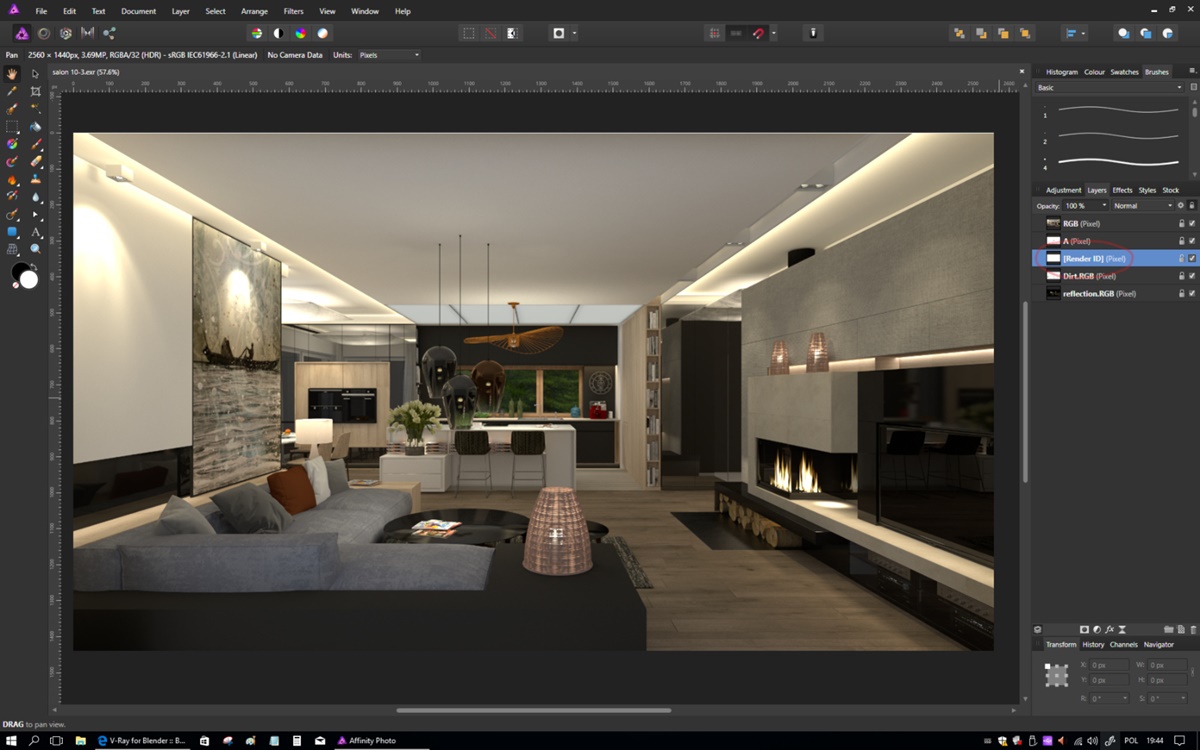
What Does EXR Stand For?
The acronym EXR stands for “Extended Dynamic Range.” It is a file format specifically designed for storing high-dynamic-range (HDR) images. HDR images capture a wider range of colors and tones than standard images, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike visuals.
The EXR file format was developed by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) in collaboration with other leading film and animation studios. It has since become widely adopted in the visual effects and computer graphics industry due to its ability to accurately preserve the details and nuances of HDR imagery.
EXR files are typically used in professional applications where image fidelity and precision are of utmost importance. They are commonly used in the fields of film production, animation, gaming, and visual effects, where maintaining the highest level of image quality is critical.
Unlike other image file formats, such as JPEG or PNG, which are limited in their ability to accurately represent HDR content, EXR files allow for the storage of pixel data with a larger dynamic range. This means that EXR images can store a greater variation in brightness levels, resulting in more detail in both the shadows and highlights of the image.
Overall, the EXR format is designed to provide artists, photographers, and designers with a powerful and flexible means of capturing and preserving images with an extended dynamic range. It offers unparalleled image quality and fidelity, making it an essential tool for professionals in the visual media industry.
Overview of EXR File Format
The EXR file format is a flexible and robust image file format specifically designed for storing high-dynamic-range (HDR) images. It was developed by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) in collaboration with other leading film and animation studios and has gained widespread adoption in the visual effects and computer graphics industry.
EXR files are capable of storing images with an extended dynamic range, which means they can capture a greater range of colors and tonal values than standard image formats like JPEG or PNG. This makes EXR files ideal for preserving the intricate details and nuances of HDR imagery.
