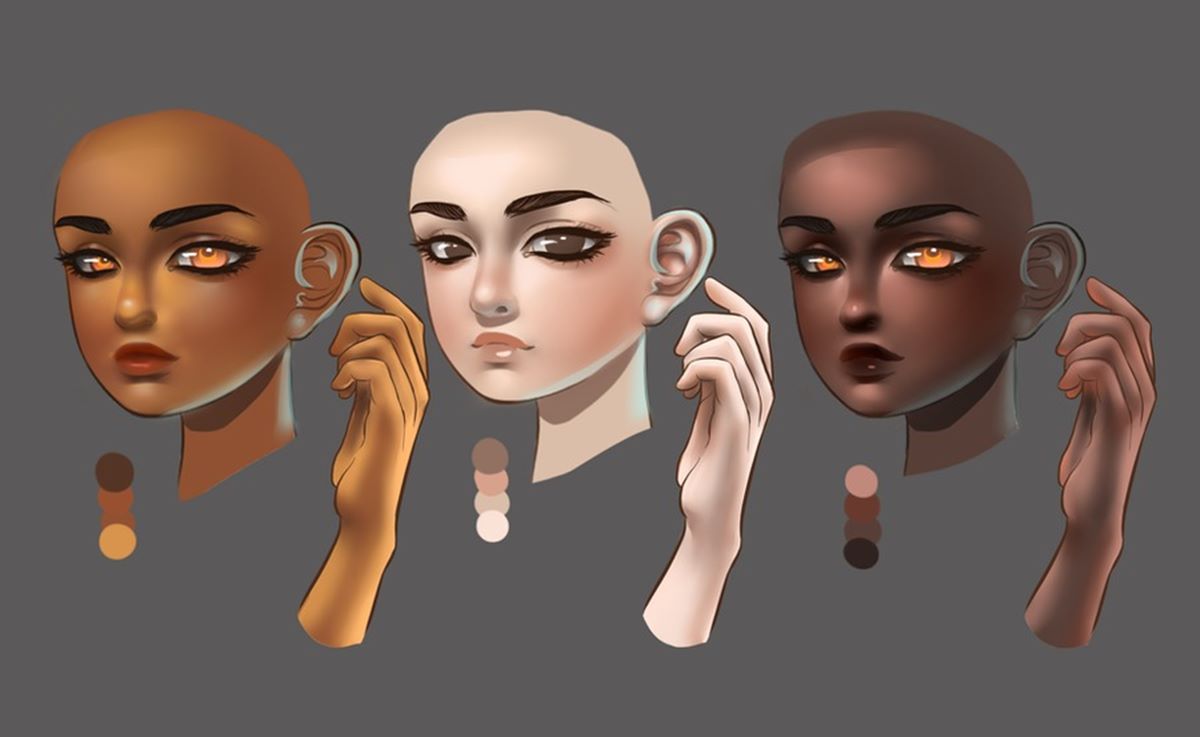Understanding Light and Shadow
When it comes to shading skin in digital art, understanding the principles of light and shadow is crucial. Properly utilizing light and shadow can add depth, dimension, and realism to your artwork. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
1. Light Source: Determine the direction of the light source in your artwork. This will establish the areas of light and shadow on the skin. Consider factors such as the position of the sun or any artificial light sources present in the scene.
2. Highlights: The areas directly hit by the light source should be the brightest on the skin. These highlights create the illusion of volume and form. Pay attention to areas such as the forehead, cheeks, nose, and chin, as these are typically more exposed to light.
3. Shadows: Shadows occur in areas that are blocked from direct light. They add depth and contour to the skin. With the light source in mind, identify the areas where shadows would naturally fall. This can include the sides of the face, under the jawline, and the hollows of the cheeks.
4. Gradual Transitions: When shading skin, avoid harsh lines between highlights and shadows. Use gradual transitions to create a smooth and realistic blend between light and dark areas. This can be achieved by using soft brushes or by blending colors together.
5. Skin Opacity: Keep in mind that the skin is not completely opaque. It allows some light to pass through, resulting in a subtle glow. Adjust the opacity of your shading accordingly to mimic this effect and achieve a more natural-looking skin tone.
