What is DNS
DNS, which stands for Domain Name System, is an essential component of the internet infrastructure. It acts as a directory that translates easy-to-remember domain names, like www.example.com, into the IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the internet. In simple terms, DNS enables users to access websites and other online resources by typing in domain names rather than lengthy numerical IP addresses.
Think of DNS as a phonebook for the internet. When you enter a website URL into your browser, your device sends a request to the DNS server to find the corresponding IP address. The DNS server then replies with the IP address, allowing your browser to establish a connection and retrieve the website’s content.
Without DNS, we would need to memorize long strings of numbers to access websites, which would be both inconvenient and impractical. DNS makes the internet user-friendly by providing a system that simplifies website addressing and navigation.
Moreover, DNS not only translates domain names into IP addresses, but it also helps to facilitate other essential internet services like email delivery and online gaming. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that data is routed accurately and efficiently across the internet.
Overall, DNS is a fundamental technology that underpins the smooth functioning of the internet. It seamlessly translates domain names into recognized IP addresses, making it easier for users to access online resources. Understanding the significance of DNS is crucial when it comes to configuring and optimizing your network settings.
Reasons to Change DNS Server Settings
Changing your DNS server settings can provide several advantages and benefits for your internet browsing experience. Here are some reasons why you might consider changing your DNS server settings:
1. Improved Speed and Performance: By using a reliable DNS server with faster response times, you can potentially speed up your internet connection. This is especially beneficial if your internet service provider’s default DNS server is slow or experiencing high traffic.
2. Enhanced Security: Some DNS servers offer additional security features, such as blocking access to malicious websites and preventing phishing attacks. Changing to a DNS server with robust security measures can help protect your system from online threats and malware.
3. Access to Geo-restricted Content: Changing your DNS server settings can enable you to bypass geographic restrictions imposed by certain websites or streaming platforms. By using a DNS server located in a different region, you can access content that may be restricted in your current location.
4. Filtering and Parental Controls: Certain DNS servers offer content filtering and parental control features. This can be beneficial for families, allowing parents to restrict access to inappropriate websites and content for their children.
5. Reliability and Redundancy: Some DNS servers are known for their high uptime and reliability. By selecting a reliable DNS server, you can ensure that your internet connection remains consistently available and responsive, even during peak usage times or server outages.
6. Customization and Configuration: Changing DNS server settings gives you the flexibility to customize and configure your internet connection according to your preferences. You can choose DNS servers that align with your specific needs, whether that’s prioritizing speed, security, or other factors.
In summary, changing your DNS server settings can result in improved speed, enhanced security, access to geo-restricted content, filtering and parental control options, reliability, and the ability to customize your internet connection. Considering these benefits, it may be worth exploring different DNS servers to optimize your online experience.
How to Find Your Current DNS Server
Before you can change your DNS server settings, it’s important to know the current DNS server used by your device or network. Here are a few methods to find your current DNS server:
1. Using Command Prompt/Terminal: On Windows, open the Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the search bar and selecting it from the results. On Mac, open the Terminal by going to Applications > Utilities > Terminal. Once opened, type “ipconfig /all” on Windows or “networksetup -getdnsservers Wi-Fi” on Mac and press Enter. Look for the “DNS Servers” or “DNS Servers configuration” section to find the IP addresses of your current DNS servers.
2. Network Settings on Windows: On Windows, you can also find the current DNS server settings through the network adapter settings. Right-click on the network icon in the system tray, select “Open Network & Internet settings,” then click on “Change adapter options.” Right-click on your active network connection, choose “Properties,” and click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” or “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6).” The DNS server addresses will be listed in the respective properties window.
3. System Preferences on Mac: On Mac, go to System Preferences from the Apple menu and click on “Network.” Select the active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), then click on “Advanced” and navigate to the “DNS” tab. You will find the current DNS server addresses listed there.
4. Router Configuration Page: If your DNS settings are configured on your router, you can find the current DNS server addresses in the router’s configuration page. Open a web browser, enter your router’s IP address in the address bar (typically 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1), and log in with your credentials. Look for the DNS settings or DHCP settings to find the current DNS server addresses.
Once you have located the current DNS server addresses, make note of them before proceeding with any changes. This will allow you to revert to your original settings if needed. Keep in mind that the methods mentioned above may vary slightly depending on your operating system version and network setup.
