Subtitle 1: Router Power Issues
When it comes to troubleshooting home network router problems, one of the first areas to investigate is router power issues. A properly functioning router requires a stable and consistent power supply. Without it, the router can experience various connectivity issues that disrupt your internet experience.
To address router power issues, there are a few steps you can take:
- Check the power source: Ensure that your router is plugged into a working power outlet. If the outlet is controlled by a switch, make sure it is turned on. If possible, try plugging the router into a different outlet to eliminate any potential power supply problems.
- Inspect the power cable: Examine the power cable for any signs of damage, such as frayed or exposed wires. If you notice any issues, replace the power cable with a new one. Make sure to use the correct voltage and amperage rating for your router.
- Reset the router: Sometimes, a simple reset can resolve power-related issues. Locate the reset button on your router, typically found on the back or bottom. Use a paperclip or a similar tool to press and hold the reset button for about 10 seconds. This will restore the router to its default settings and power cycle it.
- Consider a backup power source: To prevent power-related interruptions, you may want to invest in an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). A UPS acts as a power backup, providing temporary power in the event of an outage. This can help protect your router and maintain connectivity during power fluctuations.
By addressing router power issues, you can eliminate one potential cause of network problems. However, if the power-related troubleshooting steps do not resolve your router issues, it may be necessary to explore other areas, such as Wi-Fi connectivity problems or firmware updates and router settings.
Subtitle 2: Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems
If you’re experiencing issues with Wi-Fi connectivity, it can be frustrating and disruptive to your online tasks and activities. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve common Wi-Fi connectivity problems:
- Check Wi-Fi signal strength: Begin by ensuring that your devices are in range of the Wi-Fi signal. Walls, distance, and obstacles can weaken the signal strength. Consider repositioning your router or using Wi-Fi extenders to improve coverage in dead zones.
- Restart your router: Sometimes, Wi-Fi connectivity issues can be resolved simply by restarting the router. Unplug the power cable, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. Allow the router to fully reboot before testing the Wi-Fi connection again.
- Check for interference: Other electronic devices such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, or baby monitors can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Keep these devices away from your router and move them to a different location if possible.
- Secure your Wi-Fi network: An unsecured Wi-Fi network can allow unauthorized users to access and slow down your connection. Ensure that your Wi-Fi network is password-protected and uses encryption (such as WPA2) to keep your connection secure.
- Update router firmware: Outdated router firmware can cause connectivity issues. Visit the manufacturer’s website and check for any available firmware updates for your specific router model. Follow the instructions provided to update the firmware and improve compatibility and performance.
- Disable conflicting settings: Some advanced router settings, such as MAC address filtering or port forwarding, may conflict with certain devices or applications. Temporarily disable these settings to troubleshoot connectivity issues.
By following these steps, you can often resolve Wi-Fi connectivity problems. However, if the issues persist, it may be helpful to consult the router’s user manual or contact the manufacturer’s support for further assistance. Remember to document any changes or troubleshooting steps you have taken for easy reference if needed.
Subtitle 3: Slow Internet Speeds
Suffering from slow internet speeds can be frustrating, especially when you have important online tasks or streaming to do. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot and improve slow internet speeds:
- Check your internet plan: Verify that you are subscribed to an internet plan that meets your needs. Contact your internet service provider (ISP) to confirm your current plan and inquire about any potential upgrades or promotions that may offer faster speeds.
- Test your connection speed: Use an online speed test tool to measure your current internet speed. This will help you determine if the issue is with your ISP or your network setup.
- Restart your router and modem: Sometimes, a simple power cycle can solve slow speed issues. Unplug both your router and modem from the power source, wait for about 30 seconds, then plug them back in. Allow the devices to restart and reconnect before testing the internet speed again.
- Reduce bandwidth usage: If multiple devices are connected to your network and consuming large amounts of bandwidth, it can lead to slower speeds for all users. Prioritize essential tasks and consider temporarily disconnecting devices that are not in use.
- Check for outdated hardware: Older routers or modems may not be capable of delivering high-speed connections. Check if your hardware is outdated, and if necessary, consider upgrading to a newer model that supports faster speeds.
