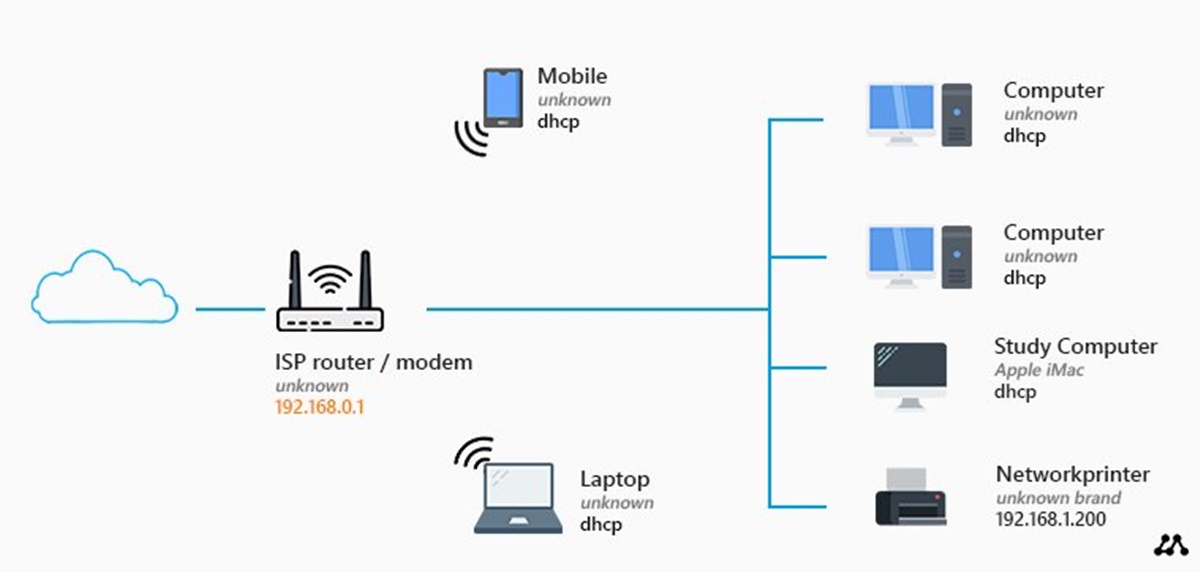
Benefits of Home Network Diagrams
Home network diagrams are essential tools for homeowners and IT professionals alike. They provide a visual representation of the network setup within a home, showcasing the various components and their connections. These diagrams offer numerous benefits, including:
- Clear Visualization: With a home network diagram, you can easily see the layout of your network infrastructure. It provides a clear visualization of how devices and equipment are connected, making it easier to troubleshoot issues or make changes.
- Troubleshooting Made Easy: When network problems arise, a home network diagram can be a lifesaver. By referring to the diagram, you can quickly identify the problem area and pinpoint the specific device or connection causing the issue. This saves valuable time in resolving issues and reduces frustration.
- Efficient Planning and Expansion: Home network diagrams are valuable tools when planning to expand or upgrade your network. By visually mapping out your current setup, you can identify areas that need improvement or areas where additional devices may be added. This ensures a more efficient and organized approach to network expansion.
- Enhanced Security: Network security is a top concern for most homeowners. A home network diagram helps you identify potential security vulnerabilities by allowing you to see all connected devices, including routers, switches, and access points. This enables you to take necessary precautions to protect your network and data.
- Documentation: Keeping a home network diagram as part of your documentation is essential. It serves as a valuable reference for future troubleshooting, repairs, or upgrades. Having a detailed and up-to-date diagram ensures that anyone working with your network can quickly understand its configuration.
- Better Communication: If you need to discuss your network setup with an IT professional or someone who may assist with troubleshooting, having a visual representation in the form of a network diagram helps facilitate better communication. It allows you to clearly explain your network setup and the specific issues you’re experiencing.
Overall, home network diagrams provide an array of benefits, including clear visualization, streamlined troubleshooting, efficient planning and expansion, enhanced security, comprehensive documentation, and improved communication. By investing time in creating and maintaining a home network diagram, you can ensure a well-organized and optimized network setup.
