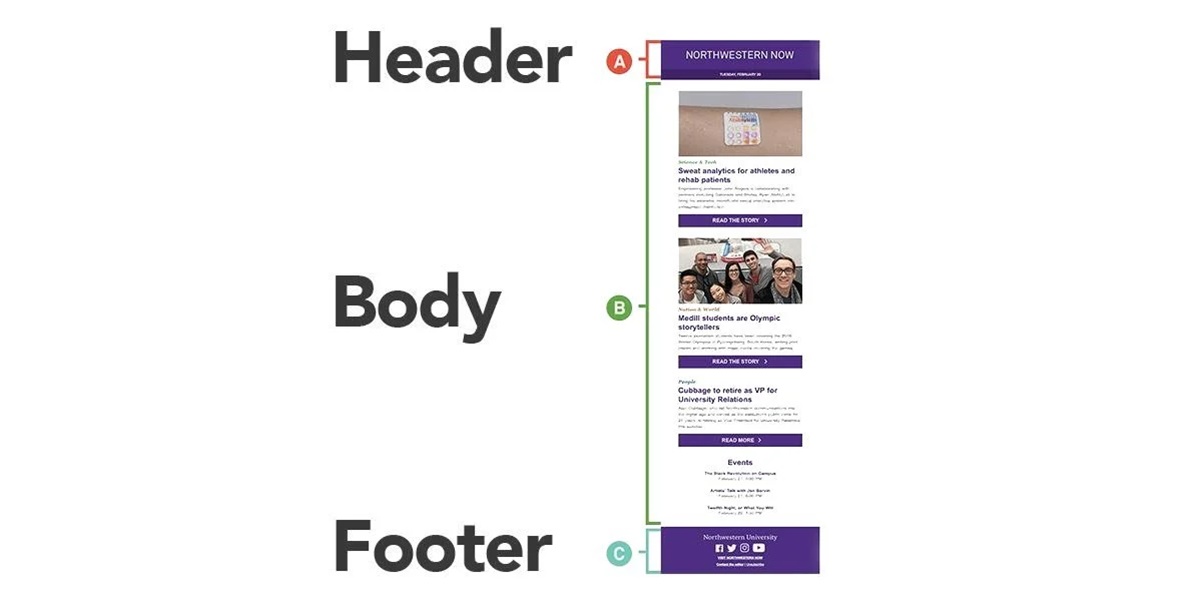
Purpose of the Header
The header of an email serves as the first point of contact with the recipient. It plays a crucial role in capturing their attention, conveying the purpose of the email, and encouraging them to open and read the message.
One of the main purposes of the header is to provide essential information about the sender, such as their name, email address, and contact details. This helps the recipient identify the sender and establish trust and credibility. Including professional branding elements, such as a company logo, can further enhance recognition and brand awareness.
Another vital function of the header is to address the recipient appropriately. Using the recipient’s name, rather than a generic greeting, creates a personal connection and shows that the email was specifically crafted for them. This attention to detail can significantly improve engagement and response rates.
Additionally, the subject line is a crucial component of the header. It aims to succinctly summarize the content of the email and entice the recipient to open it. An effective subject line should be concise, attention-grabbing, and arouse curiosity. A well-crafted subject line can significantly impact open rates and compel the recipient to prioritize reading the email.
Furthermore, the header serves as a preview or synopsis of the email’s content. It gives the recipient an overview of what to expect in the body of the email. By capturing their interest and generating intrigue, the header prompts them to continue reading and possibly take action.
Moreover, the header sets the tone and establishes the level of formality of the email. A formal header may be used when corresponding with clients, colleagues, or higher-level executives, while a more casual header might be suitable for communication with friends, family, or colleagues in a less professional setting.
Ultimately, the purpose of the header is to create a compelling first impression, ensure clear communication, and increase the chances of the email being read and responded to. By including relevant information, addressing the recipient appropriately, and crafting an attention-grabbing subject line, the header becomes a powerful tool in email communication.
Components of the Header
The header of an email consists of several key components that work together to provide essential information to the recipient. Each component serves a specific purpose and contributes to creating a professional and effective email header.
1. Sender’s Information: The sender’s information includes the name, email address, and contact details of the person or organization sending the email. This information helps the recipient identify the sender and establishes credibility and trust. Including additional professional branding elements, such as a company logo or website URL, can further enhance the sender’s identity.
2. Recipient’s Information: In the header, it is important to include the recipient’s name or a personalized greeting. Using the recipient’s name adds a personal touch to the email and shows that it was specifically intended for them. This helps create a connection and encourages the recipient to engage with the email’s content.
3. Subject Line: The subject line is a concise summary of the email’s content. It is crucial for capturing the recipient’s attention and motivating them to open the email. A well-crafted subject line should be clear, relevant, and enticing, giving the recipient an idea of what to expect in the email.
4. Salutation: The salutation is the initial greeting in the email. It can be formal, such as “Dear Mr. Smith,” or more casual, such as “Hi John.” The choice of salutation depends on the relationship between the sender and recipient and the level of formality desired for the communication.
