How to Use Export from Lightroom to Save Photo Edits
One of the powerful features of Lightroom is its ability to export photos while preserving all the edits you’ve made. Whether you want to share your images on social media, send them to clients, or print them for display, the Export function in Lightroom makes it easy to save your photo edits in various formats. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Export from Lightroom to save your photo edits.
1. Select the photos you want to export by either clicking on them individually or selecting them in the Library module using Command (Mac) or Control (Windows) key.
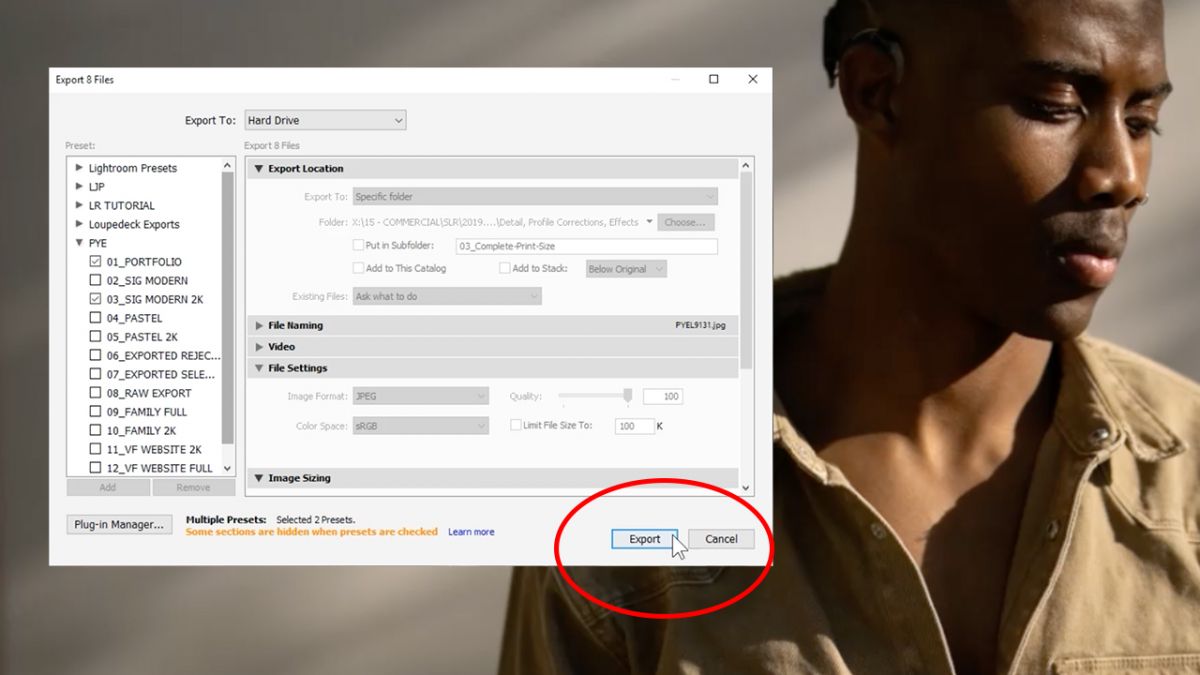
2. Navigate to the File menu at the top and choose “Export” or use the shortcut Command/Control + Shift + E.
3. In the Export window, choose the destination folder where you want to save your exported photos. You can create a new folder or select an existing one.
4. Choose the file format for your exported photos. Lightroom supports a variety of formats such as JPEG, TIFF, PNG, and DNG. Consider the purpose of your exported photos and choose the format accordingly.
5. Adjust the image quality settings. If you’re exporting photos for web or social media, you can set the quality to around 70-80 to balance file size and image clarity. For print or publication purposes, use higher quality settings to ensure the best output.
6. Resize and sharpen your images if needed. Lightroom allows you to resize your photos to specific dimensions and apply sharpening to enhance details. Consider the requirements of the platform or medium where you’ll be using the exported photos.
7. Add metadata to your exported photos. This includes information like captions, titles, copyright, and keywords to ensure proper organization and attribution of your images.
8. Consider applying watermarks for added protection or branding. Lightroom offers options to add custom watermarks to your exported photos, such as text or logos.
9. Review your export settings and make any final adjustments. Double-check that everything is set according to your preferences before clicking the “Export” button.
