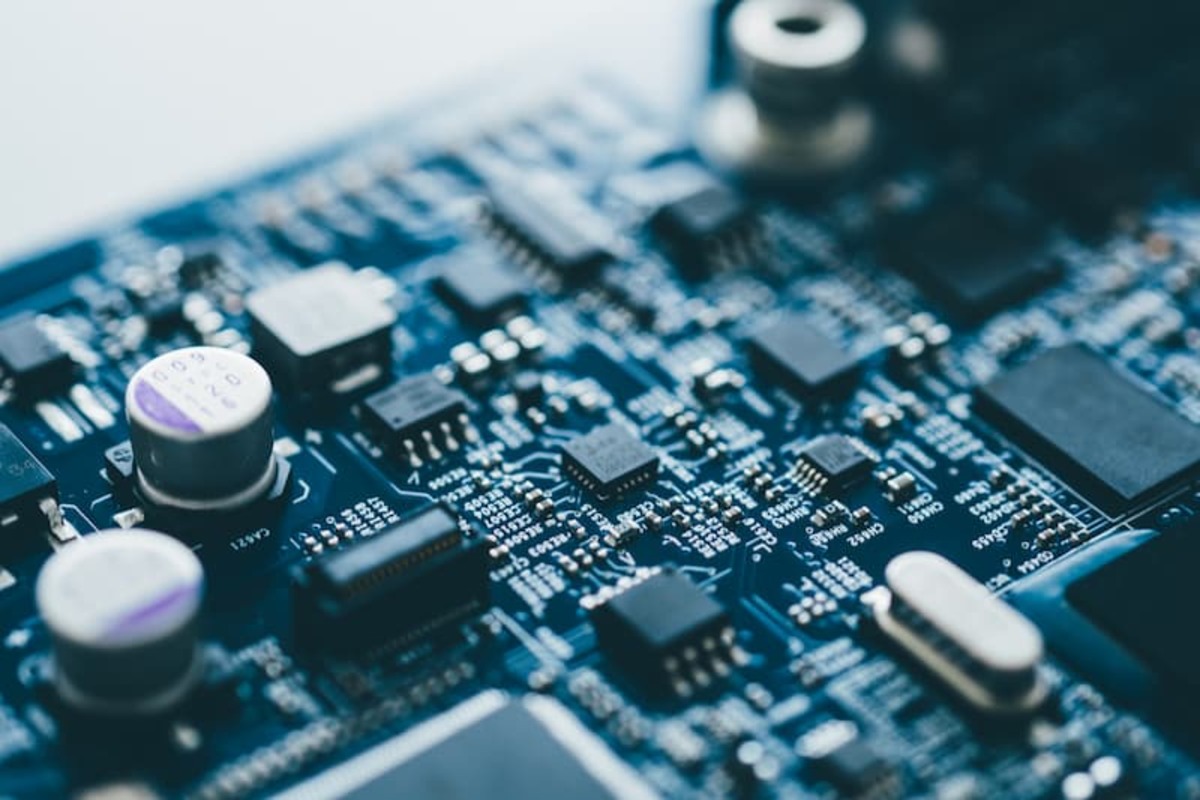
Computers and Laptops
Computers and laptops are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges. The delicate electronic components and circuitry present in these devices can be easily harmed by even a small static shock. When a static electricity discharge occurs, it can cause irreversible damage to the motherboard, processor, RAM, and other crucial components.
One of the most common ways static electricity can damage computers and laptops is by causing electrostatic discharge (ESD) onto the circuit boards. ESD can disrupt the flow of electricity and cause shorts, rendering the device inoperable. It can also lead to data loss as it can corrupt the information stored on the hard drive.
To protect computers and laptops from static electricity, it is important to take certain precautions. Always make sure to ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before handling any internal components. Additionally, keep your devices in a static-safe environment and avoid touching sensitive parts without proper grounding.
It is worth noting that static electricity discharges can lead to costly repairs or even the need to replace the entire computer or laptop. Therefore, it is crucial to be cautious and take preventive measures to avoid such incidents. Regularly cleaning the devices and ensuring proper ventilation can also help minimize the risk of static damage.
Furthermore, using surge protectors with built-in ESD protection can provide an added layer of defense against static discharges. These surge protectors help to regulate voltage fluctuations and divert excess electricity away from sensitive components.
Smartphones and Tablets
Smartphones and tablets have become an integral part of our daily lives, and they are also prone to damage from static electricity discharges. The compact size and intricate internal components of these devices make them vulnerable to static shock-induced malfunctions.