6. Texture: Consider the texture of the skin you want to portray. Different skin types, such as smooth or textured surfaces, will require different shading techniques. Pay attention to details like wrinkles, pores, and blemishes, as they can affect how light interacts with the skin surface.
7. Practice Observational Skills: Study and observe real-life references to understand how light and shadow interact on different skin tones. Pay attention to the variations in color, highlights, and shadows. Apply this knowledge to improve your digital art’s realism and accuracy.
By understanding the principles of light and shadow, you can take your digital art to the next level. Don’t be afraid to experiment and practice. With time and patience, you will develop the skills needed to create stunning and lifelike skin shading in your artwork.
Choosing the Right Colors for Skin Tones
One of the key elements in shading skin in digital art is selecting the right colors for skin tones. Accurately representing various skin tones can greatly enhance the realism and visual appeal of your artwork. Here are some important considerations when choosing colors for skin tones:
1. Undertones: Skin tones are influenced by underlying undertones, such as warm, cool, or neutral tones. Understanding these undertones is essential for capturing the natural look of skin. Warm undertones often have hints of yellow, while cool undertones have hints of blue or pink. Neutral undertones strike a balance between warm and cool.
2. Reference Images: Referencing real-life images of different skin tones can be incredibly helpful. Observe the subtle variations in colors present on the skin, such as the cheeks, nose, and forehead. This will guide you in selecting the appropriate base color for your digital art.
3. Color Mixing: Mixing multiple colors together is key to achieving realistic skin tones. Experiment with blending different shades of browns, reds, yellows, and blues to create a variety of skin colors. Remember that skin is not a flat color but rather a combination of hues that create depth and life.
4. Lighting Conditions: Consider the lighting conditions in your artwork as they can affect the appearance of skin tones. Different light sources can cast warm or cool tones on the skin. Adjust the colors accordingly to capture the desired lighting atmosphere and mood.
5. Individual Variations: Keep in mind that skin tones vary greatly among individuals. Factors such as ethnicity, age, and geographical location can influence the hue, saturation, and value of skin colors. Take these variations into account when creating diverse and accurate representation of skin tones.
6. Layering and Blending: Use multiple layers and blend the colors together to create a natural transition between different areas of the skin. This allows you to build up the complexity and depth of the skin tones. Pay attention to the subtle changes in colors as you move from highlights to shadows.
7. Test and Adjust: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different color combinations and techniques. Test your chosen colors on a separate canvas or a small area of your artwork to ensure they harmonize well and capture the desired effect. Make adjustments as needed to achieve the perfect skin tone.
Choosing the right colors for skin tones requires careful observation and experimentation. By considering undertones, referencing real-life images, and mixing colors effectively, you can achieve realistic and captivating skin tones in your digital art. Remember that practice and patience are key to mastering this essential skill.
Creating a Base Layer for the Skin
Before diving into shading and adding details, it’s important to establish a solid base layer for the skin in your digital artwork. This base layer will serve as the foundation upon which you will build your shading and highlights. Here are some essential steps to create a strong base layer:
1. Choosing a Base Color: Start by selecting a base color that closely matches the skin tone you want to portray. Refer to your chosen reference images or use a color picker tool to ensure accuracy. Apply this base color to the entire area of the skin using a large brush.
2. Variation and Subtlety: Avoid using a flat, single-color base layer. Instead, introduce subtle variations in the hue, saturation, and value of the base color. Skin tones are not uniform, and incorporating these variations will add depth and realism to the skin.
3. Layering Techniques: Use multiple layers to create the base layer for the skin. This allows you to make adjustments and refine the colors without affecting other elements in your artwork. Experiment with layer blending modes, such as Multiply or Overlay, to achieve a more natural-looking skin texture.
4. Blending and Softening: Use soft brushes and blending tools to blend the colors smoothly and soften any harsh edges. This will help to create a seamless transition between different areas of the skin and ensure a realistic appearance.