By following these steps, you can successfully export your edited photos from Lightroom while retaining all your adjustments. Saving your photo edits through the Export function ensures that you can easily share, print, or store your images, maintaining the quality and integrity of your work.
Understanding the Export Process in Lightroom
Exporting photos from Lightroom involves more than simply saving your edited images. It’s essential to understand the export process to ensure that your exported photos meet your specific needs and requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the export process in Lightroom:
1. Selecting the Export Location: Before exporting your photos, you’ll need to choose the destination folder where your exported images will be saved. Lightroom provides options to select an existing folder or create a new one.
2. Choosing the File Format: Lightroom offers various file formats for exporting your photos, including JPEG, TIFF, PNG, and DNG. Consider the purpose and intended use of your images when selecting the file format.
3. Adjusting Image Quality Settings: When exporting photos, you can control the image quality to balance file size and image clarity. For web or social media use, a quality setting around 70-80 is typically sufficient, while for print or publication, higher quality settings may be desired.
4. Resizing and Sharpening: Lightroom allows you to resize your images during the export process. This is particularly useful when exporting images for specific platforms or mediums that have specific size requirements. Additionally, you can apply sharpening to enhance the details in your exported photos.
5. Adding Metadata: Metadata is crucial for organizing and attributing your photos. When exporting from Lightroom, you have the option to include metadata such as captions, titles, copyright information, and keywords. This ensures that your images are properly labeled and searchable.
6. Applying Watermarks: Watermarks can provide added protection to your exported images or help establish your brand. Lightroom allows you to add customized watermarks, either as text or graphic logos, to your exported photos.
7. Previewing and Finalizing Settings: Before initiating the export, it’s vital to review all your export settings to ensure they align with your requirements. Lightroom provides a preview window where you can see how your exported images will appear with the selected settings. Take this opportunity to make any necessary adjustments.
Understanding the export process in Lightroom empowers you to make informed decisions when saving your edited photos. By selecting the appropriate file format, adjusting image quality, resizing and sharpening, adding metadata, and considering watermarks, you can tailor your exported photos to match your specific needs and deliver the highest quality images possible.
Choosing the Right File Format for Export
When exporting photos from Lightroom, selecting the right file format is crucial as it determines the quality and compatibility of your exported images. Here are some commonly used file formats in Lightroom and their respective benefits and considerations:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group):
JPEG is a widely supported and compressed file format commonly used for web, social media, and general sharing purposes. It offers a balance between file size and image quality. JPEG files are relatively small, making them quick to upload and easy to share. However, due to the compression, some loss of image quality may occur, particularly when using low-quality settings.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):
TIFF is an uncompressed file format that preserves all the image data, making it ideal for printing, professional use, and archiving purposes. TIFF files are larger in size compared to JPEGs due to the lack of compression, resulting in higher image quality. However, the larger file sizes consume more storage space and take longer to upload or share.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics):
PNG is a lossless file format that supports transparency and is commonly used for web graphics and logos. Unlike JPEG, PNG does not compromise image quality through compression. It preserves fine details and offers high color accuracy. However, PNG files tend to be larger than JPEG files, making them less suitable for large-scale printing or situations where file size is a concern.
DNG (Digital Negative):
DNG is an open-source raw file format developed by Adobe and compatible with most image editing software. It offers the benefit of preserving all the original data captured by the camera sensor while allowing for non-destructive edits. DNG files are flexible and offer more control over the editing process. However, they can be larger in size and not all software applications support this format.
When choosing the right file format for export, consider the purpose of your photos. For web and social media sharing, JPEG or PNG may be suitable, balancing image quality and file size. If you plan to print your images or require maximum image quality, TIFF is a better option. Additionally, if you want to preserve all the raw data and have flexibility in post-processing, DNG may be the preferred choice.
Understanding the benefits and considerations of each file format in Lightroom allows you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and the intended use of your exported photos. Experimenting with different formats and assessing the results will help you find the ideal format that perfectly suits your requirements.
Adjusting Image Quality Settings for Export
When exporting photos from Lightroom, adjusting the image quality settings is crucial to strike the right balance between file size and image clarity. The image quality settings determine the level of compression applied to the exported photos. Here’s how you can fine-tune the image quality settings for your specific needs:
1. Understanding Quality Settings:
The image quality settings in Lightroom typically range from 0 to 100, with 100 being the highest quality and 0 the lowest. Higher quality settings result in larger file sizes and better image clarity, while lower quality settings reduce file sizes but may sacrifice some perceptible details.