One of the key features of the EXR format is its ability to store high-fidelity pixel data. It uses a 16-bit or 32-bit floating-point format to ensure accurate representation of colors and luminance values. This enables artists and designers to work with images that retain the full tonal range and subtle details, resulting in a more realistic and visually appealing final product.
Furthermore, EXR files support various compression methods to optimize file size without compromising image quality. The lossless compression algorithms employed in EXR files ensure that no data is lost during storage. Additionally, the files can be stored in multi-part or tiled formats, which further enhance efficiency when working with large and complex images.
The EXR file format also includes support for channels and layers, allowing users to store multiple image layers within a single file. This feature is particularly useful in compositing and post-production workflows, as it enables efficient management and manipulation of different elements, such as background, foreground, and various visual effects.
Overall, the EXR file format offers a comprehensive and flexible solution for storing and working with high-dynamic-range images. Its advanced features and capabilities make it an essential format for professionals in the visual effects, animation, and gaming industries, where maintaining the highest level of image quality is paramount.
Advantages of Using EXR Files
The use of EXR files offers several advantages for professionals working with high-dynamic-range (HDR) images. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of using EXR files:
1. Extended Dynamic Range: EXR files can accurately preserve the wide range of colors and tonal values found in HDR images. This ensures that the final output retains the intricate details and nuances, resulting in more vibrant and realistic visuals.
2. High Fidelity: The use of 16-bit or 32-bit floating-point format in EXR files allows for precise and accurate representation of colors and luminance values. This ensures that even the smallest details and subtle variations in the image are retained, resulting in a more visually appealing final product.
3. Lossless Compression: EXR files support lossless compression algorithms, which reduce file size without sacrificing image quality. This is especially important when working with large and complex images, as it allows for efficient storage and fast data transfer.
4. Channel and Layer Support: The EXR format includes support for channels and layers, allowing users to store multiple image layers within a single file. This feature is particularly useful in post-production workflows, as it enables efficient management and manipulation of different elements, such as background, foreground, and visual effects.
5. Flexibility and Compatibility: EXR files can be easily integrated into various software applications and workflows used in the visual effects, animation, and gaming industries. Many leading software applications support the EXR format, ensuring seamless compatibility and efficient collaboration among different artists and teams.
6. Preservation of Image Quality: Since EXR files store pixel data with an extended dynamic range, they allow for greater flexibility when it comes to adjusting and manipulating the image in post-production. This ensures that the image quality remains intact, even after multiple edits and adjustments.
7. Future-Proofing: EXR files are future-proof, meaning they can adapt to advancements in technology and support higher bit depths and greater dynamic ranges as they become available. This ensures that projects created using EXR files remain compatible and can be accessed and edited in the future with minimal issues.
Overall, the use of EXR files provides a range of benefits for professionals working with HDR images. From extended dynamic range to high fidelity and flexibility, the EXR format empowers artists and designers to create stunning visuals while preserving the intricate details and nuances of their work.
Common Uses of EXR Files
EXR files find wide application in various industries that rely on high-dynamic-range (HDR) imagery. Let’s explore some common use cases where EXR files are frequently employed:
1. Film Production: In the film industry, EXR files are extensively used during the production and post-production stages. They allow filmmakers to capture and preserve the full range of colors and tonal values in scenes with challenging lighting conditions. EXR files are especially beneficial in visual effects-heavy films, where maintaining image fidelity and flexibility is crucial.
2. Animation: EXR files have become a standard in the field of animation. They allow animators to work with HDR images, ensuring that the colors and tonal values of the animations are preserved accurately. EXR files enable smoother integration of animated objects with live-action footage, resulting in seamless and visually stunning final products.
3. Gaming: The gaming industry also makes extensive use of EXR files, particularly in game development and rendering. EXR files can store HDR textures, lighting information, and visual effects data, enabling game designers to create immersive and realistic game environments. The high fidelity and flexibility offered by EXR files contribute to the overall visual quality of games.
4. Advertising and Marketing: EXR files are increasingly utilized in advertising and marketing campaigns, particularly in industries such as automotive, fashion, and product photography. These files allow photographers and designers to capture and showcase products with enhanced detail and vividness, ensuring that the final images stand out and effectively convey the desired message.
5. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): EXR files are well-suited for VR and AR applications, as they provide the necessary image fidelity and dynamic range required for a realistic and immersive experience. Whether it’s creating virtual environments or overlaying digital elements on the real world, EXR files play a crucial role in delivering high-quality visuals in these emerging technologies.
6. Scientific Visualization: EXR files are used in scientific visualization, where accurate representation of data and visualization of complex scientific concepts is vital. The extended dynamic range of EXR files allows scientists and researchers to present their findings and data in a visually compelling and precise manner.
7. Archival and Preservation: Due to their ability to store pixel data with an extended dynamic range, EXR files are also used in the archival and preservation of important historical and cultural artifacts. These files ensure that the highest level of detail and accuracy is preserved over time, allowing future generations to access and study these valuable resources.
Overall, the flexibility and capabilities of EXR files make them invaluable in various industries such as film production, animation, gaming, advertising, scientific visualization, and archival purposes. Their ability to capture and preserve the intricacies and nuances of HDR imagery contributes to the creation of visually stunning and high-quality content.
How Does EXR Compare to Other Image File Formats?
When it comes to storing and working with high-dynamic-range (HDR) images, the EXR file format offers distinct advantages over other common image file formats. Let’s compare EXR to some of the popular image formats to understand its unique features:
1. JPEG: JPEG is a widely used and highly compressed image format, but it is primarily designed for standard dynamic range images. Unlike EXR, JPEG cannot accurately represent the extended dynamic range of HDR images. This results in lost details and reduced image quality, especially in areas with high contrast. EXR, on the other hand, preserves the full range of luminance values, ensuring better fidelity and more accurate reproduction of HDR content.
2. PNG: PNG is another common image format known for its lossless compression. While it offers higher quality and supports transparency compared to JPEG, it still falls short in capturing the extended dynamic range of HDR images. EXR surpasses PNG in this aspect by providing the necessary bit depth and floating-point representation to accurately store HDR content, resulting in more detailed images with better color reproduction.
3. TIFF: TIFF is a versatile image format suitable for various purposes, including HDR imaging. Although TIFF supports higher bit depths and lossless compression, its HDR capabilities are more limited compared to EXR. TIFF files may use integer-based formats, which have a narrower dynamic range compared to the floating-point format used in EXR. As a result, EXR offers superior image quality, especially in scenes with extreme contrast and subtle details.
4. OpenEXR: OpenEXR is an open-source image format that is nearly identical to the EXR format. In fact, OpenEXR is often used interchangeably with EXR. The main distinction is that OpenEXR is an open-source implementation of the EXR format, while EXR refers specifically to files adhering to the specifications set by Industrial Light & Magic (ILM). Both formats have comparable features and capabilities in preserving HDR images.
5. RAW Formats: RAW file formats, such as CR2 (Canon), NEF (Nikon), or ARW (Sony), are used mainly for photographic purposes, capturing unprocessed sensor data. While RAW formats provide higher bit depths and more flexibility for post-processing, they are limited in terms of storing HDR images. EXR, with its extended dynamic range and floating-point precision, allows for more accurate representation of HDR content and better preservation of details and nuances.
Overall, EXR stands out among other image file formats when it comes to storing and working with HDR images. Its ability to accurately represent the extended dynamic range, higher bit depth, lossless compression options, and support for multiple channels and layers make it the go-to format for professionals in the visual effects, animation, gaming, and other industries where maintaining the highest image quality is essential.
Features and Capabilities of EXR Files
The EXR file format offers a range of features and capabilities that make it indispensable for professionals working with high-dynamic-range (HDR) images. Let’s explore some of the key attributes of EXR files:
1. Extended Dynamic Range: EXR files can accurately store and preserve the wide range of colors and tonal values found in HDR images. This means that EXR images can capture and represent the subtle nuances and details in both the shadow and highlight areas.
2. High Precision: EXR files use either 16-bit or 32-bit floating-point format to ensure high precision and accurate representation of colors and luminance values. This enables artists and designers to work with images that retain the full tonal range, resulting in more realistic and visually appealing final products.
3. Lossless Compression: EXR files support lossless compression algorithms, allowing for efficient storage of large and complex images without sacrificing image quality. The compression methods minimize file size while retaining all the pixel data, ensuring that no information is lost during the compression process.
4. Multi-Channel Support: EXR files have the capability to store multiple color channels, alpha channels, and additional user-defined channels. This feature is particularly useful in compositing and post-production workflows, as it allows for efficient management and manipulation of different elements within a single file.
