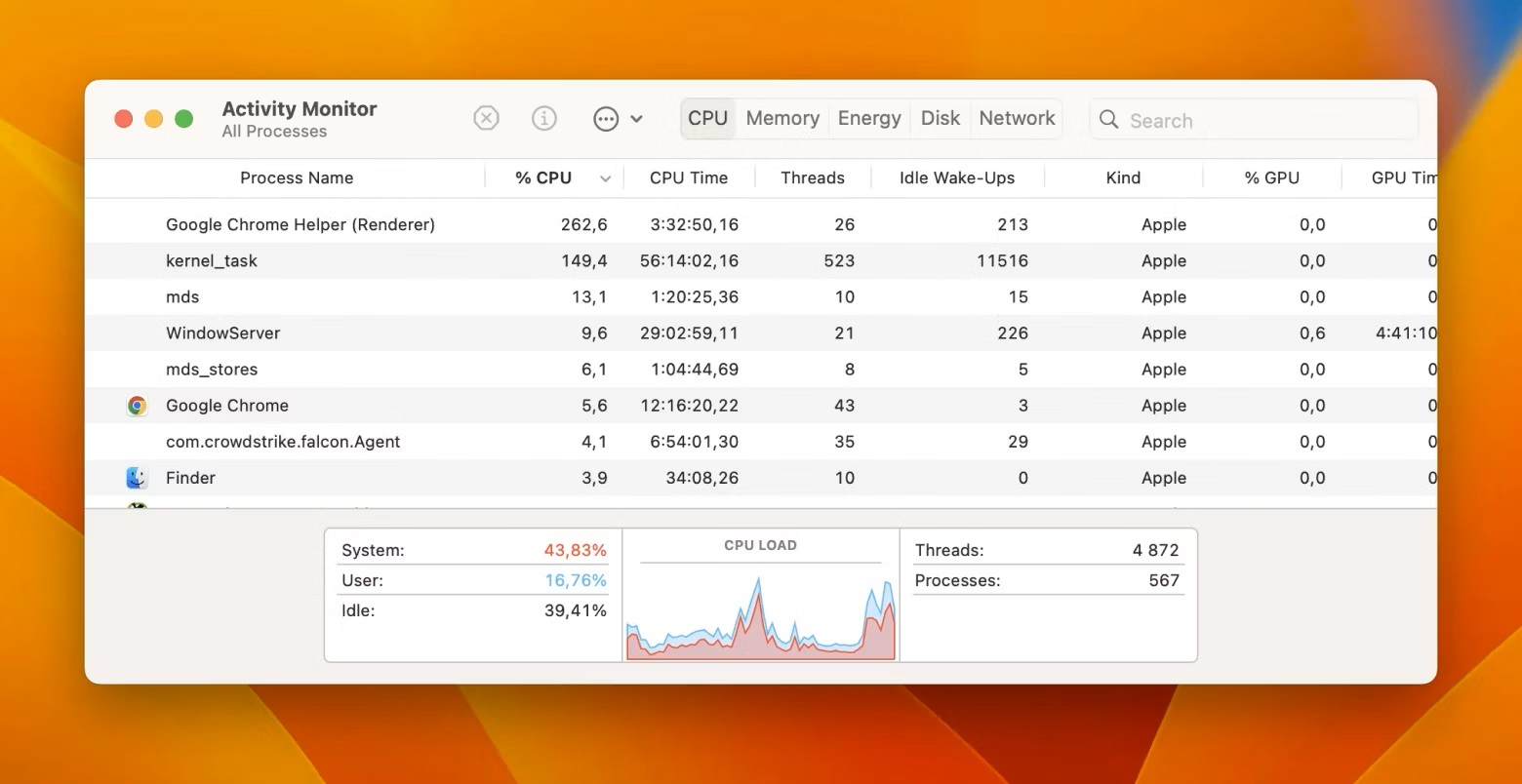
Checking CPU Usage Using Activity Monitor
The Activity Monitor is a built-in utility on Mac that allows you to monitor various system processes, including CPU usage. It provides valuable insights into the performance of your Mac and helps identify any processes that might be consuming an excessive amount of CPU resources.
To access the Activity Monitor:
- Open the “Utilities” folder, which is located within the “Applications” folder.
- Double-click on “Activity Monitor” to launch the utility.
Once you have the Activity Monitor open, you can check the CPU usage in several ways:
1. CPU Usage Overview:
The “CPU” tab in Activity Monitor provides an overview of the CPU usage on your Mac. It displays the percentage of CPU resources being used by various processes, as well as the system’s overall CPU usage.
