Prevent Physical Access to the Computer
When it comes to securing your desktop computer, preventing physical access is crucial. Unauthorized access to the computer can lead to data theft, tampering, or even hardware damage. Here are some steps you can take to prevent physical access:
- Place the computer in a secure room or area: Keep your desktop computer in a location that is not easily accessible to unauthorized individuals. A locked office, cabinet, or server room with restricted access can help safeguard your computer.
- Install security cameras: Consider installing security cameras in the vicinity of your computer to deter potential intruders. Visible cameras can serve as a deterrent and can also help in identifying any unauthorized attempts to access the computer.
- Limit access to authorized personnel: Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the computer. Restrict physical access by implementing measures such as keycards, biometric scanners, or a sign-in log to monitor who is entering the area where the computer is kept.
- Use a computer case lock: Many desktop computer cases come with built-in lock mechanisms or have provisions to install them. Use a case lock to secure the computer’s chassis and prevent unauthorized access to internal components.
- Secure the power source: Protect the power source of your computer by using power outlet locks or surge protectors with locking capabilities. This prevents someone from unplugging or tampering with the power cable.
- Secure the keyboard and mouse: Consider using keyboard and mouse locks to prevent unauthorized use or tampering. These locks physically restrain the peripherals, ensuring they cannot be easily disconnected or tampered with.
- Implement access control policies: Establish strict policies regarding who can access the computer and when. Make sure all employees are aware of these policies and enforce them consistently.
By taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized physical access to your desktop computer. Remember, physical security is an important aspect of overall computer security, so always prioritize it alongside other security measures.
Install a Locking Mechanism
An effective way to enhance the physical security of your desktop computer is to install a locking mechanism. This will provide an additional layer of protection against theft and unauthorized access. Here are some locking mechanisms you can consider:
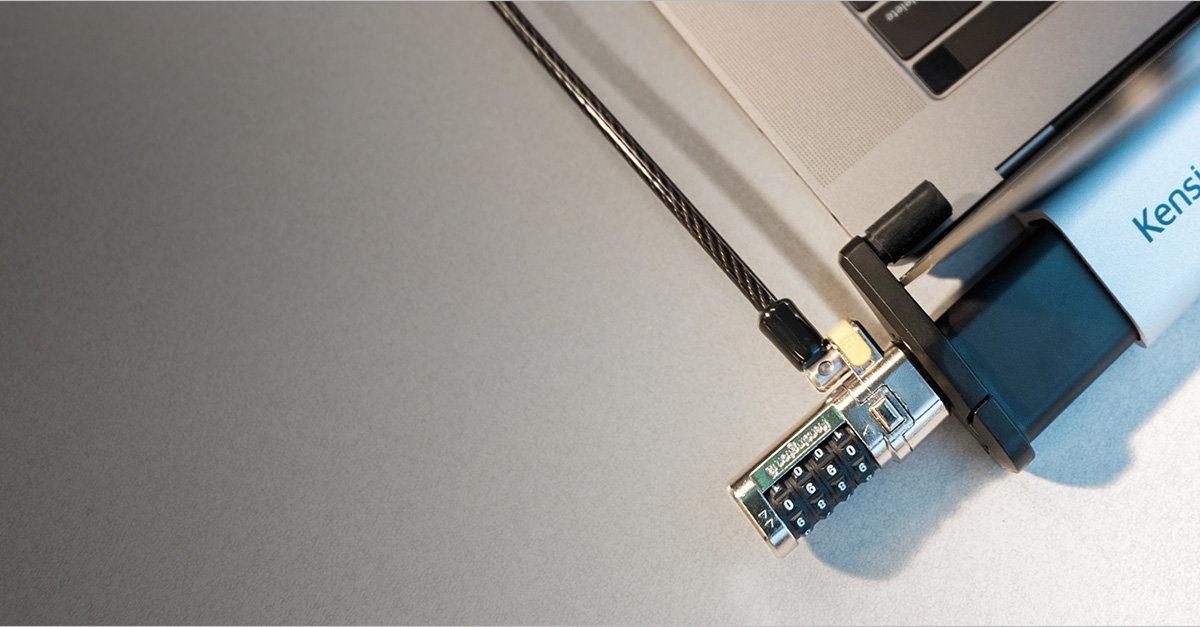
- Cable locks: Cable locks are popular and affordable options for securing desktop computers. These locks consist of a strong steel cable that attaches to a security slot on the computer or the desk. The other end of the cable can be secured to a fixed object, such as a table leg. This prevents someone from easily stealing or removing the computer.
