How to Disable Face ID on iPhone 11
Disabling Face ID on your iPhone 11 is a straightforward process that can be accomplished in just a few simple steps. Whether you're looking to temporarily turn off Face ID or completely deactivate the feature, the following instructions will guide you through the process.
-
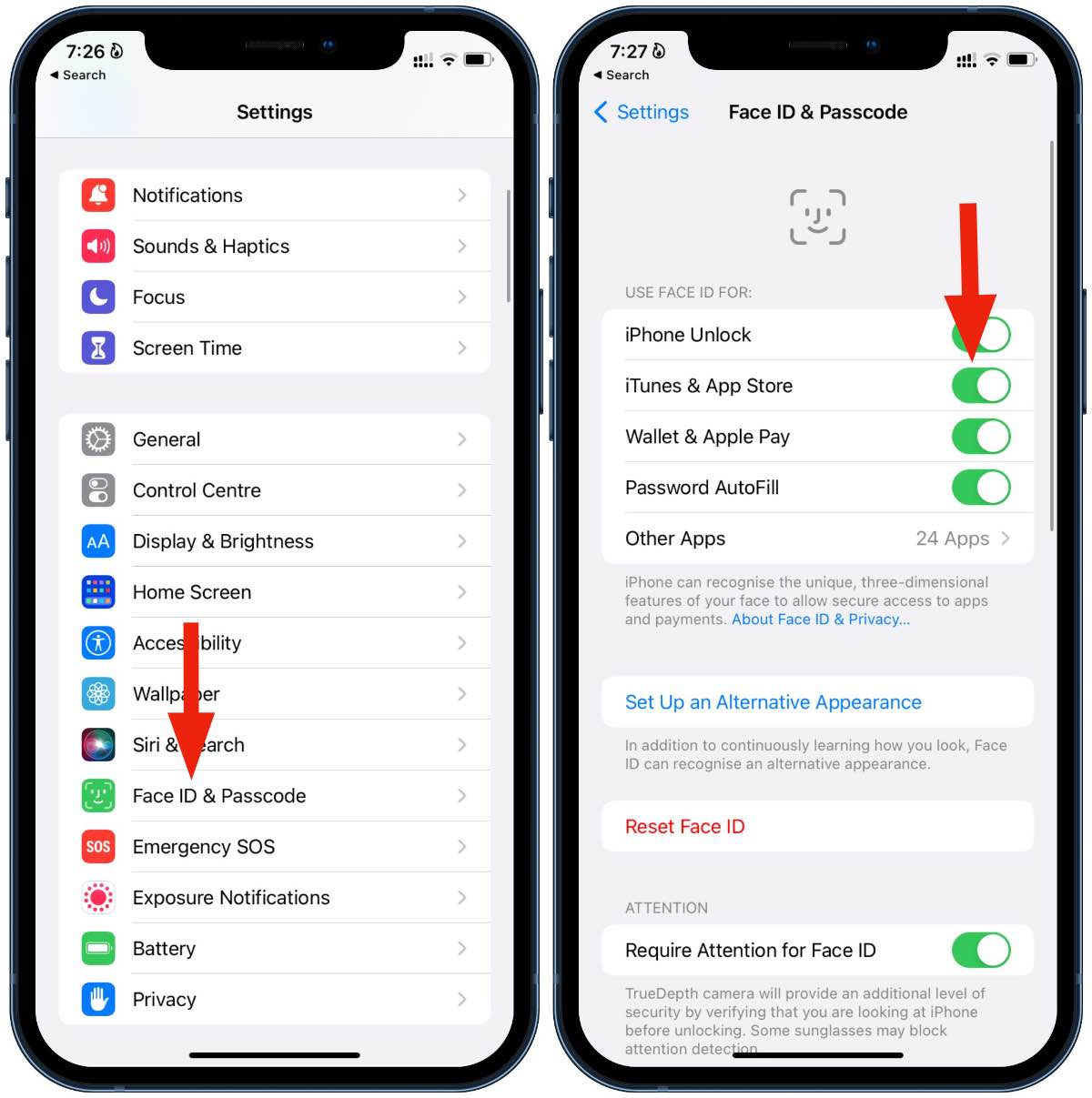
Access the Settings: Begin by unlocking your iPhone 11 and navigating to the "Settings" app on the home screen. The gear-shaped icon will lead you to the device's settings menu.
