Internet Speed vs. Internet Bandwidth: Understanding the Difference
When it comes to measuring your internet connection, you may have come across two terms: internet speed and internet bandwidth. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they actually refer to two different aspects of your internet connection.
Internet speed refers to the rate at which data is transferred from one point to another over the internet. It is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). The higher the speed, the faster data can be downloaded or uploaded.
On the other hand, internet bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time. It is usually measured in terms of network capacity, such as kilobits per second (Kbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). Essentially, bandwidth determines the capacity of your internet connection.
Think of it this way: internet speed is like the speed limit on a road, while internet bandwidth is like the number of lanes on that road. A higher speed limit allows you to drive faster, while more lanes provide a greater capacity for traffic.
Understanding the difference between internet speed and internet bandwidth is important because they both play a role in determining the overall performance of your internet connection. While a high-speed connection is desirable, it’s equally important to ensure that your connection has sufficient bandwidth to support the devices and activities on your network.
For example, if you have multiple devices simultaneously streaming high-definition videos, your internet bandwidth needs to be able to handle the data demands of all those devices. If the bandwidth is limited, it can result in slower speeds and buffering issues.
Internet service providers (ISPs) typically offer different internet plans with varying speeds and bandwidths to meet the needs of different users. It’s important to choose a plan that offers the right balance of speed and bandwidth for your specific requirements.
The Role of Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) plays a crucial role in determining the quality and stability of your internet connection. They are the company responsible for delivering internet services to your home or business.
ISPs offer a wide range of internet plans with varying speeds, bandwidths, and pricing. When choosing an ISP, it’s important to consider factors such as the reliability of their network, customer service, and the available plans in your area.
In addition to providing you with an internet connection, your ISP is also responsible for managing the network infrastructure that supports your connection. This includes maintaining the cables, routers, and other equipment needed to transmit data from their network to your location.
The quality of service you receive from your ISP can have a significant impact on your internet speed. ISPs have different levels of network performance and capacity, which can result in variations in speeds experienced by their customers.
Some ISPs may also implement data throttling, which is the intentional slowing down of internet speeds for certain types of online activities. This may be done to manage network congestion or enforce data usage policies. It’s important to review the terms and conditions of your internet plan to understand if any throttling practices are in place.
If you’re experiencing consistently slow internet speeds, it’s worth contacting your ISP to troubleshoot the issue. They may be able to diagnose any network issues or provide recommendations to optimize your connection.
Keep in mind that internet speed can also be affected by external factors beyond your ISP’s control. Issues such as network congestion, distance from the ISP’s infrastructure, the number of devices connected to your network, and the quality of your modem or router can all impact your internet speed.
Overall, your ISP plays a vital role in determining the quality of your internet connection. Choosing a reliable provider and selecting the right plan for your needs can help ensure a fast, reliable, and consistent internet experience.
The Impact of Network Congestion on Internet Speed
Network congestion can significantly impact the speed and performance of your internet connection. It occurs when the demand for data exceeds the capacity of the network infrastructure, leading to slower speeds and increased latency.
During peak usage periods, such as evenings or weekends when many people are streaming videos or playing online games, network congestion is more likely to occur. This is because the network is handling a higher volume of data traffic, causing delays in data transmission.
When network congestion happens, the data packets travelling between your device and the website or service you are accessing may need to take longer routes or wait in queues to be transmitted. As a result, you may experience slower download and upload speeds, buffering during streaming, and delays in loading webpages or accessing online applications.
Network congestion can be caused by various factors. One primary factor is the limited bandwidth capacity of the network infrastructure. If the network doesn’t have enough capacity to handle the data traffic, congestion is likely to occur.
Additionally, certain types of online activities require more bandwidth than others. For example, streaming high-quality videos or downloading large files consume a significant amount of bandwidth. If many users in your area are engaged in these activities simultaneously, it can contribute to network congestion.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) employ various techniques to manage network congestion. This can include prioritizing certain types of traffic, implementing data caps, or throttling speeds for specific applications or activities. These measures are often put in place to ensure fair usage and prevent network degradation for all users.
To mitigate the impact of network congestion on your internet speed, there are a few steps you can take. First, try accessing the internet during off-peak hours when there is likely to be less network traffic. This can result in faster speeds as the network is less congested.