5. Date and Time: Including the date and time in the header provides important context and helps the recipient understand when the email was sent. This is especially useful when referring back to previous conversations or when time-sensitive information is being shared.
6. Reply-To Information: The reply-to information allows the recipient to easily respond to the email by clicking on a designated email address or button. This simplifies the process of replying and ensures that the response reaches the intended sender.
7. Additional Information: Depending on the nature of the email, additional information may be included in the header. This could include a reference number, a customer or account ID, or any other relevant details that help classify or track the email.
Incorporating these components into the header of an email creates a well-structured and informative introduction. It provides important context, establishes credibility, and improves the overall communication experience for both the sender and recipient.
Importance of Properly Formatting the Header
The header of an email serves as the first impression and initial point of contact with the recipient. It is essential to properly format the header to ensure clarity, professionalism, and effective communication. The formatting of the header impacts the recipient’s perception of the email and influences their decision to open, read, and respond.
One of the primary reasons for proper formatting is to enhance the visual appeal of the header. A well-designed and visually appealing header grabs attention and makes a positive impression. Using appropriate fonts, colors, and layout can help create a cohesive and professional appearance.
Proper formatting also improves the readability and organization of the header. Clear and concise information, consistent alignment, and appropriate use of white space contribute to a visually pleasing and easy-to-read header. This allows the recipient to quickly locate important details such as the sender’s information, subject line, and recipient’s information.
Consistency in formatting is crucial for branding and recognition. By maintaining a consistent look and feel across all email communications, recipients will become familiar with the sender’s visual identity. This consistency strengthens the sender’s brand, creates a sense of professionalism, and fosters trust with the recipient.
Another important aspect of formatting is ensuring mobile responsiveness. With the majority of emails being read on mobile devices, it is crucial to optimize the header for mobile viewing. This includes using a responsive design that adjusts to different screen sizes, ensuring the text remains readable, and optimizing the size of images or logos included in the header.
Moreover, proper formatting helps to establish the sender’s professionalism and attention to detail. Carefully formatting the header demonstrates that the sender takes their communication seriously. It reflects positively on the sender’s credibility and can encourage the recipient to view the email as important and worthy of their attention.
Finally, the formatting of the header can also influence email deliverability. Some email clients and spam filters consider the structure and formatting of the header when evaluating the legitimacy of an email. By adhering to standard email formatting guidelines, the chances of the email reaching the recipient’s inbox and not being flagged as spam are increased.
Addressing the Recipient in the Header
Addressing the recipient properly in the header of an email is essential for establishing a personal connection and fostering effective communication. It sets the tone for the entire email and can significantly impact the recipient’s engagement and response.
Using the recipient’s name is the ideal way to address them in the header. Addressing someone by their name shows that the email was specifically crafted for them and not a generic message sent to multiple recipients. It adds a personal touch and demonstrates that the sender values the recipient’s individuality.
Addressing the recipient by name also helps capture their attention and encourages them to read the email. When someone sees their name in the header, it creates a sense of familiarity and importance. It can make the email feel more relevant and increase the recipient’s curiosity to know what the email is about.
However, it’s important to ensure the correct spelling and accuracy of the recipient’s name. Misspelling the recipient’s name can give the impression of carelessness or lack of attention to detail. It’s crucial to double-check and verify the spelling before sending the email.
In some cases, such as when the recipient’s name is unknown or when sending a generalized message to a large group, a generic greeting may be used in the header. This can include greetings like “Dear valued customer” or “Hello team.” While it lacks personalization, it can still create a sense of inclusion and professionalism.
When addressing someone formally, it is important to use appropriate titles, such as “Mr.,” “Ms.,” or “Dr.,” followed by their last name. This shows respect and acknowledges their professional standing.
In more casual or informal emails, addressing the recipient by their first name can help create a friendly and approachable tone. This is particularly suitable for emails to colleagues, friends, or acquaintances where a more relaxed style of communication is appropriate.
Addressing the recipient properly in the header sets the stage for a positive and engaging email interaction. It shows respect, personalization, and attention to detail. By using the recipient’s name or an appropriate greeting, the sender can establish a connection, increase the recipient’s interest in the email, and pave the way for effective communication.
Subject Line: Key Component of the Header
The subject line of an email is a critical component of the header and plays a crucial role in capturing the recipient’s attention and encouraging them to open the email. It serves as a concise summary of the email’s content and is often the first thing recipients see when deciding whether to open or ignore an email.
A well-crafted subject line has the power to entice and engage the recipient, leading to higher open rates and increased email effectiveness. It should be clear, compelling, and relevant to the email’s purpose, sparking curiosity and motivating the recipient to want to know more.
Using specific and descriptive language in the subject line helps set the expectations for what the email contains. It should accurately represent the content without being misleading or overly vague. An effective subject line lets the recipient know what they can expect to find in the email, leading to more targeted and relevant interactions.