5. Consider Light Source: Take the established light source into account when creating the base layer. Apply slightly lighter shades of the base color to areas where the light hits directly, such as the forehead and cheeks. Similarly, apply slightly darker shades to areas in shadow.
6. Refining and Adjusting: Step back and assess your base layer. Make any necessary refinements or adjustments to ensure that the overall skin tone is cohesive and accurate. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different colors or blending techniques until you are satisfied with the result.
7. Consistency: Ensure that the base layer is applied consistently throughout the entire skin area. This will help create a unified and balanced look. Avoid abrupt color changes or patches in the base layer, as they can appear unnatural.
Remember, the base layer sets the foundation for the rest of your shading and detailing work. Taking the time to create a strong and well-blended base layer will result in a more realistic and visually appealing representation of skin in your digital artwork.
Using a Gradient Map for Initial Shading
When it comes to shading skin in digital art, using a gradient map can be a powerful tool to establish the initial shadows and highlights. A gradient map allows you to map specific colors to the range of tones in the grayscale, providing a quick and effective way to add depth and dimension to your artwork. Here’s how you can use a gradient map for initial shading:
1. Choose a Gradient Map: Select a gradient map that closely matches the overall tone and mood of your artwork. You can either use one of the default gradient maps available in your digital art software or create a custom one by blending colors that align with the desired skin tones and lighting conditions.
2. Apply the Gradient Map: Create a new layer on top of your base layer and apply the chosen gradient map to it as an adjustment layer. This will instantly map the shades of gray in your artwork to the colors specified in the gradient map.
3. Adjust Opacity and Blending Mode: Experiment with the opacity and blending mode of the gradient map layer to achieve the desired effect. Lowering the opacity can create a more subtle shading effect, while changing the blending mode can enhance the interaction between the gradient map colors and the base skin tones.
4. Refine with Layer Masks: Use layer masks to selectively apply the gradient map to specific areas of the skin. This allows for more control and precision in shaping the shadows and highlights. Use a black brush on the layer mask to hide portions of the gradient map and reveal the underlying base layer. Adjust the brush opacity to smoothly blend the shading.
5. Experiment with Gradients and Blend if: Explore different gradient maps, as well as the Blend If option available in many digital art software. Blend If allows you to control how the gradient map interacts with the underlying layers based on the underlying grayscale values. This can result in more realistic and nuanced shading effects.
6. Refine and Adjust: Step back and assess the initial shading applied using the gradient map. Make any necessary refinements or adjustments to the opacity, blending mode, or layer masks to achieve the desired balance and depth. Consider the light source and ensure that the shading aligns with its direction and intensity.
7. Keep it Subtle: Remember that the purpose of the gradient map is to establish the initial shading. Avoid creating overly harsh or stark shadows and highlights. Gradual transitions and subtle variations in tonal values will result in a more natural and realistic appearance.
Using a gradient map for initial shading provides a convenient and effective way to establish the foundational shadows and highlights in your digital artwork. It sets the stage for further refining and detailing the skin shading to achieve a lifelike and visually captivating result.
Establishing the Light Source
Establishing the light source is a critical step in shading skin in digital art. The position, direction, and intensity of the light source determine how shadows and highlights are cast on the skin, adding depth and realism to your artwork. Here’s how you can successfully establish the light source:
1. Determine the Light Source: Consider the concept or scene you’re portraying in your artwork. Decide where the light source is coming from – is it natural sunlight, a lamp, or an artificial light? Take note of the angles and intensity of the light to accurately depict its effect on the skin.
2. Analyze Real-life References: Study photographs or observe real-life situations to understand how light interacts with the skin. Pay attention to the way shadows fall and highlights are cast on different parts of the face and body. This will help you recreate the same effect in your digital artwork.
3. Sketch the Light Source: Before shading, sketch the direction and position of the light source on a separate layer. This provides a visual guide and helps you maintain consistency during the shading process.
4. Apply Shadows: Based on the position of the light source, identify the areas that would be in shadow. On a new layer, use a darker tone or color to apply shadows to those specific areas. This will add depth and define the structure of the face and body.
