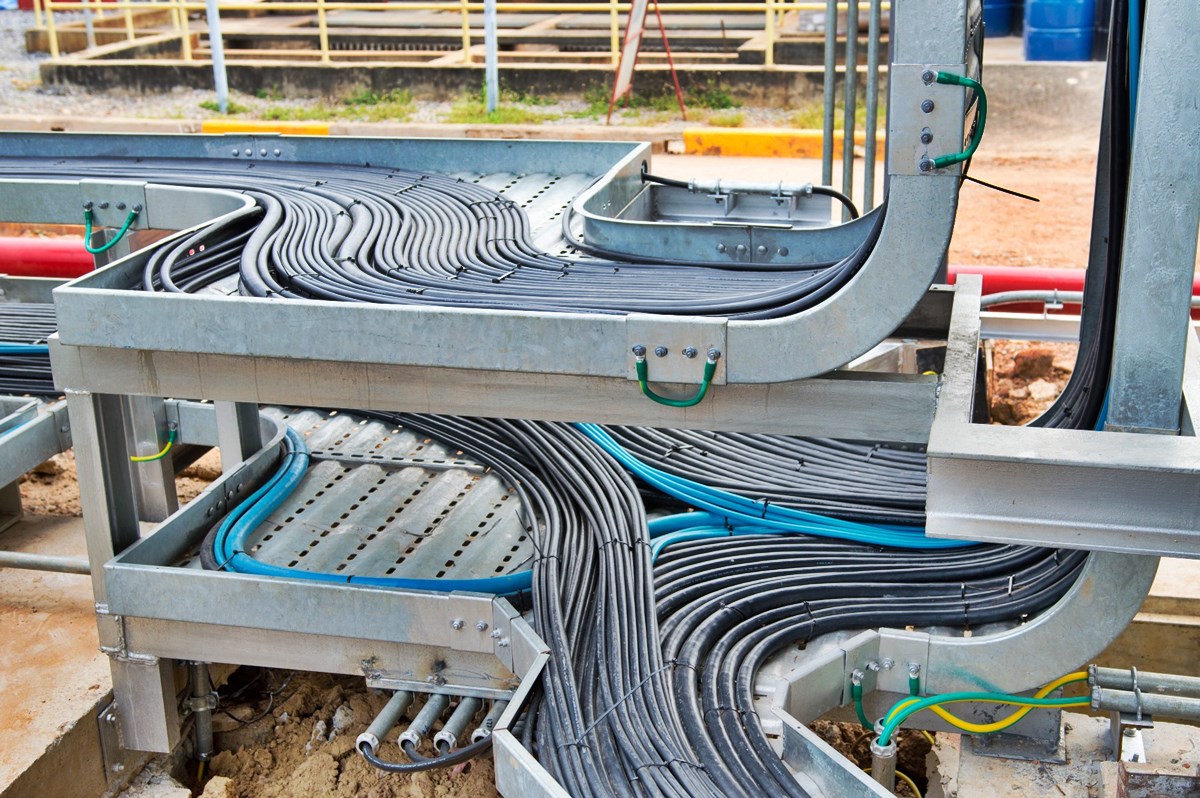
Types of Cable Trays
Cable trays are versatile and efficient systems used for organizing and supporting electrical cables and wires. They come in various types and designs to accommodate different needs and applications. Understanding the different types of cable trays available can help you determine the most suitable option for your project. Let’s explore some of the common types of cable trays:
- Ladder Tray: Ladder trays feature a ladder-like design with horizontal rungs and side rails. These trays provide excellent cable support and ventilation while allowing easy access for maintenance and reconfiguration.
- Perforated Tray: Perforated trays have a solid base with evenly spaced perforations along the sides. They offer good cable ventilation and drainage, making them ideal for indoor and outdoor applications, including industrial and commercial settings.
- Wire Mesh Tray: Wire mesh trays consist of wire mesh grids welded together to form a cable support structure. They are lightweight, cost-effective, and offer excellent cable visibility and airflow, making them suitable for data centers, telecommunications, and computer networking applications.
- Solid Bottom Tray: Solid bottom trays have a solid base with no perforations. They provide extra protection for sensitive cables against dust, debris, and moisture. These trays are commonly used in areas where cables require additional shielding, such as chemical plants and hazardous environments.