By default, the processes are listed in descending order of CPU usage, with the most resource-intensive processes shown at the top of the list.
2. Real-Time CPU Usage:
You can toggle between different real-time CPU usage views in the Activity Monitor. The “Floating CPU Window” displays a small floating window that shows CPU usage in real-time. The “Dock Icon” displays a graph in the dock icon that represents CPU usage, updating in real-time.
3. CPU History Graph:
The CPU History graph is a helpful visual representation of CPU usage over time. It provides a detailed view of how the CPU usage has fluctuated, allowing you to identify periods of high or sustained CPU usage.
4. Sorting and Filtering Processes:
You can sort the processes in Activity Monitor based on various parameters, such as CPU usage, memory usage, or energy impact. Additionally, you can use the search bar to filter the processes based on their names or other specific criteria.
By regularly monitoring the CPU usage in Activity Monitor, you can keep track of system performance and detect any unusual activity that may be impacting your Mac’s performance. This information can be particularly useful when troubleshooting high CPU usage or identifying resource-intensive processes.
Understanding CPU Usage
CPU usage refers to the amount of central processing unit (CPU) resources that are being utilized by various processes on your Mac. The CPU is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations, making it a critical component for the overall performance of your system.
Understanding CPU usage can help you identify potential performance issues and optimize your Mac’s resources. Here are a few key aspects to consider:
1. CPU Usage Percentage:
CPU usage is typically represented as a percentage, indicating the proportion of CPU resources being used at a given time. The higher the percentage, the more CPU resources are being utilized.
2. Idle CPU versus Busy CPU:
An idle CPU refers to a state when the CPU is not actively processing tasks. In contrast, a busy CPU occurs when the CPU is actively engaged in executing processes. It’s normal for a CPU to have varying levels of activity, depending on the tasks being performed.
3. System and User CPU Usage:
CPU usage can be divided into two categories: system and user CPU usage. System CPU usage includes the processing required for the operating system and system-level tasks. User CPU usage, on the other hand, involves processes initiated by applications and user interactions.
4. Impact of CPU Throttling:
In some cases, your Mac’s CPU usage may be limited or throttled to prevent overheating and conserve battery life. This can result in decreased performance, especially during high-demand tasks. Monitoring CPU usage can help you gauge whether your CPU is utilizing its full potential or if there are limitations imposed by power management mechanisms.
5. Impact of Background Processes:
Background processes, such as system maintenance tasks or third-party applications, can consume CPU resources even when you’re not actively using your Mac. Monitoring CPU usage allows you to identify any resource-intensive background processes that might be affecting system performance or draining battery life.
By understanding CPU usage and its implications, you can gain insights into how your Mac utilizes its processing power. This knowledge can aid in troubleshooting performance issues, optimizing system resources, and ensuring smoother overall operation.
Monitoring CPU Usage in Real-Time
Monitoring CPU usage in real-time allows you to have a snapshot of how your Mac’s CPU is being utilized at any given moment. This real-time information can help you identify processes that may be causing high CPU usage or excessive load on your system. Here are some methods for monitoring CPU usage in real-time:
1. Activity Monitor:
The Activity Monitor utility on your Mac provides real-time CPU usage data. Open the Activity Monitor, go to the “CPU” tab, and you’ll see a list of processes along with their CPU usage percentages. The list is automatically sorted with the most CPU-intensive process at the top. You can observe the values change in real-time, allowing you to monitor CPU usage as it happens.
2. Floating CPU Window:
In Activity Monitor, you can enable a floating CPU window that displays CPU usage in a small movable window. This window stays on top of other windows, allowing you to monitor CPU usage without needing to keep the main Activity Monitor window open. To enable this feature, go to the View menu in Activity Monitor and choose “Floating CPU Window.”
3. Dock Icon:
Activity Monitor also allows you to display CPU usage as a graph in the dock icon. This graph updates in real-time, providing you with a visual representation of CPU usage without opening the application. To enable this feature, go to the View menu and select “Dock Icon” to display the CPU usage graph in the dock.
4. Third-Party Monitoring Apps:
There are several third-party apps available that specialize in monitoring CPU usage in real-time. These apps often provide more detailed information and customizable features for monitoring CPU usage. Some popular options include iStat Menus, MenuMeters, and Intel Power Gadget.
By monitoring CPU usage in real-time, you can keep a close eye on how your Mac’s resources are being utilized. This allows you to identify any processes or applications that may be causing excessive CPU usage, enabling you to take appropriate action to optimize performance and maintain the smooth operation of your system.