- Desktop lock kits: Some desktop computers come with specially designed lock kits that provide a more secure attachment point for cable locks. These lock kits are typically mounted inside the computer case, providing a robust anchor point for the cable lock.
- Chassis locks: For added security, you can install chassis locks that directly secure the computer case. These locks typically replace some of the existing case screws and require a specific key or combination to open. Chassis locks provide a physical barrier and discourage tampering or unauthorized access to the internal components of the computer.
- Smart locks: Smart locks are a modern and innovative option for securing desktop computers. These locks use electronic authentication methods such as keycards, fingerprint recognition, or smartphone apps to grant access. Smart locks can provide detailed access logs and allow for remote monitoring and management of the lock system.
When choosing a locking mechanism, consider the level of security you require, the ease of installation, and compatibility with your computer setup. It’s important to ensure that the locking mechanism you choose is sturdy, tamper-resistant, and compatible with your computer’s design.
Remember to educate your employees or household members on how to properly use the locking mechanism and emphasize the importance of securing the computer when not in use. A visual reminder, such as a sign or poster, can also be helpful in promoting awareness and compliance with the locking procedures.
By installing a locking mechanism, you significantly reduce the risk of theft and unauthorized access to your desktop computer, providing peace of mind and ensuring the safety of your valuable data.
Position the Computer in a Secure Location
The physical placement of your desktop computer plays a crucial role in its overall security. By positioning the computer in a secure location, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access, accidental damage, and theft. Here are some important considerations:
- Choose a secluded area: Select a spot for your computer that is not easily visible or accessible to unauthorized individuals. Avoid placing it near windows or high-traffic areas where it may attract attention.
- Secure it against accidental tipping: Ensure that the computer is placed on a stable surface and is not prone to tipping over. This helps prevent accidental damage and reduces the risk of someone tampering with the computer.
- Consider the environment: Take into account the surrounding environment when positioning your computer. Keep it away from sources of moisture, extreme temperatures, or excessive dust to prevent hardware damage. If necessary, use a protective cover or casing to shield the computer from potential hazards.
- Elevate the computer: If possible, elevate the computer off the floor to protect it from potential damage caused by spills, flooding, or pests. Using a desk or a raised platform can provide an added layer of protection.
- Secure against physical damage: Consider the potential risks in the location where the computer is placed. If there is a chance of accidental bumps, falls, or impacts, use desk corner protectors or a sturdy computer case to safeguard the hardware.
- Protect against environmental threats: Position the computer away from direct sunlight or sources of excessive heat to prevent overheating. Adequate ventilation is essential to maintain optimal computer performance.
- Secure against natural disasters: In areas prone to earthquakes, hurricanes, or other natural disasters, secure the computer using earthquake straps or other anchoring methods to minimize damage and ensure it remains in place.
By carefully considering the location and surroundings of your desktop computer, you can reduce the risk of physical damage and unauthorized access. Remember to regularly assess the security of the chosen location and make any necessary adjustments to maintain the computer’s safety.
Additionally, if you have multiple computers, ensure they are positioned in a way that prevents easy access to all of them at once. This helps minimize the impact of potential security breaches.
Positioning your computer in a secure location is a proactive step towards protecting your data and ensuring the longevity of your hardware.