- Trough Tray: Trough trays are similar to solid bottom trays but have raised edges on both sides. They are designed to channel and protect cables from external elements and are often used in outdoor and industrial applications.
Each type of cable tray offers its own set of advantages and is suitable for specific applications. When choosing a cable tray type, consider factors such as cable size, weight, environment, and required cable management capabilities. It is also essential to adhere to local regulations and codes regarding cable tray installations.
With the wide range of cable tray options available, you can easily find a solution that meets your specific needs while ensuring efficient cable organization and management.
Materials Used in Cable Trays
Cable trays are manufactured using a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties and suitability for different applications. The choice of material depends on factors such as environmental conditions, load capacity requirements, and cost considerations. Let’s explore some of the common materials used in cable tray construction:
- Steel: Steel is the most commonly used material for cable trays due to its strength and durability. It offers excellent load-bearing capacity and can withstand harsh environments, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Aluminum: Aluminum cable trays are lightweight and corrosion-resistant. They are ideal for applications where weight reduction is important, or in environments where moisture and humidity are a concern.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel cable trays are highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand exposure to chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures. They are commonly used in environments such as food processing plants, pharmaceutical facilities, and offshore installations.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP): FRP cable trays are non-metallic and offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for corrosive environments, such as wastewater treatment plants, chemical plants, and marine applications.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC cable trays are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to install. They are primarily used in low-voltage and low-load applications, such as in residential buildings and small commercial installations.
Each material has its own distinct advantages and disadvantages. When selecting a material for your cable tray system, consider factors such as the installation location, environmental conditions, and the load capacity requirements of your cables. It is important to choose a material that can withstand the specific conditions of your application to ensure the longevity and performance of your cable tray system.
By understanding the different materials used in cable tray construction, you can select the most suitable option for your project, ensuring efficient cable management and protection for your electrical cables.
Advantages of Cable Trays
Cable trays offer numerous advantages over traditional methods of cable management, making them a popular choice in various industries. Whether it’s in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, or data centers, cable trays provide several benefits that contribute to efficient and organized cable management. Let’s explore some of the advantages of using cable trays:
- Optimal Cable Protection: Cable trays provide a secure and protected pathway for cables, shielding them from potential damage caused by external elements such as moisture, dust, and pests. This helps to maintain the integrity and performance of the cables over time.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Cable trays offer flexibility in terms of cable layout and routing. With various tray types, sizes, and configurations available, they can be easily adapted to meet changing needs and accommodate additional cables as the infrastructure grows.
- Enhanced Safety: Cable trays help minimize fire hazards by ensuring proper cable separation, reducing the risk of overheating and short circuits. Additionally, they provide easy access for routine maintenance, inspections, and repairs, promoting a safer working environment.
- Improved Air Circulation: Open mesh or perforated cable trays allow for better airflow around the cables, preventing heat buildup and ensuring optimal cable performance. This is particularly important in high-density installations or areas where temperature regulation is critical.
- Cost-Effective: Cable trays eliminate the need for expensive conduit systems and multiple cable supports. They require less material and labor for installation, resulting in cost savings. Additionally, their modular design allows for efficient cable management and easy system upgrades or modifications.
- Efficient Cable Organization: Cable trays enable the separation and organization of different types of cables, such as power, data, and communication cables. This reduces the potential for signal interference and simplifies cable identification, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
These advantages contribute to improved cable management efficiency, reduced downtime, and increased overall system reliability. Cable trays offer a versatile and long-lasting solution for organizing, protecting, and managing cables in a wide range of applications.
Uses of Cable Trays
Cable trays are widely used in various industries and applications to manage and support electrical cables and wires effectively. Their versatility and flexibility make them suitable for a range of installations. Let’s explore some common uses of cable trays:
- Commercial Buildings: Cable trays are commonly installed in commercial buildings, such as offices, shopping malls, hospitals, and educational institutions. They provide a neat and organized solution for routing electrical and data cables, ensuring a safe and efficient power distribution network.
- Industrial Facilities: In industrial settings like manufacturing plants, factories, and warehouses, cable trays play a crucial role in managing the complex network of power, control, and instrumentation cables. They can withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, and exposure to chemicals and are designed to support heavy-duty cables.
- Data Centers: Cable trays are extensively used in data centers to handle the large volume of data and communication cables. They provide proper cable routing and organization, ensuring efficient airflow and reducing the risk of cable damage or entanglement that could disrupt critical operations.