Components of a Home Network Diagram
A home network diagram comprises various components that are essential for understanding and visualizing the network infrastructure. These components provide valuable information about the devices and connections within the network. Here are the key components typically included in a home network diagram:
- Modem: The modem is the device that connects your home network to the internet. It receives the signals from your internet service provider (ISP) and converts them into usable data for your network.
- Router: The router is the central hub of your network that directs traffic between devices within your home network and the internet. It allows multiple devices to connect to the internet simultaneously.
- Switch: A switch is used to connect multiple devices within the network. It acts as a central point where devices can communicate with one another, improving network performance and reducing congestion.
- Access Points: Access points are used to extend the wireless network range. They enable wireless devices to connect to the network in areas where the Wi-Fi signal from the router may be weak.
- Devices: Devices such as computers, laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices are essential components of a home network. These devices connect to the network either wired or wirelessly.
- Cables: Ethernet cables are used to establish wired connections between devices and the router or switch. These cables ensure reliable and fast network connectivity.
- Firewall: A firewall is a security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. It helps protect your network from unauthorized access and potential threats.
- Printers and Network Storage: Printers and network storage devices can be included in the diagram, as they are often network-connected devices that enable easy sharing and access of resources.
It’s important to include labels and symbols in the network diagram to clearly indicate each component and its connections. This ensures that anyone viewing the diagram can easily understand the network infrastructure and identify the purpose of each device.
By including these components in your home network diagram, you can create a comprehensive representation of your network setup and gain a better understanding of how each device interacts within the network.
Different Types of Home Network Diagrams
Home network diagrams can be created in various formats, depending on the level of detail and the specific information you wish to convey. Different types of diagrams serve different purposes and allow for different levels of complexity. Here are the most commonly used types of home network diagrams:
- Physical Layout Diagrams: Physical layout diagrams provide a visual representation of the physical components of the network. This includes devices such as routers, switches, access points, and computers, as well as the cables that connect them. Physical layout diagrams focus on the actual placement and positioning of devices within the home.
- Logical Layout Diagrams: Logical layout diagrams showcase the logical connections and interdependencies of devices in the network. They highlight how devices communicate with each other, such as through the router or switch. Logical layout diagrams focus on the flow of data and the logical relationship between devices.
- Combination Layout Diagrams: Combination layout diagrams incorporate elements from both physical and logical layout diagrams. They provide a comprehensive view of the network, including the physical placement of devices and the logical connections between them. Combination layout diagrams offer a more detailed representation of the network setup.
The choice of diagram type depends on your specific needs and the level of detail required. If you are primarily interested in understanding the physical placement of devices, a physical layout diagram may suffice. On the other hand, if you need to visualize how devices communicate and the logical structure of the network, a logical layout diagram would be more appropriate.
It’s important to note that the complexity of the network will also influence the type of diagram you choose. For smaller, simpler networks, a basic physical layout diagram may be sufficient. However, for larger and more intricate networks, a combination layout diagram can provide a more comprehensive and detailed representation.
Physical Layout Diagrams
Physical layout diagrams are a type of home network diagram that visually represents the physical arrangement and placement of network components within a home. These diagrams provide a detailed and accurate depiction of the physical layout to help users better understand the spatial distribution of devices and cables. Physical layout diagrams offer several advantages:
- Clear Visualization: Physical layout diagrams provide a clear and visual representation of the physical placement of devices within the network. They showcase the location of routers, switches, access points, and other network components, allowing users to see how devices are physically connected and positioned.
- Organization and Planning: By creating a physical layout diagram, homeowners and IT professionals can effectively plan and organize their network infrastructure. They can assess the optimal positioning of devices to ensure efficient connectivity and minimize physical obstructions that may affect network performance.
- Troubleshooting Assistance: When network issues arise, physical layout diagrams play a crucial role in troubleshooting. Easily identifying the physical location of devices and cables helps narrow down the potential source of the problem. It allows users to quickly identify loose connections, faulty cables, or damaged devices, facilitating faster resolution.
- Documentation and Maintenance: Physical layout diagrams serve as valuable documentation for future reference and maintenance. They provide a record of the network’s physical setup, making it easier to plan upgrades, replacements, or expansions. Keeping the diagram up-to-date ensures that accurate information is available for ongoing network management.
- Communication with Professionals: Physical layout diagrams facilitate effective communication with network professionals or technicians. By sharing the diagram, users can easily describe their network configuration and seek guidance or assistance when needed. It helps professionals understand the physical arrangement, reducing troubleshooting time and improving the quality of support.