You can also try connecting your device to the internet using an Ethernet cable rather than relying on Wi-Fi. Wired connections are generally more stable and can provide a more consistent internet speed, especially during times of congestion.
Finally, consider contacting your ISP if you consistently experience slow internet speeds due to network congestion. They may be able to provide insights or suggest alternative plans that offer higher bandwidth or lower contention ratios, which can help alleviate the impact of congestion.
Network congestion is a common issue that can affect internet speed and performance. Understanding its causes and implementing strategies to minimize its impact can help ensure a smoother and faster browsing experience.
The Effects of Distance on Internet Speed
The distance between your location and the server or network infrastructure can have a significant impact on your internet speed. The farther the data has to travel, the more delays and latency you are likely to experience.
When you request data from a website or service, it needs to travel from the server to your device. This process is known as round-trip time or latency. The longer the distance, the more time it takes for the data packets to travel back and forth, resulting in slower response times.
For example, if you are accessing a website hosted in a different country, the data packets have to cross multiple networks and potentially traverse undersea cables, which can introduce additional delays. As a result, you may experience slower download and upload speeds and delays in loading webpages or accessing online applications.
Another factor affected by distance is the signal strength. As the data travels over longer distances, the signal strength can degrade, leading to a weaker and slower connection. This is particularly noticeable in wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi, where the signal strength decreases with distance from the router.
The physical infrastructure used by your internet service provider (ISP) also plays a role in the effects of distance on internet speed. If the network infrastructure is outdated or poorly maintained, the quality of the connection can deteriorate over long distances, resulting in slower speeds.
Moreover, certain types of internet connections, such as satellite internet, can be more susceptible to the effects of distance. Satellite internet involves transmitting data to and from satellites orbiting the Earth. Because of the vast distance that the signals have to travel, satellite connections generally have higher latency and slower speeds compared to other types of broadband connections.
To mitigate the effects of distance on internet speed, there are a few steps you can take. Firstly, choose an ISP that has a robust and well-maintained network infrastructure. This can help ensure better connectivity and less degradation over long distances.
If you frequently access websites or services hosted in distant locations, consider using a content delivery network (CDN). CDNs distribute content across multiple servers located in different regions, allowing data to be served from a server closer to your location. This can reduce the distance that data needs to travel and improve your internet speed.
Lastly, if you are experiencing significant speed issues due to distance, consider exploring alternative internet options that may be available in your area. Fiber-optic connections, for example, tend to have better performance over long distances compared to traditional copper-based connections.
While distance is a factor in internet speed, it’s important to note that it is not the only factor. Other aspects, such as network congestion, device performance, and internet plan limitations, can also contribute to slower speeds. By understanding the effects of distance and implementing strategies to minimize its impact, you can optimize your internet speed and ensure a smoother online experience.
Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speed in Your Home Network
Wi-Fi has become an essential part of our daily lives, allowing us to connect our devices to the internet without the need for physical cables. However, several factors can affect the speed and performance of your Wi-Fi network within your home.
1. Router Placement: The placement of your Wi-Fi router can greatly impact the signal strength and coverage in your home. Ideally, the router should be placed in a central location, away from obstructions such as walls, furniture, and electronic devices that can interfere with the signal. Positioning the router higher off the ground can also help improve coverage.
2. Frequency Interference: Wi-Fi signals operate on specific frequencies, usually 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwaves, can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal, causing slower speeds or dropped connections. To minimize interference, avoid placing your router near these devices.
3. Signal Obstruction: Physical obstacles, such as walls, floors, and doors, can hinder the Wi-Fi signal. The signal strength weakens as it passes through these obstacles, resulting in reduced speed. Consider the layout of your home and adjust the router placement or use Wi-Fi range extenders to improve signal coverage in areas with weak signals.
4. Number of Connected Devices: The number of devices connected to your Wi-Fi network can impact its overall speed. Each device consumes a portion of the available bandwidth, so having multiple devices simultaneously streaming videos, downloading large files, or playing online games can slow down the network. Limiting the number of connected devices or optimizing their usage can help improve Wi-Fi speed.
5. Wi-Fi Security: While important for protecting your network, enabling strong security measures such as WPA2 encryption can impact Wi-Fi speeds. However, the trade-off for improved security is generally worth it. Ensure that you are using the latest encryption standards and regularly update your router firmware for optimal performance.
