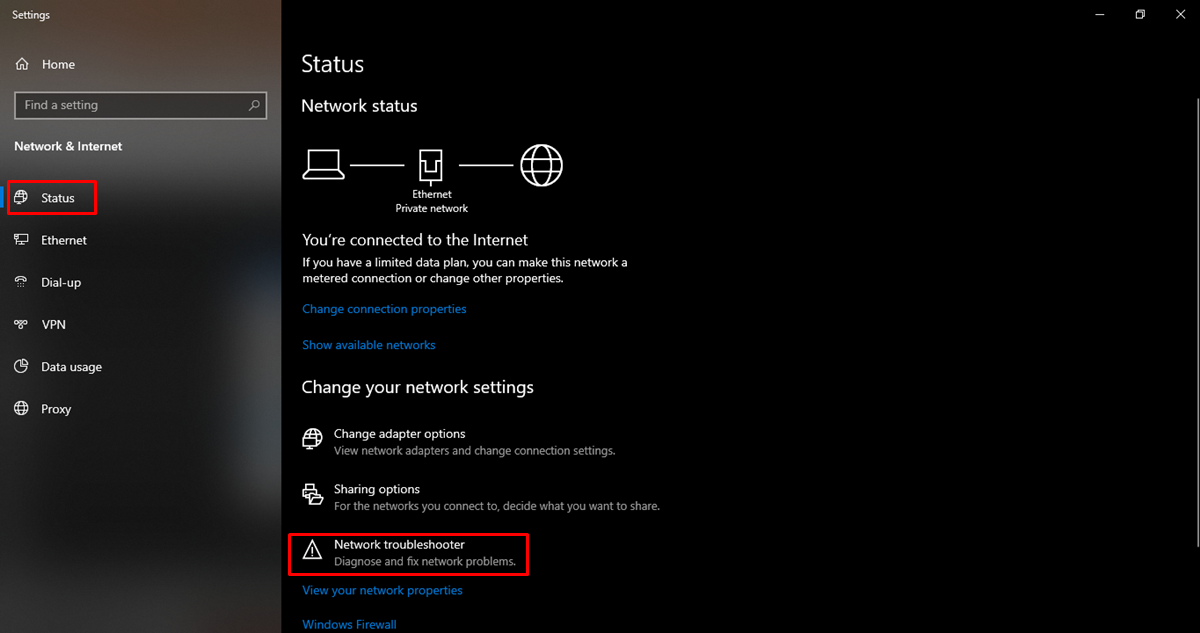
Check Wi-Fi Router
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, the first step is to check your Wi-Fi router. The router is the central device that allows your devices to connect to the internet and creates the wireless network. Here are some important things to check:
- Power and connectivity: Ensure that your router is powered on and properly connected to the modem. Check all the cables and make sure they are securely plugged in.
- Indicator lights: Most routers have indicator lights that show the status of the network. Take a look at the lights and make sure they are all functioning as expected. If any lights are off or blinking unexpectedly, it could indicate a problem with the router.
- Reset button: Some routers have a reset button that can help resolve minor issues. You can press and hold the reset button (usually located on the back of the router) for about 10 seconds to reset the router to its default settings. Keep in mind that this will erase any personalized configurations, so proceed with caution.
- Check router settings: Access the router’s settings page by typing its IP address into a web browser. This will usually be something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, but can vary depending on the manufacturer. Once you’re in the settings page, ensure that the Wi-Fi functionality is enabled and the network name (SSID) is properly set.
- Update firmware: It’s also worth checking if there are any firmware updates available for your router. Manufacturers often release updates that fix bugs or improve performance. Consult the router’s documentation or the manufacturer’s website for instructions on how to update the firmware.
By checking your Wi-Fi router and ensuring that all the necessary settings are properly configured, you can eliminate any potential router-related issues that may be causing your Wi-Fi network to not appear. If the problem persists, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose the issue.
Restart Wi-Fi Router
If you’re experiencing the issue of your Wi-Fi network not showing up, a simple yet effective solution is to restart your Wi-Fi router. Restarting the router can resolve various connectivity problems and refresh its settings. Here’s how you can do it:
- Power off the router: Locate the power button on your Wi-Fi router and switch it off. Alternatively, you can unplug the power cord from the router. Wait for about 10-15 seconds to ensure that the router is completely powered off.
- Power on the router: Plug the power cord back into the router or press the power button to turn it on. Wait patiently for the router to boot up and establish a stable connection with your internet service provider.