Analyzing CPU Usage Using CPU History Graph
The CPU History graph in Activity Monitor provides a visual representation of CPU usage over a specific period. Analyzing this graph allows you to gain insights into how CPU usage fluctuates and identify patterns or trends that may indicate performance issues or resource-intensive processes. Here’s how you can effectively analyze CPU usage using the CPU History graph:
1. Understanding the Graph:
The CPU History graph in Activity Monitor displays CPU usage over time, with the x-axis representing time and the y-axis representing CPU usage percentage. The graph consists of colored lines or bars, each corresponding to a different CPU core or thread. By default, Activity Monitor displays a combined view of all CPU cores or threads, but you can also view individual cores for more granular analysis.
2. Examining CPU Usage Trends:
By observing the CPU History graph, you can identify trends or patterns in CPU usage over a specified time period. Look for patterns of spikes, sustained high usage, or periods of low or idle CPU usage. These trends can indicate when the CPU is under heavy load, experiencing performance issues, or running efficiently.
3. Identifying High CPU Usage:
High CPU usage is often represented by spikes or prolonged periods of high usage on the CPU History graph. These spikes indicate that certain processes or applications are consuming a significant amount of CPU resources. By identifying these instances of high CPU usage, you can investigate and determine which processes may be responsible for the increased load on your system.
4. Correlating CPU Usage with Activities:
Correlating CPU usage with your activities on the Mac can provide valuable insights. For example, if you notice high CPU usage during specific tasks or when running certain applications, it may indicate that those activities or applications are particularly resource-intensive. This information can help you make informed decisions about managing CPU resources and optimizing performance.
5. Comparing CPU Usage across Cores:
If you have a multi-core CPU, the CPU History graph allows you to compare CPU usage across different cores. This can help you identify imbalances in CPU usage or uneven distribution of workload. Monitoring individual cores can also aid in troubleshooting CPU-related performance issues.
The CPU History graph in Activity Monitor is a powerful tool for analyzing CPU usage trends and identifying resource-intensive processes. By thoroughly examining the graph and understanding its implications, you can make informed decisions to optimize CPU performance and maintain the overall stability and efficiency of your Mac.
Identifying High CPU Usage Processes
High CPU usage can cause a significant impact on your Mac’s performance, leading to slow response times, reduced battery life, and increased system heat. Identifying the processes responsible for high CPU usage allows you to pinpoint the culprits and take appropriate action to optimize performance. Here are some effective methods for identifying high CPU usage processes:
1. Activity Monitor:
The Activity Monitor utility in Mac provides detailed information about CPU usage by various processes. Open Activity Monitor and go to the “CPU” tab. The processes are listed in descending order of CPU usage, with the most resource-intensive processes appearing at the top. Identify any processes that are consistently using a significant amount of CPU resources, as they may be causing high CPU usage.
2. CPU Usage Histogram:
Activity Monitor’s CPU Usage Histogram provides a graphical representation of CPU usage by individual processes. It allows you to visualize CPU usage over a specified time period, making it easier to identify any spikes or sustained high CPU usage by specific processes. Look for processes with consistently high CPU usage to pinpoint potential culprits.
3. Sorting by CPU Usage:
In Activity Monitor, you can sort the processes based on the CPU usage percentage. Click on the “CPU% column” to arrange the processes in ascending or descending order, with the highest CPU usage processes appearing at the top. Sorting by CPU usage helps identify resource-intensive processes that might be causing high levels of CPU usage.
4. Other Resource Impact Metrics:
Activity Monitor also provides additional resource impact metrics, such as memory usage, energy impact, and disk usage. These metrics can help provide a more comprehensive understanding of the overall impact of a process on your Mac’s performance. Consider evaluating processes with high CPU usage in conjunction with their impact on memory, energy, and disk usage.
5. Third-Party Monitoring Tools:
There are third-party monitoring tools available, such as iStat Menus and MenuMeters, that offer more advanced features for monitoring and identifying high CPU usage processes. These tools provide real-time data and customizable options to track CPU usage and identify resource-intensive processes in a more detailed and user-friendly manner.
By using Activity Monitor or third-party monitoring tools, you can effectively identify high CPU usage processes. Once identified, you can take appropriate action, such as quitting or restarting resource-intensive applications, updating software, or troubleshooting potential issues, to optimize CPU usage, enhance performance, and ensure the smooth operation of your Mac.