6. Internet Plan Limitations: It’s essential to understand the limitations of your internet plan and the maximum speeds it offers. Even with a high-speed internet connection, you may not achieve the maximum speed over Wi-Fi due to various factors. Consider upgrading your plan or contacting your ISP to discuss any speed-related concerns.
7. Router Performance: The performance capabilities of your router can significantly impact Wi-Fi speed. Older router models may not support the latest Wi-Fi standards or offer advanced features like beamforming or MU-MIMO, which can enhance speed and performance. Upgrading to a newer, more advanced router can improve Wi-Fi speeds in your home.
By addressing these factors affecting Wi-Fi speed, you can optimize your home network performance and enjoy a faster and more reliable internet connection. Experiment with router placement, manage the number of connected devices, and ensure that your equipment is up-to-date to achieve the best possible Wi-Fi speeds.
The Importance of Router Placement for Optimal Internet Speed
The placement of your Wi-Fi router plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal internet speed and performance within your home. The location of your router can significantly impact signal strength, coverage, and overall Wi-Fi speed. Here are some key considerations for router placement:
1. Central Location: Positioning your router in a central location within your home is essential for maximizing signal coverage. By placing the router in the middle of your home, the Wi-Fi signal can reach all areas more evenly, reducing dead zones or areas with weak connection.
2. Avoid Obstructions: Walls, furniture, and other objects can obstruct the Wi-Fi signal and reduce its strength. Placing the router in an open space, free from barriers, allows for better signal transmission. Avoid placing the router near large metal objects or appliances that can interfere with the signal.
3. Height Placement: Keeping the router elevated off the ground can help improve signal coverage as Wi-Fi signals tend to spread out and travel downward. Mounting the router on a wall or placing it on a high shelf can provide a clearer line of sight for the signal, resulting in better Wi-Fi performance.
4. Minimize Interference: Other electronic devices, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwave ovens, emit signals that can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal. Keep the router away from these devices to minimize interference and ensure a stronger, more reliable connection.
5. Test Different Locations: If you’re unsure about the best placement for your router, try experimenting with different locations. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app or software to assess signal strength in different areas of your home. By testing various placements, you can find the optimal position that provides the best coverage and speed.
6. Wi-Fi Range Extenders: In larger homes or spaces where a single router may not provide sufficient coverage, consider using Wi-Fi range extenders or mesh Wi-Fi systems. These devices can extend the Wi-Fi signal to reach areas that are further away from the router, ensuring a consistent and strong connection throughout your home.
By paying attention to the placement of your router, you can optimize your Wi-Fi network for better internet speed and performance. A well-placed router minimizes signal interference, maximizes coverage, and ensures that the Wi-Fi signal can reach all areas of your home. Remember to regularly check and update your router’s firmware to take advantage of any performance-enhancing updates provided by the manufacturer.
How Many Devices are Connected to Your Network?
The number of devices connected to your network can have a significant impact on your internet speed and overall network performance. Every device that connects to your network consumes a portion of the available bandwidth, which can result in slower speeds for each device. Here are some considerations regarding the number of devices connected to your network:
1. Bandwidth allocation: Each device connected to your network requires a certain amount of bandwidth to perform its tasks effectively. If you have multiple devices performing data-intensive activities simultaneously, such as streaming high-definition videos or online gaming, it can strain your network and lead to slower speeds for all connected devices.
2. Network congestion: When too many devices are connected to the same network, it can lead to network congestion. Network congestion occurs when the available bandwidth is divided among numerous devices, resulting in slower speeds and increased latency. This can particularly impact Wi-Fi networks, as the wireless signal has limited capacity.
3. Router capacity: The capacity of your router can also influence the number of devices it can handle simultaneously. Some older or low-end routers may struggle to handle a large number of devices, leading to slower speeds. Upgrading to a more powerful router with higher capacity can help ensure smoother performance and accommodate more devices.
4. Network management: Managing the number of connected devices and their bandwidth usage is crucial for maintaining optimal network performance. Some routers offer features such as Quality of Service (QoS), which allows you to prioritize certain devices or types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications or devices receive the necessary bandwidth and minimizing the impact on other devices.