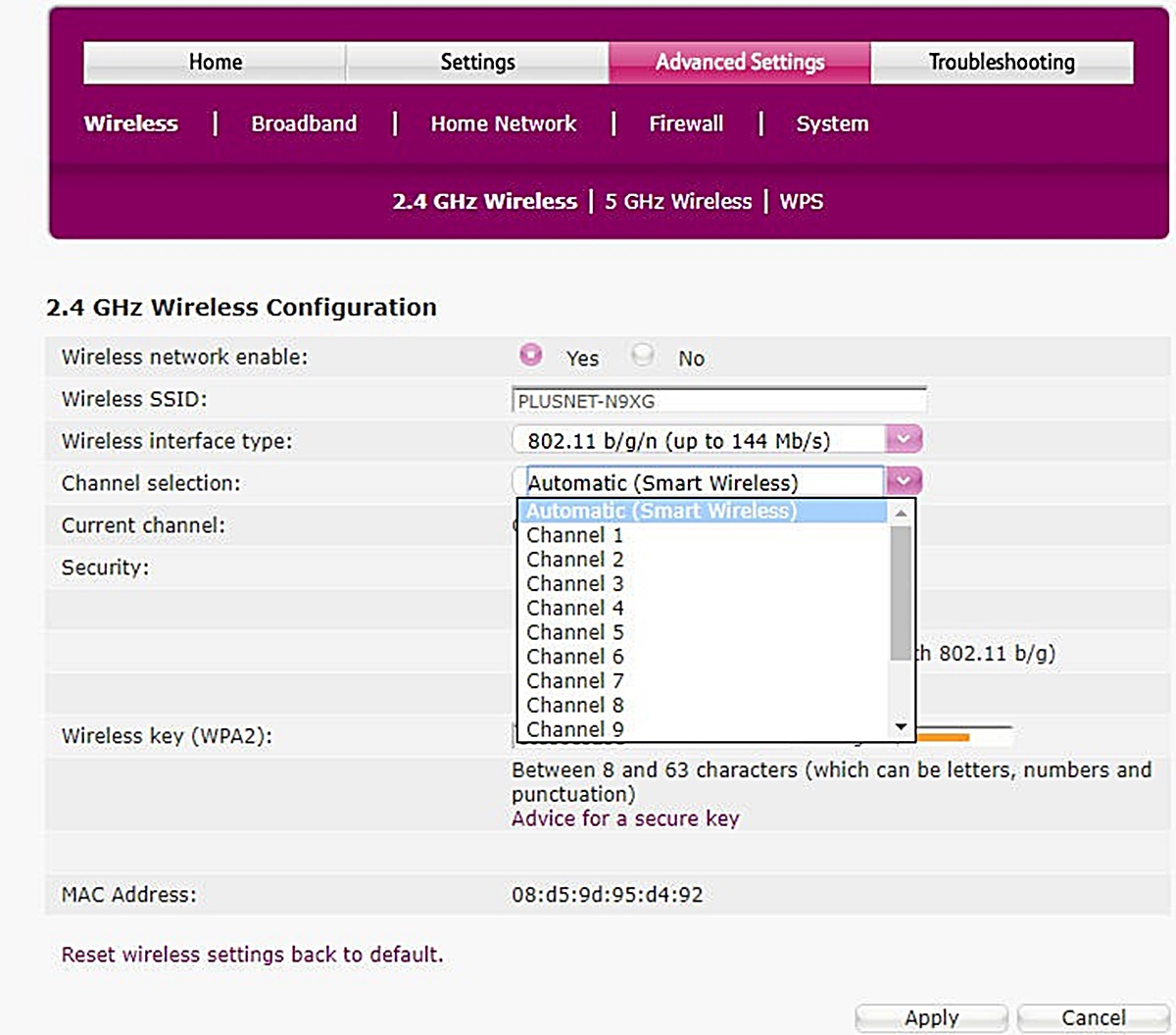
- Optimize your Wi-Fi signal: Position your router in a central location away from obstructions and interference. Additionally, adjust the channel on which your router operates to avoid congestion from neighboring networks.