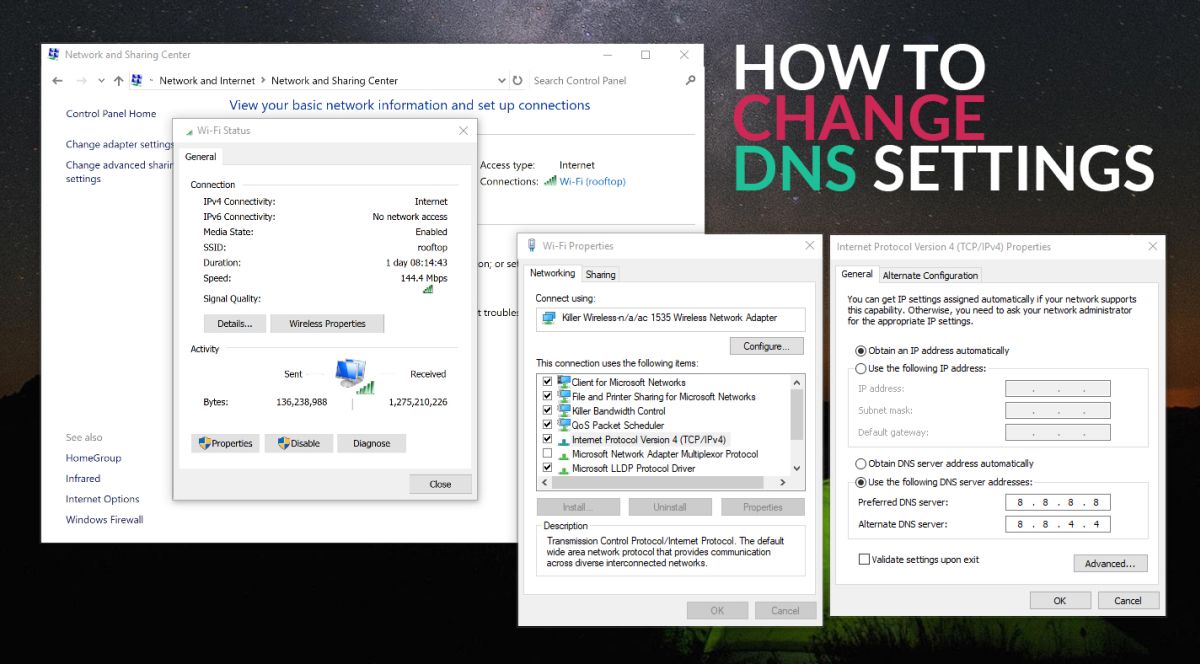
Changing DNS Server Settings on Windows
If you’re using a Windows operating system, you can easily change your DNS server settings by following these steps:
1. Open Network Settings: Click on the Start menu and go to “Settings” (the Gear icon). Select “Network & Internet” to open the network settings.
2. Select Network Connection: In the left-hand menu, choose the type of network connection you want to change the DNS settings for (such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
3. Open Adapter Properties: Under the “Related settings” section, click on “Change adapter options.” This will open the network connections window.
4. Access Network Adapter Properties: Right-click on the network connection you want to modify (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and select “Properties” from the context menu.
5. Choose Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4): In the network properties window, scroll down and locate “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” in the list. Select it and click on the “Properties” button.
6. Specify Custom DNS Server: In the properties window, select the option “Use the following DNS server addresses.” Enter the preferred DNS server address provided by your DNS provider in the “Preferred DNS server” field. If available, enter the alternate DNS server address in the “Alternate DNS server” field. You can also use public DNS servers such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
7. Save Changes: After entering the DNS server addresses, click on the “OK” button to save the changes and exit the properties window.
8. Flush DNS Cache: Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (right-click on the Start button and select “Command Prompt (Admin)”). Type the command “ipconfig /flushdns” and press Enter to clear the DNS cache and apply the changes immediately.
Once you have completed these steps, the DNS server settings for your selected network connection will be updated. Repeat the process for any other network connections you want to modify. Keep in mind that changing DNS server settings on a Windows device will only affect that specific device and not the entire network.
Changing DNS Server Settings on Mac
If you’re using a Mac computer, adjusting the DNS server settings is a straightforward process. Follow the steps below to change the DNS server settings on your Mac:
1. Open System Preferences: Click on the Apple menu icon in the top-left corner of your screen and select “System Preferences” from the dropdown menu.
2. Select Network: In the System Preferences window, locate and click on the “Network” icon. This will open the network settings.
3. Choose Network Connection: From the left-hand sidebar, select the network connection you want to change DNS settings for (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
4. Access Advanced Settings: Click on the “Advanced” button located in the bottom-right corner of the Network settings window. This will open the advanced settings for the selected network connection.
5. Navigate to DNS Tab: In the advanced settings window, click on the “DNS” tab. This is where you can modify the DNS server settings.
6. Add or Remove DNS Servers: By default, you’ll see a list of DNS servers that your Mac currently uses. To add a new DNS server, click on the “+” button beneath the DNS servers list. Enter the IP address of your preferred DNS server and press Enter. To remove a DNS server, select it from the list and click on the “-” button.