Use Security Cables or Chain Locks
To further enhance the physical security of your desktop computer, utilizing security cables or chain locks can be a reliable solution. These locks provide an additional layer of protection against theft and unauthorized access. Here’s how you can benefit from using them:
- Security Cables: Security cables are flexible, durable cables that can be looped around the computer and connected to a secure anchor point. These cables are typically made of steel and come with a combination lock or key lock mechanism. By attaching one end of the cable to a secure object, such as a desk or wall mount, you can prevent someone from easily stealing the computer.
- Chain Locks: Chain locks are heavy-duty, hardened chains that are designed to resist cutting or tampering. These locks often come with a robust padlock mechanism and can be wrapped around the computer or the computer case, securing it to a fixed object. Chain locks provide a strong physical barrier and act as a visual deterrent against theft attempts.
When using security cables or chain locks, consider the following tips:
- Choose high-quality locks with sturdy construction: Invest in reliable, high-quality security cables or chain locks. Look for products that are specifically designed for computer security and have the necessary strength to resist prying or cutting attempts.
- Select the appropriate length and thickness: Ensure that the security cable or chain lock is long enough to reach the anchor point without causing unnecessary strain on the computer. The thickness of the cable or chain should also be sufficient to withstand forceful attempts to break through.
- Secure both the computer and peripherals: If you have peripherals such as monitors or printers connected to your desktop computer, consider using additional security cables or chain locks to prevent their theft or tampering as well.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the locks: Routinely check the condition of the security cables or chain locks to ensure they are functioning properly. Replace any worn-out or damaged components promptly to maintain the effectiveness of the locks.
- Communicate the importance of using the locks: Educate your employees or household members about the significance of using security cables or chain locks. Emphasize the role they play in protecting valuable equipment and data, and encourage each individual to take responsibility for securing the computer.
By using security cables or chain locks, you significantly decrease the chances of theft and unauthorized access to your desktop computer. These simple yet effective measures can provide peace of mind while ensuring the physical security of your valuable assets.
Keep the Computer Out of Sight
One effective way to enhance the physical security of your desktop computer is to keep it out of sight from prying eyes. By minimizing its visibility to unauthorized individuals, you can reduce the risk of theft and targeted attacks. Here are some strategies to keep your computer discreetly hidden:
- Secure, enclosed storage: Consider using locked cabinets, drawers, or desks with lockable compartments to store your desktop computer. This provides an extra layer of security by physically concealing the computer from view.
- Use privacy screens: Privacy screens are filters that can be attached to your computer monitor. These screens limit the viewing angle, making it difficult for individuals nearby to see the contents of your screen. This is especially useful in open office environments or public spaces.
- Arrange the furniture layout: Position your computer desk in a way that it is not easily visible from windows or common areas. Rearranging the furniture layout can help to obstruct direct views of the computer setup.
- Use covers or cases: Consider using covers or cases that match your room decor to camouflage your computer. These covers can blend in with the surrounding environment and help your computer go unnoticed.
- Keep the computer hidden during non-use: If you are leaving your computer unattended for an extended period, such as overnight or during vacation, make sure to close doors, blinds, or use curtains to prevent outsiders from seeing the computer from outside the room.
- Employ screen timeout settings: Configure your computer to automatically activate the screen timeout feature after a certain period of inactivity. This will prevent anyone passing by from seeing potentially sensitive information displayed on the screen.
- Implement remote wiping capabilities: In the event of theft or unauthorized access, having remote wiping capabilities enables you to erase sensitive data remotely. This ensures that even if the physical computer is compromised, your data remains secure.
By keeping your computer out of sight, you decrease the likelihood of opportunistic theft or targeted attacks. Remember to strike a balance between keeping the computer hidden and maintaining accessibility for authorized users.
Additionally, it is important to educate employees or household members about the importance of keeping the computer concealed and the potential risks associated with leaving it in plain sight. Encourage them to be mindful of their surroundings and take proactive measures to keep the computer hidden when not in use.
By adopting these practices, you can enhance the physical security of your desktop computer and minimize the chances of unauthorized access or theft.