When creating a physical layout diagram, it’s essential to accurately represent the physical location and connectivity of devices. Using clear labels, symbols, and lines to depict devices and their connections ensures readability and ease of understanding for anyone viewing the diagram.
Physical layout diagrams are valuable tools for understanding and managing the physical aspects of a home network. By utilizing these diagrams, homeowners and IT professionals can optimize network performance, simplify troubleshooting, and ensure effective organization and planning of their network infrastructure.
Logical Layout Diagrams
Logical layout diagrams are a type of home network diagram that focuses on illustrating the logical connections and relationships between devices within a network. These diagrams provide a visual representation of how data flows and how devices communicate with each other, regardless of their physical placement. Logical layout diagrams offer several benefits:
- Clarity of Communication: Logical layout diagrams make it easier to understand the logical structure of a network. They depict how devices are logically connected, such as through the router or switch, and how data is transmitted between devices. This clear visualization enhances communication among network administrators, IT professionals, and even individuals looking to troubleshoot network issues.
- Identification of Dependencies: Logical layout diagrams help identify dependencies and interdependencies between devices. They showcase how devices rely on each other for proper functioning and data transmission. By understanding these dependencies, network administrators can ensure that the network is designed and configured in an efficient and reliable manner.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: When network problems arise, logical layout diagrams aid in troubleshooting by providing insights into the flow of data. They assist in identifying potential bottlenecks, routing issues, or misconfigurations that may be affecting network performance. By following the logical connections shown in the diagram, administrators can narrow down the problem areas and resolve them promptly.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Logical layout diagrams help plan for network expansion and accommodate changes. They offer a blueprint to understand the current logical structure, making it easier to add or remove devices, modify configurations, or implement new technologies. By having a well-defined logical diagram, administrators can ensure a scalable, flexible, and future-proof network.
- Collaboration and Documentation: Logical layout diagrams are valuable tools for collaboration among network administrators and IT teams. They provide a shared understanding of the network’s logical structure, facilitating effective teamwork and collaboration in managing and maintaining the network. Additionally, logical layout diagrams serve as important documentation for future reference, ensuring continuity and easier troubleshooting.
When creating a logical layout diagram, it is crucial to accurately represent the logical connections between devices. Utilize standardized symbols and labels to indicate devices, protocols, and logical pathways. This ensures consistency and enhances the readability of the diagram.
Logical layout diagrams play a vital role in understanding and managing the logical aspects of a home network. By utilizing these diagrams, network administrators can optimize network performance, facilitate troubleshooting, plan for future growth, collaborate effectively, and maintain accurate documentation of the network’s logical structure.
Combination Layout Diagrams
Combination layout diagrams, as the name suggests, combine elements of both physical and logical layout diagrams to provide a comprehensive representation of a home network. These diagrams offer a holistic view that incorporates the physical placement of devices and the logical connections between them. Combination layout diagrams offer several advantages:
- Complete Visualization: Combination layout diagrams provide a complete and integrated view of the home network. They showcase both the physical placement of devices and the logical connections between them. This comprehensive visualization allows users to understand how devices are physically arranged and how they interact with one another.
- Clear Communication: Combination layout diagrams facilitate effective communication by providing a unified representation that covers both physical and logical aspects. This ensures that all parties involved have a shared understanding of the network infrastructure and its functioning. It improves communication among network administrators, IT teams, and even non-technical personnel.
- Comprehensive Troubleshooting: Combination layout diagrams simplify troubleshooting by offering a complete overview of the network. Users can easily identify the physical location of devices and cables, as well as the logical connections between them. This helps isolate issues, whether they are physical in nature, such as faulty cabling, or logical, such as misconfigured routers or switches.
- Documentation and Planning: Combination layout diagrams serve as valuable documentation for the network, capturing both physical and logical aspects. They enable network administrators to document the network’s current state, plan for future expansions or modifications, and maintain an accurate record of the network infrastructure. Combination layout diagrams also aid in implementing changes by understanding the interdependencies between physical and logical aspects of the network.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Combination layout diagrams allow for flexibility and scalability in network design. They provide insights into the physical layout and logical connections, facilitating planning for network expansion or adding new devices. By having a comprehensive overview, network administrators can make informed decisions and smoothly adapt to changing network requirements.