- Monitor the indicator lights: As the router restarts, pay attention to the indicator lights on the front panel. These lights usually indicate the status of the internet and wireless connections. Ensure that all the lights are stable and not displaying any unusual blinking patterns.
- Reconnect your devices: Once the router has fully restarted, reconnect your devices to the Wi-Fi network. Look for the network in the list of available networks and enter the Wi-Fi password if prompted.
Restarting your Wi-Fi router can help resolve temporary issues with the network, such as interference or connectivity glitches. It refreshes the router’s settings and establishes a fresh connection with your devices. If the network still does not appear after restarting the router, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose the issue.
Check Wi-Fi Network Settings
When your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, it’s important to evaluate and verify the Wi-Fi network settings. Sometimes, incorrect or misconfigured settings can lead to the network not being visible. Here are some steps to check and adjust the Wi-Fi network settings:
- Check device Wi-Fi settings: Make sure that Wi-Fi is enabled on the device you are using to connect to the network. Look for the Wi-Fi icon in your device’s settings or taskbar and ensure that it is turned on.
- Verify SSID (network name): Double-check the SSID (network name) of your Wi-Fi network. It should be displayed in the available networks list on your device. If it is not appearing, or if it is different from what you expect, there may be an issue with the network settings.
- Ensure correct security settings: Check that the security settings for your Wi-Fi network match those of your device. If your network is using WPA2 encryption, make sure your device is set to use the same security protocol. If the settings don’t align, you may not be able to see or connect to the network.
- Verify password: Confirm that you are entering the correct Wi-Fi password when prompted. It’s easy to mistype or forget the password, so take the time to enter it carefully. If you suspect that the password is incorrect, consider changing it in the router settings and updating it on all your devices.
- Check DHCP settings: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is responsible for assigning IP addresses to devices on the network. Ensure that DHCP is enabled in your router settings to automatically assign IP addresses. If DHCP is disabled or the IP address range conflicts with other networks, it may prevent the Wi-Fi network from being visible.
By thoroughly examining and adjusting the Wi-Fi network settings, you can resolve issues related to the visibility of the network. Ensure that your device’s Wi-Fi settings align with the network settings, including the correct SSID, security settings, and password. If the problem persists, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose the issue.
Check Wi-Fi Network Visibility
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, there could be an issue with its visibility. Here are some steps to check and improve the visibility of your Wi-Fi network:
- Physical proximity: Make sure you are within the range of your Wi-Fi network. Walls, furniture, and other physical obstructions can weaken the signal, reducing the visibility of the network. Move closer to the router or consider repositioning it to a central location in your home or office.
- Signal interference: Check for potential sources of signal interference, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, microwave ovens, or other electronic devices. These devices can operate on the same frequency as your Wi-Fi network, causing interference and affecting the network visibility. Try turning off or relocating such devices to minimize interference.
- Channel congestion: Wi-Fi networks operate on different channels within a frequency range. If multiple nearby Wi-Fi networks are using the same or overlapping channels, it can result in congestion and reduced visibility. Access your router’s settings and switch to a less congested channel to improve network visibility.
- Wi-Fi extender or repeater: If you have a large home or office space, consider using a Wi-Fi extender or repeater. These devices can boost the Wi-Fi signal strength and extend the network’s coverage, making it more visible in distant areas.
- Check router antenna: Ensure that the antenna on your Wi-Fi router is properly attached and positioned. Sometimes, a loose or poorly positioned antenna can weaken the signal and affect network visibility. Adjust the antenna for the best possible signal.
By addressing the factors that impact Wi-Fi network visibility, you can enhance the chances of your network appearing in the available networks list. Ensure your device is within range, eliminate signal interference, switch to a less congested channel, consider using Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters, and optimize the router antenna position. If the network still does not show up, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose the issue.
Update Wi-Fi Drivers
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, outdated or faulty Wi-Fi drivers could be the culprit. Drivers are software programs that facilitate communication between your operating system and hardware devices, such as your Wi-Fi adapter. Here’s how you can update your Wi-Fi drivers to improve network visibility:
- Check for driver updates: Visit the website of your device’s manufacturer or the Wi-Fi adapter manufacturer and look for the latest driver updates. Search for the specific model and download the appropriate driver for your operating system.
- Device Manager: Press the Windows key + X and select “Device Manager” from the menu. Expand the “Network adapters” category and locate your Wi-Fi adapter. Right-click on it and select “Update driver”. Choose the option to search automatically for updated driver software. If a new driver is found, follow the on-screen instructions to install it.
