Reasons to Enable or Disable the Administrator Account
The Administrator Account is a powerful user account in Windows that has unrestricted access to the system. By default, this account is disabled to prevent unauthorized access and potential security risks. However, there are certain situations where you may need to enable or disable the Administrator Account. Here are some common reasons:
- System Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Enabling the Administrator Account can be beneficial when performing system maintenance tasks or troubleshooting issues. With administrative privileges, you can make system-wide changes, install/uninstall programs, and modify security settings without any restrictions.
- Legacy Software Compatibility: Some older software or system utilities may require administrative privileges to run properly. By enabling the Administrator Account, you can ensure that these legacy applications have the necessary permissions, thus allowing them to function correctly.
- Security Measures: On the other hand, disabling the Administrator Account can help enhance the security of your system. Without an active Administrator Account, it becomes more challenging for potential attackers to gain unauthorized access to your computer. This is particularly important if you share your computer with other users or if you frequently connect to public networks.
- User Error Prevention: Disabling the Administrator Account can help prevent accidental system modifications. By using a standard user account for day-to-day tasks, you reduce the risk of unintentional changes to critical system settings or files that could lead to system instability or data loss.
These are just a few examples of why you might consider enabling or disabling the Administrator Account in Windows. Before making any changes, it’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the security implications and ensure you understand the consequences.
How to Enable the Administrator Account using the Command Prompt
Enabling the Administrator Account using the Command Prompt is a straightforward process that requires administrative privileges. Follow these steps:
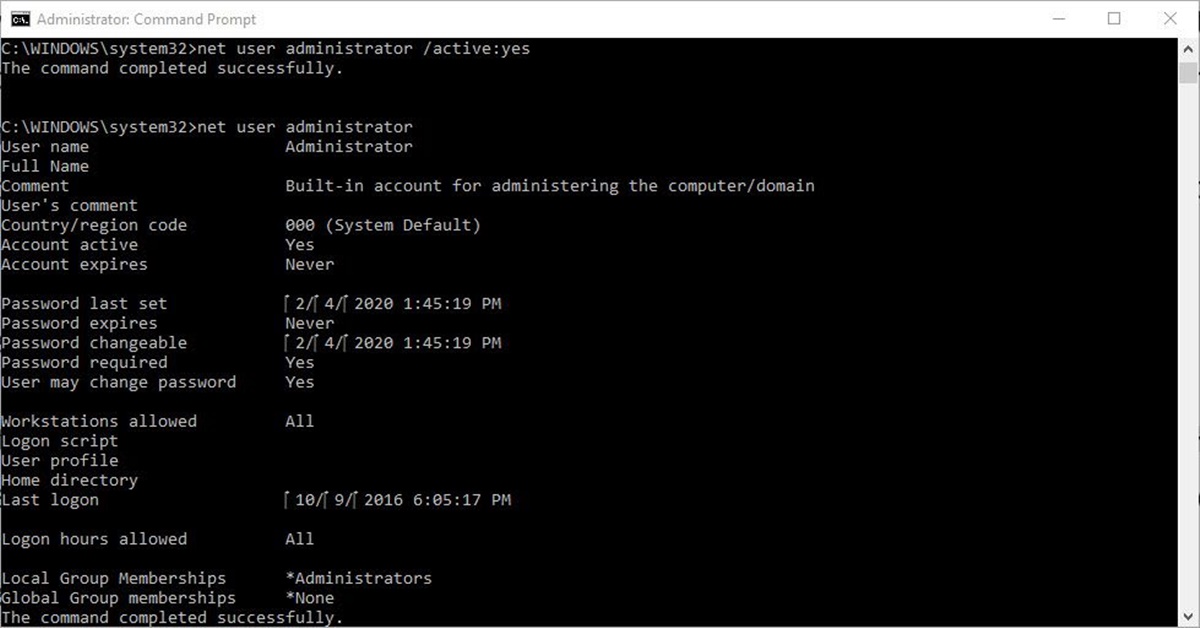
- Press the Windows Key + X on your keyboard to open the Power User Menu. From the list of options, select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin). This will launch the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
net user administrator /active:yes
This command enables the Administrator Account. - You should see a message that says, “The command completed successfully.” This indicates that the Administrator Account has been enabled.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Once you’ve completed these steps, the Administrator Account will be active, allowing you to log in using that account.