-
Locate Face ID & Passcode: Within the "Settings" menu, scroll down and tap on "Face ID & Passcode." You will be prompted to enter your device passcode to access the Face ID settings.
-
Disable Face ID: Once you have entered your passcode, you will see the option to "Turn Off Face ID." Tap on this option to disable Face ID on your iPhone 11. You may be asked to confirm your decision by entering your passcode once again.
-
Confirmation: After turning off Face ID, the feature will be disabled, and your iPhone 11 will no longer use facial recognition for authentication.
It's important to note that disabling Face ID can impact the convenience of unlocking your device and accessing secure apps and data. However, there are situations where temporarily turning off Face ID may be necessary, such as when traveling to countries where biometric data privacy is a concern or when interacting with individuals who may need to access your device in an emergency.
By following these steps, you can easily disable Face ID on your iPhone 11, providing you with greater control over the security and privacy of your personal data.
Reasons to Disable Face ID on iPhone 11
There are several valid reasons why individuals may choose to disable Face ID on their iPhone 11. While Face ID offers a convenient and secure method of unlocking the device and authenticating various actions, there are circumstances where disabling this feature becomes necessary. Understanding these reasons can help users make informed decisions about when to utilize or deactivate Face ID.
Privacy Concerns
In today's digital age, privacy has become a paramount concern for many individuals. Some users may feel uncomfortable with the idea of their facial biometric data being stored and utilized by their devices. Disabling Face ID can provide a sense of control over personal biometric information, especially for those who prioritize privacy and data security.
Accessibility for Others
In certain situations, individuals may need to grant access to their iPhone 11 to others who are unable to use Face ID due to physical limitations or other reasons. By disabling Face ID, users can ensure that alternative authentication methods, such as a passcode, can be used to allow access to the device, accommodating the needs of others.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
In some regions or professions, there may be legal or regulatory restrictions related to the use of biometric data. Individuals operating in such environments may choose to disable Face ID on their iPhone 11 to comply with specific laws or industry regulations governing the collection and use of biometric information.
Travel and Security
When traveling to certain countries or regions where biometric data privacy laws and regulations differ from those in the user's home country, disabling Face ID can serve as a proactive measure to protect personal data. This can be particularly relevant for individuals concerned about potential unauthorized access to their devices or the collection of biometric information by foreign entities.
Temporary Security Measures
In specific scenarios, users may opt to temporarily disable Face ID as a security precaution. For instance, during periods of heightened security concerns or when interacting with individuals who may need to access the device in an emergency, disabling Face ID can provide an additional layer of control over the security of the iPhone 11.
By considering these reasons, individuals can make informed decisions about when to disable Face ID on their iPhone 11, aligning the device's security features with their specific privacy, accessibility, and regulatory needs.
Security Concerns with Face ID on iPhone 11
As with any biometric authentication technology, Face ID on the iPhone 11 presents certain security concerns that users should be mindful of. While Face ID offers a convenient and sophisticated method of unlocking the device and securing sensitive information, it is essential to understand the potential vulnerabilities associated with this feature.
One of the primary security concerns with Face ID pertains to the possibility of unauthorized access through facial recognition spoofing. Although Apple has implemented advanced anti-spoofing measures to prevent unauthorized individuals from bypassing Face ID using photos or masks, the potential for sophisticated spoofing techniques remains a consideration. This raises concerns about the reliability of Face ID in scenarios where unauthorized individuals attempt to gain access to a user's iPhone 11 by replicating their facial features.
Additionally, there are privacy implications related to the storage and usage of facial biometric data for Face ID. While Apple emphasizes the security and encryption of biometric information stored on the device, some users may have reservations about the potential risks associated with the storage of their facial data. Concerns about data breaches, unauthorized access to biometric templates, and the implications of compromised facial recognition data contribute to the overall security considerations associated with Face ID.
Furthermore, the reliance on facial recognition as the primary authentication method raises questions about the device's security in scenarios where the user's face may not be readily available or recognizable. For instance, low-light environments, facial obstructions, or changes in the user's appearance due to factors such as illness or injury may impact the effectiveness of Face ID. These limitations underscore the importance of alternative authentication methods to ensure consistent and reliable access to the iPhone 11, particularly in challenging or unforeseen circumstances.