5. Add Highlights: Determine the areas that would be directly hit by the light source and apply highlights to these areas. Use a lighter tone or color to mimic the effect of light reflecting off the skin. This will create a focal point and bring attention to certain features.
6. Consider Light Falloff: Take into account the concept of light falloff, where the intensity of light diminishes as it moves further away from the source. Gradually reduce the strength of shading and highlights as you move away from the focal point, ensuring a realistic and gradual transition.
7. Experiment and Adjust: Don’t be afraid to experiment and make adjustments as needed. Try different shading techniques, blending modes, and brush opacities to create the desired effect. Continuously evaluate your artwork and make refinements to accurately portray the light source and its impact on the skin.
Establishing the light source is fundamental to creating realistic skin shading. By understanding the direction and intensity of the light and applying shadows and highlights accordingly, you’ll achieve a sense of depth and dimension in your digital art.
Applying Basic Shadows and Highlights
Applying basic shadows and highlights is an essential step in shading skin in digital art. Shadows and highlights add depth, dimension, and realism to your artwork by mimicking how light interacts with the skin. Here’s how you can effectively apply basic shadows and highlights:
1. Observe the Light Source: Referencing your established light source, identify the areas where shadows would naturally fall. These areas are typically on the opposite side of the light source and include parts of the face like the sides of the nose, under the chin, and around the eyes.
2. Creating Shadows: On a new layer set to a multiply blending mode, use a brush with a darker color to apply shadows to the identified areas. Start with a lower opacity and gradually build up the intensity, focusing on creating a smooth transition from light to dark tones.
3. Gradual Transitions: Avoid harsh lines between shadows and the surrounding skin. Use soft brushes or blending tools to carefully blend the shadow edges, creating a gradual transition and a more natural appearance. Pay attention to areas where shadows meet highlights to ensure a seamless blend.
4. Understanding Local Color: Consider the concept of local color, which refers to the natural hue of an object or skin tone in this case. Shadows are not simply black or gray – they retain the underlying color. Incorporate subtle variations of the local color in your shadows to add richness and depth.
5. Highlight Placement: Determine the areas that would be directly hit by the light source and would have the most intense reflections. These areas typically include the forehead, cheekbones, tip of the nose, and the chin. On a new layer set to a screen blending mode, use a brush with a lighter color to apply highlights to these areas.
6. Contouring: Use highlights strategically to accentuate the contours and features of the face or body. Focus on areas such as the bridge of the nose, the top of the cheekbones, and the brow ridge. This helps to create a three-dimensional effect and enhance the visual appeal of the artwork.
7. Balance and Refinement: Step back frequently to evaluate the overall balance of shadows and highlights. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure that the shading is even and accurate. Regularly zoom in to refine the details and make fine-tuned adjustments to achieve a more realistic representation.
Applying basic shadows and highlights is crucial for creating depth and realism in shading skin. By observing the light source, understanding local color, and carefully blending transitions, you can effectively capture the interplay of light and shadow on the skin in your digital art.
Adding Depth with Midtones
While shadows and highlights are vital in shading skin, adding depth to your digital art requires the careful incorporation of midtones. Midtones bridge the gap between light and dark areas, providing subtle variations in color and tonal values. Here’s how you can effectively add depth with midtones when shading skin:
1. Observe Realistic Skin: Study real-life references or photographs of different skin tones to understand the range of midtones present. Pay attention to the variations in color, warmth, and coolness within the midtone range. This will help you accurately replicate the complexities of the skin in your digital art.
2. Select Midtone Colors: Choose a range of midtone colors that align with the desired skin tone, paying attention to the warm and cool undertones. Utilize the color picker tool or create a custom palette that includes shades resembling the natural skin variations you observed.
3. Apply Midtones: On a new layer between the shadow and highlight layers, use a brush with a medium opacity to apply the selected midtone colors to the appropriate areas of the skin. Focus on blending these colors smoothly into the shadows and highlights, creating a seamless transition.
4. Gradual Build-up: Start with lighter midtones and gradually build up the depth by layering darker midtones. This layering technique adds subtle variations and richness to the skin, enhancing its three-dimensional appearance. Avoid using flat colors and aim for a gradual transition from light to dark midtones.