Creating a combination layout diagram requires attention to detail in representing both the physical and logical aspects of the network. Clear labels, symbols, and lines should be used to depict devices, cables, and connections, ensuring the diagram is easy to understand for all viewers.
Combination layout diagrams offer a holistic and detailed representation of a home network, merging the physical and logical aspects. By utilizing these diagrams, network administrators can effectively communicate network structures, simplify troubleshooting, document the network infrastructure, and plan for future growth and changes in the network.
How to Create a Home Network Diagram
Creating a home network diagram is a straightforward process that allows you to visually represent the layout and connections of your network. Follow these steps to create your own home network diagram:
- Determine the Scope of the Diagram: Decide what information you want to include in your diagram. Consider whether you want to focus on the physical layout, logical connections, or both.
- Identify the Components and Connections: Take an inventory of all the devices and equipment in your network, including routers, switches, access points, computers, and other connected devices. Map out the connections between these components, including both wired and wireless connections.
- Choose the Layout Type: Decide on the type of layout that best suits your needs – physical, logical, or a combination of both. This will determine how you arrange and represent the components and connections in your diagram.
- Use a Software or Online Tool: Select a diagramming tool that allows you to create professional-looking diagrams. There are various software options and online tools available, such as Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, or draw.io, that offer pre-built networking shapes and templates.
- Organize and Label the Diagram: Arrange the components and connections in a logical and visually appealing manner within the software or online tool. Label each device and connection clearly to ensure clarity and understanding.
- Share and Update the Diagram: Once your home network diagram is complete, consider sharing it with others who may need to understand or troubleshoot your network setup. Additionally, regularly update the diagram as you make changes to your network or add new devices to keep it accurate and up to date.
Remember to keep your home network diagram easily accessible and make any necessary updates whenever significant changes occur within your network. This will ensure that you have an accurate representation of your network’s configuration and aid in troubleshooting or future planning.
Determine the Scope of the Diagram
Before creating a home network diagram, it is important to determine the scope of the diagram and decide what information you want to include. The scope refers to the extent of detail and the specific aspects of your network that you intend to represent. Consider the following factors when determining the scope:
- Physical Layout: Decide if you want to focus on illustrating the physical placement of devices within your network. This involves capturing the physical location of devices such as routers, switches, access points, and computers, as well as the cabling infrastructure connecting them.
- Logical Connections: Determine if you want to depict the logical connections between devices in your network. This includes illustrating how data flows between devices, the role of routers and switches in routing data, and the logical structure of your network.
- Type of Diagram: Choose whether you want to create a physical layout diagram, a logical layout diagram, or a combination layout diagram that incorporates both physical and logical aspects. Each type of diagram has its own benefits and serves different purposes in illustrating your network.
- Level of Detail: Consider the level of detail you want to include in your diagram. This could include labeling each device, specifying the type of connections (wired or wireless), indicating IP addresses, or even showcasing the network topology.
By determining the scope of the diagram, you can establish a clear objective and ensure that the diagram accurately represents the aspects of your network that are most relevant to your needs.
It is important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the diagram informative and understandable, while also avoiding unnecessary complexity that may clutter the diagram. Consider who the intended audience of the diagram is – whether it’s for personal reference, documentation, or communication with IT professionals – and tailor the level of detail accordingly.
Taking the time to determine the scope of your home network diagram will help you create a focused and purposeful representation of your network setup, making it easier for you and others to understand the specific aspects of your network that are most important.
Identify the Components and Connections
Once you have determined the scope of your home network diagram, the next step is to identify the components and connections within your network. This involves taking an inventory of all the devices and equipment that make up your network and mapping out the connections between them. To effectively identify the components and connections, follow these steps:
- Device Inventory: Make a list of all the devices in your network, including routers, switches, access points, computers, printers, and any other network-connected devices. Include both wired and wireless devices.
- Device Details: Gather relevant information about each device, such as its make and model, IP address, MAC address, and any specific configuration details that are important for your network.
- Cable Connections: Identify the physical connections between devices using Ethernet cables. Determine which devices are connected directly to the router or switch and which devices are connected through intermediate devices (e.g., switches or access points).
- Wireless Connections: Take note of the wireless connections in your network. Identify the devices that are connected to your Wi-Fi network and understand the relationships between wireless access points, routers, and devices.