- Scan for malware or viruses: Malware or viruses on your devices can consume bandwidth and slow down your internet speeds. Run a comprehensive scan with reputable antivirus software to detect and remove any potential threats.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can often identify and address the factors contributing to slow internet speeds. However, if the issue persists, it is advisable to reach out to your ISP for further assistance or consider consulting a professional network technician.
Subtitle 4: Network Dropping or Disconnecting
Experiencing frequent network drops or disconnections can be frustrating, especially when you’re in the middle of important tasks or online activities. Here are some troubleshooting steps to help you address network dropping or disconnecting issues:
- Restart your router and modem: Often, a simple reset can fix intermittent connectivity problems. Unplug both your router and modem from the power source, wait for about 30 seconds, then plug them back in. Allow the devices to restart and reconnect before testing the network connection again.
- Check the Wi-Fi signal: Ensure that your devices are within range of a strong Wi-Fi signal. Walls, furniture, or other objects can weaken the signal strength. Consider moving closer to the router or using Wi-Fi extenders to improve coverage.
- Update router firmware: Outdated firmware can cause network issues. Visit the manufacturer’s website to check for any available firmware updates for your router model. Follow the instructions provided to update the firmware and improve compatibility and stability.
- Change Wi-Fi channel: Wi-Fi congestion from neighboring networks operating on the same channel can cause connectivity problems. Access your router’s settings, usually through a web interface, and change the Wi-Fi channel to a less congested one.
- Disable energy-saving mode: Some routers have an energy-saving mode that can cause intermittent disconnections. Access your router’s settings and ensure that energy-saving mode is disabled to maintain a stable network connection.
- Check for interference: Electronic devices like cordless phones, baby monitors, or microwave ovens can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Keep these devices away from the router to minimize potential interference.
- Consider a hardwired connection: If possible, connect your devices to the router using an Ethernet cable. A wired connection provides a more stable and reliable connection, especially for devices requiring consistent network access.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can often resolve network dropping or disconnecting issues. However, if the problem persists, it may be worth contacting your internet service provider (ISP) for further assistance or considering professional help to diagnose and fix any underlying network issues.
Subtitle 5: Firmware Updates and Router Settings
Firmware updates and router settings play a crucial role in maintaining the performance and security of your home network. If neglected, outdated firmware or incorrect router settings can cause various connectivity issues. Here’s how you can troubleshoot and optimize firmware updates and router settings:
- Check for firmware updates: Regularly check the manufacturer’s website for firmware updates for your router model. Outdated firmware can lead to compatibility issues and security vulnerabilities. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to update the firmware to the latest version.
- Reset router settings: If you’ve made changes to your router settings and are experiencing issues, consider performing a factory reset. This will revert the router to its default settings. Make sure to document any custom settings before resetting as you will need to reconfigure them afterward.
- Ensure correct Wi-Fi password: Double-check that the Wi-Fi password on your router matches the password you’re using to connect your devices. A mismatched password will result in failed authentication and connectivity issues.
- Optimize Quality of Service (QoS) settings: Quality of Service allows you to prioritize certain types of network traffic. Configure your router’s QoS settings to allocate adequate bandwidth to critical applications or devices, such as online gaming or video streaming, ensuring a smoother experience.
- Enable guest network: If you frequently have guests who need Wi-Fi access, consider enabling a guest network. This separate network allows guests to connect without compromising the security of your main network.
- Set up port forwarding: If you’re running specific applications or services that require inbound connections, configure port forwarding in your router settings. This directs incoming traffic to the appropriate device on your network.
- Enable firewall settings: Ensure that your router’s firewall is enabled to protect your network from unauthorized access and potential security threats. Check your router settings for firewall options and adjust them according to your needs.
Regularly updating firmware and optimizing router settings is essential for a smooth network experience. By following these troubleshooting steps, you can ensure your router is running the latest software, configured correctly, and offering the best performance and security for your connected devices.
Subtitle 6: Interference from Electronic Devices
Interference from electronic devices can disrupt the performance and stability of your home network, leading to connectivity issues. Identifying and minimizing such interference is crucial in troubleshooting network problems. Here’s how you can address interference from electronic devices:
- Identify potential sources: Identify any electronic devices located near your router that may be causing interference. Common culprits include cordless phones, microwave ovens, baby monitors, and Bluetooth devices.