Similar to computers and laptops, the circuit boards and delicate electronic components inside smartphones and tablets can be easily damaged by static electricity. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and cause irreversible damage to the device.
To prevent static electricity damage to smartphones and tablets, it is essential to handle these devices with care. Avoid touching the exposed circuitry without proper grounding, as even a small static discharge can lead to costly repairs or the need for a replacement.
Using an anti-static bag or sleeve when storing or transporting smartphones and tablets can provide an added layer of protection against static discharges. These specially designed storage solutions help to prevent the buildup of static electricity and shield the device from potential damage.
It is also recommended to avoid using smartphones and tablets in environments with extremely dry or humid conditions, as these conditions can increase the likelihood of static discharges. Additionally, regularly cleaning the devices with a soft, anti-static cloth can help remove any accumulated static charge and keep them in optimal condition.
Investing in high-quality protective cases with built-in ESD protection can also help mitigate the risk of static electricity damage. These cases provide an extra barrier against static discharges and shield the device from potential harm.
By following these precautions and handling smartphones and tablets with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and prolong the lifespan of your devices.
Gaming Consoles
Gaming consoles, such as PlayStation, Xbox, and Nintendo Switch, are widely popular for their immersive gaming experiences. However, these powerful devices are not immune to static electricity damage. The sensitive electronic components and delicate circuitry inside gaming consoles can be easily affected by static discharges.
A static electricity discharge can disrupt the electrical flow within the gaming console and cause various malfunctions. It may lead to system crashes, freezing, or even complete failure of the device. Additionally, static electricity can negatively impact the performance of the console, resulting in slower loading times, graphical glitches, and audio distortions.
To protect gaming consoles from static electricity damage, it is essential to adopt preventive measures. When handling the console or its accessories, make sure to ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat. Avoid touching the internal components or delicate circuitry without proper grounding.
Proper storage and maintenance also play a crucial role in preventing static damage to gaming consoles. When not in use, store the console in a cool, dry place away from potential sources of static electricity. Dust accumulation can exacerbate static-related issues, so regular cleaning with a soft, anti-static cloth is recommended.
Furthermore, it is vital to protect the console’s ports and connectors from static discharges. Ensure that HDMI, USB, and power cables are securely connected and free from dust or debris. Using surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection can help safeguard the console from sudden power surges and static shocks.
In multiplayer gaming setups, where multiple consoles are connected, it is important to ensure that all the consoles are properly grounded. Unbalanced charges between the consoles can lead to static electricity discharges and subsequent damage.
By following these precautions and taking care of your gaming console, you can minimize the risk of static electricity damage and enjoy uninterrupted gaming sessions.
TV and Home Theater Systems
TV and home theater systems provide us with hours of entertainment and immersive viewing experiences. However, these devices can be susceptible to static electricity damage, which can impact their performance and longevity. The delicate electronic components present in TVs and home theater systems can easily be damaged by static discharges.
When a static electricity discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electrical currents within the device. This disruption can lead to various issues, such as distorted or flickering images, loss of audio, or complete failure of the system. Static electricity can also cause permanent damage to the internal circuitry of the TV or home theater system.
To protect your TV and home theater system from static electricity damage, it is important to handle these devices with care. Avoid touching the screen or any exposed circuitry without proper grounding. Use an anti-static cloth or microfiber cloth to clean the screen and external surfaces regularly, as dust accumulation can worsen static-related issues.
When connecting cables or peripherals, make sure to do so when both the device and the peripherals are powered off. This helps to prevent static electricity discharge between the connectors and reduces the risk of damage.
In addition, ensuring a proper grounding connection for your TV and home theater system is crucial. Use surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection to regulate voltage fluctuations and divert excess electricity away from the delicate components.
Proper ventilation is also essential in preventing static electricity damage. Ensure that the airflow around the TV and home theater system is unobstructed, as excessive heat can increase the risk of static discharges. Avoid placing these devices near sources of heat or in humid environments.
Lastly, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for handling and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent static electricity-related issues.
By taking these precautions and being mindful of static electricity, you can extend the lifespan of your TV and home theater system, and continue enjoying your favorite shows and movies without any disturbances.
Printers and Scanners
Printers and scanners are essential devices for both personal and professional use, allowing us to create physical copies and digitize documents. However, these devices are prone to damage from static electricity discharges, which can significantly impact their functionality.