- Network Configuration: Assess the configuration settings of your network devices, such as IP addresses, subnet masks, gateway addresses, SSIDs, and security settings. This information can be useful for accurately representing your network in the diagram.
- Label and Document: Clearly label each device and connection in your inventory. Use standardized symbols or annotations to distinguish between different types of devices and connections. This will make it easier to create the diagram accurately and consistently.
By identifying the components and connections in your network, you gain a comprehensive understanding of how your devices are interconnected and can accurately represent this information in your home network diagram.
When creating the diagram, consider using a diagramming tool or software that provides predefined network shapes and symbols to represent different devices and connections. This will help you create a professional-looking diagram that is easy to understand for yourself and others who may view it.
Remember to periodically update the diagram as you make changes to your network or add new devices. Keeping the diagram up to date ensures that it remains an accurate representation of your network architecture.
Choose the Layout Type
When creating a home network diagram, choosing the right layout type is crucial to effectively represent the structure and connections within your network. The layout type determines how the components and connections are arranged in the diagram. There are three main types of layout to consider:
- Physical Layout Diagrams: Physical layout diagrams focus on illustrating the physical placement and positioning of devices within your network. This type of diagram provides a visual representation of where each device is located in your home or office. It helps you understand the spatial distribution of devices and the layout of the network infrastructure.
- Logical Layout Diagrams: Logical layout diagrams emphasize the logical connections and communication pathways between devices in your network. This type of diagram highlights how data flows between devices, how devices are logically interconnected through routers and switches, and how different network protocols are employed to facilitate communication.
- Combination Layout Diagrams: Combination layout diagrams incorporate elements from both physical and logical layouts to provide a comprehensive view of your network. These diagrams capture the physical placement of devices while also showcasing the logical connections between them. Combination layout diagrams offer a holistic representation of your network, integrating both physical and logical aspects for a more detailed analysis.
When choosing the layout type, consider your specific goals and the audience of the diagram. If you need to emphasize the physical arrangement of devices and cables, a physical layout diagram may be most suitable. Alternatively, if your focus is on illustrating logical connections and data flow, a logical layout diagram would be more appropriate.
If you want to provide a complete overview of your network, showcasing both physical and logical aspects, a combination layout diagram is the right choice. This type of diagram allows you to capture the relationships between physical placement and logical connections, providing a more comprehensive understanding of your network infrastructure.
Whichever layout type you choose, remember to use clear labels, symbols, and lines to represent devices and connections accurately. This will ensure that the diagram is easily understandable and can effectively convey the structure and connections within your home network.
Use a Software or Online Tool
Creating a home network diagram can be made easier and more efficient by utilizing dedicated software or online tools specifically designed for diagramming. These tools provide a user-friendly interface and pre-built networking shapes and templates to help you create professional-looking diagrams. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Research and Choose a Tool: Explore different software or online tools that offer network diagramming capabilities. Consider factors like ease of use, flexibility, available features, and compatibility with your operating system.
- Sign Up or Install: Create an account on the chosen online tool or download and install the selected software on your computer, following the provided instructions.
- Access Networking Shapes and Icons: Most diagramming tools offer pre-built shapes and icons specifically tailored for network diagrams. These include symbols for routers, switches, computers, servers, and other network components. Access and familiarize yourself with these resources within the tool.
- Create a New Diagram: Open a new project or diagram within the software or online tool. Select the appropriate networking template or start with a blank canvas, depending on your preference and the available options.
- Add Devices and Connections: Use the provided networking shapes and icons to represent devices and connections in your network. Drag and drop the shapes onto the canvas and arrange them according to the physical or logical layout you desire.
- Label and Annotate: Add labels, annotations, and descriptions to the devices and connections to provide clarity and context within the diagram. Use text boxes or other annotation tools available in the software or online tool.
- Customize and Format: Modify the appearance of the diagram by adjusting colors, line styles, fonts, and other formatting options as needed. This can help differentiate between devices, connections, and other elements within the diagram.
- Save and Export: Once the diagram is complete, save the project or diagram within the software or online tool. Consider exporting the diagram in a suitable format, such as PNG, JPEG, or PDF, to share it with others or include it in documentation.