Conciseness is key when it comes to subject lines. Keeping it short and to the point ensures that the message is easily scannable and quickly understood. Most email clients display only a limited number of characters in the subject line, so it is crucial to make the most of that space. Aim for around 50 characters or less to ensure the subject line is fully visible on various devices and screens.
Personalization is another effective technique to make subject lines more engaging. Addressing the recipient by name or using personal pronouns can create a sense of importance and connection. This personal touch can attract the recipient’s attention and make them feel more inclined to open the email.
Consider using actionable language in the subject line to motivate the recipient to take a specific action. Use verbs and phrases that convey a sense of urgency, curiosity, or benefit. For example, “Limited Time Offer: Save 20% on Your Order Today!” or “You’re Invited: Join Our Exclusive Webinar Now!” These types of subject lines create a sense of FOMO (fear of missing out) and make the recipient more likely to open the email.
Avoid using spammy or misleading subject lines, as they can damage the sender’s reputation and lead to low open and engagement rates. Subject lines in all capital letters, excessive punctuation, or overly hyped language can trigger spam filters and make the email appear less legitimate. Be truthful and relevant in the subject line, ensuring it accurately represents the email’s content.
Regularly testing different subject lines and analyzing their effectiveness can help improve email open rates and engagement. A/B testing subject lines with a subset of recipients can provide valuable insights into what types of subject lines are most effective for your audience. Use analytics to track open rates and click-through rates to determine which subject lines resonate best with your recipients.
Best Practices for Writing an Effective Subject Line
The subject line of an email plays a crucial role in grabbing the attention of recipients and enticing them to open the message. To maximize the impact of your subject line and improve email open rates, it’s important to follow some best practices for writing an effective subject line.
1. Be Clear and Concise: Keep your subject line short and to the point. Aim for around 50 characters or less to ensure it is fully visible on various devices. Clearly convey the main purpose or benefit of the email in a concise manner.
2. Personalize When Possible: Addressing recipients by their name or using personalized pronouns can create a sense of connection and importance. Personalization enhances engagement and makes recipients more likely to open the email.
3. Be Specific and Descriptive: Clearly state what the email is about so that recipients have a clear understanding of what to expect. Use descriptive language that accurately represents the content of the email and sparks interest.
4. Use Actionable Language: Use verbs and phrases that create a sense of urgency, curiosity, or benefit. Encourage recipients to take action or highlight what they stand to gain by opening the email. This can increase open rates and engagement.
5. A/B Test Subject Lines: Experiment with different subject lines and analyze their performance. Test variations of subject lines with a subset of recipients to determine which ones resonate best with your audience and improve open rates.
6. Avoid Spam Trigger Words: Stay away from using spammy or misleading language in your subject lines. Words like “free,” “urgent,” or excessive punctuation can trigger spam filters and cause your email to be flagged. Be truthful, relevant, and professional in your subject lines.
7. Create a Sense of Urgency or FOMO: Use phrases that create a sense of urgency or fear of missing out (FOMO). Limited-time offers, exclusive opportunities, or time-sensitive information can drive recipients to open the email right away.
8. Test Across Devices and Email Clients: Ensure your subject lines display effectively across different devices and email clients. Test them on mobile devices, various email platforms, and popular web browsers to ensure they are well-optimized.
9. Analyze Metrics and Adjust: Monitor open rates and engagement metrics to assess the effectiveness of your subject lines. Analyze which subject lines perform best and make adjustments accordingly. Pay attention to feedback and adjust your subject lines to meet the preferences of your audience.
By following these best practices, you can craft compelling subject lines that capture the attention of your recipients and improve the effectiveness of your email campaigns.
Length of the Header: Short and Concise or Detailed?
When it comes to the length of the header in an email, finding the right balance between being short and concise or detailed can greatly impact its effectiveness. Different situations may call for different approaches, so considering the context and purpose of the email is key.
Short and concise headers are often preferred in most email communication. Keeping the header brief and to the point allows recipients to quickly grasp the main purpose of the email. A concise header ensures that the essential information, such as the sender’s details and subject line, are easily visible and scannable on various devices and email clients. This approach is particularly useful when sending emails to individuals or when there is a need to capture the attention of busy recipients.
On the other hand, there are instances when a more detailed header is necessary. When sending formal or official emails, such as business proposals, reports, or legal documents, a detailed header helps establish professionalism and ensures that all the necessary information is included. This may involve including additional details such as the recipient’s name, job title, or company name for formal correspondence. However, even in these cases, it is still important to keep the header concise and avoid unnecessary information that clutters the email.
Another consideration is the use of additional formatting elements in the header, such as logos or images. While these can add visual appeal and branding, they should be used judiciously to ensure that they do not overpower the header or increase its length excessively. Responsive design techniques should be employed to ensure that the header remains well-optimized and visible on different devices and screen sizes.
Ultimately, the length of the header should strike a balance between capturing attention and conveying necessary information. Whether it is short and concise or detailed, the header should always be clear, easily scannable, and relevant to the email’s purpose. It is important to remember that the header serves as the initial point of contact and should make a positive first impression without overwhelming the recipient.