7. Reorder DNS Servers (Optional): You can prioritize the order in which your Mac uses DNS servers by clicking and dragging the entries in the list.
8. Save Changes: Once you’ve made the necessary adjustments to the DNS server settings, click on the “OK” button to save the changes and close the network settings window.
9. Apply Changes: To ensure that the changes take effect, you may need to disconnect and reconnect to your network connection or restart your Mac.
It’s worth noting that modifying DNS server settings on your Mac will only affect the selected network connection on that particular device. If you want to change DNS settings for multiple devices on your network, you may need to adjust the settings on your router or access point instead.
Changing DNS Server Settings on iPhone/iPad
If you’re using an iPhone or iPad, you can adjust the DNS server settings by following these simple steps:
1. Open Settings: Tap on the “Settings” app on your iPhone or iPad’s home screen to open the settings menu.
2. Select Wi-Fi: In the settings menu, tap on the “Wi-Fi” option. This will display the available Wi-Fi networks.
3. Choose your Wi-Fi Network: Locate and select the Wi-Fi network that you are currently connected to. You will see a blue checkmark next to the network name once it’s selected.
4. Configure DNS Settings: On the Wi-Fi network details screen, scroll down until you find the “DNS” section. By default, it is set to “Automatic.” Tap on the “DNS” option to change it.
5. Remove Existing DNS Servers: If you see any existing DNS server addresses listed under “DNS,” tap on the “-” button next to each entry to remove them.
6. Add Custom DNS Server: To add a custom DNS server, tap on the “+” button. Type in the IP address of your preferred DNS server and tap on “Save” or “Done” when you’re finished. You can use public DNS servers like Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1). Repeat this step if you want to add multiple DNS servers.
7. Verify DNS Settings: Double-check the DNS server addresses listed under “DNS” to ensure they are correct.
8. Connect to the Network: Once you have configured the DNS settings, tap on the back arrow to return to the Wi-Fi settings menu. To apply the changes, either connect to a different Wi-Fi network and then reconnect to your preferred network, or turn off Wi-Fi and then turn it back on.
By following these steps, you can easily change the DNS server settings on your iPhone or iPad. It’s important to note that these changes will only affect the Wi-Fi network you configured and not your cellular network.
Changing DNS Server Settings on Android Devices
If you’re using an Android device, you can modify the DNS server settings by following these steps:
1. Open Settings: From your Android device’s home screen, swipe down from the top to access the notification panel, then tap on the gear-shaped Settings icon to open the Settings menu.
2. Select Wi-Fi or Network & Internet: Depending on your Android device and the version of Android OS you’re running, look for either the “Wi-Fi” or “Network & Internet” option and tap on it. This will bring up the network settings.
3. Choose Wi-Fi Settings: In the Wi-Fi or Network & Internet settings, locate and tap on the Wi-Fi network that you are currently connected to. This will open the Wi-Fi network settings.
4. Modify Network Options: On the Wi-Fi network details screen, look for and tap on the “Advanced” or “Edit” button, which will open the advanced network options.
5. Change IP Settings: In the advanced network options, find and tap on the “IP settings” or “IP configuration” field. A dropdown menu will appear with different options. Select “Static” as the IP configuration.
6. Enter DNS Server Addresses: After selecting “Static” as the IP configuration, a set of fields will appear where you can enter the DNS server addresses. Tap on the “DNS 1” field and enter the IP address of your preferred DNS server. If available, you can also enter an optional secondary DNS server address in the “DNS 2” field.
7. Save Changes: Once you have entered the DNS server addresses, tap on the “Save” or “Apply” button to save the changes and exit the settings menu. Some devices may require you to tap on a checkmark or “Done” button to confirm the changes.
8. Reconnect to Wi-Fi: To apply the changes, disconnect from the Wi-Fi network by tapping on the network name and selecting “Forget” or “Disconnect.” Then reconnect to the same Wi-Fi network by selecting it from the available networks list.
By following these steps, you can easily change the DNS server settings on your Android device. It’s important to note that the process may vary slightly depending on your device model and Android OS version. These changes will only affect the Wi-Fi network you configured and not your mobile data connection.
Changing DNS Server Settings on Router
If you want to change the DNS server settings for your entire network, you can do so by accessing your router’s configuration page. The steps to change the DNS server settings on a router may vary depending on the router model and brand, but the following general steps should guide you through the process:
1. Access Router Configuration: Open a web browser on a device connected to your network and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar. This IP address is usually found on the bottom of the router or in the manual. Common default IP addresses include 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, or 192.168.2.1.