- Utilities and Power Generation: Cable trays are essential in utility facilities and power generation plants, where a vast network of power cables is needed. They allow for easy access, maintenance, and troubleshooting, minimizing downtime and ensuring a reliable power supply.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: Cable trays are used in transportation infrastructure, including tunnels, bridges, and airports. They provide a safe and organized cable management system for electrical and communication cables, ensuring reliable operation and easy access for maintenance and repairs.
- Renewable Energy: Cable trays are utilized in renewable energy installations, such as solar farms and wind turbines, to manage the intricate web of power and communication cables. Their durable construction and ability to withstand outdoor elements make them ideal for these environmentally exposed applications.
These are just a few examples of the many applications where cable trays are employed. Their versatility, durability, and ease of installation make them a go-to solution for cable management needs in various industries and sectors.
Considerations for Installing Cable Trays
Proper installation of cable trays is crucial for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. When planning the installation of cable trays, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. Let’s explore some key factors to consider:
- Load Capacity: Before installing cable trays, it is essential to determine the load capacity requirements of the cables they will support. Consider the weight of the cables, future growth, and any additional loads that may be placed on the trays, such as equipment or conduits.
- Location and Environment: Assess the installation location and environmental conditions to select the appropriate type of cable tray. Factors to consider include temperature extremes, moisture levels, exposure to chemicals or corrosive elements, and the presence of vibrations or abrasions that may affect the durability of the tray material.
- Proper Supports and Spacing: Ensure that the cable trays are adequately supported to prevent sagging, excessive vibrations, or bending. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended spacing between supports to maintain the structural integrity of the system and prevent excessive cable tray deflection.
- Proper Cable Routing: Carefully plan the cable routing within the cable trays to ensure adequate separation and avoid overcrowding. Separate power and data cables to minimize interference and follow industry standards and regulations for proper cable separation and grounding.
- Accessibility: Consider accessibility requirements for future maintenance and expansion. Plan for sufficient clearance and access points to allow for easy cable installation, inspections, and repairs. Incorporating cable tray closures and cable management accessories can help improve the accessibility and organization of the system.
- Compliance with Codes and Standards: Familiarize yourself with local electrical codes, building regulations, and industry standards governing cable tray installation. Ensure that your installation adheres to these requirements and consider engaging a professional electrician or engineer to inspect and approve the installation.
By considering these important factors, you can ensure a proper and effective installation of cable trays. Taking the time to plan and execute the installation correctly will result in a reliable and efficient cable management system that meets your specific needs and requirements.
Common Myths About Cable Trays
Cable trays are widely used in various industries and applications for effective cable management. However, there are some common myths and misconceptions surrounding cable trays that may lead to misunderstandings or incorrect installation practices. Let’s debunk some of these myths:
- Myth 1: Cable Trays Are Only Suitable for Large Installations: This is not true. Cable trays come in various sizes and configurations, making them suitable for installations of all scales, from small residential buildings to large industrial complexes. They offer flexibility in cable routing and can accommodate different cable types and sizes.
- Myth 2: Cable Trays Restrict Cable Movement: On the contrary, cable trays provide a secure and organized pathway for cables while allowing flexibility for future modifications or cable re-routing. With proper planning and design, cable trays can facilitate easy access and maintenance without hindering cable movement.
- Myth 3: Cable Trays Are Difficult to Install: Cable trays are designed for easy installation. They are available in modular designs that allow for quick and straightforward assembly. With proper planning, the right tools, and following manufacturer guidelines, cable tray installation can be a cost-effective and time-efficient process.
- Myth 4: Cable Trays Do Not Provide Sufficient Cable Protection: Cable trays actually offer excellent cable protection. They shield cables from external elements such as dust, moisture, and physical damage. By properly selecting the appropriate type of cable tray and utilizing accessories like covers or shields, the cables within the trays can remain well-protected.
- Myth 5: Cable Trays Are Expensive: While the initial cost of cable trays may be higher than other cable management solutions, they offer long-term cost savings. Cable trays eliminate the need for expensive conduit systems, are reusable, and require minimal maintenance. Their durability and adaptability make them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
- Myth 6: Cable Trays Are Obsolete in the Modern Era: With the increasing demand for efficient cable management in a technology-driven world, cable trays remain highly relevant. They provide a reliable solution for organizing and supporting electrical and data cables, ensuring proper cable routing, protection, and maintenance for various industries.