Header Style: Formal vs Informal
The style of the header in an email plays a significant role in setting the tone and establishing the level of formality of the communication. Whether to use a formal or informal header depends on the nature of the relationship between the sender and recipient, the purpose of the email, and the desired level of professionalism.
In formal settings, such as business or professional communication, a formal header is typically preferred. This includes using the recipient’s full name (e.g., Mr. John Smith or Dr. Jane Doe) and appropriate titles. Formal headers are commonly used when corresponding with clients, business partners, colleagues, or higher-level executives. They create a sense of respect, professionalism, and adherence to proper etiquette.
Formal headers often require additional details, such as the sender’s name, job title, and company name. Including these elements helps establish credibility and reliability. When crafting a formal header, it’s important to pay attention to spelling, capitalization, and correct use of titles to maintain the desired level of professionalism.
On the other hand, there are situations where an informal header may be more appropriate. Informal headers are commonly used in personal or casual communication, such as emails to friends, family, or colleagues in a less professional setting. In these cases, addressing the recipient by their first name or using a casual greeting (e.g., Hi John or Hey Sarah) can create a friendly and approachable tone.
Using an informal header is a way to foster a more relaxed and personal connection, allowing for a more conversational style of communication. However, it’s important to maintain a level of professionalism even in an informal setting, being mindful of the language, tone, and content of the email.
When deciding between a formal or informal header style, it’s crucial to consider the context and the relationship between the sender and recipient. Understanding the purpose of the email and the desired tone of the communication will guide the choice of the appropriate header style.
It’s also worth noting that some emails may fall in between formal and informal, depending on the nature of the relationship. In these cases, it’s important to strike a balance and adopt a semi-formal or friendly-professional tone in the header, catering to the specific dynamics of the relationship.
Regardless of the chosen style, it is crucial to maintain consistency throughout the email. This includes aligning the tone of the header with the body of the email to ensure a harmonious and coherent communication experience.
Importance of Including Relevant Information in the Header
The header of an email serves as the gateway to the content within. It is important to include relevant information in the header to provide recipients with essential details and establish a clear purpose of the email. Including relevant information in the header enhances communication effectiveness and promotes a positive user experience.
One of the primary reasons to include relevant information in the header is to provide recipients with clear identification of the sender. Including the sender’s name, email address, and contact information helps recipients quickly recognize and associate the email with the sender. This can enhance professionalism, establish credibility, and build trust.
In addition to identifying the sender, including relevant information in the header is crucial for addressing the recipient appropriately. By including the recipient’s name or a personalized greeting, the email becomes more personalized and tailored to the individual recipient. This simple touch improves engagement and response rates.
Another important aspect of including relevant information in the header is to convey the subject or purpose of the email. This can be achieved through a well-crafted subject line or a concise summary of the email’s content. The subject line should be clear, descriptive, and enticing, providing recipients with a compelling reason to open, read, and respond to the email.
Furthermore, including relevant information in the header can help recipients prioritize and organize their emails. By including details such as the date and time of the email, recipients can easily locate and reference the email in the future. This is especially useful when managing a high volume of emails and when time-sensitive information needs to be tracked.
Properly labeled and organized header information also facilitates effective email management and filtering. Recipients can use filters or search functions to sort, categorize, and locate specific emails based on the information provided in the header. This improves efficiency and saves time for both the sender and recipient.
Moreover, including relevant information in the header is important for compliance and legal purposes. Depending on the nature of the email and its recipients, certain information may need to be included for regulatory or contractual requirements. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the email is compliant and protects the interests of the sender and recipient.
Including relevant information in the header is essential for effective communication in email exchanges. By identifying the sender, addressing the recipient, providing a clear subject line, and offering necessary organizational details, the header sets the foundation for a successful email interaction.
Designing an Eye-Catching Header
The header of an email is the first thing recipients see when opening a message. Designing an eye-catching and visually appealing header can capture their attention, make a positive first impression, and enhance the overall email experience. Here are some tips for designing an eye-catching header:
1. Use a Professional and On-Brand Design: Incorporate your brand’s visual elements, such as colors and logo, into the header to reinforce brand recognition and establish a professional image. Ensure that the design aligns with your brand guidelines to maintain consistency across all communications.
2. Balance Text and Visual Elements: Avoid overwhelming the header with excessive text. Keep it clean and balanced by strategically placing key details, such as the sender’s name and subject line, alongside visual elements. This helps alleviate visual clutter and guides the recipient’s attention to essential information.
3. Choose Fonts Wisely: Select fonts that are easy to read and align with your brand’s style. Use font sizes that are legible, even on smaller screens. Maintaining consistency in font usage throughout the header creates a visually appealing and polished look.
4. Incorporate Engaging Images or Icons: Including relevant images or icons can make the header more visually appealing. Consider incorporating a professional headshot, product images, or relevant symbols to enhance the visual impact. Ensure that the images are optimized for different screen sizes and devices.
5. Utilize White Space: White space (also known as negative space) is the empty space surrounding design elements. It is crucial for creating a clean and organized header. Adequate white space around text and images helps improve legibility and allows the content to breathe, making the header more visually appealing.
