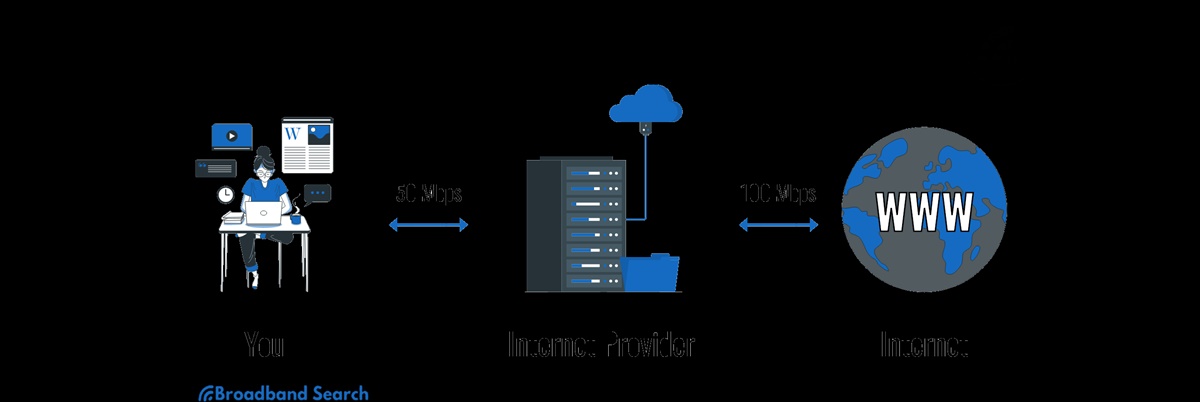
What Is Bandwidth Throttling?
Bandwidth throttling is a technique used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network administrators to intentionally limit the speed or amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection. It involves slowing down or capping the network bandwidth, which directly affects the speed at which data can be uploaded or downloaded.
Essentially, bandwidth throttling is like putting a speed limit on your internet connection. It regulates the flow of data, ensuring that certain tasks or activities do not consume an excessive amount of network resources. This practice is employed to manage network congestion, control data usage, and prioritize traffic.
When bandwidth is throttled, it can affect various aspects of your online experience. It can result in slower website loading times, buffering videos, interrupted streaming, and delayed file downloads. These restrictions are imposed by the ISP or network administrator, who have the ability to monitor and manipulate the flow of data through your connection.
Bandwidth throttling is often used during periods of high network traffic, such as peak hours when many users are simultaneously accessing the internet. By reducing the data transfer speed, ISPs can ensure that their network remains stable and reliable for all users. Additionally, throttling can also be imposed on specific types of content or applications that are known to consume a large amount of bandwidth, such as video streaming or file sharing services.
The practice of bandwidth throttling has been a topic of debate and controversy, particularly in relation to net neutrality. Net neutrality is the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, without any discrimination or preference given to certain websites, services, or applications. Bandwidth throttling can be seen as a violation of net neutrality, as it allows ISPs to control and manipulate the flow of data based on their own priorities and motivations.
The Definition of Bandwidth Throttling
Bandwidth throttling, also known as data throttling or internet throttling, refers to the intentional limitation or restriction of network bandwidth by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network administrators. It involves controlling the speed or amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection.
In simpler terms, bandwidth throttling is a deliberate act of slowing down the internet connection, reducing its capacity to transmit and receive data. This is done by imposing limitations on the maximum speed at which data can be transferred or by setting caps on the amount of data that can be consumed within a certain time frame.
Bandwidth throttling operates by regulating the flow of data packets, the fundamental units of information sent and received over the internet. This can be accomplished through various techniques such as traffic shaping, packet scheduling, or rate limiting.
By implementing bandwidth throttling, ISPs aim to manage network congestion and optimize the overall performance of their networks. During times of high internet usage, such as peak hours, network resources can become strained, leading to slower speeds and reduced quality of service for users. Throttling helps alleviate this congestion by limiting the amount of bandwidth available for certain activities or applications.