Checking CPU Usage for Individual Applications
Monitoring CPU usage for individual applications allows you to identify whether specific programs are causing high CPU usage and impacting the overall performance of your Mac. By checking the CPU usage of individual applications, you can make informed decisions about managing resources, optimizing performance, and troubleshooting any issues. Here are some ways to check CPU usage for individual applications:
1. Activity Monitor:
The Activity Monitor utility in Mac provides detailed information about CPU usage for each running application. Open Activity Monitor, go to the “CPU” tab, and you’ll see a list of processes along with their CPU usage percentages. Identify the applications you want to check, and observe their individual CPU usage values. This allows you to determine which applications are consuming the most CPU resources.
2. Sorting Processes:
In Activity Monitor, you can sort the processes based on the CPU usage column. Click on the “CPU%” column to arrange the applications in ascending or descending order of CPU usage. This allows you to quickly identify the applications that are utilizing the most CPU resources, making it easier to pinpoint resource-intensive programs.
3. Application-Specific Monitoring:
Some applications come with built-in monitoring tools to check CPU usage within their own interface. These tools provide real-time data on how much CPU resources an application is utilizing. Check the application’s documentation or preferences to see if it offers any CPU monitoring features.
4. Third-Party Monitoring Tools:
There are third-party monitoring tools available that provide more advanced features for monitoring CPU usage of individual applications. Tools like iStat Menus or MenuMeters allow you to see real-time CPU usage for specific applications in a user-friendly interface, providing a more detailed breakdown of resource consumption.
5. Activity Monitor Energy Impact:
In Activity Monitor, you can also check the “Energy” tab to view the energy impact of individual applications. Higher energy impact may indicate higher CPU usage along with increased power consumption. By monitoring the energy impact, you can identify applications that are resource-intensive and may be causing higher CPU usage.
By checking CPU usage for individual applications, you can better understand how different programs are affecting your Mac’s CPU resources. This knowledge can help you make informed decisions about managing applications, optimizing performance, and troubleshooting any issues related to high CPU usage.
Monitoring CPU Usage on macOS Menu Bar
macOS provides a convenient way to monitor CPU usage right from the menu bar. By adding a CPU usage monitor to the menu bar, you can keep a close eye on the performance of your Mac’s CPU without the need to open any specific applications or utilities. Here’s how you can monitor CPU usage on the macOS menu bar:
1. Activity Monitor:
The built-in Activity Monitor utility in macOS allows you to display CPU usage as a graph in the menu bar. Open Activity Monitor, go to the “View” menu, and select “Dock Icon” or “Floating CPU Window.” This will display a graph representing CPU usage in real-time on the menu bar or as a floating window, respectively.
2. iStat Menus:
iStat Menus is a popular third-party application that offers a range of system monitoring tools, including a customizable CPU usage monitor for the menu bar. With iStat Menus, you can choose to display CPU usage as a graph or numerical value in the menu bar, allowing you to monitor CPU performance with ease.
3. MenuMeters:
MenuMeters is another third-party application that provides system monitoring features, including CPU usage monitoring. It allows you to add CPU usage indicators in the menu bar, providing you with real-time CPU usage information at a glance.
4. Other Third-Party Tools:
There are various other third-party applications available in the App Store that provide CPU usage monitoring in the menu bar. These tools often offer additional features such as customizable appearance, history graphs, and the ability to monitor other system resources alongside CPU usage.
By monitoring CPU usage in the macOS menu bar, you can have continuous visibility into the performance of your Mac’s CPU. This real-time information enables you to identify any abnormal spikes or sustained high usage and take appropriate action to optimize performance and maintain the overall smooth operation of your system.
Using Terminal to Check CPU Usage
For those who prefer command-line tools, the Terminal application in macOS provides a built-in way to check CPU usage. By using specific commands, you can access real-time CPU usage information directly from the Terminal. Here are the steps to check CPU usage using the Terminal:
1. Open Terminal:
Open the Terminal application on your Mac. You can find it in the “Utilities” folder within the “Applications” folder.
2. Use the “top” Command:
In the Terminal, type the command “top” and press Enter. This command provides live data about various system processes, including CPU usage.
3. Observe CPU Usage:
The Terminal window will display a table with information about different processes. The “%” column represents CPU usage. Processes with high CPU usage will be listed at the top. The “CPU usage” value displayed represents the percentage of CPU resources being utilized by that specific process.
4. Sort Processes by CPU Usage:
By default, the “top” command displays processes sorted by the “%CPU” column in descending order. This means that the most CPU-intensive processes are shown at the top. You can press “Shift + P” to toggle between sorting by CPU usage or by process name.
5. Exit the “top” Command:
To exit the “top” command and go back to the Terminal prompt, press “Control + C”. This will stop the continuous update of CPU usage data.