5. Wi-Fi network limitations: Wi-Fi networks have inherent limitations in terms of range and capacity. If you have a large property or multiple floors in your home, it may be necessary to set up additional access points or use Wi-Fi range extenders to ensure adequate coverage for all connected devices.
It’s important to be mindful of the number of devices connected to your network to ensure smooth performance. If you notice significant slowdowns or network congestion, consider prioritizing devices, managing bandwidth usage, or upgrading to a more robust router if necessary. Additionally, regular monitoring and optimization of your network can help identify and resolve any issues related to the number of connected devices.
The Influence of Internet Plan Tiers on Speed
The internet speed you experience is closely tied to the type and tier of internet plan you subscribe to. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) offer a range of plans, each with different speeds and pricing options. Here is how the internet plan tier can influence your internet speed:
1. Speed Options: ISPs typically offer different tiers or levels of internet plans, each with a specified speed range. These tiers can range from basic plans with lower speeds to higher-tier plans with faster speeds. The speed advertised for each plan represents the maximum potential speed that can be achieved.
2. Bandwidth Allocation: Internet plan tiers often come with different bandwidth allocations. Higher-tier plans typically offer larger bandwidth allowances, enabling you to consume and transfer more data within a given timeframe. This means that users on higher-tier plans may experience faster speeds, especially during times of heavy usage.
3. Download and Upload Speeds: Internet plans can also vary in terms of download and upload speeds. Download speed refers to how quickly data can be retrieved from the internet, such as when you stream videos or download files. Upload speed, on the other hand, determines how quickly you can transmit data to the internet, which is relevant for activities like video conferencing or uploading files.
4. Network Prioritization: ISPs may prioritize certain traffic or services based on the plan tier. For example, higher-tier plans might offer enhanced streaming quality or lower latency for online gaming. This prioritization ensures that users on higher-tier plans receive a better experience for specific types of activities.
5. Plan Limitations: While higher-tier plans generally offer faster speeds, it’s essential to review the fine print of your chosen plan. Some ISPs may impose data caps or throttling—reducing speeds after a certain amount of data has been consumed. These limitations can affect the actual speed you experience, particularly if you engage in data-intensive activities.
6. Network Infrastructure: Faster internet speeds are also influenced by the quality and capabilities of the ISP’s network infrastructure. ISPs invest in upgrading their networks to support higher speeds, and higher-tier plans often benefit from these infrastructure improvements. The network’s capacity, technology, and geographical coverage can impact the speed potential for each plan.
When selecting an internet plan, it’s crucial to consider your specific needs and usage patterns. If you engage in activities that require high-speed, uninterrupted connections, such as streaming 4K videos or online gaming, opting for a higher-tier plan can provide a better experience. Conversely, if you have minimal internet requirements, a lower-tier plan may suffice.
Remember that the advertised speeds are typically maximum speeds and actual speeds can vary depending on factors such as network congestion, distance from the ISP’s infrastructure, and the quality of your equipment. Consulting with your ISP or researching customer reviews can provide additional insights into the actual speeds experienced by users on different plan tiers.
The Impact of Outdated Modems or Routers on Internet Speed
Your modem and router play a crucial role in delivering internet connectivity to your devices. However, using outdated or older models can significantly impact your internet speed and overall network performance. Here’s how outdated modems or routers can affect your internet speed:
1. Compatibility with Internet Standards: Internet technology is constantly evolving, with new standards and protocols being introduced to enable faster speeds and improved performance. Outdated modems or routers may not support the latest standards, resulting in slower speeds and reduced compatibility with newer devices.
2. Limited Speed Capabilities: Older modems or routers may have limited speed capabilities, typically due to outdated hardware or technology. For example, older routers may only support slower Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11n, which can result in slower speeds compared to newer routers that support faster standards like 802.11ac or 802.11ax.
3. Inadequate Processing Power: The processing power of a modem or router plays a vital role in handling the data flow and managing network connections. Outdated models may have slower processors or less memory, making them less efficient in handling high-speed internet connections and multiple devices simultaneously.
4. Limited Network Coverage: If your home or office has expanded or has numerous walls and obstacles, an outdated router may struggle to provide sufficient coverage. Newer routers often have improved antenna technology and signal amplification features that provide better coverage, ensuring a strong and stable connection throughout your space.