6. Apply Responsive Design Techniques: With the prevalence of mobile devices, it is important to ensure that the header is responsive and adaptable to different screen sizes. Test the header on various devices and screen resolutions to ensure that it maintains its visual impact and functionality across platforms.
7. Consider Animation or Interactive Elements: When appropriate, adding subtle animation or interactive elements to the header can attract attention and make it more engaging. However, use these features sparingly and ensure they enhance the user experience rather than distract from the message.
8. Test and Optimize: Regularly test different header designs and monitor analytics to assess their impact. A/B test different variations to determine which design resonates best with your target audience. Gather feedback and make data-driven improvements to optimize the visual appeal and effectiveness of the email header.
An eye-catching header design enhances the overall email experience, improves brand recall, and boosts recipient engagement. By applying visual design principles, incorporating brand elements, and staying mindful of user experience, you can create a header that stands out and captures the attention of your recipients.
Differences in Length between the Email Body and the Header
When composing an email, there are typically differences in the length of the header compared to the email body. These differences arise due to the specific requirements and purposes of each section. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure effective communication and optimal use of space within the email.
The header of an email is typically shorter in length compared to the email body. This is because the header’s primary function is to provide essential information and grab the recipient’s attention. Including excessive or unnecessary text in the header can clutter the email and make it unclear or unengaging.
Headers are often concise and to the point. They typically consist of key elements, such as the sender’s name, recipient’s name, subject line, salutation, and other relevant details. Aim to keep the header within 1-2 lines or a limited number of characters to ensure it remains visually appealing and scannable on various devices and email clients.
On the other hand, the email body can be more extensive and detailed. It is the main section where the sender conveys their message, provides information, or engages in a conversation with the recipient. The length of the email body can vary depending on the content and purpose of the email.
The email body allows for more in-depth explanation, elaboration, or storytelling. It may contain paragraphs, bullet points, headings, images, links, and other formatting elements to enhance readability and convey information effectively. However, it is still important to maintain clarity and conciseness to avoid overwhelming the recipient with excessive text.
When composing the email body, ensure that the content is relevant, organized, and structured in a logical manner. Use concise and clear language to convey the intended message and make it easily digestible for the recipient. Break up long paragraphs into smaller ones and utilize formatting options, such as bullet points or headings, to improve readability.
It is important to strike a balance between the length of the header and email body to maintain a visually appealing and engaging email. A concise and attention-grabbing header captures the recipient’s interest, while a well-structured and informative email body holds their attention and effectively communicates the desired message.
By understanding and adhering to the distinctions in length between the header and email body, you can craft emails that are visually appealing, concise, and informative, facilitating effective communication with your recipients.
Content of the Email Body
The email body contains the main content and message that you want to convey to the recipient. It is the heart of your email and where you provide the necessary information, ask questions, or engage in a conversation. Crafting effective email body content is essential for engaging the recipient and achieving the desired response or action.
The content of the email body should be clear, concise, and relevant. Start by introducing yourself or reminding the recipient of your relationship if needed. Provide context and background information to ensure the recipient understands the purpose of the email. Highlight the key points or main message early on to capture their attention and encourage them to continue reading.
Organize the information in a logical manner using paragraphs, bullet points, subheadings, or numbered lists to improve readability. Break down complex concepts or ideas into bite-sized and easily digestible chunks of information. Use a friendly and conversational tone to make the email more approachable and engaging.
Ensure that the content is tailored to the recipient’s needs and interests. Use empathy and consider their perspective to make your message more relatable. Personalize the email body whenever possible by referencing previous conversations or specific details that are relevant to the recipient. This shows that you value the recipient and have taken the time to craft a personalized email.
Use clear and concise language to convey your message effectively. Avoid using jargon or complex terminology that might confuse the recipient. Be mindful of your tone and strive to maintain a professional and courteous approach, regardless of whether the email body is formal or informal.
Consider including a call to action to guide the recipient’s response or next steps. Make it clear and specific, whether it is to reply to the email, visit a website, schedule a meeting, or take any desired action. A well-placed and compelling call to action helps increase engagement and encourages the recipient to take the desired action.
Proofreading and editing the email body is essential to ensure clarity, correctness, and professionalism. Check for any grammatical or spelling errors, and ensure that the content is coherent and flows smoothly. Read the email body aloud to assess its readability and make necessary revisions before sending.
Finally, keep in mind that the content of the email body should be focused and concise. Avoid overloading the recipient with unnecessary information or unrelated details, as this can hinder understanding and engagement. Make every word count and ensure that the content is valuable, informative, and aligns with the purpose of the email.
Organizing Information in the Email Body
Organizing information in the email body is crucial to ensure clarity, readability, and effective communication. A well-structured email body allows recipients to quickly understand the content and find the information they need. Here are some best practices for organizing information:
1. Use Paragraphs: Break up the email body into paragraphs to separate different ideas or topics. Restrict each paragraph to a single idea or thought to enhance readability. This helps avoid overwhelming the recipient with large blocks of text and makes it easier for them to follow the flow of the email.
