitive information or ask you to download files or enter login credentials.
- Outdated Encryption Software: Ensure that you’re using the latest encryption software or tools. Outdated software may have vulnerabilities or compatibility issues that can hinder the encryption process or compromise the security of your emails.
- Recipient Verification: Before sending encrypted emails, verify the recipient’s email address to ensure that it’s accurate. Sending encrypted information to the wrong recipient can result in the exposure of sensitive data.
- Recipient Education: If your recipients are not familiar with email encryption methods, provide clear instructions on how to decrypt the emails or attachments. Offer assistance or support in case they encounter any issues during the decryption process.
If you continue to experience difficulties with email encryption, consider reaching out to technical support or seeking guidance from encryption software providers or online forums. Additionally, staying updated with the latest encryption technologies and best practices can help mitigate potential issues and maintain a secure email communication.
By addressing and troubleshooting these common email encryption issues, you can ensure a smooth and secure exchange of sensitive information, protecting the confidentiality and integrity of your communications.
Best Practices for Ensuring Email Privacy and Security
Ensuring the privacy and security of your email communication is essential in today’s digital landscape. By following best practices, you can safeguard your sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. Here are some key practices to implement for email privacy and security:
- Use Strong and Unique Passwords: Create strong passwords for your email accounts, utilizing a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as birthdays or pet names. Additionally, use different passwords for each of your accounts to prevent one compromised password from jeopardizing all of your accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for your email accounts whenever possible. With 2FA, you provide an additional layer of security by requiring a second verification step, such as a unique code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Attempts: Be vigilant when opening emails, especially those from unfamiliar senders or those that seem suspicious. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from emails that may be phishing attempts. Verify the sender’s email address and scrutinize email content for signs of phishing, such as misspellings, grammatical errors, or requests for personal information.
- Regularly Update Software and Operating Systems: Keep your email client, antivirus software, and operating system up to date. Software updates often include security patches and enhancements that protect against known vulnerabilities and threats.
- Encrypt Your Emails: Utilize encryption methods, such as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) or Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME), to encrypt the content of your emails. Encryption adds an extra layer of protection to ensure that only the intended recipients can access and read your email messages.
- Use Secure Wi-Fi Networks: When accessing your email account, make sure to connect to trusted and secure Wi-Fi networks. Avoid using public or unsecured networks, as they increase the risk of data interception and unauthorized access to your email.
- Regularly Back Up Your Emails: Create regular backups of your important emails. This practice ensures that even if your email account is compromised or data is lost, you can still retrieve and restore your essential communications.
- Educate Yourself and Stay Informed: Stay updated with the latest email security practices and threats. Familiarize yourself with various security features and tools available in your email client. Regularly educate yourself on common email scams, phishing techniques, and emerging security trends.
By implementing these best practices, you can significantly enhance the privacy and security of your email communication. Remember, email security is a continuous effort, and staying vigilant and proactive is essential in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your sensitive information.