The sensitive electronic components and intricate circuitry inside printers and scanners can be easily affected by static discharges. When a static electricity discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and cause malfunctions. Common issues caused by static electricity include paper jams, print quality problems, and even complete failure of the device.
To protect printers and scanners from static electricity damage, it is crucial to take appropriate precautions. Always ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices. Avoid touching the internal components or paper path without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
Proper maintenance and cleaning are also important in preventing static-related issues. Regularly clean the printer’s paper feed rollers and scanning glass with an anti-static cloth to prevent dust accumulation and static buildup. Ensure that the printer’s ink cartridges and toner units are securely installed to minimize the risk of static discharge.
When connecting cables or peripherals, ensure that both the printer/scanner and the peripherals are powered off. This helps to prevent static charges from being transferred between the connectors and reduces the risk of damage.
Using anti-static bags or sleeves when storing or transporting printers and scanners can provide an extra layer of protection against static discharges. These specially designed storage solutions help to minimize the buildup of static electricity and shield the device from potential damage.
Furthermore, it is advisable to use surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection to safeguard printers and scanners from sudden power surges and static shocks.
By following these precautions and handling printers and scanners with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the continued functionality of these important devices.
External Hard Drives and USB Drives
External hard drives and USB drives are widely used for data storage and transfer, providing us with convenience and portability. However, these devices are susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can result in data loss and even render the drives unusable.
The delicate electronic components and sensitive circuitry inside external hard drives and USB drives make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the electrical flow within the device and cause issues such as corruption of stored data or complete failure of the drive.
To protect external hard drives and USB drives from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Before connecting or disconnecting the drive, make sure to properly ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat. Avoid touching the exposed connectors or circuitry without proper grounding, as even a minor static shock can cause damage.
Store external hard drives and USB drives in a static-safe environment when not in use. Avoid exposing them to areas with high static electricity, such as carpets or synthetic materials that generate static charges. Additionally, using anti-static storage cases or bags can help minimize the risk of static discharges and protect the drives from potential damage.
When inserting or removing the drive from a computer or other electronic device, ensure that both the drive and the device are powered off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the drive.
In terms of maintenance, regularly clean the connectors and external surfaces of the drives with an anti-static cloth to remove dust and prevent static buildup. Properly eject the drives from the computer or device using the appropriate software or system function to avoid any sudden disconnection that could lead to static electricity damage.
Using surge protectors with built-in ESD protection when connecting external hard drives or USB drives to the power source can provide an added layer of defense against static discharges.
By following these precautions and handling external hard drives and USB drives with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and preserve the integrity of your valuable data.
Digital Cameras and Camcorders
Digital cameras and camcorders allow us to capture precious moments and create lasting memories. These devices, however, are susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can affect their performance and image quality.
The intricate electronic components and delicate circuitry inside digital cameras and camcorders make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal electrical flow within the device and cause malfunctions. This can result in issues such as corrupted image files, distorted video footage, or even complete failure of the camera.
To protect digital cameras and camcorders from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Before touching the device or its components, ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat. Avoid directly touching the internal circuitry or lens without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
When storing or transporting digital cameras and camcorders, it is advisable to use protective cases with built-in ESD protection. These cases help to minimize the buildup of static electricity and shield the devices from potential damage.
In addition, it is important to avoid using digital cameras and camcorders in environments with extremely dry or humid conditions, as these conditions can increase the likelihood of static discharges. Regularly clean the outer surfaces of the devices with a soft, anti-static cloth to remove dust and minimize static buildup.
When connecting the cameras or camcorders to other devices or peripherals, ensure that both the camera and the connected device are powered off. This helps to prevent static discharges between the connectors and reduces the risk of damage to the devices.
Using surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection when connecting the camera or camcorder to the power source can provide an additional safeguard against static discharges and power surges.
By following these precautions and handling digital cameras and camcorders with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and continue capturing beautiful moments with confidence.
Audio Equipment (Headphones, Speakers, etc.)
Audio equipment, including headphones, speakers, and amplifiers, allows us to enjoy music and immersive audio experiences. However, these devices can be affected by static electricity discharges, which can degrade sound quality and damage internal components.
The sensitive electronic components and delicate circuitry inside audio equipment make them susceptible to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and introduce unwanted noise or distortion into the audio signal. It can also cause permanent damage to the drivers, amplifiers, or other internal components.