2. Consider the Purpose of the Exported Photos:
The purpose of your exported photos determines the appropriate image quality setting. For web and social media sharing, a quality setting of around 70-80 usually provides a good balance between file size and image clarity. For printing or publication purposes, it’s recommended to set the quality to a higher level to ensure the best output.
3. Assessing Image Compression:
It’s important to evaluate the level of compression applied to your exported photos. While compression reduces file size, it can also introduce artifacts or visible degradation in image quality, especially at lower quality settings. Use the preview option in Lightroom to examine the exported images at different quality levels and choose the one that maintains the desired level of detail and visual integrity.
4. Iterative Approach:
If you’re unsure about which quality setting to use, consider adopting an iterative approach. Start with a moderately higher quality setting and export a test image. Assess the file size and visual quality of the exported photo. If the file size is too large or the image quality is satisfactory, gradually decrease the quality setting until you find the desired balance.
5. Batch Export Considerations:
If you’re exporting a large batch of photos, using consistent image quality settings across all images can help maintain a cohesive look. Consider the purpose and usage of the photos in the batch and choose the quality setting accordingly. Creating export presets with predefined settings can streamline the process and ensure consistency.
By adjusting the image quality settings during export, you can optimize the file size without compromising too much on image clarity. Prioritize the purpose of your exported photos and evaluate the balance between storage constraints and desired visual quality. Being mindful of these considerations will result in well-optimized exported photos that effectively convey your vision without excessive file sizes.
Resizing and Sharpening Images for Export
When exporting photos from Lightroom, resizing and sharpening your images can help optimize them for specific platforms or mediums, ensuring they look their best. Here’s how you can resize and sharpen your images during the export process:
1. Resizing Images:
Resizing your images allows you to adjust them to specific dimensions, which is especially important when uploading to websites, sharing on social media, or printing for specific frame sizes. In the Export window, under the Image Sizing section, you can set the dimensions for the exported photos. You can choose to resize your images based on pixel dimensions or physical dimensions like inches or centimeters.
2. Aspect Ratio and Crop:
When resizing your images, it’s important to consider the aspect ratio. An aspect ratio is the proportional relationship between the width and height of an image. Lightroom gives you options to constrain the aspect ratio during resizing or apply a specific crop to ensure your exported photos have the desired composition.
3. Sharpening:
Sharpening is a crucial step that enhances the details and crispness of your exported photos. In the Export window, you’ll find the Sharpening section where you can adjust the sharpening settings. Use the Amount slider to control the intensity of sharpening. The Radius slider determines the size of the area around edges that will be sharpened, and the Detail slider determines the level of sharpening applied to smaller details. Experiment with these settings to find the right balance that enhances the details without creating artifacts or overly harsh edges.
4. Previewing the Resized and Sharpened Images:
Before initiating the export, it’s important to preview the resized and sharpened images to ensure they meet your expectations. Use the preview window in Lightroom to examine the exported images and assess the level of detail, sharpness, and composition. This allows you to make any necessary adjustments to achieve the desired outcome.
5. Batch Exporting:
If you are exporting a batch of photos with similar resizing and sharpening requirements, consider creating export presets. Presets allow you to save your preferred settings for future use, ensuring consistency and saving time in your workflow.
By resizing and sharpening your images during the export process, you can optimize them for their intended use. Whether you’re sharing them online, printing for display, or preparing them for a specific platform, resizing ensures the images display correctly, while sharpening enhances the details to make them visually appealing. Experiment with different settings and preview the results to achieve the best outcome for your exported photos.
Adding Metadata to Exported Photos
Metadata plays a crucial role in organizing, identifying, and protecting your photos. When exporting photos from Lightroom, you have the option to include various types of metadata, such as captions, titles, copyright information, and keywords. Adding metadata to exported photos ensures proper organization, attribution, and easy searchability. Here’s how you can add metadata to your exported photos:
1. Captions and Titles:
Captions and titles provide additional context or information about your photos. Lightroom allows you to add captions and titles during the export process. You can include details like location, event, or any other relevant information that helps tell the story behind the image.