Bandwidth throttling can be applied globally to all users on a network or selectively targeted at specific types of traffic. For example, an ISP might limit the speed of peer-to-peer file sharing or video streaming services to prevent any individual user from monopolizing network resources.
It’s important to note that bandwidth throttling is distinct from bandwidth capping. While throttling involves reducing the speed of data transmission, capping refers to placing a limit on the amount of data that can be consumed within a given billing cycle. Both practices are used by ISPs to regulate network usage and ensure fair allocation of resources.
Overall, bandwidth throttling is a method employed by ISPs and network administrators to control and manage network traffic. While it can help maintain stable network performance, it has sparked debates around net neutrality and the potential for discriminatory practices.
How Bandwidth Throttling Works
Bandwidth throttling is a complex process that involves various techniques and mechanisms to control the speed and flow of data within a network. ISPs and network administrators employ a range of methods to implement bandwidth throttling effectively.
The first method of bandwidth throttling involves Deep Packet Inspection (DPI). With DPI, the network equipment examines the data packets traveling through the network in real-time, analyzing the content and classifying the traffic based on certain criteria. This allows the ISP to identify specific types of data, such as video streaming or file sharing, and then apply throttling measures accordingly.
Another common technique used for bandwidth throttling is traffic shaping or packet prioritization. Traffic shaping involves prioritizing certain types of traffic over others, effectively allocating more bandwidth to high-priority applications or services. This ensures a smoother user experience for critical activities like web browsing or VoIP communication, while other data-intensive tasks may be throttled to prevent congestion.
A closely related method is Quality of Service (QoS) management. QoS assigns different levels of priority to different types of traffic, allowing network administrators to give preference to time-sensitive applications such as video conferencing or online gaming. By setting specific QoS rules, the network can prioritize these real-time activities and limit or delay other less critical traffic.
ISPs can also regulate bandwidth by imposing data caps or limits. With this method, users are given a specific amount of data that they can consume within a certain period, such as a monthly billing cycle. Once the data cap is reached, the user’s connection speed is typically reduced significantly. This technique helps ISPs manage network congestion and ensure fair usage among their customers.
Bandwidth throttling can be implemented in different ways, depending on the goals and priorities of the ISP or network administrator. It can be applied on a per-connection basis, targeting individual users based on their IP address or account. Alternatively, it can be applied globally to all users on a particular network segment or during specific high-traffic periods.
It’s worth noting that some ISPs may employ more sophisticated and subtle methods of bandwidth throttling to avoid detection by users. They may dynamically adjust throttling thresholds, change the specific techniques used, or limit throttling to specific times of day or types of activities to minimize customer complaints.
The Purpose and Benefits of Bandwidth Throttling
Bandwidth throttling is implemented by ISPs and network administrators to serve a variety of purposes and provide certain benefits for both the service provider and the users. While it may seem frustrating for users experiencing slower internet speeds, bandwidth throttling can have valid reasons and advantages.
One of the primary purposes of bandwidth throttling is to manage network congestion. During peak usage hours or in areas with high internet traffic, networks can become overwhelmed, resulting in slower speeds and poor quality of service. By throttling the bandwidth, ISPs can regulate the flow of data and prevent congestion, ensuring a more stable and reliable connection for all users.
Bandwidth throttling also helps ISPs control and allocate network resources effectively. By limiting the amount of data that can be transferred within a given timeframe, ISPs can prevent excessive consumption by individual users and ensure fair usage among their customer base. This allows for a more balanced utilization of network resources and helps maintain a consistent level of service for all users.
Another benefit of bandwidth throttling is cost management. Data transmission and network infrastructure can be expensive to maintain and expand. By implementing throttling measures, ISPs can control the amount of data being transferred, reducing the strain on their infrastructure and potentially avoiding costly upgrades to handle peak usage periods.