2. Use Headings and Subheadings: If your email includes multiple sections or different topics, use headings or subheadings to guide the reader. This helps the recipient navigate through the email and locate specific information quickly. Headings make the email body more scannable and improve overall readability.
3. Utilize Bullet Points or Numbered Lists: When presenting a series of related points, instructions, or items, it is helpful to use bullet points or numbered lists. This breaks down the information into bite-sized chunks, making it easier to read and comprehend. Bullet points also draw attention to key details and improve overall clarity.
4. Prioritize Important Information: Place the most important information at the beginning or in prominent positions within the email body. This ensures that recipients immediately understand the key points and purpose of the message. Prioritizing information prevents the risk of essential details being buried or overlooked.
5. Provide Context and Link Relevant Information: When discussing complex topics or referring to previous conversations, it is important to provide context and link relevant information. This helps the recipient understand the connections between different pieces of information and provides a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
6. Segment Lengthy Emails: If you have lengthy or detailed information to convey, consider segmenting it into multiple, shorter emails. This makes the information more digestible and prevents overwhelming the recipient with a long, dense email. If segmentation is not possible, consider inserting clear headers or markers within the email body to guide the reader through different sections.
7. Make Use of White Space: Don’t underestimate the importance of white space. Leaving some empty space between paragraphs, sections, and elements makes the email body appear less cluttered and allows the reader’s eyes to rest. White space improves readability, creates a visually pleasing layout, and helps highlight important information.
Remember, the goal of organizing information in the email body is to present the content in a logical and easy-to-follow manner. By using paragraphs, headings, bullet points, and white space effectively, you can enhance the readability of your email and ensure that the recipient can absorb and understand the information more efficiently.
Importance of Clear and Concise Language in the Email Body
Using clear and concise language in the email body is essential for effective communication that is easily understood by the recipient. Clear and concise language ensures that your message comes across accurately, reduces the risk of misinterpretation, and enhances overall engagement. Here are some reasons why clear and concise language is important:
1. Enhanced Understanding: Clear language allows the recipient to understand your message without confusion or ambiguity. When your words are concise and to the point, the recipient can easily grasp the key information and follow your intended line of thought. By avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex language, you ensure that your message is accessible and understandable to a wide range of recipients.
2. Increased Efficiency: Brevity is key when it comes to email communication. Using concise language allows you to convey your message efficiently and effectively. Conciseness also respects the recipient’s time, making it more likely that they will read and respond to your email promptly. By eliminating filler words and unnecessary details, you can communicate your ideas with clarity and efficiency.
3. Reduced Miscommunication: In the absence of nonverbal cues and tone of voice, written communication can be more prone to misinterpretation. By using clear and concise language, you minimize the risk of miscommunication and ensure that your intended message is accurately conveyed. Avoiding ambiguous terms or vague language helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes better communication.
4. Improved Professionalism: Clear and concise language showcases professionalism and attention to detail. It demonstrates that you value the recipient’s time and have taken care to craft a well-thought-out message. Professionalism in written communication is crucial for establishing credibility, maintaining a positive image, and fostering strong business relationships.
5. Stronger Impact: By using concise language, you can make your email more impactful. Clear and concise messages are more memorable and easier to comprehend. They grab the recipient’s attention and leave a lasting impression. When information is presented in a concise manner, it allows recipients to focus on the essence of your message, increasing the chances of them taking the desired action or responding to your email.
6. Global Accessibility: Clear and concise language is especially important when communicating with a diverse audience. It helps overcome language and cultural barriers, making your message more accessible and inclusive. By using plain and straightforward language, you can ensure that your email can be understood by recipients who may have different levels of proficiency or backgrounds.
Tone and Language Differences between the Email Body and the Header
The tone and language used in the email body and header can differ based on their respective functions and purposes. Understanding and effectively utilizing these differences is crucial for maintaining consistency and achieving communication goals. Here are some considerations for tone and language differences:
1. Formality: The tone and language in the header usually follow a more formal style, especially when corresponding with clients, supervisors, or individuals in a professional capacity. The header sets the initial impression and conveys professionalism and respect. In contrast, the email body allows for a more conversational tone, depending on the relationship with the recipient and the purpose of the email.
2. Clarity and Conciseness: Both the email body and the header should strive for clarity and conciseness in language. However, the header requires even more brevity due to its limited space. It should convey essential information without unnecessary elaboration. The email body allows for more detailed explanations or discussions, but even then, it should prioritize clear and concise language to prevent confusion and maintain the reader’s interest.
3. Personalization: While the header may include personalization elements such as the recipient’s name, the overall tone may still lean more towards formality. In contrast, the email body allows for a more personalized approach, addressing the recipient’s specific needs or concerns, and fostering a sense of connection and empathy.
4. Language Complexity: The language in both the header and the email body should be accessible and easy to understand. In the header, it is especially important to use simple, direct language to ensure quick comprehension. In the email body, while maintaining clarity, there may be more room for using appropriate industry-specific terms or technical jargon based on the recipient’s familiarity with the subject matter.