2. Copyright Information:
Adding copyright information to your exported photos is essential for protecting your work and asserting your ownership. In Lightroom’s Export window, you can include your copyright information, such as your name or the copyright symbol, along with the year. This helps ensure proper attribution and discourages unauthorized use of your images.
3. Keywords:
Keywords are descriptive terms that you assign to your photos to make them easily searchable. Lightroom’s Export window allows you to include keywords in the metadata. Consider relevant keywords that describe the subject, location, theme, or any other significant elements of your photos. Taking the time to add meaningful keywords will greatly enhance the discoverability of your images.
4. Custom Metadata:
If you have specific metadata fields that are important for your workflow or if you are exporting photos for a particular purpose, Lightroom offers the flexibility to include custom metadata. You can create custom metadata fields to add specific information like client names, project details, or any other relevant data that helps categorize and manage your exported photos.
5. Preserving Existing Metadata:
When exporting photos, it’s important to ensure that any existing metadata associated with the images is preserved. By default, Lightroom retains the already present metadata in the exported files. However, it’s always a good practice to double-check the export settings to make sure that the metadata you want to keep is included in the exported photos.
By adding metadata to your exported photos, you create a valuable digital footprint for your images. Captions, titles, copyright information, and keywords make it easier to organize and find your photos, protect your work, and enhance their marketability. Take advantage of Lightroom’s metadata options to ensure your photos are properly labeled, attributed, and easily discoverable by others.
Applying Watermarks during Export
Watermarks serve as a means to protect your images and establish your brand identity. They can be applied as visible overlays during the export process in Lightroom. Adding watermarks to your exported photos ensures proper attribution, discourages unauthorized use, and enhances brand recognition. Here’s how you can apply watermarks during export in Lightroom:
1. Creating a Watermark:
In Lightroom’s Export window, you can create a customized watermark to apply to your exported photos. You have the option to use either a text-based watermark or an image-based watermark. For a text watermark, you can specify the text, font, size, color, and position. If you prefer an image watermark, you can choose an image file to use as your watermark.
2. Positioning and Opacity:
Lightroom provides options to adjust the positioning and opacity of your watermark. You can choose to position the watermark in a specific corner, center it horizontally or vertically, or place it anywhere you desire. Additionally, you can control the opacity of the watermark to achieve the desired visibility without overpowering the image itself.
3. Sizing the Watermark:
Consider the size of your watermark relative to the exported photo. Lightroom allows you to adjust the size of the watermark based on a percentage of the photo’s width or height. It’s important to find a balance where the watermark is clearly visible but doesn’t detract from the overall composition.
4. Applying Watermarks Consistently:
If you’re exporting a series of photos or have a particular watermark design that you use consistently, creating a watermark preset can save you time and ensure consistency across your exports. By saving your watermark settings as a preset, you can easily apply it to future exports without having to set up the watermark each time.
5. Previewing the Watermarked Images:
Before finalizing the export, it’s important to preview the watermarked images to ensure they look as expected. Use the preview option in Lightroom to examine the exported photos with the applied watermark. This allows you to make any necessary adjustments to the watermark settings and ensure it complements the image without overpowering it.
Applying watermarks during export adds an extra layer of protection and branding to your exported photos. Whether you choose a text-based or image-based watermark, it’s important to strike a balance between visibility and subtlety. Watermarks not only deter unauthorized use but also help establish your professional identity and increase brand recognition. Take advantage of Lightroom’s watermarking capabilities to protect and promote your work effectively.
Creating Export Presets for Efficient Workflow
Export presets in Lightroom are a powerful tool that allows you to save your frequently used export settings for quick and efficient exporting. By creating export presets, you can streamline your workflow, ensure consistency across your exports, and save valuable time. Here’s how you can create export presets in Lightroom:
1. Configuring your Export Settings:
Before creating an export preset, configure your desired export settings, including file format, image quality, image sizing, metadata, watermarks, and any other relevant options. Fine-tune the settings until they match your preferred output.
2. Accessing the Export Dialog:
To create an export preset, navigate to the Export dialog in Lightroom. You can access the Export dialog by going to the File menu and selecting “Export” or by using the shortcut Command/Control + Shift + E.