It is important to dispel these myths and misconceptions about cable trays to make informed decisions when it comes to cable management. Understanding the true capabilities and benefits of cable trays can help you make the right choice in selecting a reliable and efficient cable management solution for your specific needs.
Cable Tray Accessories
When it comes to cable tray systems, accessories play a significant role in enhancing their functionality, organization, and safety. Cable tray accessories are designed to complement and optimize the performance of cable trays. Let’s explore some common cable tray accessories:
- Cable Tray Covers: These covers are used to enclose cable trays, providing additional protection against dust, debris, and moisture. They help prevent cable damage and maintain a clean and tidy appearance.
- Cable Tray Dividers: Dividers are used to separate and manage different types of cables within the cable tray. They help improve cable organization, reduce the risk of cable entanglement, and enable easy identification and access to specific cables when needed.
- Cable Tray Clamps: Clamps are used to secure and fasten individual cables to the cable tray. They ensure proper cable routing and prevent movement or sagging of the cables, ensuring a neat and organized cable installation.
- Cable Tray Splices: Splices are used to join two sections of cable trays together, allowing for seamless and continuous cable routing. They provide structural integrity and maintain proper cable support throughout the installation.
- Elbows and Bends: Elbows and bends are used to change the direction of the cable tray system. They facilitate smooth cable routing around corners and obstacles, offering flexibility in designing cable tray installations.
- Mounting Brackets and Supports: Mounting brackets and supports provide additional stability and strength to the cable tray system. They ensure proper load distribution and prevent excessive deflection of the cable tray, minimizing the risk of cable damage or system failure.
- Cable Tray Labels and Markers: Labels and markers are used to identify and label individual cables within the cable tray. They help with cable management, troubleshooting, and maintenance, ensuring easy cable identification and reducing downtime.
- Cable Tray Grounding Accessories: Grounding accessories, such as grounding clamps and bonding jumpers, are used to establish a proper grounding connection for the cable tray system. They enhance safety by mitigating the risk of electrical surges and ensuring proper grounding of the cables.
These accessories can significantly enhance the efficiency, organization, and safety of cable tray installations. By utilizing the appropriate cable tray accessories, you can optimize your cable management system and ensure reliable and secure cable routing for your specific application.
Maintenance and Safety Tips for Cable Trays
Maintaining cable trays is crucial for ensuring their long-term performance and preventing potential hazards. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines can help extend the lifespan of the cable tray system and promote a safe working environment. Here are some maintenance and safety tips to keep in mind:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of the cable trays to check for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Look for any cable tray accessories that may need replacement or repair. Regular inspections help identify and address issues before they lead to cable damage or system failure.
- Cable Cleanliness: Keep the cable trays clean and free from debris and dust accumulation. Regularly remove any dirt or foreign objects that may obstruct cable access or impede airflow. This not only ensures proper cable functionality but also reduces the risk of fire hazards and electrical faults.
- Proper Cable Support: Ensure that cables within the cable trays are properly supported and secured. Use appropriate cable clamps or ties to prevent excessive movement or bending of the cables. This helps to maintain cable integrity and prevent damage that may lead to performance issues or safety hazards.
- Temperature Regulation: Monitor and control the temperature within the area where cable trays are installed, especially for sensitive cables or equipment. Proper ventilation and climate control help prevent overheating, ensuring optimal cable performance and preventing potential fire risks.
- Proper Cable Loading: Do not exceed the recommended load capacity of the cable trays. Overloading the trays can cause them to bend or sag, potentially damaging the cables or compromising the structural integrity of the system. Follow manufacturer guidelines for load ratings and consult an expert for complex installations.
- Qualified Maintenance Personnel: Engage qualified electricians or technicians to perform maintenance tasks on the cable tray system. They have the expertise and knowledge to handle electrical components and ensure proper installation, maintenance, and repairs.
- Adhere to Safety Standards: Follow industry safety standards and regulations when working with cable trays. Ensure proper grounding, proper electrical insulation, and compliance with national and local electrical codes. This minimizes the risk of electrical shocks, fire hazards, and ensures a safe working environment.
By following these maintenance and safety tips, you can ensure the longevity and reliability of the cable tray system. Regular inspections, cleanliness, proper cable support, and adherence to safety guidelines contribute to the efficient operation of the cable tray system and help prevent potential hazards.