Additionally, bandwidth throttling can facilitate prioritization of critical applications and services. By allocating higher bandwidth to time-sensitive activities such as video conferencing or voice calls, ISPs can provide a smoother and more reliable experience for these important tasks. This ensures that essential communications are not negatively impacted by bandwidth-intensive activities occurring simultaneously on the network.
Bandwidth throttling can also be used as a means to enforce fair usage policies and discourage abusive and excessive data consumption. It allows ISPs to discourage activities such as peer-to-peer file sharing or excessive downloads/uploads that can disproportionately consume network resources and affect the overall performance for other users.
However, it’s worth noting that bandwidth throttling has its downsides. It can potentially impede users from accessing their desired content and limit their online experiences. Furthermore, concerns of net neutrality arise when ISPs selectively throttle certain services or prioritize certain types of traffic over others, potentially creating an unfair advantage for specific content providers or stifling competition in the online space.
Overall, the purpose and benefits of bandwidth throttling lie in maintaining network stability, managing resource allocation, and prioritizing critical applications. However, striking a balance between network management and user experience remains a challenge, prompting ongoing discussions around net neutrality and the fair implementation of bandwidth throttling measures.
Common Methods of Bandwidth Throttling
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network administrators use various techniques and methods to implement bandwidth throttling effectively. These methods aim to control and restrict the flow of data, ensuring fair allocation of network resources and managing network congestion.
One common method of bandwidth throttling is rate limiting. This technique involves setting a maximum limit on the data transfer speed for a specific connection or user. By capping the speed at which data can be transmitted, the ISP can effectively control the amount of bandwidth allocated to that user, preventing excessive consumption and ensuring fair usage among all users on the network.
Traffic shaping is another widely used method of bandwidth throttling. It involves prioritizing or deprioritizing certain types of network traffic. By allocating more bandwidth to critical or time-sensitive applications like web browsing or VoIP calls, ISPs can provide a smoother user experience for these activities. On the other hand, bandwidth-intensive services, such as file sharing or video streaming, may be deprioritized or throttled to prevent them from overwhelming the network and affecting other users.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is a technique employed to examine the content of data packets traveling through the network. It allows ISPs to analyze the type of traffic and apply specific bandwidth restrictions or prioritizations based on the content. For example, an ISP might identify video streaming traffic and limit its bandwidth to ensure a fair distribution of network resources.
Quality of Service (QoS) management is another method used for bandwidth throttling. QoS assigns different levels of priority to different types of network traffic. This allows critical traffic, such as real-time video conferencing or online gaming, to be given higher priority and allocated more bandwidth, while less time-sensitive activities are managed with lower priority and limited bandwidth.
Bandwidth throttling can also be implemented through data caps or usage quotas. ISPs may set a specific limit on the amount of data that can be consumed within a given time period, such as a monthly billing cycle. Once this cap is reached, the user’s connection speed is typically significantly reduced. Data caps help ISPs manage network congestion and prevent excessive data usage by individual users.
Some ISPs may utilize time-based throttling, where bandwidth restrictions are imposed during specific periods of the day or week when network usage is high. This approach allows for more efficient management of network resources and ensures a better user experience during peak usage times.
It’s important to note that these methods of bandwidth throttling can be employed individually or in combination, depending on the ISP’s goals and network requirements. ISPs may use a range of techniques, tailored to their specific network infrastructure and customer demands, to effectively manage bandwidth and ensure fair distribution of resources.
Reasons Why Internet Service Providers Implement Bandwidth Throttling
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) resort to implementing bandwidth throttling for various reasons. While it can be frustrating for users experiencing slower internet speeds, ISPs employ this technique to address several challenges and ensure a reliable network experience for all customers.
One primary reason for implementing bandwidth throttling is to manage network congestion. During peak usage hours or in densely populated areas, network resources can become strained, resulting in slower speeds and degraded performance. By throttling bandwidth, ISPs can regulate and control the flow of data, preventing congestion and maintaining stable network performance.