3. Saving the Export Settings as a Preset:
In the Export dialog, once you’ve configured all the desired export settings, click on the “Add” button to save the settings as a new export preset. Give the preset a descriptive name that reflects the purpose or style of the preset.
4. Customizing Additional Export Preset Options:
Lightroom offers additional options to customize your export presets. You can choose to include or exclude specific metadata, sharpening settings, post-processing actions, and more. Explore these options to tailor your presets to your specific workflow needs.
5. Managing and Organizing Presets:
As you create multiple export presets, Lightroom provides options to manage and organize them. You can edit, delete, or reorder your presets from the Preset Browser within the Export dialog. Organize your presets into folders to keep them organized and easily accessible.
6. Applying Export Presets:
Once you’ve created and organized your export presets, applying them to your photos is simple. In the Export dialog, select the preset you want to use from the Preset Browser, and all the export settings will be automatically applied to the current selection of photos. This allows you to export images efficiently and consistently without manually adjusting each setting every time.
7. Reviewing and Adjusting Settings:
Before initiating the export, it’s important to review the applied preset settings to ensure they are appropriate for the current batch of photos. Double-check any specific export parameters, such as resizing, sharpening, or watermarks, to guarantee they are suitable for the images being exported.
Creating export presets in Lightroom is a valuable way to streamline your workflow and maintain consistency in your exports. By configuring and saving your frequently used export settings, you can save time and ensure that your exported images meet your desired specifications. Experiment with different presets and fine-tune them to maximize efficiency and productivity in your photography workflow.
Exporting Images for Social Media or Web Use
Exporting images from Lightroom for social media or web use requires careful consideration of the specific requirements and limitations of these platforms. By optimizing your exported photos, you can ensure they look their best and load quickly on different devices. Here’s how you can export images for social media or web use:
1. Selecting the Appropriate File Format:
For social media or web use, JPEG is the most commonly used file format. It provides a good balance between image quality and file size, ensuring your images load quickly on different platforms and devices.
2. Adjusting Image Quality and File Size:
Since web platforms often have file size restrictions, it’s important to find the right balance between image quality and file size. While higher quality settings may result in better image clarity, they can also lead to larger file sizes, impacting loading times. Aim for a quality setting of around 70-80 to maintain a good balance between visual appeal and optimized file size.
3. Resizing Images for Web:
To ensure your images fit well within the dimensions of social media or web platforms, resize them accordingly. Consider the recommended image sizes or aspect ratios for each platform, such as Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter. Lightroom’s export settings allow you to specify the dimensions of your exported photos to match these requirements.
4. Applying Sharpening:
Sharpening your images for web use helps enhance the details and ensure they appear crisp and clear. During the export process, adjust the sharpening settings to optimize the sharpness without introducing artifacts or excessive halos. Preview the exported images to ensure the sharpening effect is appropriate and doesn’t compromise image quality.
5. Compressing Image Files:
While export settings control image quality and file size, additional image compression can further optimize loading times. Use web-based compression tools or plugins to compress the exported JPEG files without compromising image quality. These tools can reduce the file size without significant loss in visual appeal.
6. Embedding Metadata:
When exporting images for social media or web use, it’s important to embed relevant metadata, such as captions, titles, and copyright information. This ensures proper attribution and aids in searchability across platforms.
7. Previewing Exported Images:
Before sharing your exported images, take the time to preview them in different web browsers and devices. This step allows you to ensure they appear as intended, without any color shifts, distortion, or loss of detail.
Exporting images for social media or web use requires attention to detail to ensure optimal visual presentation and loading times. By selecting the appropriate file format, adjusting image quality and file size, resizing, applying sharpening, compressing files, embedding metadata, and previewing the results, you can effectively share your photos on social media and web platforms, reaching a wider audience while maintaining the visual integrity of your images.
Exporting Images for Print or Publication
When exporting images from Lightroom for print or publication, it is essential to take into consideration the specific requirements and limitations of these mediums. By optimizing your exported photos for print or publication, you can ensure they reproduce accurately and meet the desired standards. Here’s how you can export images for print or publication:
1. Choosing the Right File Format:
For print or publication, the commonly recommended file formats are TIFF or JPEG. TIFF is a lossless format that preserves all the image data, making it ideal for high-quality printing. JPEG is a compressed format that strikes a balance between file size and image quality, suitable for most print and publication needs.