Using a software or online tool streamlines the diagram creation process, allowing you to create professional-quality diagrams efficiently. These tools typically offer features that simplify adding, editing, and formatting network components, ensuring that your home network diagram is clear, organized, and visually appealing.
Before finalizing your choice of software or online tool, consider factors such as cost, collaboration features, integration with other software, and customer support to ensure the tool meets your specific requirements.
Organize and Label the Diagram
Once you have created the components and connections of your home network diagram, it is essential to organize and label the diagram effectively. This ensures clarity and improves the understanding of the diagram for both yourself and others. Consider the following steps to organize and label your diagram:
- Arrange Components: Arrange the devices and connections in a logical and visually appealing manner within the diagram. Group related devices together and consider the flow of data between devices to determine their positioning.
- Provide Clear Labels: Label each device and connection in your diagram to provide clear identification. Use concise and descriptive labels or text annotations to indicate the purpose or role of each element in the network.
- Use Standardized Symbols: Utilize standardized symbols or icons to represent different types of devices within your diagram. This helps maintain consistency and enhances the readability of the diagram for those familiar with networking conventions.
- Indicate Connection Types: Clearly indicate the types of connections between devices, whether they are wired or wireless connections. Use appropriate lines or arrows to represent the connections and ensure they are appropriately labeled.
- Consider Color Coding: Use color coding to differentiate between different categories of devices or to identify specific properties of components. For example, color code devices based on their function or highlight critical connections with a distinct color.
- Keep it Neat and Readable: Avoid cluttering the diagram with excessive text or unnecessary elements. Maintain an organized layout, leaving sufficient space between devices and ensuring that labels do not overlap or obstruct the diagram’s clarity.
- Create a Legend: If your diagram includes unique symbols, colors, or notation, consider creating a legend or key to explain their meaning. This helps viewers understand the diagram and its various elements.
- Review and Iterate: Conduct a thorough review of the diagram to ensure its accuracy and readability. Make any necessary adjustments or refinements, and seek feedback from others to ensure the diagram effectively communicates the structure of your home network.
By organizing and labeling your home network diagram thoughtfully, you make it easier to understand and interpret. Following these steps ensures that the diagram effectively represents the components, connections, and relationships within your network.
Remember to keep the diagram up-to-date as you make changes to your network or introduce new devices. Regularly reviewing and updating the diagram ensures its accuracy and usefulness as a reference tool for troubleshooting, maintenance, or future network planning.
Share and Update the Diagram
Sharing and regularly updating your home network diagram are essential steps to ensure its usefulness and accuracy over time. By sharing the diagram, you can provide others with a clear understanding of your network setup, while updating it allows you to reflect any changes or additions to your network infrastructure. Follow these steps to share and update your diagram effectively:
- Choose a Suitable Format: Determine the most appropriate format to share your home network diagram. This could be a digital file (such as PNG, JPEG, or PDF) or a printed hard copy, depending on the needs and preferences of the intended audience.
- Select the Right Medium: Determine the most suitable medium for sharing the diagram based on the intended recipients. This could include email, file-sharing platforms, project management tools, cloud storage services, or simply printing copies to distribute physically.
- Provide Context and Explanation: Accompany the shared diagram with a brief explanation or documentation, providing context about the purpose and scope of the diagram. This helps ensure that others understand the diagram and how it should be interpreted.
- Consider Accessibility: Ensure that the shared diagram is easily accessible to those who may need it. If using a digital format, consider sharing it with relevant team members, network administrators, or other individuals involved in the network management process.
- Notify About Updates: Whenever you make changes to your home network, update the diagram accordingly and inform others who have access to the diagram. This keeps everyone informed about the current network configuration and ensures they are working with the most up-to-date information.
- Request Feedback: Encourage others to provide feedback on the diagram, particularly if they have insights or suggestions for improvements. Feedback helps identify areas for enhancement and ensures the ongoing accuracy and usefulness of the diagram.
- Create a Versioning System: If you anticipate frequent updates or changes to your network, consider establishing a versioning system for your diagram. This allows you to track and manage different iterations of the diagram, ensuring a clear record of the network’s evolution over time.
Sharing and updating your home network diagram fosters collaboration and ensures that all stakeholders have the most accurate and current representation of your network infrastructure. By consistently maintaining and sharing the diagram, you enable efficient communication, informed decision-making, and simplified troubleshooting within your network management process.