Bandwidth throttling is also used as a means of fair resource allocation. In a shared network environment, it is crucial to ensure that every user has equitable access to network resources. By implementing throttling measures, ISPs can prevent some users from monopolizing bandwidth, ensuring fair usage and a more consistent experience for all customers.
ISPs also utilize bandwidth throttling to manage their infrastructure costs. Upgrading and expanding network infrastructure can be expensive and time-consuming. By throttling bandwidth, ISPs can limit the strain on their network, potentially avoiding unnecessary costs associated with infrastructure upgrades. This cost management aspect allows ISPs to provide affordable services to a larger customer base.
Bandwidth throttling can also be employed to prioritize essential services and applications. By allocating more bandwidth to critical activities such as real-time video conferencing, online gaming, or VoIP calls, ISPs can ensure a smoother and more reliable experience for these time-sensitive applications. Throttling other less critical activities, such as large file downloads or video streaming, can help prevent them from impacting the performance of essential services.
Moreover, bandwidth throttling can be used to discourage abusive or excessive bandwidth consumption. Certain activities like peer-to-peer file sharing or continuous high-volume data transfers can put a strain on network resources and negatively impact the experience for other users. By implementing throttling measures, ISPs can discourage and regulate these activities, promoting fair usage and a balanced network experience.
It’s important to note that while ISPs have justifiable reasons for implementing bandwidth throttling, concerns regarding net neutrality arise. Some critics argue that ISPs may use throttling techniques to gain unfair advantages or discriminate against specific services or content providers. This ongoing debate highlights the need for transparent and fair practices in implementing bandwidth throttling measures.
Overall, the reasons for implementing bandwidth throttling include managing network congestion, ensuring fair resource allocation, managing infrastructure costs, prioritizing critical services, and regulating abusive bandwidth consumption. Finding the right balance between network management and providing a satisfactory user experience remains a constant challenge for ISPs.
Bandwidth Throttling and Net Neutrality
Bandwidth throttling has been a subject of contention and debate, particularly in relation to the principle of net neutrality. Net neutrality is the belief that all internet traffic should be treated equally, without any discrimination or preference given to certain websites, services, or applications.
One of the concerns with bandwidth throttling is that it can potentially violate the principles of net neutrality. By selectively slowing down or limiting certain types of traffic, ISPs have the power to control and manipulate the flow of data based on their own motivations or business interests. This creates a situation where some content or services may receive preferential treatment while others suffer from reduced speeds or restricted access.
Without net neutrality protections, ISPs could potentially throttle or block access to certain websites or services that they deem as competitors or that do not align with their financial interests. This raises concerns about censorship, stifling of innovation, and limited choices for internet users. It could create an environment where ISPs have the power to influence the availability and accessibility of online content.
Net neutrality advocates argue that all internet traffic should be treated equally, regardless of the type of content, application, or service being accessed. They believe that bandwidth should be allocated fairly among all users and that ISPs should not have the authority to discriminate based on the source or nature of the traffic.
Conversely, proponents of bandwidth throttling argue that it is necessary for efficient network management and the prevention of network congestion. They contend that without some form of throttling, certain activities or users could monopolize bandwidth, resulting in a poor experience for others. They claim that by implementing bandwidth throttling, ISPs can ensure fair and reliable access for all users by managing network resources effectively.
Regulations and policies regarding net neutrality vary in different countries and regions. Some jurisdictions have implemented laws or regulations to enforce net neutrality principles, while others have taken a more hands-off approach, allowing ISPs more discretion in managing their networks. This ongoing debate over net neutrality and its relationship to bandwidth throttling highlights the need for transparency, accountability, and user protection in the management and regulation of internet services.
Efforts to maintain net neutrality protections continue as advocates push for legislation and regulations that prevent ISPs from engaging in discriminatory practices such as blocking, throttling, or prioritizing certain types of internet traffic. This ongoing battle strives to ensure equal access, fair competition, and the open exchange of information and ideas in the digital age.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Bandwidth Throttling
The legal and regulatory aspects surrounding bandwidth throttling are complex and vary across different jurisdictions. Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in establishing guidelines and frameworks to ensure fair practices and protect consumers in the context of bandwidth throttling.