To protect audio equipment from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Before using or handling headphones, speakers, or amplifiers, ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat. Avoid touching the connectors or internal components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can affect sound quality or cause damage.
When storing audio equipment, use protective cases or covers to shield them from potential static discharges. These cases help to minimize the buildup of static electricity and protect the devices from potential damage.
In addition, avoid using audio equipment in environments with high static electricity, such as carpeted areas or synthetic fabric. Regularly clean the external surfaces of the devices with a soft, anti-static cloth to remove dust and minimize the potential for static buildup.
When connecting audio equipment to other devices or using cables and adapters, ensure that all devices are powered off. This helps to prevent static electricity discharge between the connectors, reducing the risk of damage to the audio equipment.
Using surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection when connecting audio equipment to the power source can also provide an extra layer of defense against sudden power surges and static discharges.
By following these precautions and handling audio equipment with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and enjoy high-quality audio for a long time.
Network Equipment (Routers, Modems, etc.)
Network equipment, such as routers, modems, switches, and network interfaces, play a crucial role in our connected world. These devices facilitate internet connectivity and data communication. However, they are not immune to damage caused by static electricity discharges, which can disrupt network operations and affect data transfer speeds.
The sensitive electronic components and delicate circuitry inside network equipment make them susceptible to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and lead to malfunctions in the device. This can result in intermittent connectivity issues, slow network speeds, or even complete failure of the equipment.
To protect network equipment from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before handling the equipment is crucial. Avoid touching the internal components or circuitry without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
Proper installation and placement of network equipment can also minimize the risk of static discharges. Avoid placing routers, modems, and switches on or near surfaces that generate static charges, such as carpets or synthetic fabrics. Opt for dry, well-ventilated areas for installation to reduce the buildup of static electricity.
Ensuring a stable power supply is essential in protecting network equipment from static discharges. Use surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection to regulate voltage fluctuations and divert excess electricity away from the equipment.
Regular maintenance is important to prevent static-related issues in network equipment. Keep the devices clean by using a soft, anti-static cloth to remove dust or debris that can contribute to static buildup. Perform firmware updates as recommended by manufacturers to ensure optimal performance and security.
When connecting cables or peripherals to network equipment, ensure that both the equipment and the peripherals are powered off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the equipment.
By following these precautions and handling network equipment with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and maintain a reliable and efficient network infrastructure.
Power Supplies and Chargers
Power supplies and chargers are essential components for keeping our electronic devices powered and ready for use. However, these devices can be susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can lead to malfunctions or even render them unusable.
The delicate electronic components inside power supplies and chargers are vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and cause issues such as voltage spikes, erratic charging, or complete failure of the device.
To protect power supplies and chargers from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Before plugging or unplugging the device, ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat. Avoid touching the connectors or internal components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
Proper storage of power supplies and chargers when not in use can help minimize the risk of static discharges. Keep them in a cool, dry environment away from potential sources of static electricity, such as carpets or synthetic materials.
Regular cleaning is also important in preventing static-related issues. Use a soft, anti-static cloth to remove any dust or debris that can contribute to static buildup on the surface of the power supply or charger.
When connecting power supplies or chargers to electronic devices, ensure that both the device and the power supply/charger are powered off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the equipment.
Using surge protectors or power strips with built-in ESD protection when plugging power supplies or chargers into the power source can provide an additional layer of defense against static discharges and power surges.
Regular inspection of the cables and connectors for any signs of wear or damage is also advisable. Damaged cables or connectors can increase the risk of static discharges and subsequent damage to the power supply or charger.
By following these precautions and handling power supplies and chargers with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure reliable power delivery to your electronic devices.
Circuit Boards and Motherboards
Circuit boards and motherboards are the backbone of electronic devices, responsible for housing and connecting various components. These intricate components, however, are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can cause irreversible harm and render the devices inoperable.
When a static electricity discharge occurs near circuit boards or motherboards, it can disrupt the delicate electronic pathways and components. This disruption can lead to shorts, burning of traces, or even complete failure of the board.
To protect circuit boards and motherboards from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with utmost care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before handling these components is essential. Avoid touching the exposed circuitry or connectors without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
Ensure that the work area is free from any static-prone materials, such as carpets or synthetic fabrics, which can contribute to static buildup. Use an anti-static workbench or mat to provide an additional layer of protection against static discharges and minimize the risk of damage to the circuit boards or motherboards.