Choosing the Right Cable Tray System
Choosing the right cable tray system is crucial for ensuring effective cable management and the overall success of your project. With various types, materials, and sizes available, understanding the key considerations can help you make an informed decision. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a cable tray system:
- Application Requirements: Assess the specific requirements of your application, such as cable type, size, weight, and environmental conditions. Consider the anticipated cable load, level of corrosion resistance needed, and any unique installation challenges to determine the most suitable cable tray system.
- Materials and Coatings: Select a material that matches the environmental conditions and durability requirements of your application. Common materials used in cable trays include steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP). Consider whether a specific coating or finish is necessary for additional protection against corrosion or other hazards.
- Load Capacity: Ensure the chosen cable tray system can support the anticipated cable load without deformation or overloading. Consider both the static and dynamic load requirements, factoring in future growth and any additional loads that may be added to the system.
- Installation Flexibility: Evaluate the flexibility of the cable tray system in terms of routing options, configurations, and adaptability to changing needs. Look for a system that can accommodate complex installations, changes in cable routing, and future expansion requirements.
- Fire Rating and Safety: Check the fire rating of the cable tray system to ensure it meets fire safety regulations. Consider options with fire-resistant properties or additional fire protection coatings if needed. Also, prioritize safety features such as proper cable separation, grounding provisions, and integrated accessories that enhance system integrity and reduce the risk of electrical faults.
- Manufacturer Reputation and Support: Research the reputation of cable tray manufacturers and their track record for quality, reliability, and customer support. Look for manufacturers who provide technical assistance, installation guidance, and warranty coverage to ensure a smooth and successful cable tray installation process.
- Cost Considerations: Balance the cost of the cable tray system with the desired features and performance. Evaluate the long-term benefits and potential savings from choosing a durable and efficient system that requires minimal maintenance and offers ease of installation.
By considering these factors and consulting with industry professionals, you can choose the right cable tray system that meets the specific requirements of your project. A well-selected cable tray system will provide effective cable management, ensure cable protection and organization, and contribute to the overall success and efficiency of your electrical infrastructure.
DIY Cable Tray Installation Guide
Installing a cable tray system is a manageable project that can be done DIY, provided you have the necessary tools, materials, and knowledge. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure a successful cable tray installation:
- Plan and Design: Begin by carefully planning the cable routing, taking into consideration the layout, cable types, load capacity, and any specific requirements of your application. Create a detailed diagram or layout to guide the installation process.
- Gather Materials and Tools: Collect all the necessary materials, including cable trays, supports, connectors, and accessories based on your design. Ensure you have the required tools, such as drill, screwdriver, measuring tape, level, and cable cutters.
- Prepare the Mounting Surfaces: Clean and prepare the mounting surfaces where the cable trays will be installed. Ensure they are free from dust, debris, and any obstructions.
- Install Supports: Begin by installing the support brackets or hangers at the designated intervals along the cable tray route. Ensure they are level and securely fastened to provide proper support.
- Assemble the Cable Trays: Assemble the cable trays according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Connect the tray sections using appropriate connectors or splice plates to create a continuous pathway.
- Mount the Cable Trays: Securely attach the assembled cable trays onto the support brackets. Use appropriate screws or clamps to fasten the trays, ensuring they are level and properly aligned.
- Route and Secure Cables: Begin routing the cables through the cable trays, ensuring proper separation and organization according to your design plan. Use cable clamps or ties at appropriate intervals to secure the cables to the tray.
- Install Accessories: As needed, install cable tray accessories such as dividers, covers, or grounding clamps for added functionality, protection, and safety.
- Test and Inspect: Once the installation is complete, conduct a thorough inspection of the cable tray system. Ensure all connections are secure, cables are properly supported, and there are no loose or exposed wires. Test the system to ensure proper cable functionality and conductivity.
- Document and Label: Document the installation details, including cable types, routing, and any specific notes that may be helpful for future maintenance or modifications. Label the cables and cable trays for easy identification and troubleshooting.
Note: It is crucial to follow all relevant electrical codes, guidelines, and safety precautions during the installation process. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with any aspect of the DIY installation, it is recommended to consult a professional electrician or seek assistance from an experienced contractor.
By following this DIY cable tray installation guide, you can successfully implement a cable management system that promotes efficient cable routing, organization, and protection in your residential or commercial setting.