2. Configuring Image Resolution:
Image resolution is an important factor when exporting photos for print or publication. The resolution determines the level of detail and sharpness of the printed image. It is measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). For print, a resolution of 300 PPI or higher is generally recommended to ensure crisp and detailed output. For online or digital publications, a resolution of 72-150 PPI is sufficient.
3. Adjusting Color Space:
Color space defines the range of colors that can be reproduced in an image. For print or publication, the commonly used color space is Adobe RGB or sRGB. Adobe RGB provides a wider gamut of colors, suitable for professional printing. sRGB is a smaller color space, widely used for web and digital purposes. Consider the specific requirements of your printing or publication medium and choose the appropriate color space accordingly.
4. Soft Proofing:
Soft proofing allows you to simulate the output of your exported images before printing or publishing. Use Lightroom’s soft proofing feature to preview how your photos will look in different print or publication mediums, taking into account factors like paper type, ink saturation, and color profiles. This helps you make any necessary adjustments to ensure accurate color representation.
5. Embedding Metadata:
When exporting images for print or publication, it’s important to embed relevant metadata, such as copyright information and captions. This ensures proper attribution and provides important information for readers, viewers, or buyers of your printed or published work.
6. Reviewing the Exported Images:
Before sending your images for printing or publication, carefully review the exported files. Zoom in to check for any artifacts, noise, or compression issues that may have occurred during the export process. Ensure that the colors, details, and overall appearance of the images meet your expectations.
Exporting images for print or publication requires attention to detail to ensure accurate reproduction and the desired visual impact. By choosing the right file format, configuring image resolution and color space, performing soft proofing, embedding metadata, and thoroughly reviewing the exported images, you can confidently share your work in printed materials or publications, ensuring the highest quality output.
Troubleshooting Common Export Issues in Lightroom
While Lightroom provides a seamless export function, issues may sometimes arise during the export process. Understanding and troubleshooting these common export issues can help you resolve them quickly and ensure that your exported images meet your desired specifications. Here are some common export issues in Lightroom and their possible solutions:
1. Missing or Incorrect Metadata:
If you notice that the exported images are missing metadata or have incorrect metadata, double-check your export settings. Ensure that you have included the correct metadata fields and that they are configured correctly. Review your metadata presets or adjust the settings manually to ensure the desired metadata is associated with the exported images.
2. Decreased Image Quality:
If you find that your exported images have a noticeable decrease in quality or appear pixelated, revisit your export settings. Check the image quality settings and adjust them accordingly. Increase the quality setting or consider exporting the images in a different file format, such as TIFF, to retain more detail and minimize compression.
3. Incorrect Color or Contrast:
If you notice that the exported images have inconsistent color or contrast compared to what is displayed in Lightroom, review your color space settings. Ensure that the correct color profile is selected during export. If you are exporting for a specific printing or publishing medium, soft proof your images to simulate the output and make any necessary adjustments to maintain accurate color representation.
4. Export Size Limitations:
Sometimes, you may encounter limitations on export size, either due to file size restrictions or pixel dimensions. If your images exceed the limitations set by the export destination, consider resizing them or adjusting the image quality settings to reduce the file size. You can also check the requirements of the specific platform or medium and make the necessary adjustments to meet their specifications.
5. Watermark Issues:
If your watermarks are not appearing or appearing incorrectly on the exported images, check your watermark settings. Ensure that the watermark is properly positioned, sized, and has the desired opacity. Preview the exported images to verify that the watermark is applied as intended. If necessary, edit your watermark settings or create a new watermark preset that addresses the issue.
6. Slow Export Times:
If you experience slow export times, there are several factors to consider. First, ensure that your computer’s performance meets the requirements for running Lightroom smoothly. Close any unnecessary applications or processes that may be affecting the export performance. You can also try exporting smaller batches of images instead of exporting all at once. Consider optimizing your Lightroom catalog and preview cache to improve overall performance.
By troubleshooting common export issues in Lightroom, you can overcome technical challenges and ensure that your exported images meet your desired specifications. By carefully reviewing your export settings, adjusting image quality and color space, verifying metadata inclusion, and troubleshooting specific issues as they arise, you can achieve seamless exports of your images and achieve the desired visual outcome.