Moreover, the potential for coercion or unauthorized access through physical force raises security concerns for individuals using Face ID. While Face ID is designed to require the user's attention and active participation for authentication, there are conceivable scenarios where users may face coercion or physical pressure to unlock their device using Face ID, compromising their security and privacy.
By acknowledging these security concerns, users can make informed decisions about the utilization of Face ID on their iPhone 11, taking into account the potential vulnerabilities and privacy implications associated with this biometric authentication technology. Understanding these considerations can empower users to implement additional security measures and make conscious choices regarding the use of Face ID in various contexts.
Alternative Security Measures for iPhone 11
In addition to Face ID, the iPhone 11 offers a range of alternative security measures that users can leverage to enhance the protection of their device and sensitive data. These supplementary security features provide users with flexibility and options to customize their device's security based on their specific needs and preferences.
Passcode Authentication
The traditional passcode authentication method remains a fundamental and reliable security measure for the iPhone 11. By setting a strong alphanumeric passcode, users can establish a robust barrier against unauthorized access to their device. The passcode serves as a fail-safe authentication method, particularly in situations where Face ID may not be feasible or when users prefer a more conventional approach to device security.
Two-Factor Authentication
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to the iPhone 11. By requiring a secondary verification step, such as a unique code sent to a trusted device or phone number, 2FA mitigates the risk of unauthorized access, especially in the event of a compromised password. This additional security measure fortifies the protection of sensitive accounts and data linked to the iPhone 11.
Biometric Restrictions
In conjunction with Face ID, users can implement biometric restrictions to control the accessibility of certain features and sensitive data on their iPhone 11. By configuring settings to require Face ID or Touch ID for specific actions, such as unlocking the device, authorizing app purchases, or accessing sensitive information, users can tailor the level of biometric authentication required for different aspects of their device usage.
Find My iPhone
The "Find My" app, integrated with the iPhone 11, offers a suite of security features that enable users to locate, lock, and remotely erase their device in the event of loss or theft. By leveraging the capabilities of Find My iPhone, users can safeguard their device and personal data, adding an additional layer of security beyond biometric authentication methods.
Secure Enclave and Data Encryption
The iPhone 11 incorporates a secure enclave and robust data encryption to protect sensitive information stored on the device. Leveraging hardware-based security features, the secure enclave ensures the integrity of biometric data and cryptographic operations, while data encryption safeguards user data, preventing unauthorized access in the event of device theft or unauthorized tampering.
By embracing these alternative security measures, users can bolster the protection of their iPhone 11, complementing the functionality of Face ID with additional layers of security tailored to their individual preferences and security requirements. These measures collectively contribute to a comprehensive security posture, empowering users to safeguard their device and personal data effectively.
How to Re-enable Face ID on iPhone 11
Re-enabling Face ID on your iPhone 11 is a simple process that allows you to restore the convenience and security of facial recognition authentication. Whether you previously disabled Face ID for specific reasons or temporarily turned off the feature, re-enabling it involves navigating through the device settings to reactivate this biometric authentication method.
To re-enable Face ID on your iPhone 11, follow these straightforward steps:
-
Access the Settings: Begin by unlocking your iPhone 11 and locating the "Settings" app on the home screen. The gear-shaped icon will lead you to the device's settings menu.
-
Navigate to Face ID & Passcode: Within the "Settings" menu, scroll down and tap on "Face ID & Passcode." You will be prompted to enter your device passcode to access the Face ID settings.
-
Enable Face ID: Once you have entered your passcode, you will see the option to "Turn On Face ID." Tap on this option to re-enable Face ID on your iPhone 11. You may be asked to re-register your face to ensure accurate and secure facial recognition.
-
Confirmation: After re-enabling Face ID, the feature will be activated, allowing you to utilize facial recognition for unlocking your device, authorizing secure actions, and accessing personal data.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly re-enable Face ID on your iPhone 11, restoring the advanced biometric authentication feature to enhance the security and convenience of your device usage.
Re-enabling Face ID provides users with the flexibility to leverage the advanced security and convenience benefits offered by facial recognition technology. Whether for personal preference, situational requirements, or regulatory compliance, the ability to easily re-enable Face ID empowers users to tailor their device's security features to align with their specific needs and preferences.
With Face ID re-enabled, users can once again experience the seamless and intuitive authentication process that enhances the overall user experience while maintaining robust security measures to safeguard their iPhone 11 and sensitive data.