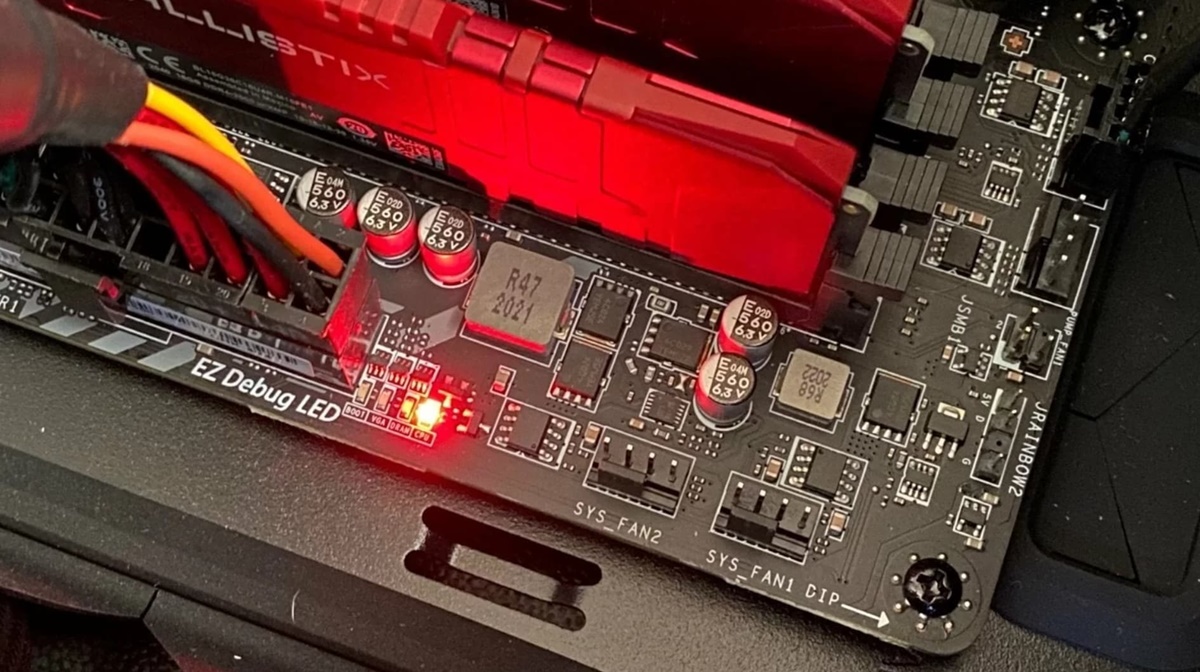
Common Red Light Indicators on a Motherboard
A red light glowing on your motherboard can be an alarming sight for any computer user. It serves as a warning sign that something is amiss with your system. Understanding the meaning behind these red lights can help you diagnose and resolve the issues promptly. Here are some of the most common red light indicators you may encounter on a motherboard:
- CPU Error: A red light indicating a CPU error typically suggests that there might be a problem with the processor. It could be due to a loose connection, a damaged CPU, or an incompatible processor. This issue should be addressed promptly to avoid further damage to the system.
- RAM Issue: If you see a red light associated with the RAM, it indicates a problem with the memory modules. This could be due to faulty RAM sticks, incorrect seating, or incompatible RAM with the motherboard. Reseating the RAM or replacing faulty modules can often resolve this issue.
- Graphics Card Error: A red light related to the graphics card points to a potential problem with the GPU. This can occur due to a faulty graphics card, insufficient power supply, or incompatible drivers. Troubleshooting the graphics card or seeking professional assistance may be necessary.
- Overheating Warning: Overheating is a common cause of red lights on motherboards. When components such as the CPU or GPU reach unsafe temperatures, the motherboard triggers the red light as a protective measure. Ensuring proper airflow, cleaning dust buildup, and applying thermal paste can help alleviate overheating issues.
- Power Supply Failure: In some cases, a red light on the motherboard can indicate a problem with the power supply unit (PSU). This could be due to a faulty PSU, insufficient power delivery, or incompatible power cables. Replacing the PSU or checking the power connections may be necessary to resolve this issue.
While these are the most common reasons for a red light on a motherboard, it’s important to note that the exact indicators and their meanings can vary depending on the manufacturer and specific model of your motherboard. Checking the motherboard manual or consulting with technical support can provide further insights specific to your system.