- Automatic driver update tools: If manually updating drivers seems daunting, you can use automatic driver update tools. These tools scan your system, identify outdated drivers, and download and install the latest versions. Popular tools include Driver Booster, Driver Easy, and Snappy Driver Installer.
- Restart your device: After updating your Wi-Fi drivers, restart your device to apply the changes. This allows the system to fully recognize and utilize the updated drivers.
Updating your Wi-Fi drivers can resolves issues related to compatibility, performance, and network visibility. By ensuring that you have the latest drivers installed, you maximize the chances of your Wi-Fi network showing up in the available networks list. If the network still does not appear after updating the drivers, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further diagnose the issue.
Disable Airplane Mode
When experiencing the issue of a Wi-Fi network not showing up, it’s important to check if Airplane Mode is enabled on your device. Airplane Mode is a setting that disables all wireless connectivity features, including Wi-Fi, cellular data, and Bluetooth. Here’s how you can disable Airplane Mode:
- Open device settings: Go to the settings menu on your device. The location of this menu may vary depending on the operating system and device model.
- Look for Airplane Mode: In the settings menu, look for the Airplane Mode option. It is usually represented by an airplane icon.
- Disable Airplane Mode: If Airplane Mode is currently enabled, toggle the switch or button to turn it off. In some cases, you may need to confirm your action by selecting “OK” or a similar prompt.
After disabling Airplane Mode, your device’s wireless connectivity features, including Wi-Fi, will be reactivated. Check if the Wi-Fi network you were trying to connect to now appears in the list of available networks.
Airplane Mode is often enabled to comply with airline regulations or to conserve battery life when not using wireless connections. However, if Airplane Mode is unintentionally left enabled, it can prevent your device from detecting Wi-Fi networks. By ensuring Airplane Mode is disabled, you can restore the visibility of Wi-Fi networks and reconnect to the desired network.
If the Wi-Fi network is still not visible after disabling Airplane Mode, it is advised to move on to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Enable Wi-Fi Service
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, it’s important to ensure that the Wi-Fi service is enabled on your device. Disabling the Wi-Fi service can result in the network not being detected. Here’s how you can check and enable the Wi-Fi service:
- Open device settings: Go to the settings menu on your device. The location of this menu may vary depending on the operating system and device model.
- Wi-Fi settings: Look for the Wi-Fi option in the settings menu. It is usually represented by a Wi-Fi icon.
- Enable Wi-Fi: If the Wi-Fi service is currently disabled, toggle the switch or button to turn it on. In some cases, you may need to confirm your action by selecting “OK” or a similar prompt.
Enabling the Wi-Fi service will activate the wireless connectivity feature on your device, allowing it to search for and detect available Wi-Fi networks. Check if the Wi-Fi network you were trying to connect to now appears in the list of available networks.
Disabling the Wi-Fi service is often done to conserve battery power or to disable internet connectivity temporarily. However, if the Wi-Fi service is left disabled, it will prevent your device from detecting and connecting to Wi-Fi networks. By ensuring that the Wi-Fi service is enabled, you can restore the network visibility and reconnect to your desired Wi-Fi network.
If the Wi-Fi network is still not visible after enabling the Wi-Fi service, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Reset Network Settings
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, resetting the network settings on your device can help resolve any underlying issues that may be preventing the network from appearing. Resetting the network settings will clear all saved network configurations and restore the network settings to their default state. Here’s how you can reset the network settings:
- Open device settings: Go to the settings menu on your device. The location of this menu may vary depending on the operating system and device model.
- Find network settings: Look for the network settings option. It may be listed as “Network & Internet,” “Connections,” or something similar.
- Reset network settings: Within the network settings, look for an option to reset or restore network settings. This option may be called “Reset Wi-Fi,” “Reset Network,” or similar.
- Confirm reset: When prompted, confirm that you want to reset the network settings. Keep in mind that this action will remove all saved Wi-Fi networks, passwords, and other network-related configurations. Proceed with caution as you will need to set up your Wi-Fi network connections again.
After resetting the network settings, your device will restart and the network settings will be restored to their default state. Reconnect to your Wi-Fi network and check if it now appears in the list of available networks.