Note that it’s important to exercise caution when using the Administrator Account since it has full control over the system. Make sure to create a strong password for the account and only use it when necessary.
Step-by-step Guide to Enable the Administrator Account using Computer Management
If you prefer using the graphical interface, you can enable the Administrator Account using the Computer Management tool in Windows. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Press the Windows Key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type compmgmt.msc in the text field and click OK. This will launch the Computer Management window.
- In the Computer Management window, expand the Local Users and Groups folder.
- Click on the Users folder to display a list of user accounts on the right pane.
- Right-click on the Administrator account and select Properties.
- In the Administrator Properties window, uncheck the Account is disabled checkbox.
- Click OK to save the changes.
After following these steps, the Administrator Account will be enabled, and you can use it to log into your Windows system.
Remember to exercise caution when using the Administrator Account since it has full control over the system. It’s recommended to create a strong password for the account to enhance security and only use it when necessary.
How to Disable the Administrator Account using the Command Prompt
If you no longer need the Administrator Account or want to enhance the security of your system, you can disable the Administrator Account using the Command Prompt. Follow these simple steps:
- Begin by opening the Command Prompt with administrative privileges. To do this, press the Windows Key + X on your keyboard, then select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin) from the Power User Menu.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
net user administrator /active:no
This command deactivates or disables the Administrator Account. - You should see a message that says, “The command completed successfully.” This indicates that the Administrator Account has been disabled.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
By following these steps, the Administrator Account will be disabled, and it will no longer be available for use.
Disabling the Administrator Account can help safeguard your system against potential security threats and prevent unauthorized access. However, make sure you have an alternative administrative account to manage your computer effectively.
Step-by-step Guide to Disable the Administrator Account using Computer Management
If you prefer using the graphical interface, you can disable the Administrator Account using the Computer Management tool in Windows. Follow these steps:
- Press the Windows Key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type compmgmt.msc in the text field and click OK. This will open the Computer Management window.
- In the Computer Management window, expand the Local Users and Groups folder.
- Click on the Users folder to display a list of user accounts on the right pane.
- Right-click on the Administrator account and select Properties.
- In the Administrator Properties window, check the Account is disabled checkbox.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Following these steps will disable the Administrator Account, and it will no longer be visible as an option for logging into Windows.
Disabling the Administrator Account can help prevent unauthorized access and enhance the security of your system. However, ensure that you have an alternative administrative account to manage your computer effectively.
Precautions to Take When Enabling or Disabling the Administrator Account
Enabling or disabling the Administrator Account in Windows can have significant implications for the security and functionality of your system. It’s important to take certain precautions to ensure a smooth and secure experience. Here are some precautions to consider:
- Use Strong Passwords: Whether you enable or disable the Administrator Account, it is crucial to set a strong, unique password. A strong password helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures the integrity of your system.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If available, consider enabling two-factor authentication for your Administrator Account. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a secondary authentication method, such as a code sent to your mobile device, in addition to the password.
- Regularly Update and Patch: Ensure that your Windows operating system and all installed software are up to date with the latest security patches. Regularly installing updates helps protect against known vulnerabilities and keeps your system secure.
- Minimize Account Exposure: Only enable the Administrator Account when necessary. Using a standard user account for day-to-day activities can minimize the risk of accidental system changes or unauthorized access.
- Create Backup Accounts: It’s a good practice to have additional user accounts with administrative privileges. Having backup admin accounts ensures that you can still access and manage your system even if the Administrator Account is disabled or inaccessible.