Using the Terminal to check CPU usage provides a lightweight and efficient method for obtaining real-time information about the CPU performance on your Mac. It can be particularly useful for power users, developers, or those who prefer working with the command line interface.
Troubleshooting High CPU Usage Issues
Experiencing high CPU usage on your Mac can significantly impact performance and responsiveness. If you notice persistent high CPU usage or your system feels sluggish, it’s important to troubleshoot and identify the underlying cause. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot high CPU usage issues:
1. Identify Resource-Intensive Processes:
Use Activity Monitor or the Terminal to identify processes that are consuming a significant amount of CPU resources. Determine if any specific applications or processes are consistently causing high CPU usage.
2. Quit or Restart Resource-Intensive Applications:
If you identify any resource-intensive processes or applications, try quitting or restarting them. This can help alleviate high CPU usage and free up system resources.
3. Update Applications and macOS:
Ensure that your applications and macOS are up to date. Developers often release updates that address performance issues and optimize CPU usage. Updating your system and applications may resolve any underlying software-related troubles causing high CPU usage.
4. Disable Startup Items:
Review and disable any unnecessary startup items that may be launching and consuming CPU resources upon system boot. You can manage startup items within the “Users & Groups” section of System Preferences.
5. Check for Malware or Background Processes:
Perform a scan using reliable antivirus software to check for any malware or malicious processes that could be causing high CPU usage. Additionally, ensure that there are no unnecessary background processes or tasks running that are consuming CPU resources.
6. Adjust Energy Saver Settings:
Review your Energy Saver settings and adjust them according to your needs. Reducing screen brightness, enabling Power Nap, or adjusting sleep settings can help optimize CPU usage when your Mac is idle.
7. Reset SMC and PRAM/NVRAM:
Resetting the System Management Controller (SMC) and the parameter random access memory (PRAM) or non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) can help resolve hardware-related issues that may result in high CPU usage. Instructions for resetting these can be found on Apple’s support website.
8. Consider Hardware Upgrades:
If you consistently experience high CPU usage and your Mac’s performance is impacted across various tasks, it might be worth considering a hardware upgrade, such as adding more RAM or upgrading to a faster processor.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can pinpoint the source of high CPU usage and take appropriate action to optimize performance, enhance system responsiveness, and ensure the smooth functioning of your Mac.
Tips for Optimizing CPU Usage on a Mac
Optimizing CPU usage on your Mac can help improve overall performance, enhance system responsiveness, and prolong battery life. By implementing these tips, you can effectively manage CPU resources and ensure efficient utilization. Here are some recommendations for optimizing CPU usage on a Mac:
1. Limit Startup Items:
Minimize the number of applications and processes that launch at startup. This reduces the burden on the CPU and allows your Mac to allocate resources more efficiently.
2. Close Unused Applications:
Regularly close applications that you’re not actively using. Keeping multiple applications open consumes CPU resources, even if they’re running in the background. Closing them frees up CPU power for the tasks at hand.
3. Update Software and Drivers:
Keep your Mac’s operating system, applications, and drivers up to date. Developers often release updates that optimize CPU performance, fix bugs, and improve overall efficiency.
4. Manage Background Processes:
Review and manage background processes running on your Mac. Some apps or processes run in the background and consume CPU resources. Disable or quit unnecessary background processes to optimize CPU usage.
5. Utilize CPU Scheduling:
Use macOS’s built-in CPU scheduling options to prioritize specific applications or processes. This ensures that CPU resources are allocated based on priority, improving performance for critical tasks.
6. Optimize Web Browser Performance:
Web browsers can consume a significant amount of CPU resources. Optimize browser performance by minimizing the number of open tabs and using browser extensions that block resource-heavy ads and scripts.
7. Monitor Resource-Hungry Applications:
Regularly check the CPU usage of applications using Activity Monitor or third-party monitoring tools. Identify any resource-hungry apps and consider alternatives or optimizations to reduce their CPU usage.
8. Manage Graphics Settings:
Adjust your Mac’s graphics settings to optimize CPU usage. Lowering display resolutions, disabling visual effects, and reducing transparency can help free up CPU resources.
9. Upgrade Hardware Components:
If you consistently perform resource-intensive tasks, consider upgrading your Mac’s hardware components. Adding more RAM or upgrading to a faster processor can significantly improve CPU performance.
10. Restart Your Mac:
Regularly restart your Mac to clear temporary files, cache, and processes that might be consuming CPU resources. A fresh start can help optimize CPU usage and improve overall system performance.
By following these tips, you can effectively optimize CPU usage on your Mac, leading to improved performance, better multitasking capabilities, and an overall smoother user experience.