Understanding these common red light indicators can help you troubleshoot issues with your motherboard more effectively. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the meaning of each red light indicator and provide solutions to resolve these problems.
Understanding the Meaning of the Red Light
When faced with a red light on your motherboard, it’s crucial to understand its meaning in order to diagnose and address the issue effectively. While the specific indications can vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer and model, there are some common meanings behind these red lights:
Hardware Failure: In many cases, a red light indicates a hardware failure or error within the system. This could be related to the CPU, RAM, graphics card, or power supply. It serves as a warning sign that something is wrong and requires attention.
Overheating: One common cause of red lights on a motherboard is overheating. When components reach unsafe temperatures, the motherboard triggers a red light as a precautionary measure. This helps protect the system from potential damage due to excessive heat.
Incompatible or Faulty Components: Another possible reason for a red light is the use of incompatible or faulty components. This could include RAM modules, graphics cards, or even the CPU itself. It’s essential to ensure compatibility and quality when selecting and installing components to avoid compatibility issues.
Power Supply Problems: The power supply unit (PSU) plays a critical role in supplying power to the system. If there are issues with the power supply, such as insufficient power delivery or damaged cables, it can cause a red light to appear on the motherboard.
BIOS Errors: Sometimes, a red light can indicate errors within the system’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). This can be due to outdated or corrupt BIOS firmware, misconfigured settings, or issues during the BIOS update process.
It’s important to note that the specific indicators and their meanings can vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer and model. To gain a better understanding of the red light indicators, it is recommended to consult the motherboard manual or reach out to the manufacturer’s technical support.
By understanding the meaning behind the red light on your motherboard, you can start troubleshooting the issue. In the following sections, we will discuss common red light error codes and their solutions, as well as steps to troubleshoot and resolve specific hardware-related problems associated with the red light indicator.
Red Light Error Codes and Their Solutions
When encountering a red light on your motherboard, it often comes with error codes that can provide valuable insight into the underlying issue. These error codes can vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the motherboard. Here are some common red light error codes and their potential solutions:
- CPU Error: If you receive a CPU-related error code, it could indicate a problem with the processor. Start by ensuring that the CPU is properly seated and connected to the motherboard. If the issue persists, try reseating the CPU, checking for bent pins, and updating the BIOS to the latest version to address any compatibility issues.
- RAM Issue: When faced with a RAM-related error code, begin by reseating the RAM modules to ensure a secure connection. If the problem persists, try testing the RAM modules individually to identify any faulty sticks. Updating the motherboard’s BIOS and installing the latest chipset drivers can also help resolve compatibility issues.
- Graphics Card Error: Error codes related to the graphics card can often be resolved by ensuring that the GPU is properly seated in the PCIe slot. Check that the power connectors are securely attached and that the card is compatible with the motherboard. Updating the graphics card drivers to the latest version and adjusting the BIOS settings may also help resolve this issue.
- Overheating Warning: If the red light is triggered due to overheating, the first step is to address the cooling system. Ensure that all fans are functional and properly cooling the components. Clean any dust buildup that may be obstructing airflow. Applying high-quality thermal paste to the CPU and GPU can also help dissipate heat more effectively.
- Power Supply Failure: In the case of a power supply issue, check that all power connectors are securely attached to the motherboard and other components. Verify that the PSU is supplying sufficient power to meet the system’s requirements. If the power supply unit itself is faulty, it may need to be replaced with a new one.
Remember, specific error codes and their solutions can vary depending on the motherboard model and manufacturer. Consulting the motherboard manual or reaching out to technical support can provide more accurate solutions tailored to your system.
In the next section, we will delve into common hardware-related problems that can cause the red light to appear on the motherboard and discuss troubleshooting steps to resolve them.
Overheating Issues and the Red Light Indicator
One of the most common causes of a red light appearing on a motherboard is overheating. When components within the system, such as the CPU or GPU, reach unsafe temperatures, the motherboard triggers the red light as a warning sign. Understanding and addressing overheating issues promptly is crucial to prevent potential damage to your system.
Several factors can contribute to overheating, including poor airflow, dust buildup, improper cooling, or inadequate thermal paste application. Here are some steps you can take to address overheating issues and resolve the red light indicator:
- Ensure Proper Airflow: Make sure that your system has adequate airflow by organizing the cables within your case, maintaining a clean and unobstructed path for air to flow, and positioning the case in a well-ventilated area.