5. Contouring with Midtones: Use midtones strategically to contour and define the facial features. Apply slightly darker midtones to the areas where the skin recedes, such as the sides of the nose, the hollows of the cheeks, or the jawline. This creates a sense of depth and structure.
6. Blend and Refine: Use soft brushes and blending tools to blend the midtones seamlessly into the shadows and highlights. Pay attention to the transitions between the different tonal values, ensuring a natural and realistic appearance. Continuously evaluate and refine the midtones to achieve the desired depth and dimension.
7. Modulate Midtones for Realism: Keep in mind that the intensity of the midtones can vary based on factors such as lighting conditions, translucency of the skin, and individual differences. Modulate the opacity and layer blending modes to achieve the most realistic and visually appealing midtones for your specific artwork.
Adding depth with midtones is crucial to bringing realism and dimension to shaded skin in digital art. By carefully selecting and applying midtone colors, blending them effectively, and strategically contouring the features, you’ll enhance the visual impact and depth of your artwork.
Blending and Smoothing the Shading
Blending and smoothing the shading in your digital art is essential for achieving a seamless and realistic appearance. These techniques help merge the different tonal values, transitions, and textures of the shaded areas, creating a cohesive and polished look. Here are some effective strategies for blending and smoothing the shading:
1. Soft Brushes: Use soft brushes with low opacity for blending. Soft brushes create smoother transitions between shades and help avoid sharp edges. Experiment with different brush sizes and hardness to find the best brush for your artwork.
2. Layer Opacity: Adjust the opacity of your shading layers to control the intensity of the shadows and highlights. Lower opacities allow for more subtle blending, while higher opacities can create more defined edges and contrast.
3. Layer Blending Modes: Explore different blending modes in your digital art software to achieve the desired blending effect. Common blending modes for shading include Multiply, Overlay, Soft Light, and Screen. Each blending mode interacts with the layers beneath it in a unique way, allowing for customizing the blending outcome.
4. Smudge and Blur Tools: Utilize smudge and blur tools to gently smooth out any rough or harsh edges in your shading. These tools can be especially useful for softening transitions between different shades and areas of the skin.
5. Gradient and Gradient Maps: Incorporate gradient or gradient maps in your workflow to create smoother and more natural transitions. Apply gradients selectively to certain areas, such as the cheeks or forehead, to further enhance the blending of shadows and highlights.
6. Pay Attention to Detail: Zoom in and scrutinize your artwork for any noticeable inconsistencies or abrupt transitions in the shading. Refine these areas by carefully blending and adjusting the colors and values to create a more cohesive look.
7. Build Layers gradually: Start with a solid base layer and gradually build up the shading layers, paying attention to the subtleties of the skin. This approach allows you to adjust and refine the shading gradually, ensuring a more realistic appearance.
8. Take Breaks: Take regular breaks and revisit your artwork with fresh eyes. This will help you spot any areas that need further blending or smoothing. Distance and time away from your artwork can provide a valuable perspective on its overall coherence.
Blending and smoothing the shading in your digital art requires patience and attention to detail. By mastering these techniques, you can achieve a more polished and lifelike representation of the skin in your artwork.
Enhancing Realism with Texture and Details
Adding texture and details to your shaded skin in digital art is crucial for enhancing realism and capturing the intricate characteristics of human skin. Texture and details help breathe life and depth into your artwork, making it more believable and visually engaging. Here are some effective strategies for enhancing realism with texture and details:
1. Study Reference Images: Observe real-life references or high-quality photographs to understand the unique textures found in different skin types and tones. Pay attention to the fine details, such as pores, wrinkles, freckles, and blemishes. This will guide you in recreating these textures in your digital artwork.
2. Texture Brushes and Stamp Brushes: Utilize texture brushes and stamp brushes specifically designed to mimic skin textures. These brushes often include variations like pore brushes, wrinkle brushes, or freckle brushes. Experiment with different brushes to add realistic surface details to your shaded skin.