- Monitor Account Activity: Keep an eye on any suspicious activity related to the Administrator Account. Regularly review account logs, security event logs, and system audit logs to detect and mitigate any potential security breaches.
- Restrict Remote Access: If you enable the Administrator Account and plan to use it for remote access, ensure that remote desktop access is configured securely. Use strong passwords, enable Network Level Authentication (NLA), and limit remote access to trusted networks only.
- Disable the Account When Not in Use: If you have enabled the Administrator Account for a specific task or purpose, make sure to disable it once you have completed your intended actions. Leaving the Administrator Account enabled unnecessarily increases the risk of unauthorized access or accidental system changes.
By following these precautions, you can better protect your system and maintain a secure environment when enabling or disabling the Administrator Account in Windows.
What to Do If You Forget the Administrator Account Password
Forgetting the Administrator Account password can be a frustrating situation. However, there are a few steps you can take to regain access to your Windows system. Here’s what you can do:
- Use Password Reset Disk: If you’ve previously created a password reset disk, you can use it to reset the Administrator Account password. Insert the password reset disk into your computer, click on the “Reset Password” option on the login screen, and follow the prompts to set a new password.
- Try Other User Accounts: Check if there are other user accounts on your system with administrative privileges. You can use these accounts to reset the Administrator Account password. Simply log in with the alternate account, go to the User Accounts settings, and reset the password for the Administrator Account.
- Use Command Prompt: Boot your computer into Safe Mode and access the Command Prompt. From there, type a command to reset the Administrator Account password. For example, you can use the
net usercommand to change the password. Restart your computer and log in with the new password. - Third-Party Password Recovery Tools: There are various third-party password recovery tools available that can help you reset the Administrator Account password. These tools are typically bootable USB drives or CDs that can bypass or reset Windows passwords. Research and choose a reputable tool that suits your needs.
- Contact Technical Support: If none of the above methods work or if you’re uncomfortable with performing the steps yourself, consider reaching out to technical support services. They can guide you through the necessary steps or provide further assistance in recovering your Administrator Account password.
Remember, it’s always a good idea to keep a backup of important files and create a password reset disk to avoid being locked out of your system in the future. Additionally, ensure that your passwords are secure and not easily guessable.
If you’re unable to regain access to your Administrator Account, you may need to reinstall the operating system. However, this should be considered as a last resort, as it will result in data loss and additional setup time.
Alternatives to Using the Administrator Account in Windows
While the Administrator Account provides full control over your Windows system, there are alternative methods that can help you perform administrative tasks without relying solely on the Administrator Account. Consider these alternatives:
- Standard User Account: Instead of using the Administrator Account for everyday tasks, create a standard user account with limited privileges. This adds an extra layer of security by preventing unintentional system changes or the execution of potentially harmful programs.
- Run as Administrator: For certain tasks that require elevated privileges, you can right-click on a program or shortcut and select “Run as Administrator.” This allows you to temporarily escalate your user account privileges without logging in as the Administrator.
- Windows User Account Control (UAC): UAC is a security feature in Windows that prompts for permission or an administrator password whenever system changes are requested. UAC helps prevent unauthorized actions and potential malware from making changes to your system.
- Group Policy: Group Policy allows system administrators to define and manage various settings for multiple users and computers. By utilizing Group Policy, administrators can control permissions, software installations, and other configuration settings without directly using the Administrator Account.
- PowerShell: PowerShell is a powerful command-line tool in Windows that allows you to perform a wide range of administrative tasks. With the appropriate commands and scripting abilities, you can accomplish administrative tasks without relying solely on the Administrator Account.
These alternatives provide more granular control over system administration, allowing you to perform administrative tasks without the continuous use of the Administrator Account. By utilizing these methods, you can strike a balance between maintaining security and carrying out necessary administrative tasks.
Remember to create strong passwords for your user accounts, regularly update your operating system and software, and exercise caution when granting elevated privileges or executing unknown programs.