Resetting the network settings can resolve issues caused by misconfigured network settings or conflicting configurations. It provides a fresh start for your network settings and can help restore the visibility of your Wi-Fi network. If the network is still not visible after resetting the network settings, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Use Command Prompt
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, using the Command Prompt can help diagnose and resolve any underlying issues that may be affecting the visibility of the network. Here’s how you can use the Command Prompt to troubleshoot the problem:
- Open Command Prompt: On your Windows device, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Type “cmd” and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
- Run netsh command: In the Command Prompt, type “netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid” and press Enter. This command will display a list of all available Wi-Fi networks along with their details.
- Check for your network: Look through the list of networks and check if your Wi-Fi network is listed. If it is listed, ensure that the SSID (network name) matches the one you are trying to connect to.
- Scan for networks: If your network is not listed, you can try running the command “netsh wlan show networks mode=ssid” to perform a scan for available networks.
- Restart WLAN AutoConfig service: In some cases, restarting the WLAN AutoConfig service can help resolve network visibility issues. To do this, type “net stop WLANAutoConfig” and press Enter, followed by “net start WLANAutoConfig” and press Enter.
Using the Command Prompt allows you to view a detailed list of available Wi-Fi networks, ensuring that your desired network is properly detected. It also provides the option to perform a network scan and restart the WLAN AutoConfig service, which can potentially resolve network visibility problems.
If your Wi-Fi network still does not appear after using the Command Prompt, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Rename Wi-Fi SSID
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, renaming the Wi-Fi SSID (Service Set Identifier) can help refresh the network visibility and make it easier to locate. SSID is the name of your Wi-Fi network that appears in the list of available networks on devices. Here’s how you can rename your Wi-Fi SSID:
- Access router settings: Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address into the address bar. This address is usually mentioned in the router’s documentation or printed on the device itself. Press Enter to access the router’s settings page.
- Login to router: Enter the username and password for your router. If you haven’t changed the default login credentials, they might be mentioned in the router’s documentation or on the device. If you can’t find them, try searching online using the model number of your router.
- Navigate to wireless settings: Once logged in, navigate to the wireless settings section. Look for an option labeled “Wireless,” “Wi-Fi,” or similar.
- Change SSID: Locate the field that displays the current SSID and enter a new name for your Wi-Fi network. Try choosing a unique and identifiable name that is not used by other nearby networks. Avoid using personal information or sensitive data as the SSID.
- Save settings: After renaming the SSID, scroll down to the bottom or look for a “Save” or “Apply” button. Click this button to save the changes and update the Wi-Fi network with the new name.
Renaming the Wi-Fi SSID can help refresh the network’s visibility on devices and make it easier to differentiate from other networks. After renaming, reconnect your devices to the newly named Wi-Fi network and check if it now appears in the list of available networks.
If the Wi-Fi network still does not appear after renaming the SSID, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Modify Wi-Fi Channel
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, modifying the Wi-Fi channel can help resolve any interference issues that may be affecting the visibility of the network. Wi-Fi networks operate on different channels within a specific frequency range. Changing the channel can help avoid congestion and improve the network’s visibility. Here’s how you can modify the Wi-Fi channel:
- Access router settings: Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address into the address bar. This address is usually mentioned in the router’s documentation or printed on the device itself. Press Enter to access the router’s settings page.
- Login to router: Enter the username and password for your router. If you haven’t changed the default login credentials, they might be mentioned in the router’s documentation or on the device. If you can’t find them, try searching online using the model number of your router.
- Navigate to wireless settings: Once logged in, navigate to the wireless settings section. Look for an option labeled “Wireless,” “Wi-Fi,” or similar.
- Channel selection: Locate the channel selection option or the channel settings. Depending on your router, you may see a drop-down menu or a list of channels to choose from.
- Choose a different channel: Select a different channel from the available options. Try different channels to see which one works best for your network. It is recommended to choose a channel that is less congested and not overlapping with other nearby networks.
- Save settings: After selecting the desired channel, scroll down to the bottom or look for a “Save” or “Apply” button. Click this button to save the changes and apply the modified channel settings.
Modifying the Wi-Fi channel can help reduce interference and congestion, improving the visibility and performance of your Wi-Fi network. After modifying the channel, reconnect your devices to the network and check if it now appears in the list of available networks.
If the Wi-Fi network still does not show up after modifying the channel, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Check for Interference
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, interference from other devices or objects can be a common cause. Interference can weaken the Wi-Fi signal and affect the visibility and performance of your network. Here are some steps to check for and minimize interference:
- Identify potential sources of interference: Look for devices or objects that could potentially interfere with the Wi-Fi signal. Common sources of interference include cordless phones, microwave ovens, baby monitors, Bluetooth devices, and neighboring Wi-Fi networks.