Implement Biometric Access Control
Implementing biometric access control is a cutting-edge method to enhance the physical security of your desktop computer. Biometric technology utilizes unique physical characteristics to verify and grant access to authorized individuals. Here are some key benefits and considerations for implementing biometric access control:
- Enhanced Security: Biometric access control provides a high level of security by utilizing individual characteristics such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial recognition. These unique physical attributes are difficult to replicate, making it challenging for unauthorized individuals to gain access to your computer.
- Ease of Use: Biometric systems are user-friendly and convenient to use. Users can quickly and easily authenticate themselves by scanning their fingerprint, looking into a camera, or positioning their eye. This eliminates the need to remember and enter complex passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized individuals guessing or obtaining login information.
- Audit Trail: Biometric systems often include logging and auditing capabilities. This means that you can track and review access logs to monitor who has accessed the computer and when. This can be useful for identifying any suspicious or unauthorized entry attempts.
- Integration with Other Security Measures: Biometric access control can seamlessly integrate with other security measures, such as surveillance cameras or alarm systems. This provides a comprehensive security solution that covers both physical and digital aspects of computer security.
- Considerations for Implementation: Before implementing biometric access control, consider factors such as cost, compatibility with your computer system, and the number of users who would require access. Biometric systems may require initial setup and calibration, so it’s important to plan accordingly and ensure proper training for users.
- Privacy and Data Protection: When implementing biometric access control, it’s essential to prioritize privacy and protect the biometric data being collected. Ensure that the system follows privacy regulations and uses encryption and secure storage techniques to safeguard the stored biometric information.
Implementing biometric access control provides an advanced and highly secure method of granting access to your desktop computer. It not only ensures the physical security of your computer but also simplifies the authentication process for authorized users.
When implementing biometric access control, ensure that you educate your employees or household members about how the system works, address any concerns they may have, and emphasize the importance of keeping their biometric credentials confidential.
By incorporating biometric access control, you can significantly enhance the physical security of your desktop computer and protect against unauthorized access or data breaches.
Enable BIOS and Boot Passwords
To further fortify the physical security of your desktop computer, enabling BIOS and boot passwords is an effective measure. These passwords provide an additional layer of protection by restricting access to the computer’s internal settings and boot process. Here’s why you should enable BIOS and boot passwords:
- Prevent Unauthorized System Access: BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) passwords require users to enter a password before they can access the computer’s BIOS settings. By setting a strong BIOS password, you prevent unauthorized individuals from making changes to crucial system settings or even booting the computer.
- Secure the Boot Process: Boot passwords add an extra level of security by requiring users to enter a password during the boot-up process. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing the operating system and the data stored on the computer.
- Deter Physical Theft: Enabling BIOS and boot passwords acts as a deterrent against theft. If a thief or unauthorized user attempts to boot up the computer, they will be prompted to enter the password, making it more challenging for them to access your data.
- Compatibility Considerations: When enabling BIOS and boot passwords, ensure that you consider compatibility with your system hardware and operating system. Some older systems or certain configurations may have limitations or issues with password implementation, so it’s important to verify compatibility before enabling these passwords.
- Strong Password Practices: To maximize the effectiveness of BIOS and boot passwords, use strong and unique passwords that are not easily guessable. Include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Regularly update and change the passwords to maintain security.
- Document and Store Passwords Safely: Keep a record of the BIOS and boot passwords in a secure and separate location. Store them in an encrypted file or password manager to prevent unauthorized access. Remember to update the password records if you change or update the passwords.
Enabling BIOS and boot passwords provides an additional layer of defense against unauthorized access to your desktop computer. It is important to balance the added security with practicality, ensuring that authorized users can easily access the system while maintaining protection against potential threats.
When enabling BIOS and boot passwords, consider educating your employees or household members about the importance of these passwords and the potential consequences of unauthorized access. This will help foster awareness and encourage responsible usage of the computer.