5. Security Vulnerabilities: Outdated modems or routers may not receive regular firmware updates or security patches from their manufacturers. This can leave your network vulnerable to security threats and make it easier for malicious actors to exploit your connection, resulting in degraded speed and compromised performance.
To optimize your internet speed and network performance:
– Consider upgrading your modem or router to a newer model that supports faster speeds and the latest Wi-Fi standards.
– Ensure that the modem or router you purchase is compatible with your internet service provider’s network and supports the speed capabilities of your internet plan.
– Regularly check for firmware updates from your modem or router manufacturer and install them to improve security, performance, and compatibility.
– Place your modem and router in an optimal location, away from obstructions and interference sources, to maximize signal strength and coverage.
A modern and capable modem and router can significantly enhance your internet speed and overall network performance, allowing you to fully utilize the speed capabilities of your internet plan and achieve a seamless online experience.
The Potential for Signal Interference in Your Home
Signal interference can have a significant impact on your Wi-Fi connectivity and internet speed within your home. Various factors can cause signal interference, leading to a degraded wireless network performance. Understanding the potential sources of interference can help you address these issues and optimize your Wi-Fi signal. Here are some common causes of signal interference:
1. Other Wireless Networks: If there are multiple wireless networks in close proximity, such as in an apartment building or densely populated area, they may interfere with each other’s signals. This can result in decreased Wi-Fi speed and performance. Selecting the least congested Wi-Fi channel or using a different Wi-Fi frequency band can help reduce interference.
2. Electronic Devices: Electronics and appliances that operate on the same frequency as Wi-Fi, such as cordless phones, baby monitors, microwave ovens, and Bluetooth devices, can interfere with Wi-Fi signals. Keep your Wi-Fi router away from these devices to minimize interference and maintain a strong Wi-Fi signal.
3. Physical Obstacles: Walls, floors, and other physical structures can weaken Wi-Fi signals, leading to reduced signal strength and slower speeds in different areas of your home. The materials used in constructing walls, such as concrete or brick, can be particularly effective at blocking or attenuating Wi-Fi signals. Re-positioning your router or using Wi-Fi range extenders can help overcome this interference.
4. Home Appliances and Wiring: Electrical appliances, such as refrigerators, televisions, and fluorescent lights, can produce electromagnetic interference that affects Wi-Fi signals. Additionally, faulty or poorly shielded electrical wiring in your home can generate interference. Keeping your Wi-Fi router away from these devices and ensuring proper electrical wiring can minimize signal interference.
5. Wi-Fi Channel Overlapping: Wi-Fi routers operate on various channels, and when there are multiple routers in close proximity using the same or overlapping channels, it can result in interference. Using a Wi-Fi analyzer tool can help you identify the least congested channels and make the necessary adjustments to improve signal quality.
6. Wi-Fi Router Position: The placement of your Wi-Fi router plays a crucial role in signal strength and coverage. Positioning your router in a central location, away from obstructions and at an optimal height, can help ensure a strong and consistent Wi-Fi signal throughout your home.
When addressing signal interference in your home, some steps can be taken to optimize your Wi-Fi signal:
– Keep your router away from electronic devices and appliances that can cause interference.
– Ensure your router is positioned in a central location, free from physical obstructions.
– Use Wi-Fi range extenders or mesh Wi-Fi systems to extend signal coverage in larger homes or areas with weak signals.
– Regularly update your router’s firmware to access performance improvements and security updates.
By identifying and addressing potential sources of signal interference, you can significantly improve your Wi-Fi signal strength, enhance internet speed, and enjoy a reliable and seamless wireless network experience throughout your home.