3. Layering Techniques: Use layering techniques to build up texture and details. Start with a base layer and gradually add additional layers for specific details. This allows you to have more control and flexibility when refining the different textures and adjusting their opacity and blending modes.
4. Pay Attention to Skin Variations: Capture the natural variations found in skin tones and textures by incorporating subtle color shifts, variations in values, and small imperfections. This includes adding slight changes in hue and saturation to mimic the natural diversity and complexities of human skin.
5. Suggested Brush Strokes: Mimic the natural brush strokes of a physical painter by utilizing brush techniques that add texture and details. Experiment with cross-hatching, stippling, or dithering techniques to replicate the organic appearance of skin textures.
6. Highlighting and Shading Textures: Apply highlights and shadows selectively to emphasize the texture and details of the skin. Highlights can accentuate the raised areas, while shadows can define the recessed areas, such as wrinkles or pores. Be mindful of the light source and ensure that the shading corresponds to the texture being depicted.
7. Balance Realism and Artistic Interpretation: Remember to find a balance between capturing realism and maintaining your artistic style. While adding texture and details is important, avoid overwhelming the artwork with excessive details that distract from the overall composition. Use your artistic intuition to determine the level of detail that best suits your vision.
8. Regularly Zoom In and Assess: Zoom in on your artwork regularly to inspect the details and overall consistency of the skin texture. This allows you to identify areas that need adjustment, blending, or additional details to enhance realism further.
Enhancing realism with texture and details elevates the quality of your shaded skin in digital art. By studying references, utilizing texture brushes, layering techniques, and paying attention to subtle variations, you can bring your artwork to life with intricate and believable skin textures.
Fine-tuning the Shading for Different Skin Types
When shading skin in digital art, it’s important to understand that different skin types require specific approaches to achieve realism. Fine-tuning the shading for different skin types allows you to capture the unique qualities and characteristics of each skin type. Here are some strategies to consider when fine-tuning the shading for different skin types:
1. Study Skin Type References: Research and study references specific to the skin type you are working on. This will help you understand the distinct characteristics and shading requirements of that particular skin type. Pay attention to variations in color, texture, and light interaction.
2. Identify Skin Undertones: Determine the undertones of the skin type you are shading. Undertones can range from warm (yellow, peach) to cool (pink, blue) or neutral. Adjust the shading colors and intensity accordingly to accurately represent the undertones of the skin.
3. Assess Texture and Glossiness: Different skin types have varying levels of texture and glossiness. Pay attention to the level of smoothness or roughness, the presence of pores, and how light reflects off the skin’s surface. Adjust the shading to capture these specific textural characteristics.
4. Consider Ethnicity and Diversity: Skin shading requirements can differ based on ethnicity and racial diversity. Take into account the specific characteristics of different ethnicities, such as melanin levels, and adjust the shading accordingly to accurately represent the skin tones of diverse individuals.
5. Adjust Saturation and Hue: Fine-tune the saturation and hue of the shading for different skin types. Some skin types may require warmer or cooler hues, while others may need higher or lower saturation levels. These adjustments help bring out the unique tones and qualities of each skin type.
6. Pay Attention to Lighting Conditions: Lighting conditions play a crucial role in how skin is shaded. Consider the intensity, direction, and color temperature of the light source. Adjust the shading to reflect the specific lighting conditions to create the desired atmosphere and mood in your artwork.
7. Consult Real-life References and Seek Feedback: Refer to real-life references, photographs, and feedback from individuals with the specific skin type you are shading. Their input can provide valuable insight and help you accurately represent their skin type and personal experiences in your digital art.
8. Experiment and Refine: Be open to experimentation and refining your techniques when fine-tuning the shading for different skin types. Adjustments may be necessary to achieve the most realistic and authentic representation. Continuously evaluate and make refinements to ensure accuracy and believability.
Fine-tuning the shading for different skin types is essential for capturing the diversity and uniqueness of individuals in your digital artwork. By studying references, adjusting colors and techniques, and seeking feedback, you can achieve realistic and culturally sensitive portrayals of various skin types.