By enabling BIOS and boot passwords, you significantly enhance the physical security of your desktop computer and protect your valuable data from unauthorized access.
Secure Peripherals and Cables
When it comes to physical security, it’s important not to overlook the peripherals and cables connected to your desktop computer. Securing these components is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to your data and protect against potential theft. Here are some key measures to secure peripherals and cables:
- Cable Management: Proper cable management is essential to minimize clutter and secure cables. Use cable ties, clips, or cable sleeves to keep cables organized and prevent them from being easily disconnected or tampered with.
- Secure USB Ports: Disable unused USB ports or use USB port locks to prevent unauthorized devices from being plugged into your computer. This protects against potential data breaches, malware infections, or unauthorized data transfers.
- Lock Down Peripherals: Use locking mechanisms or security brackets to secure peripherals such as monitors, keyboards, and mice. This prevents them from being easily stolen or tampered with. If possible, choose peripherals with built-in locking features.
- Protect External Storage Devices: External hard drives, USB flash drives, and other portable storage devices should be kept in locked drawers or secure compartments when not in use. Consider using encrypted storage devices to protect sensitive data even if they are lost or stolen.
- Secure Network Cables: Network cables, such as Ethernet cables, should be securely connected to prevent unauthorized access to your network. Use cable locks or position network equipment in locked cabinets or secure areas to safeguard against physical tampering.
- Secure Printer and Scanner: If you have a connected printer or scanner, ensure that it is in a secure location. Consider implementing printer access control measures to restrict unauthorized usage or access to sensitive documents.
- Regularly Inspect and Maintain Cables and Connections: Routinely check the condition of cables, connectors, and ports. Replace any damaged or frayed cables and tighten loose connections promptly to maintain the integrity of your setup.
By securing peripherals and cables, you minimize the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and equipment theft. Implementing these measures helps maintain the physical security of your desktop computer and protects your sensitive information.
Additionally, educating employees or household members about the importance of securing peripherals and cables is crucial. Emphasize the role they play in overall computer security and encourage them to report any suspicious activity or tampering.
Remember, physical security measures should work in conjunction with digital security practices to provide comprehensive protection for your desktop computer setup.
Protect Against Power Surges and Outages
Power surges and outages can not only disrupt your workflow but also pose a risk to the physical integrity of your desktop computer. Protecting your computer against these electrical disturbances is crucial to ensure its proper functioning and prevent damage. Here are some steps you can take to protect your computer:
- Use Surge Protectors: Invest in high-quality surge protectors to safeguard your computer and peripherals against sudden power surges. Surge protectors are equipped with built-in circuitry that diverts excess voltage away from your devices, preventing potential damage. Connect your computer and other sensitive equipment to these surge protectors.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Consider using a UPS to protect your computer from both power surges and outages. A UPS provides a battery backup that allows your computer to stay powered for a limited time during an outage. This gives you the opportunity to save your work and safely shut down your computer to prevent data loss or hardware damage.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure that your computer and electrical outlets are properly grounded. Grounding is essential to divert electrical surges and prevent damage to your computer’s sensitive components. Consult a professional electrician if you are unsure about the grounding of your electrical system.
- Regularly Test and Replace Surge Protectors and UPS Batteries: Over time, surge protectors and UPS batteries can lose effectiveness. Routinely test your surge protectors to ensure they are still providing proper protection, and replace them if necessary. Similarly, monitor the condition of your UPS battery and replace it when its capacity diminishes.
- Shut Down During Prolonged Power Outages: If faced with a prolonged power outage, it is advisable to shut down your computer completely. This protects against potential power fluctuations when the power is restored, which can damage the computer’s hardware.
- Backup Power Source: In areas prone to frequent power outages, consider investing in a backup power source, such as a generator. This ensures uninterrupted power supply to your computer and ensures that critical work and data remain secure.