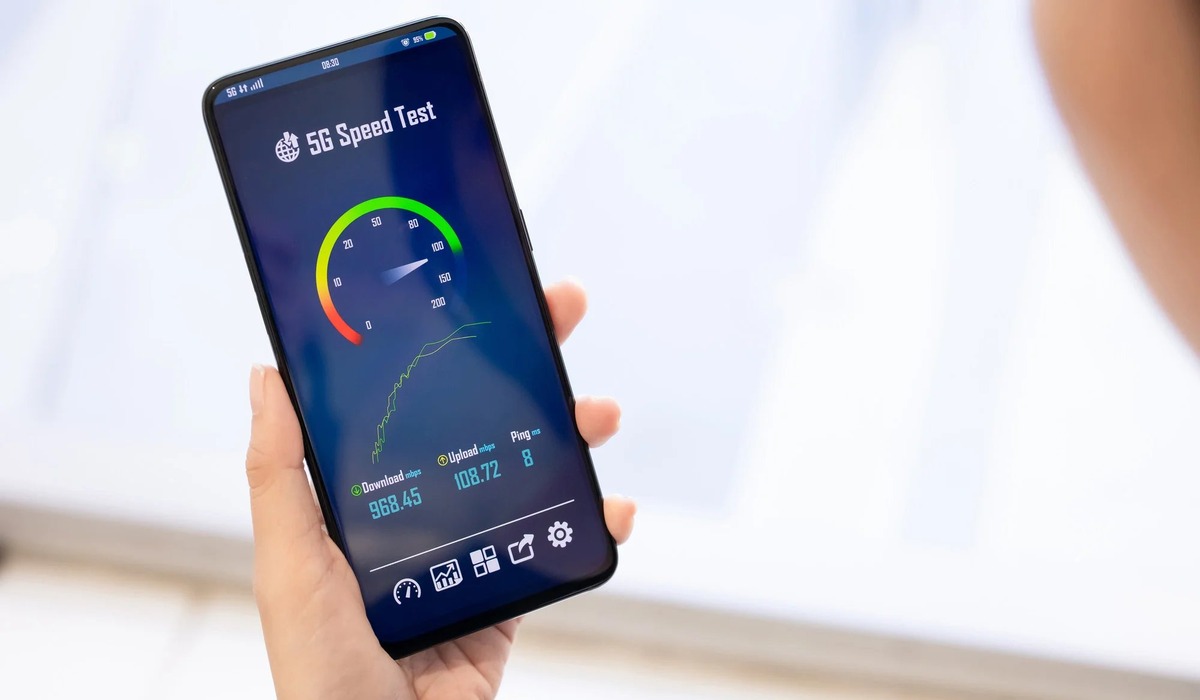
The Role of Internet Speed Test Tools in Monitoring Performance
Internet speed is a crucial factor that directly impacts your online experience. To ensure that you are getting the speed you are paying for and to monitor the performance of your internet connection, it’s essential to utilize internet speed test tools. These tools allow you to measure and analyze your internet speed and detect any potential issues. Here’s how internet speed test tools play a role in monitoring performance:
1. Speed Measurement: Internet speed test tools provide a precise measurement of your internet speed. They measure important metrics such as download speed, upload speed, and latency, giving you insight into how your connection is performing. This can help you determine if your current internet plan is delivering the promised speed.
2. Real-Time Monitoring: Internet speed tests provide real-time monitoring of your internet connection. By running these tests periodically, you can track any fluctuations or inconsistencies in your internet speed. This can help identify patterns of slow speeds or network issues that may require attention from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
3. Troubleshooting Network Issues: If you are experiencing slow internet speeds, internet speed test tools can help you identify potential causes. By comparing your test results with the expected speeds for your internet plan, you can determine if the issue lies with your ISP, network congestion, or other factors. This information can assist you in troubleshooting and resolving any connectivity issues.
4. Network Performance Comparison: Internet speed test tools also allow you to compare your internet performance with others in your region or around the world. This provides a benchmark for evaluating the quality of your connection and helps identify if your speed falls within the expected range for your location.
5. Feedback for ISPs: ISPs often rely on customer feedback and speed test results to assess their network performance. By regularly running internet speed tests and reporting any significant discrepancies between the advertised speeds and actual speeds, you can help ISPs identify areas for improvement and hold them accountable for delivering the promised service.
When using internet speed test tools, it’s important to keep a few things in mind:
– Perform tests on different devices and at different times to account for any device-specific issues or network congestion.
– Use reputable and reliable speed test tools from trusted sources to ensure accurate measurements.
– Consider testing your speed at different locations within your home to detect any Wi-Fi coverage issues.
By utilizing internet speed test tools, you can actively monitor the performance of your internet connection, identify any issues affecting your speed, and work with your ISP to ensure you are receiving the internet speed you are paying for.