2. Enter Login Credentials: You will be prompted to enter your router’s username and password. If you haven’t changed them, the default credentials are often found in the router’s manual or on the manufacturer’s website. If you’ve previously changed the login details and don’t remember them, you may need to perform a factory reset on the router.
3. Navigate to DNS Settings: Once logged in, look for the DNS settings or DHCP settings in the router’s configuration page. The location of these settings may vary depending on your router’s interface. It is often found under network settings or internet settings.
4. Modify DNS Server Addresses: In the DNS settings or DHCP settings section, you will find fields to enter Primary DNS or DNS Server 1 and Secondary DNS or DNS Server 2. You can enter the IP addresses of your preferred DNS servers here. If you don’t know the IP addresses, you can use public DNS servers such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
5. Save Changes and Restart Router: After entering the DNS server addresses, save the changes and restart your router. This will apply the new DNS server settings to your entire network.
Keep in mind that changing DNS server settings on your router will affect all devices connected to the network. It allows every device on your network to use the new DNS servers without needing to individually configure each device. If you encounter any issues or difficulties during the process, consult your router’s manual or contact your router’s manufacturer for further assistance.
Testing Your New DNS Settings
After changing your DNS server settings, it’s important to test whether the new settings are functioning correctly. Here are a few methods to verify and test your new DNS settings:
1. Browsing Tests: Open a web browser on your device and visit various websites. If web pages load quickly and without any errors, your DNS settings are likely functioning properly. Be sure to visit a few different websites to get a comprehensive test.
2. DNS Leak Test: Perform a DNS leak test to ensure that your DNS requests are being handled by the new DNS servers. There are several online tools available that can help you check for DNS leaks. Simply search for “DNS leak test” and choose a reputable tool to use. The test should confirm whether your DNS requests are being sent to the DNS servers you specified in your settings.
3. Ping Test: Open the command prompt or terminal on your device and enter the command “ping
4. Flush DNS Cache: Flush the DNS cache on your device to ensure that any old DNS settings are cleared. The process of flushing the DNS cache varies depending on your operating system. You can search online for the specific steps on how to flush the DNS cache for your particular device and operating system.
5. External DNS Tools: There are online tools available that allow you to check whether your DNS settings have successfully propagated. These tools can provide information about the DNS servers your device is using and the IP addresses associated with them. Some popular tools include “DNS Checker,” “DNS Propagation Checker,” and “What’s My DNS.”
By performing these tests, you can ensure that your new DNS settings are correctly functioning and providing the expected benefits. If you encounter any issues or inconsistencies during the testing process, double-check your DNS server configurations and verify that you have entered the correct IP addresses. Additionally, if you experience any problems with certain websites or services, you may consider reverting to your previous DNS settings or contacting your DNS provider for further assistance.
Common DNS Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
While changing DNS server settings can enhance your internet experience, you may encounter some common DNS issues along the way. Here are a few common DNS issues and troubleshooting tips to help you resolve them:
1. Slow or Unresponsive Internet: If you’re experiencing slow or unresponsive internet after changing DNS settings, try reverting to your previous DNS settings or switch to a different DNS server. Sometimes, the DNS server you selected may be experiencing high traffic or connectivity issues.
2. DNS Server Not Responding: If you receive a “DNS server not responding” error message, try restarting your router and device. This can often resolve temporary connectivity issues. Additionally, ensure that the DNS server addresses you entered are correct.
3. DNS Cache Issues: Your device maintains a DNS cache to store recent DNS lookup results. If you’re having trouble accessing a specific website after changing DNS settings, try clearing your DNS cache. This can be done by flushing the DNS cache through command prompt or terminal, or by restarting your device.
4. Incorrectly Entered DNS Server: Double-check that you have entered the correct DNS server addresses in your network settings. Even a single digit or character error can cause connectivity issues. If possible, copy and paste the DNS server addresses to avoid any typographical mistakes.
5. Firewall or Security Software: Some firewall or security software may interfere with DNS server settings. If you’re experiencing issues, temporarily disable any firewall or security software and check if the DNS issue persists. Adjust the settings of the software if necessary.
6. Clear Browser Cache: In some cases, DNS-related issues can be resolved by clearing your web browser’s cache. This helps to eliminate any stored DNS-related data that may be causing conflicts or delays. Clearing the cache differs between browsers, so check your browser’s support documentation for specific instructions.
7. Contact Your DNS Provider: If you have followed the troubleshooting steps above and are still encountering DNS issues, it may be worth reaching out to your DNS provider for further assistance. They can offer insights specific to their own service and help troubleshoot any issues.
By applying these troubleshooting tips, you can effectively resolve common DNS issues and ensure a smooth and reliable internet browsing experience. If the issue persists or you require further assistance, consider consulting with a technical expert or contacting your internet service provider for additional support.