- Move devices away from the router: Physically separate any devices that could potentially interfere with your router’s signal. Distance your router from other electronic devices as much as possible to minimize interference.
- Change wireless channel: Access your router’s settings and consider changing the wireless channel to avoid congestion caused by neighboring networks. Experiment with different channels to find the one with the least interference.
- Upgrade to a dual-band router: Consider upgrading to a dual-band router that operates on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 5 GHz band is less crowded and can offer faster speeds with less interference from other devices.
- Implement wired connections: For devices that require a stable and uninterrupted connection, consider using wired Ethernet connections instead of relying on Wi-Fi. Ethernet connections are not susceptible to interference from electronic devices.
- Utilize Wi-Fi repeaters or extenders: If your Wi-Fi coverage is limited due to interference, use Wi-Fi repeaters or extenders to boost the signal and extend the range. This can help overcome potential interference from electronic devices.
- Upgrade older devices: Older devices may not be equipped with the latest wireless technology or have inferior antennas, which can contribute to interference. Consider upgrading outdated devices to newer models that offer better performance and fewer interference issues.
By taking these steps to minimize interference from electronic devices, you can enhance the stability and reliability of your home network. However, if you continue to experience connectivity issues, it may be necessary to explore other troubleshooting options such as checking DNS and IP address issues or seeking professional help.
Subtitle 7: Configuring DNS and IP Address Issues
Configuring DNS (Domain Name System) and IP (Internet Protocol) address settings properly is crucial for ensuring a smooth and stable network connection. If you’re experiencing connectivity problems, it’s worth troubleshooting and addressing any DNS or IP address-related issues. Here’s how you can do it:
- Check DNS settings: Ensure that your router’s DNS settings are correctly configured. You can manually set DNS servers, such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or OpenDNS (208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220). Alternatively, you can use automatic DNS assignment provided by your ISP.
- Flush DNS cache: Sometimes, DNS-related issues can be resolved by flushing the DNS cache. Open the command prompt or terminal on your computer and enter the appropriate command, such as “ipconfig /flushdns” on Windows or “sudo dscacheutil -flushcache” on macOS.
- Renew IP address: If your device is experiencing IP address conflicts or connectivity problems, renewing the IP address can help. Open the command prompt or terminal and enter the command “ipconfig /release” followed by “ipconfig /renew” on Windows, or “sudo ifconfig [interface] down” followed by “sudo ifconfig [interface] up” on macOS.
- Manually assign IP addresses: Ensure that your devices are properly assigned IP addresses. You can set them to obtain IP addresses automatically (DHCP) or assign static IP addresses within your router’s settings. Incorrect IP address assignments can lead to connectivity issues.
- Restart your devices: Sometimes, simple restarts can resolve DNS or IP address-related issues. Restart both your router and devices connected to the network to refresh the settings and establish a new connection.
- Disable IPv6: If you’re facing compatibility issues or experiencing slow connections with IPv6, consider disabling it on your router and devices and rely solely on IPv4.
- Check for firmware updates: Outdated router firmware can sometimes cause DNS or IP address problems. Check for any available firmware updates on the manufacturer’s website and update your router’s firmware to the latest version.
By addressing DNS and IP address issues, you can improve the stability and efficiency of your network connection. However, if you continue to experience problems, it may be necessary to consider further troubleshooting or seek professional assistance.
Subtitle 8: Troubleshooting Ethernet Connection Problems
Troubleshooting Ethernet connection problems is essential when experiencing issues with wired network connectivity. Whether you’re unable to establish a connection or experiencing intermittent disruptions, here are some steps to help you troubleshoot Ethernet connection problems:
- Check cable connections: Ensure that the Ethernet cable is securely plugged into both the router/modem and your device. A loose or damaged cable can result in a weak or inconsistent connection.
- Swap Ethernet cables: If possible, try using a different Ethernet cable to see if the issue lies with the cable itself. Sometimes, a faulty or damaged cable can cause connectivity problems.