5. Emotional Tone: The tone of the email body can vary based on the intention and context. It can range from being informative and professional to supportive, empathetic, or persuasive, depending on the desired outcome. The header typically maintains a more neutral and professional tone while still being respectful and engaging.
6. Cultural Sensitivity: When communicating with individuals from different cultural backgrounds, it is important to be mindful of language and tone. The choice of words, tone, and level of formality should align with the cultural norms and expectations of the recipient to ensure clear and respectful communication.
Ultimately, maintaining consistency between the tone and language of the email body and header is important for creating a cohesive and effective communication experience. By understanding the differences in their functions and aligning them appropriately, you can craft emails that effectively convey your message while establishing professionalism and building rapport with the recipient.
Formatting the Email Body: Paragraphs, Bullets, and Headings
The formatting of the email body plays a crucial role in enhancing readability and conveying information effectively. By using paragraphs, bullets, and headings strategically, you can structure your email body in a way that is visually appealing and easy to follow. Here are some tips for formatting the email body:
1. Paragraphs: Break your email body into paragraphs to separate different ideas or topics. Each paragraph should focus on a single thought or point. This not only improves readability but also helps the recipient quickly grasp the main ideas you are conveying. Keep paragraphs concise and use white space effectively to create a visually appealing layout.
2. Bullets or Numbered Lists: When presenting a series of related points, instructions, or items, use bulleted or numbered lists. This helps break up information into bite-sized chunks, making it easier for the recipient to read and comprehend. Bulleted or numbered lists also draw attention to important details or key elements in a visually organized way.
3. Headings or Subheadings: If your email contains multiple sections or different topics, consider using headings or subheadings to provide a visual hierarchy. Headings make it easier for the recipient to navigate through the email and locate specific information quickly. Use clear and descriptive headings that accurately reflect the content of each section.
4. Consistency: Maintain consistent formatting throughout your email body. Use the same font, font size, and spacing to ensure a cohesive and professional look. Consistency in formatting helps establish visual harmony and makes the email body easier to read and understand.
5. Emphasis and Formatting: Use formatting techniques to emphasize important points, such as bold or italicized text. However, use these formatting options sparingly and purposefully to avoid overwhelming the recipient with a visually cluttered email. Remember that the purpose of formatting is to enhance understanding and draw attention to key information.
6. White Space: Leave enough white space between paragraphs, lists, and headings to improve readability and create a clean visual appearance. White space helps prevent the email body from looking crowded and allows the recipient’s eyes to navigate through the content more easily.
7. Mobile Optimization: When formatting the email body, consider how it will appear on different devices, especially mobile devices. Use responsive design techniques to ensure that the email body adapts to different screen sizes, maintaining legibility and visual appeal.
By using paragraphs, bullets, headings, and other formatting techniques strategically, you can structure your email body in a way that is visually appealing and easy to read. Clear and organized formatting enhances the recipient’s understanding of your message and improves the overall communication experience.
Including Relevant Links or Attachments in the Email Body
When composing an email, including relevant links or attachments can enhance the effectiveness and clarity of your message. By providing additional resources or materials, you can further engage the recipient and facilitate their understanding or action. Here are some considerations when including links or attachments in the email body:
1. Link Placement: When including links in the email body, consider their placement and relevance. Insert links at appropriate points within the email body, ensuring they are easily identifiable and provide additional information or context. You can use descriptive anchor text or phrases to make it clear what recipients can expect when they click on the link.
2. Hyperlink Format: Use hyperlink formatting for the links in your email body. This makes them stand out visually and signals to recipients that they are clickable. Underlining or using a different text color for hyperlinks helps recipients recognize that they can interact with the link to access further resources or information.
3. Attachments: When including attachments, ensure they are relevant, necessary, and appropriately sized. Consider the file format to ensure compatibility with common software applications. Be mindful of the recipient’s preferences and any potential constraints, such as file size limits or security measures that may prevent the delivery of attachments.
4. Providing Context: When including links or attachments, provide context to explain their relevance or purpose. Briefly describe what recipients can expect to find or achieve by accessing the link or opening the attachment. This ensures they understand the value or importance of engaging with the provided resources.
5. File Naming: If you choose to include attachments, name the files in a way that clearly identifies their content or purpose. Use descriptive and concise file names to help recipients quickly understand the nature of the attachment. This can aid organization and facilitate easier retrieval for future reference.
6. Confirm Accessibility: Before sending the email, verify that the links are active and that the attachments can be opened without any issues. Test the links on different devices and browsers to ensure they direct recipients to the intended destination. Double-check that the attachments are properly attached and intact, as broken links or missing attachments can lead to frustration and confusion.
7. Follow Applicable Policies and Etiquette: Ensure that linking to external websites or including certain attachments complies with internal policies, regulations, and email etiquette. Respect copyright laws, data protection guidelines, and any restrictions on sharing certain types of files or information.