In some countries, there are specific laws or regulations that govern how ISPs can implement bandwidth throttling. These regulations may require ISPs to disclose their throttling practices, provide information on the specific types of traffic that are being throttled, and ensure transparency in their network management practices. Such regulations aim to prevent ISPs from engaging in anti-competitive behaviors, discriminatory practices, or blocking/throttling specific types of content or services.
Net neutrality regulations exist in several countries, which aim to prevent ISPs from blocking, throttling, or discriminating against certain types of internet traffic. These regulations may enforce the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally, regardless of its source, destination, or content. However, the specifics of these regulations can vary, and there may be debates around the appropriate scope and enforcement mechanisms.
It is worth noting that in some instances, ISPs may have valid reasons and justifications for bandwidth throttling, such as managing network congestion or protecting the overall integrity of their networks. Regulatory frameworks and legislation need to strike a balance between allowing ISPs to manage their networks efficiently while ensuring consumer rights and preventing anti-competitive practices.
Consumer protection laws may also come into play in relation to bandwidth throttling. These laws aim to protect consumers from misleading or deceptive practices by ISPs. They may require ISPs to provide accurate and clear information about their services, including any limitations or restrictions on bandwidth, so that consumers can make informed decisions when choosing an internet service provider.
Privacy laws and regulations also play a role in the context of bandwidth throttling. ISPs may collect data on internet usage, including the types of services or applications accessed by users. Privacy laws govern the collection, use, storage, and sharing of this data, ensuring that ISPs protect user privacy and obtain appropriate consent for data collection and processing activities.
In some cases, regulatory agencies or national authorities may oversee and enforce compliance with these laws and regulations. They may investigate consumer complaints, conduct audits, and impose penalties or sanctions on ISPs that violate the rules surrounding bandwidth throttling or engage in unfair practices.
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding bandwidth throttling is continuously evolving. As technology advances and internet usage patterns change, governments and regulatory bodies will continue to consider and adapt their legal frameworks to ensure fair practices, protect consumers, and strike a balance between network management and user rights.
The Impact of Bandwidth Throttling on Users
Bandwidth throttling can have various impacts on users’ internet experience and overall satisfaction. While its purpose is to manage network resources and ensure fair distribution, the effects of throttling can be both positive and negative.
One of the main impacts of bandwidth throttling is reduced internet speeds. When ISPs throttle bandwidth, users may experience slower browsing speeds, longer load times for websites and online videos, and delays in downloading or uploading files. This can be frustrating, especially for tasks that require fast and reliable internet connections, such as video conferencing or online gaming.
Bandwidth throttling can also result in buffering and poor video streaming quality. Streaming services that require a significant amount of bandwidth, such as Netflix or YouTube, may be affected by throttling. This can lead to interruptions in video playback, lower video quality, and a less enjoyable streaming experience for users.
Activities that heavily rely on fast and consistent internet connections, such as online gaming or large file transfers, can be significantly impacted by bandwidth throttling. Gamers may experience increased lag and latency, negatively affecting their gameplay. Similarly, users trying to download or upload large files may face delays and longer transfer times due to the restricted bandwidth.
Another impact of bandwidth throttling is the potential restriction or limitation of certain services or applications. ISPs may choose to throttle specific types of traffic, such as peer-to-peer file sharing or streaming services, to manage network congestion or prioritize other applications. This can restrict users’ access to these services or make them less enjoyable to use.
Bandwidth throttling can also have financial implications for users. Some ISPs offer tiered pricing plans based on different levels of bandwidth or data allotments. If bandwidth throttling is implemented to enforce data caps, users who exceed their allotted data limit may incur additional charges or be subjected to further speed reductions, affecting their overall internet costs.