- Clean Dust Buildup: Dust can accumulate on fans, heat sinks, and other components, hindering proper heat dissipation. Regularly clean your system using compressed air or an anti-static brush to remove any dust buildup.
- Check Cooling System: Make sure that all fans, including CPU and case fans, are functioning properly. Replace any faulty or ineffective fans that are not adequately cooling the system.
- Apply Thermal Paste: Proper application of thermal paste between the CPU and its heat sink is crucial for efficient heat transfer. Follow manufacturer recommendations and reapply thermal paste if necessary.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use software tools to monitor your system’s temperature and detect any abnormalities. If you notice temperatures consistently reaching critical levels, consider adjusting fan speeds or investing in additional cooling solutions.
- Consider Liquid Cooling: If your system consistently experiences high temperatures, even after addressing airflow and cleaning, you may want to explore advanced cooling options like liquid cooling. Liquid cooling offers superior heat dissipation and can help keep your components at optimal temperatures.
By addressing overheating issues, you not only resolve the red light indicator on your motherboard but also improve your system’s overall performance and longevity. However, if the red light persists even after implementing these steps, it may indicate a more severe problem that requires professional assistance.
In the next section, we will discuss RAM-related problems that can trigger the red light on the motherboard and explore troubleshooting steps to resolve them.
RAM-related Problems and the Red Light
A red light indicating an issue with the RAM (Random Access Memory) on your motherboard is not uncommon. RAM-related problems can cause the red light to appear, indicating a potential memory issue that requires attention. Here are some common RAM-related problems and troubleshooting steps to resolve them:
Loose Connection: Ensure that the RAM modules are properly seated in their slots on the motherboard. Sometimes, a loose connection can cause the red light to appear. Gently remove and reinsert the modules to ensure a secure connection. Ensure that the locking mechanisms are engaged to hold the RAM secure.
Faulty RAM Sticks: RAM sticks can sometimes become faulty or develop errors over time. If you suspect a faulty RAM module, try testing each module individually by removing all but one and booting up the system. If the red light disappears, it may indicate a problem with one of the RAM sticks. Replace the faulty RAM module to resolve the issue.
Incompatible RAM: Sometimes, using incompatible RAM with the motherboard can trigger the red light indicator. Check the motherboard’s specifications and ensure that the RAM modules are compatible in terms of type (DDR3, DDR4, etc.), speed, and capacity. If the RAM is incompatible, replace it with compatible modules.
Mismatched RAM Modules: Mixing different RAM modules with varying specifications (speed, capacity, timings, etc.) can also cause issues and trigger the red light. It is recommended to use identical RAM modules for optimal compatibility and performance.
Updating BIOS and Drivers: Outdated BIOS firmware or incompatible drivers can also lead to RAM-related issues. Ensure that you have the latest BIOS version for your motherboard and install the latest chipset drivers. Updating the BIOS and drivers can help resolve compatibility issues and improve RAM performance.
Reseating RAM and Clearing CMOS: In some cases, reseating the RAM modules and clearing the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) can help resolve RAM-related issues. Clearing the CMOS restores the BIOS settings to their default values and can eliminate any conflicts or errors that may be causing the red light.
By troubleshooting RAM-related problems, you can address the red light indicator on your motherboard and ensure smooth functioning of your system. However, if the issue persists even after attempting these troubleshooting steps, it is advisable to seek professional assistance or contact the manufacturer’s support for further guidance.
In the next section, we will explore how hard drive and storage issues can cause the red light to appear on the motherboard and discuss potential solutions.
Hard Drive and Storage Issues Causing the Red Light
A red light on your motherboard can also be indicative of hard drive and storage issues. Problems with your hard drive or storage devices can trigger the red light, alerting you to potential errors that need to be addressed. Here are some common issues related to hard drives and storage devices that may cause the red light to appear:
Hard Drive Failure: A failing or malfunctioning hard drive can trigger the red light on the motherboard. This could be due to bad sectors, mechanical failures, or other issues. If you suspect hard drive failure, it is crucial to backup your data immediately and seek professional assistance for repair or replacement.
Storage Connection Problems: Loose or faulty connections between the motherboard and the storage device can cause the red light to appear. Ensure that the cables connecting the hard drive or SSD (Solid State Drive) to the motherboard are securely attached. Try reconnecting the cables or using different cables to rule out any connection issues.