- Protect Data with Uninterrupted Power Supply: In addition to protecting your computer, a UPS also helps avoid data loss by providing a reliable power source during outages. It gives you the opportunity to save your work and properly shut down your system, minimizing the risk of data corruption or loss.
By taking measures to protect your computer against power surges and outages, you can minimize the risk of hardware damage, data loss, and system malfunctions. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to protecting your computer against electrical disturbances.
It is important to educate your employees or household members on the importance of proper power management and the risks associated with power surges and outages. Encourage them to follow the recommended procedures and guidelines to maintain the physical integrity of your desktop computer.
By implementing these protective measures, you ensure the longevity and reliable performance of your desktop computer, even in the face of electrical disturbances.
Regularly Update and Patch the Operating System and Software
Regularly updating and patching your operating system and software is a crucial aspect of maintaining the physical security of your desktop computer. Keeping your system up to date with the latest security updates and patches helps protect against vulnerabilities and potential exploits. Here’s why regular updates are important and how to implement them:
- Security Patches: Software vendors release security patches to address vulnerabilities and weaknesses that can be exploited by hackers. Apply these patches promptly to ensure your desktop computer is protected against known security risks.
- Bug Fixes and Performance Enhancements: Updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements, addressing issues that can impact the stability and functionality of your computer. Keeping your system updated ensures that you have the latest features and optimizations available.
- Operating System Updates: Operating system updates provide critical security fixes, feature improvements, and compatibility enhancements. Set your computer to automatically download and install operating system updates to stay up to date effortlessly.
- Application Updates: Regularly check for updates for all installed software and applications. Enable automatic updates whenever possible, or manually check for updates and apply them as soon as they are available. This includes not only productivity applications but also web browsers, security software, and plugins.
- Antivirus and Firewall Updates: Ensure your antivirus software and firewall are updated with the latest virus definitions and security rules. Regular updates provide protection against emerging threats and help keep your computer secure from malware and unauthorized access attempts.
- Review Vendor Security Notices: Stay informed about security advisories and notices from the software vendors. These notifications provide important information about potential vulnerabilities, recommended patches, or workarounds for known issues.
- Implement Change Management Practices: For businesses, implement change management practices to ensure a controlled and systematic approach to updates. This allows you to test updates before deploying them in your production environment, ensuring compatibility and minimizing potential disruptions.
Regularly updating and patching your operating system and software is a proactive measure to enhance the physical security of your desktop computer. By doing so, you reduce the risk of exploits, ensure optimal performance, and protect against emerging threats.
It is essential to educate your employees or household members about the importance of updates and their role in maintaining computer security. Encourage them to be vigilant in keeping their systems updated and to report any unusual behavior or issues they encounter.
By implementing a regular update routine, you can maintain the physical security of your desktop computer and mitigate potential security risks that could compromise your data and overall system integrity.
Encrypt Sensitive Data on the Hard Drive
Encrypting sensitive data on your desktop computer’s hard drive is an essential step in securing your information against unauthorized access. Encryption converts your data into an unreadable format, which can only be decrypted with the correct encryption key or password. Here’s why encrypting sensitive data is crucial and how to implement it:
- Data Protection: Encrypting sensitive data on your hard drive provides an additional layer of security. In the event of physical theft or unauthorized access, encrypted data remains unreadable, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your sensitive information.
- Compliance with Regulations: Depending on your industry or the type of data you handle, you may have legal obligations to protect sensitive information. Encrypting data helps meet compliance requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or data breach notification laws.
- Full Disk Encryption (FDE): Full disk encryption protects the entire hard drive, including the operating system and all data stored on it. This ensures comprehensive protection across all files and folders, preventing unauthorized access to any sensitive information.
- File-Level Encryption: Alternatively, you can choose to encrypt specific files or folders containing sensitive data. This approach allows you to selectively encrypt only the necessary files, providing flexibility and reducing encryption overhead.
- Strong Encryption Algorithms: Ensure that you use strong encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), to encrypt your data. These algorithms are considered highly secure and are widely adopted by various industries and government organizations.