5. Multi-Layer Support: EXR files also support multiple layers, enabling the storage of different image elements within a single file. This feature is beneficial in workflows that involve complex compositions, as it allows for efficient organization and management of different image components like background, foreground, visual effects, and more.
6. Tiled and Multi-Part EXR Files: EXR files can be stored in tiled or multi-part formats, which enhance efficiency and performance when working with large images. Tiled EXR files divide the image into small tiles, enabling faster access to specific regions of the image. Multi-part EXR files, on the other hand, allow for even larger images to be split into multiple files, making it easier to handle and work with massive image data sets.
7. Flexibility and Compatibility: EXR files are widely supported by various software applications used in the visual effects, animation, and gaming industries. This ensures compatibility and seamless integration into different production pipelines, enabling efficient collaboration between artists and teams.
How to Open and View EXR Files
To open and view EXR files, you can use a variety of software applications that support the EXR file format. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to open and view EXR files:
1. Professional Image Editing Software: Software applications like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe After Effects, and Nuke are commonly used for working with EXR files. Simply open the software and select “Open” or “Import” from the file menu. Browse to the location of the EXR file on your computer and select it. The software will display the EXR file, allowing you to view and edit the image.
2. Open Source Software: Open source software applications like GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program) and Blender also support EXR files. After installing the software, go to the “File” menu and choose “Open.” Locate the EXR file on your computer and open it. The software will load the EXR file, enabling you to view and edit the image.
3. Image Viewers: Various image viewer programs can open and display EXR files. One popular option is the EXR Display application, which is specifically designed for viewing EXR files. After installing the software, launch the program and use the file browser to locate the EXR file. The program will open the EXR file, and you can navigate through the image and view it in its full HDR glory.
4. Online Converters: If you prefer to view EXR files online, you can use online converters that support the EXR format. These converters allow you to upload your EXR file to their website, and they will convert and display the image in a compatible format that can be viewed in a web browser.
5. HDR Image Viewer Plugins: Some web browsers or image viewers offer plugins or extensions specifically for viewing HDR images, including EXR files. These plugins enhance the capabilities of the viewer, allowing you to open and display EXR files directly in your browser or image viewer.
6. Third-Party Plugins: Depending on the software you are using, there may be third-party plugins available for opening and viewing EXR files. These plugins extend the functionality of the software and enable you to work with EXR files seamlessly.
Remember that the ability to view and edit EXR files may vary depending on the software and its version. It’s a good practice to keep your software up to date and check the documentation or support resources provided by the software developers for specific instructions on opening and viewing EXR files.
How to Convert EXR Files to Other Formats
Converting EXR files to other formats can be useful when you need to share, display, or work with images in different software applications that do not support the EXR file format. Here are several methods to convert EXR files to other formats:
1. Image Editing Software: Use professional image editing software like Adobe Photoshop or GIMP to open the EXR file and save it in a different format. Open the EXR file in the software, make any necessary adjustments, and then use the “Save As” option to choose a new format such as JPEG, PNG, TIFF, or BMP. Adjust the settings for desired quality and compression, and save the file with the new format.
2. Dedicated File Conversion Software: There are specialized file conversion programs available that can convert EXR files to other formats. These programs offer a simple and straightforward approach to convert multiple EXR files at once. You can select the EXR files you want to convert, choose the desired output format, and initiate the conversion process with a few clicks.
3. Online File Conversion Services: Online file conversion services allow you to upload your EXR files and convert them to various formats without the need to install any software on your computer. Simply find a reputable online file converter that supports EXR files, upload the file, select the desired output format, and start the conversion process. After the conversion is complete, you can download the converted file to your computer.
4. Batch Conversion Scripts or Plugins: Some image editing software or scripting languages provide batch conversion capabilities. These scripts or plugins can streamline the process of converting multiple EXR files to different formats simultaneously. By specifying the input folder, output folder, and desired output format, you can automate the conversion process and save time.
5. Online Image Editors: Some online image editing platforms offer the ability to open and edit EXR files, allowing you to convert them to other formats. These platforms typically provide an interface similar to desktop image editing software, allowing you to make adjustments and then save the edited image in a format of your choice.
Keep in mind that when converting EXR files to other formats, some of the advanced features and dynamic range of the original HDR image may be lost, depending on the capabilities of the chosen output format. It is recommended to save the EXR file as a lossless format, such as TIFF, to retain as much image information as possible during the conversion process.