On the positive side, bandwidth throttling can be beneficial in improving network stability and reducing network congestion during peak usage hours. By managing traffic and limiting excessive consumption, ISPs can ensure a more stable and consistent internet experience for all users. Throttling can help prevent network slowdowns and failures caused by a few users monopolizing resources.
Additionally, bandwidth throttling can encourage responsible internet usage and discourage excessive data consumption. By implementing limitations, ISPs can incentivize users to manage their data usage more efficiently and prevent the overuse of network resources. This can result in a more balanced and fair internet experience for all users.
Ultimately, the impact of bandwidth throttling on users will vary depending on the specific practices and management strategies employed by ISPs. Balancing the need for network management with maintaining satisfactory internet experiences for users remains a challenge that ISPs must navigate carefully.
How to Detect if Your Internet Connection is Being Throttled
If you suspect that your internet connection is being throttled, there are several methods you can use to detect and confirm if bandwidth throttling is occurring. While ISPs may use sophisticated techniques to implement throttling that may not be easily detectable, there are still some indicators that can help you determine if your connection is being throttled.
The first step is to run a speed test on your internet connection using a reliable online speed test tool. Compare the results with the speeds promised by your ISP in your service plan. If you consistently receive significantly slower speeds than what you’re paying for, it could indicate that your connection is being throttled.
It’s also helpful to perform multiple speed tests at different times of the day, including during peak usage hours. If you notice a significant drop in speeds during busy periods, it might suggest that your ISP is implementing throttling measures to manage network congestion.
Another method is to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a different location. By using a VPN, your traffic appears as if it’s coming from the VPN server, rather than your actual ISP. If you notice a significant improvement in internet speeds when connected to a VPN, it may indicate that your ISP is throttling specific types of traffic.
If you suspect specific applications or services are being throttled, you can conduct tests by using different applications and observing the performance. For example, try streaming videos from different platforms or using different file-sharing applications. If you notice consistently slow speeds or poor performance with certain services, it may suggest that your ISP is throttling that specific type of traffic.
Monitoring your network traffic and analyzing patterns can also help identify potential throttling. Network monitoring tools or applications can show the amount of data being transmitted and received over time. If you notice a significant drop in data transfer rates during certain periods, it could be an indication of throttling.
However, it’s important to note that there are other factors that can contribute to slower or inconsistent internet speeds, such as network congestion, device limitations, or issues with your equipment. It’s recommended to rule out these factors before concluding that bandwidth throttling is occurring.
If you suspect bandwidth throttling, it’s advisable to contact your ISP to inquire about their network management practices. They may provide information about any throttling policies they have in place. It’s also worth reviewing your ISP’s terms of service or acceptable use policy to understand their policies regarding bandwidth management.
Keep in mind that proving bandwidth throttling can be challenging, as ISPs may employ sophisticated techniques or may not explicitly disclose their throttling practices. However, by monitoring your internet speeds, testing different applications, and gathering evidence, you can make a more informed assessment of whether your internet connection is being throttled.
Tips to Prevent or Bypass Bandwidth Throttling
If you’re experiencing bandwidth throttling and want to prevent or bypass it, there are a few tips and techniques you can try. While it’s important to note that these methods may not always be successful or recommended, they can offer potential ways to mitigate the impact of bandwidth throttling.
1. Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): Using a VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a different location. This can help mask your online activities from your ISP and potentially bypass bandwidth throttling. However, not all VPNs are created equal, and some may still be detected and throttled by ISPs. Choose a reliable and reputable VPN service to maximize your chances of success.
2. Opt for an ISP with net neutrality policies: Do some research and choose an internet service provider (ISP) that supports net neutrality principles and has a clear policy against bandwidth throttling. Look for ISPs that have publicly committed to treating all internet traffic equally and not engaging in discriminatory practices.
3. Monitor and optimize your network usage: Keep track of your internet usage and identify data-intensive applications or services that may trigger throttling. By managing your usage patterns and avoiding excessive data consumption during peak hours, you may be able to mitigate the effects of bandwidth throttling.