Corrupted File System: A corrupted or damaged file system on your storage device can also lead to the red light indicator. Running a disk check or diagnostic tool can help identify and repair any file system errors. However, be cautious as this process can sometimes result in data loss, so it’s important to have a backup of your important files.
Insufficient Storage Space: If your storage device is running low on space, it can cause system performance issues and trigger the red light. Ensure that you have sufficient free space on your storage device by deleting unnecessary files or moving data to an external drive. Maintaining a healthy amount of free storage space can help improve performance and prevent further issues.
Firmware Updates: Some hard drives and SSDs require firmware updates to address compatibility issues or fix bugs. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available firmware updates for your storage devices. Updating the firmware can often resolve issues and prevent the red light from appearing.
It is important to note that hard drive and storage-related problems can sometimes be complex and require professional expertise. If the red light persists or if you encounter data loss, it is recommended to seek professional assistance to diagnose and resolve the issue.
In the next section, we will discuss power supply problems that can trigger the red light on the motherboard and explore potential solutions.
Power Supply Problems and the Red Light Indicator
A red light on the motherboard can also indicate power supply problems. Issues with the power supply unit (PSU) can trigger the red light, signaling a potential problem that requires attention. Here are some common power supply-related problems that may cause the red light to appear:
Faulty Power Supply: If the power supply unit itself is faulty or malfunctioning, it can cause the red light to appear. This could be due to a component failure, inadequate power delivery, or power surges. In such cases, replacing the power supply with a new, reliable unit is often necessary to resolve the issue.
Insufficient Power Delivery: If the power supply does not provide enough power to meet the system’s requirements, it can trigger the red light. This can occur if the power supply wattage is too low for your components or if there are multiple power-hungry devices connected to the system. Upgrading to a higher wattage power supply can help alleviate this issue.
Incompatible Power Cables: Using incompatible or incorrectly connected power cables can cause the red light to appear. Ensure that the power cables are securely attached to the motherboard and other components, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Using the wrong cables or connecting them improperly can lead to power supply issues.
Overheating or Dust Buildup: Overheating or excessive dust accumulation within the power supply unit can also cause problems and trigger the red light. Ensure that the PSU fans are operational and not obstructed by dust or other debris. Regularly cleaning the power supply and ensuring proper ventilation can help prevent these issues.
Power Fluctuations: Power fluctuations, such as voltage spikes or drops, can impact the functionality of the power supply and trigger the red light. Investing in a good surge protector or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can help protect your system from power fluctuations and provide a more stable power source.
If you are uncertain whether the red light is caused by power supply problems, you can try testing the power supply using a multimeter or seeking assistance from a professional. A power supply tester can also help determine whether the PSU is functioning correctly.
It is important to approach power supply issues cautiously, as improper handling or repair attempts can lead to electrical hazards. If the red light persists even after troubleshooting or if you are unsure about the cause, it is recommended to seek professional help to diagnose and resolve power supply-related problems.
In the next section, we will discuss how graphics card errors can trigger the red light on the motherboard and explore potential solutions.
Graphics Card Errors and the Red Light
Another common cause of a red light indicator on the motherboard is graphics card errors. Problems with the graphics card can trigger the red light, signaling an issue that needs to be addressed. Here are some common graphics card-related problems that may cause the red light to appear:
Faulty Graphics Card: A faulty or malfunctioning graphics card can be the culprit behind the red light. This can occur due to manufacturing defects, overheating, or physical damage. If you suspect a faulty graphics card, try reseating the card in its PCIe slot and ensure that the power connectors are securely attached. If the issue persists, consulting with a professional or replacing the graphics card may be necessary.
Incompatible Drivers: Incorrect or incompatible graphics card drivers can also cause the red light to appear. Make sure you have the latest driver software installed for your graphics card. Upgrading to the latest drivers can help resolve compatibility issues and improve the performance of your graphics card.
Insufficient Power Supply: Graphics cards often require sufficient power supply to function properly. If the power supply is not delivering enough power for the graphics card, it can trigger the red light. Check that the power supply is compatible with the graphics card and providing enough wattage. If necessary, upgrade to a higher wattage power supply to meet the requirements of your graphics card.
Improper Installation: Incorrectly installing the graphics card or not securing it properly in the PCIe slot can cause connection issues, leading to the red light. Ensure that the card is seated securely and that the locking mechanism is engaged to hold it in place.