- Secure Key Management: Implement proper key management practices to safeguard the encryption keys. Choose strong and unique passwords or passphrases for your encryption keys and avoid using easily guessable information. Store the keys separately from the computer or use secure key storage solutions.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your encrypted data to ensure you have a recent, secure copy of your information. This protects against data loss in case of hardware failure, accidental deletion, or other unforeseen events.
- Test and Verify Encryption: After encrypting your sensitive data, perform tests and verification to ensure the encryption is functioning correctly. Verify that the encrypted data remains inaccessible without the proper decryption key.
Encrypting sensitive data on your desktop computer’s hard drive is vital in safeguarding your information from unauthorized access. Remember, encryption should not replace other security measures but should be used in conjunction with physical security practices, access control, and secure network configurations.
Educate your employees or household members about the importance of encrypting sensitive data and the potential consequences of data breaches. Encourage them to follow encryption best practices and provide training on how to handle encryption keys properly.
By encrypting sensitive data on your desktop computer, you significantly mitigate the risk of data breaches and protect your valuable information from falling into the wrong hands.
Use a Firewall and Antivirus Software
Utilizing both a firewall and antivirus software is crucial for protecting your desktop computer from various online threats. A firewall acts as a barrier between your computer and the external network, while antivirus software helps detect and remove viruses, malware, and other malicious programs. Here’s why using a firewall and antivirus software is essential and how to implement them effectively:
- Firewall Protection: A firewall monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, allowing only authorized connections and blocking potential threats. It acts as a barrier, preventing unauthorized access attempts and protecting against network-based attacks.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software detects and removes viruses, malware, ransomware, and other malicious programs from your computer. It scans files, processes, and emails for known threats, and often includes real-time protection to prevent malicious programs from executing.
- Regular Updates: Keep your firewall and antivirus software up to date with the latest security patches and virus definitions. Updates ensure that you have the latest protections against emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Enable Automatic Updates and Scans: Configure your firewall and antivirus software to automatically download and install updates. Set up regular system scans to detect and remove any potential threats that may have bypassed your initial defenses.
- Configure Firewall Settings: Optimize your firewall settings to strike a balance between security and usability. Ensure that the firewall is enabled, blocking unauthorized access, and only allowing necessary network connections. Consider configuring outbound traffic rules to prevent the transmission of sensitive data without proper authorization.
- Choose a Reliable Antivirus Solution: Select a reputable antivirus software from a trusted vendor. Look for features such as real-time scanning, email protection, web browsing protection, and the ability to quarantine or remove infected files.
- Practice Safe Browsing Habits: Even with a firewall and antivirus software, it’s important to practice safe browsing habits. Be cautious when clicking on links or downloading files, and avoid visiting suspicious or untrusted websites. Exercise caution when opening email attachments or following links from unknown sources.
- Regularly Perform System Scans: Run periodic full system scans with your antivirus software to detect any hidden or dormant threats. Schedule scans during off-peak hours when your computer usage is minimal.
Using a firewall and antivirus software together significantly enhances the security of your desktop computer by providing a multi-layered approach to defending against online threats. It’s important to remember that these tools require constant monitoring and updating to effectively protect your system.
Educate your employees or household members about the importance of firewall and antivirus software usage, safe browsing practices, and the potential risks of unprotected systems. Encourage them to report any suspicious activities or system warnings to the IT department or a trusted technical support resource.
By implementing a firewall and using reliable antivirus software, you establish strong defenses against malware, viruses, and other online threats, protecting the integrity and security of your desktop computer.
Create and Enforce Strong User Passwords
Creating and enforcing strong user passwords is a fundamental aspect of securing your desktop computer. Strong passwords are essential for protecting user accounts, preventing unauthorized access, and safeguarding sensitive data. Here’s why strong passwords are important and how to create and enforce them effectively:
- Enhanced Security: Strong passwords significantly increase the difficulty for hackers or unauthorized individuals to guess or crack user accounts. This helps prevent unauthorized access to your desktop computer and the sensitive information it contains.