- Position your router: Ensure that your Wi-Fi router is positioned away from potential sources of interference. Keep it away from cordless phones, microwaves, and other electronic devices. Also, avoid placing it near thick walls or metal objects that could obstruct the signal.
- Adjust router antenna: Check the position of the router’s antenna. Ensure that it is fully extended and positioned vertically for maximum signal reception. Experiment with different angles to find the best signal strength.
- Switch to a different Wi-Fi channel: Access your router’s settings and switch to a less congested channel. This can help avoid interference from neighboring networks operating on the same channels.
- Upgrade your router: If interference issues persist, consider upgrading to a dual-band router or a router that supports advanced technologies like beamforming. These routers can provide better signal strength and handle interference more effectively.
- Use Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters: If you have a large home or office space, consider using Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters to expand your network’s coverage. These devices help boost the Wi-Fi signal and mitigate the effects of interference.
By checking for potential sources of interference and taking measures to minimize their impact, you can improve the visibility and performance of your Wi-Fi network. Positioning the router away from sources of interference, adjusting the antenna, switching to a different Wi-Fi channel, upgrading the router, and using Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters can all help reduce interference and enhance the network’s visibility.
If the Wi-Fi network is still not visible after addressing potential sources of interference, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Check Device Compatibility
If your Wi-Fi network is not showing up, it’s important to consider the compatibility of your device with the network. Incompatibility issues can prevent your device from detecting or connecting to certain Wi-Fi networks. Here are some steps to check device compatibility:
- Wi-Fi standard: Verify that your device supports the Wi-Fi standard used by your network. The most common Wi-Fi standards are 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac. Consult your device’s specifications or documentation to determine the supported Wi-Fi standard.
- Frequency band: Ensure that your device is compatible with the frequency band used by your Wi-Fi network. The two primary frequency bands are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Some older devices may only support the 2.4 GHz band, while newer devices typically support both bands. Check your device’s specifications to confirm compatibility.
- Security protocols: Check if your device supports the security protocols used by your Wi-Fi network, such as WEP, WPA, or WPA2. Ensure that the device’s Wi-Fi settings are configured to use the same security protocol as the network.
- Network encryption: Confirm that your device supports the encryption method used by your Wi-Fi network. Encryption methods like AES or TKIP ensure secure transmission of data over the network. Check if your device’s Wi-Fi settings are set to use the same encryption method as the network.
- Hardware limitations: Some older or budget devices may have hardware limitations that affect their ability to detect or connect to certain Wi-Fi networks. Ensure that your device meets the minimum hardware requirements for the network, such as the required processing power or network adapter capabilities.
Checking the compatibility of your device with the Wi-Fi network can help identify any limitations that may be causing the network to not show up. If your device is incompatible with the network, you may need to consider using a different device or upgrading your device’s hardware or software to establish a connection.
If the Wi-Fi network is still not visible after checking device compatibility, proceed to the next troubleshooting steps to further investigate and resolve the issue.
Factory Reset Wi-Fi Router
If all else fails and your Wi-Fi network is still not showing up, performing a factory reset on your Wi-Fi router can help resolve any persistent issues. A factory reset restores your router to its original settings, erasing all customized configurations. Here’s how you can perform a factory reset on your Wi-Fi router:
- Locate the reset button: Look for a small reset button on your Wi-Fi router. This button is typically recessed and may require a pin or paperclip to press.
- Power off the router: While the router is powered on, press and hold the reset button for about 10-15 seconds. This duration may vary depending on the router model. Make sure to hold the button until the lights on the router blink or flash, indicating that the reset process has begun.
- Power on the router: After releasing the reset button, wait for the router to restart. This could take a few minutes. Once the router has fully booted up, it will be restored to its factory default settings.
- Reconfigure the router: Now that the router has been reset, you’ll need to reconfigure it to your preferences. Access the router’s settings through a web browser using its default IP address, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions to set up your Wi-Fi network name (SSID), password, and security settings.
Performing a factory reset on your Wi-Fi router can effectively eliminate any persistent issues that may have been causing your network to not appear. It essentially provides a fresh start and allows you to rebuild your network configuration from scratch.
Remember that performing a factory reset will erase all personalized settings, including any port forwarding or IP address assignments. Make sure to take note of any custom configurations you want to preserve before proceeding with the factory reset.
If the Wi-Fi network still does not show up after performing a factory reset, there may be deeper underlying issues. Consider reaching out to your internet service provider or contacting the router manufacturer for further assistance.