4. Adjust your internet habits: Alter your online activities to prioritize essential or time-sensitive tasks. For example, schedule large file downloads or updates during off-peak hours when network congestion is less likely. By avoiding bandwidth-intensive activities during busy periods, you may experience less throttling and better overall performance.
5. Upgrade your internet plan: Consider upgrading to a higher-tier internet plan with a higher data cap or more generous bandwidth allocation. Some ISPs offer plans that are less likely to be subject to throttling or have higher thresholds before throttling is implemented. However, this option may involve additional costs.
6. Contact your ISP: Reach out to your ISP’s customer support to inquire about their bandwidth management policies and express your concerns about throttling. While this may not necessarily resolve the issue, it can provide you with more information about their practices and potentially result in improvements or adjustments to your service.
7. Support net neutrality advocacy: Get involved in advocacy efforts and organizations that promote net neutrality and fight against discriminatory practices such as bandwidth throttling. By supporting these initiatives, you can contribute to creating a more open and fair internet environment.
It’s important to note that while these tips may help mitigate the effects of bandwidth throttling in some cases, they may not guarantee complete avoidance or successful bypassing of throttling measures. ISPs may employ advanced techniques that make bypassing throttling more challenging. Additionally, some methods may violate the terms of service or acceptable use policies of your ISP, so it’s important to use caution and consider the legal and ethical implications before attempting to bypass throttling.
Consumers’ Rights and Remedies Against Bandwidth Throttling
As a consumer, you have certain rights and remedies when it comes to dealing with bandwidth throttling by your Internet Service Provider (ISP). While the specific rights and remedies may differ based on your jurisdiction and applicable laws, there are some common avenues you can explore in addressing this issue.
1. Transparency and Disclosure: ISPs should provide clear and transparent information about their network management practices, including any policies related to bandwidth throttling. You have the right to be informed about how your internet connection may be affected and what measures the ISP takes to manage network congestion. If your ISP fails to provide sufficient disclosure, you can consider filing a complaint with the appropriate regulatory authority.
2. Consumer Protection Laws: Explore your country or region’s consumer protection laws, which may offer remedies for deceptive, unfair, or anti-competitive practices by ISPs. These laws may provide recourse for consumers affected by undisclosed or discriminatory bandwidth throttling. Familiarize yourself with your rights as a consumer and consider seeking legal advice to understand the specific remedies available to you.
3. Net Neutrality Advocacy: Support and engage with organizations or initiatives that advocate for net neutrality and the fair treatment of internet traffic. By joining these efforts, you can contribute to the fight against discriminatory practices like bandwidth throttling and help raise awareness about the importance of an open and neutral internet.
4. File a Complaint: If you believe your ISP is engaging in unfair bandwidth throttling practices, you can file a complaint with the relevant regulatory authority or consumer protection agency in your jurisdiction. Provide evidence and document instances of throttling, such as speed test results or data showing inconsistent performance. The regulatory authority can investigate the complaint and take appropriate action if your rights as a consumer have been violated.
5. Seek Alternative ISPs: Research and explore alternative ISPs that offer more transparent practices regarding bandwidth management. Look for ISPs that have clear net neutrality policies in place and prioritize providing consistent and fair access to their customers. By switching to an ISP with better practices, you can voice your concerns and choose a service that aligns with your values and expectations.
It’s important to be aware that the legal and regulatory landscape surrounding bandwidth throttling and consumer remedies can vary across different jurisdictions. Stay informed about the specific laws, regulations, and consumer protection mechanisms that apply in your area, and consult with relevant legal professionals or consumer advocacy groups for guidance.
Remember, collective action and consumer advocacy play a significant role in influencing industry practices and shaping regulations. By raising awareness, sharing experiences, and actively participating in discussions and initiatives, consumers can contribute to a fairer and more transparent internet ecosystem.