- Password Complexity: Encourage users to create passwords that are complex and difficult to guess. Strong passwords typically include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using common dictionary words or easily guessable information like birthdays or pet names.
- Length and Complexity: The longer the password, the more secure it generally is. Encourage users to create passwords that are at least eight characters long, but aim for longer passwords when possible. Consider using passphrases, which are longer phrases that are easier to remember but still difficult for others to guess.
- Regular Password Changes: Implement a policy of regular password changes to ensure that accounts remain secure over time. Set a specific timeframe, such as every 90 days, for users to change their passwords. This helps protect against potential compromises and ensures that old passwords do not remain accessible.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA whenever possible. This adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a fingerprint, to access their accounts. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
- Enforce Password Complexity: Configure your computer’s settings or use password management tools to enforce password complexity requirements. This ensures that users create passwords that meet specific criteria and cannot choose weak or easily guessable passwords.
- Education and Awareness: Educate your employees or household members about the importance of strong passwords and the potential risks of weak passwords. Promote password best practices, such as not sharing passwords, avoiding password reuse, and being cautious of phishing attempts.
Creating and enforcing strong user passwords is an integral part of maintaining the physical security of your desktop computer. Additionally, it’s crucial to keep in mind that passwords should not be the sole security measure but should be complemented with other security practices for comprehensive protection.
Regularly remind users to update their passwords and provide resources or tools to help them create and manage strong passwords. Encourage them to use password managers to securely store and generate unique passwords for each account.
By implementing strong password practices, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, protect sensitive data, and enhance the overall security of your desktop computer.
Educate Users on Physical Security Best Practices
Educating users on physical security best practices is vital for maintaining the overall security of your desktop computer. User awareness and adherence to proper security protocols can greatly reduce the risk of physical breaches or unauthorized access. Here are some important practices to educate your employees or household members about:
- Securing Work Areas: Emphasize the importance of keeping work areas clean and tidy. Encourage users to lock their computers when they step away from their desk and store confidential documents and access cards in locked drawers or cabinets.
- Safe Computing Practices: Educate users about the risks of downloading files or opening email attachments from unknown or untrusted sources. Encourage them to practice safe browsing habits, use trusted websites, and avoid clicking on suspicious links.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Train users to recognize and report any suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or unfamiliar individuals wandering in sensitive areas. Establish clear protocols for reporting incidents or security concerns to relevant personnel or the IT department.
- Physical Device Security: Stress the importance of securing other physical devices, such as laptops, smartphones, or external hard drives. Educate users on how to secure their devices through built-in security features, password protection, and encryption.
- Visitor Management: Establish protocols for managing and monitoring visitors in the workplace. Require visitors to sign in and provide identification when entering secure areas. Employees should be vigilant in challenging unidentified individuals and reporting any suspicious behavior.
- Protection Against Tailgating: Teach users the significance of not allowing unauthorized individuals to enter secure areas behind them without proper authorization. Encourage users to challenge unfamiliar individuals and report any incidents of tailgating.
- Travel Security: Inform users about security precautions when traveling with company-owned or personal devices. Emphasize the importance of keeping devices with them at all times, using secure network connections, and being mindful of physical security risks in public places.
- Physical Security Audits: Conduct periodic physical security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities and evaluate the effectiveness of existing security measures. Involving users in this process can foster awareness and encourage proactive engagement in maintaining security standards.
Regularly reinforcing these security best practices and providing ongoing training and reminders will help create a culture of physical security awareness. Encourage open communication, establish reporting channels for security concerns, and reward users for proactive security behavior.
Furthermore, consider creating easily accessible documentation or visual aids that summarize key physical security practices. This can serve as a reference and training resource for users, ensuring consistent adherence to security protocols.
By educating users on physical security best practices, you empower them to take an active role in maintaining the security of your desktop computer and the protection of sensitive data.