Overheating: Like other components, graphics cards can overheat, triggering the red light on the motherboard. Make sure that the fans on the graphics card are functioning correctly and that there is proper airflow in the case. Cleaning any dust buildup on the graphics card and applying fresh thermal paste can help dissipate heat more effectively.
It is crucial to handle graphics card-related issues with care, as mishandling or improper repairs can further damage the card. If the red light persists or if you are unsure about the cause of the issue, consider seeking professional assistance to diagnose and resolve graphics card-related problems.
In the next section, we will explore troubleshooting steps to address the red light issues on the motherboard.
Troubleshooting Steps for Red Light Issues
Encountering a red light on your motherboard can be concerning, but there are several troubleshooting steps you can take to identify and resolve the underlying issues. Here are some general steps that can help you address red light problems:
- Check Connections: Ensure that all cables and components are properly connected to the motherboard. Check the power cables, data cables, and any expansion cards to make sure they are securely attached.
- Inspect Hardware: Carefully examine all hardware components for any signs of damage or defects. Look for physical damage on the motherboard, GPU, RAM modules, or any other components that may be causing the red light.
- Clear CMOS: Clearing the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) can reset the motherboard’s BIOS settings to default. This can help resolve any configuration or compatibility issues that may be triggering the red light.
- Update BIOS and Drivers: Ensure that you have the latest BIOS firmware and drivers installed for your motherboard and other components. Outdated firmware or drivers can cause conflicts and errors, leading to the red light.
- Test Components Individually: If possible, test each component individually to identify any faulty parts. Remove all non-essential components and test them one by one to isolate the problematic hardware causing the red light.
- Check Temperature and Cooling: Monitor the temperature of critical components such as the CPU and GPU. Ensure that cooling systems, such as fans and heat sinks, are functioning properly and dust-free. Cleaning dust buildup and applying thermal paste can help alleviate overheating issues.
- Verify Compatibility: Check that all components are compatible with each other and with the motherboard. Incompatibility can cause errors and trigger the red light. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and documentation for compatibility information.
- Consult Manufacturer Support: If you’ve followed the above steps and the red light persists, it may be time to seek assistance from the manufacturer’s technical support or consult with a professional technician. They can provide tailored guidance and further troubleshooting steps specific to your motherboard model.
Remember, these are general troubleshooting steps, and specific solutions may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of your motherboard. It’s recommended to consult the motherboard manual and reach out to technical support for more precise guidance.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and resolve the underlying issues causing the red light on your motherboard. However, if you are not comfortable performing these steps yourself or if the problem persists, it is advisable to seek professional help to avoid further damage to your system.
When to Seek Professional Help for Red Light Problems
While troubleshooting steps can often help resolve red light problems on a motherboard, there are instances when seeking professional help becomes necessary. Here are some indicators of when it’s time to consult a professional technician:
Complex Hardware Issues: If you have followed all the troubleshooting steps and the red light problem persists, it may indicate a more complex hardware issue that requires professional expertise. Professional technicians have the knowledge and diagnostic tools to identify and resolve intricate hardware problems.
Data Loss or Security Risks: If the red light is accompanied by data loss, it is important to seek professional help immediately. Professional technicians can provide data recovery services and minimize the risk of permanent data loss. Similarly, if you suspect a security breach or malware attack, a professional can help ensure your system is secure.
Warranty Coverage: If your system is under warranty, seeking professional help can ensure that any repairs or replacements are covered by the manufacturer. Attempting repairs yourself may void the warranty, leaving you responsible for the costs.
Lack of Technical Expertise: If you are not well-versed in computer hardware or lack the necessary skills and knowledge to perform advanced troubleshooting, seeking professional help is a wise decision. Professionals have the experience and expertise required to handle complex issues safely and effectively.
Time and Convenience: Sometimes, the red light issue may be a time-consuming process to troubleshoot, especially if you have limited experience or access to technical resources. Seeking professional help saves time and ensures that the problem is addressed efficiently.
When deciding to seek professional help, consider factors such as cost, reputation of the service provider, and the urgency of the issue. Look for reputable computer repair centers, certified technicians, or contact the manufacturer’s support for guidance.
Remember, professional assistance can save you from potential further damage to your system and provide peace of mind. However, it’s important to communicate the specific details of the problem and any troubleshooting steps you have already taken to help the technician diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.