By including relevant links or attachments in the email body, you can provide recipients with additional resources, references, or supporting materials that enhance their understanding or enable them to take the desired action. Thoughtfully incorporating these elements contributes to a more engaging and effective communication experience.
Proper Etiquette for the Email Body
Practicing proper etiquette in the email body is essential for effective and respectful communication. By following these guidelines, you can convey your message clearly, maintain professionalism, and foster positive relationships with your recipients:
1. Use a Professional and Polite Tone: Always maintain a professional tone in your email body, even in more casual or informal settings. Be courteous, respectful, and avoid using overly casual language or slang. Choose your words carefully to ensure clarity and avoid any unintended negative tone or misunderstanding.
2. Be Mindful of Formatting: Keep your email body clean and well-organized by using paragraphs, bullet points, and headings when appropriate. Ensure that your font choice, font size, and overall formatting are clear and easy to read. Avoid using excessive formatting styles or an overwhelming number of different fonts or colors, as this can distract from your message.
3. Respect Recipients’ Privacy: Be mindful of the privacy of your recipients when composing your email body. Avoid sharing sensitive or confidential information that is not meant to be shared with others. Be cautious when using the “CC” or “BCC” fields, ensuring that the recipients’ email addresses are protected and not exposed to unauthorized individuals.
4. Properly Cite and Attribute Sources: If you include information or ideas from external sources in your email body, be sure to properly cite and attribute them. Give credit to the original author or source of the information to avoid plagiarism and uphold ethical standards of communication.
5. Be Concise and to the Point: While it is important to provide sufficient information, strive to be concise and avoid unnecessary elaboration or repetition in your email body. Be mindful of your recipients’ time and attention. Aim to communicate your message clearly and efficiently, focusing on the most relevant information.
6. Use Proper Grammar and Spelling: Maintain professionalism by using correct grammar, punctuation, and proper spelling in your email body. Poor grammar or spelling errors can detract from your message and diminish your credibility. Use proofreading tools or ask a colleague to review your email before sending it to ensure accuracy and clarity.
7. Respond in a Timely Manner: Show respect for your recipients’ time by responding promptly to their emails. Strive to reply within a reasonable time frame, especially when the nature of the email requires a timely response. Even if you cannot provide a complete response immediately, acknowledge receipt of the email and provide an estimated timeframe for a more comprehensive reply.
8. Avoid Overusing Reply-All: Be selective when using the “Reply-All” function. Consider whether all recipients need to be included in your response. In most cases, responding only to the necessary parties helps avoid overwhelming others with unnecessary emails and keeps communication streamlined.
By following proper email etiquette in the email body, you can ensure your message is well-received, maintain professionalism, and promote positive interactions with your recipients.
Proofreading and Editing the Email Body
Proofreading and editing your email body is essential before sending it to ensure clarity, accuracy, and professionalism. By following these practices, you can catch errors, improve readability, and leave a positive impression on your recipients:
1. Take a Break and Return with Fresh Eyes: After drafting your email body, step away from it for a while. This allows you to return with fresh eyes and a clear mind, making it easier to spot errors or areas that need improvement.
2. Read the Email Aloud: Reading your email body aloud can help you identify any awkward phrasing, grammatical errors, or sentences that need revision. Listening to the words can often highlight issues that are not easily caught by silent proofreading.
3. Check Grammar, Spelling, and Punctuation: Review your email body for correct grammar, spelling errors, and punctuation. Use grammar and spell check tools, but also be vigilant in catching any additional errors that may not be picked up by automated tools.
4. Ensure Clarity and Coherence: Ensure that your email body communicates your message clearly and concisely. Check for any sentences or paragraphs that may be confusing or could be condensed to improve clarity. Ensure that your thoughts flow logically, and each paragraph is coherent.
5. Simplify and Condense: Review your email body for any areas where you can simplify your language or condense your sentences. Removing unnecessary words or phrases helps your message come across more clearly and concisely.
6. Double-check Names and Details: Verify that you have spelled names correctly and included accurate and up-to-date information. Mistakenly getting someone’s name or details wrong can convey carelessness or lack of attention to detail.
7. Review Attachments and Links: If you have included any attachments or links, ensure they are accurate and functioning correctly. Double-check that the recipients have the necessary access or permissions to open attachments or access the linked content.
8. Consider Tone and Tone Consistency: Read through the email body to ensure that the tone is appropriate for the intended recipient and the nature of the communication. Maintain tone consistency throughout the email body to avoid any mixed messages or inadvertently changing the tone.
9. Pay Attention to Formatting and Layout: Check the formatting and layout of your email body to ensure it is visually appealing and easy to read. Ensure that paragraphs are properly indented, bullet points or numbered lists are formatted correctly, and any headers or subheadings are consistent and distinguishable.
10. Proofread Twice: After making any necessary edits, proofread the email body at least one more time. A second review can help catch any remaining errors or inconsistencies that may have been overlooked during the first round of proofreading.
By taking the time to proofread and edit your email body, you can refine your message, correct any errors, and present yourself professionally. A well-edited email body demonstrates your attention to detail and ensures effective communication with your recipients.