- Restart your devices: Restart both your router/modem and the device you’re trying to connect via Ethernet. This can help refresh the network connections and resolve any temporary issues.
- Update network drivers: Outdated or incompatible network drivers can cause Ethernet connection problems. Visit your device manufacturer’s website or the network adapter manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest network drivers for your specific hardware.
- Check network adapter settings: Ensure that the network adapter settings on your device are configured correctly. Check for any unusual settings or changes that may be impacting the Ethernet connection. You can access these settings through the device’s network or adapter properties.
- Disable network security software: Sometimes, security software or firewalls can interfere with Ethernet connections. Temporarily disable any network-related security software and check if that resolves the issue.
- Reset network settings: Resetting network settings can often help in resolving Ethernet connection problems. Go to the network settings on your device and choose the option to reset or refresh the network settings.
- Test with a different device: If possible, try connecting a different device via Ethernet to determine if the issue is specific to the device or the network. If the second device works fine, it indicates that there may be a problem with the initial device’s network adapter.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can often identify and resolve Ethernet connection problems. However, if the issues persist, it may be necessary to seek professional assistance or contact your internet service provider (ISP) for further support.
Subtitle 9: Resetting the Router to Factory Settings
Resetting your router to factory settings can be an effective solution when dealing with persistent network issues or if you need to start fresh with your router configuration. However, it’s important to note that performing a factory reset will erase all customized settings and return the router to its default state. Here’s how you can reset your router:
- Locate the reset button: Find the reset button on your router. It is usually a small, recessed button located on the back or bottom of the router. You may need a paperclip or a similar tool to press and hold the reset button.
- Press and hold the reset button: Press and hold the reset button for about 10-15 seconds. Make sure to keep the button depressed for the entire duration to ensure a successful reset.
- Wait for the router to reboot: After releasing the reset button, give the router a few moments to complete the reset process. During this time, the router will restart and restore the factory default settings.
- Reconfigure the router: Once the router has fully rebooted, you will need to reconfigure its settings. This includes setting up a new Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and password, as well as any other desired customization such as port forwarding or parental controls.
- Refer to the user manual: If you encounter any difficulties or confusion during the reconfiguration process, consult the user manual that came with your router. It should provide detailed instructions on how to set up and customize your router settings.
Performing a factory reset can often resolve persistent network issues by eliminating any previously misconfigured settings or software glitches. However, it’s important to note that you will lose all customized settings in the process. Therefore, it’s advisable to document and backup your router settings before performing a factory reset.
Subtitle 10: Seeking Professional Help
When troubleshooting home network router problems, it’s not uncommon to encounter complex issues that require more advanced knowledge or expertise. If you’ve exhausted all the available troubleshooting steps and are still facing persistent connectivity problems, it may be time to seek professional help. Here are some situations where professional assistance can be beneficial:
- Advanced network configuration: If you require specific network configurations that go beyond basic settings, a network professional can help set up complex setups such as VLANs, VPNs, or advanced firewall rules to meet your specific requirements.
- Hardware failures: If you suspect that your router or networking hardware is malfunctioning, a professional technician can diagnose the issue and provide the necessary repairs or replacements.
- Intermittent connection issues: If you’re experiencing sporadic or intermittent connection problems that are difficult to troubleshoot on your own, a professional can utilize advanced diagnostic tools to identify the underlying cause and implement an effective solution.
- Network security concerns: If you suspect that your network has been compromised or want to enhance the security of your home network, seeking professional assistance can ensure that your network is properly protected from potential threats.
- Network scalability: If you’re planning to expand your network or add new devices and want to ensure optimal performance and scalability, a professional can provide guidance and assistance in designing and implementing a network infrastructure that meets your needs.
- ISP-related issues: If you suspect that the problems you’re experiencing are related to your internet service provider (ISP), contacting their technical support or a professional can help facilitate communication with the ISP and ensure a prompt resolution.
Professional help can provide the necessary expertise and tools to troubleshoot and resolve complex network issues. Whether it’s configuring advanced settings, diagnosing hardware problems, or optimizing network performance, a professional technician can help ensure a reliable and efficient home network.