When installing or removing circuit boards or motherboards, it is important to follow proper ESD (electrostatic discharge) precautions. Avoid sliding the boards across surfaces and use grounded mats or containers to lay them on during the process.
Storing circuit boards and motherboards in anti-static bags or containers when not in use can help prevent static electricity buildup and protect them from potential damage. These specially designed storage solutions minimize the risk of discharges and shield the components from static-related issues.
Regularly inspect circuit boards and motherboards for any signs of damage or wear. Look for bent pins, burnt traces, or swollen capacitors, as these can indicate potential issues caused by static electricity. Replace any damaged components promptly to avoid further damage.
By taking these precautions and handling circuit boards and motherboards with care, you can significantly reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable functionality of your electronic devices.
Microcontrollers and Arduino Boards
Microcontrollers and Arduino boards are widely used in electronics and prototyping projects, providing a platform for controlling and interacting with various components. However, these devices are sensitive to static electricity discharges, which can degrade their performance or even cause permanent damage.
The delicate electronic components and circuitry present in microcontrollers and Arduino boards make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can disrupt the normal flow of electricity and introduce erroneous signals or cause malfunctions in the device.
To protect microcontrollers and Arduino boards from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices is essential. Avoid touching the exposed circuitry or connectors without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can have adverse effects.
When storing or transporting microcontrollers and Arduino boards, use anti-static bags or containers designed for this purpose. These specialized storage solutions help minimize the buildup of static electricity and shield the devices from potential damage.
Proper installation and connections are also important in preventing static-related issues. When connecting components or peripherals, ensure that both the microcontroller/Arduino board and the connected device are powered off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the components.
Regular inspections for any visible damage or wear on the microcontrollers and boards are essential. Look for bent pins, burnt traces, or swollen capacitors, as these can indicate potential issues caused by static electricity. Promptly replace any damaged components to avoid further damage.
It is advisable to work in an ESD-safe environment when dealing with microcontrollers and Arduino boards. Use anti-static workbenches and mats, and keep synthetic materials or surfaces that generate static charges away from the workspace.
By following these precautions and handling microcontrollers and Arduino boards with care, you can significantly reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable operation of your electronics projects.
Integrated Circuits (ICs) and Transistors
Integrated circuits (ICs) and transistors are fundamental components in electronic devices, serving as the building blocks of modern technology. These devices, however, are highly sensitive to static electricity discharges, which can cause permanent damage and impact the functionality of the entire system.
The miniature size and intricate design of integrated circuits and transistors make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs, it can generate high voltages and currents, leading to the breakdown of the delicate internal components within the ICs and transistors.
To protect integrated circuits and transistors from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with extreme care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these components is essential. Avoid touching the exposed pins or junctions without proper grounding, as even the tiniest static shock can cause irreversible damage.
When working with or handling integrated circuits and transistors, it is advisable to do so in an ESD-safe environment. Anti-static workbenches, grounded mats, and proper grounding practices will help minimize the risk of static discharges and potential damage to these components.
Proper storage is also vital in preventing static electricity damage. Store integrated circuits and transistors in anti-static bags or containers designed to dissipate static charges. These specialized storage solutions will shield the components from potential static buildup and minimize the risk of damage.
When installing or replacing integrated circuits and transistors, ensure that you are working in a controlled environment with low static electricity levels. Avoid sliding or dragging the components across surfaces, as friction can generate static charges.
Regular inspection is important to identify any signs of damage or wear on integrated circuits and transistors. Look for cracked packaging, bent pins, or any visible abnormalities. Replace any damaged components promptly to avoid further damage to the system.
By following these precautions and handling integrated circuits and transistors with extreme care, you can reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable operation of electronic systems.
Sensors and Detectors
Sensors and detectors play a vital role in various fields, including industrial automation, environmental monitoring, and security systems. These devices are designed to detect and measure changes in physical or environmental conditions. However, they are highly sensitive to static electricity discharges, which can cause inaccurate readings, malfunctions, or even permanent damage.
The delicate components and circuitry inside sensors and detectors make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these devices, it can disrupt the electrical signals and lead to erroneous readings or complete failure of the sensor or detector.
To protect sensors and detectors from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices is essential. Avoid touching the sensitive components or connectors without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can disrupt their operation.
When installing or replacing sensors and detectors, it is advisable to work in an ESD-safe environment. Anti-static workbenches, grounded mats, and proper grounding practices will help minimize the risk of static discharges and potential damage to these devices.
Proper storage is also vital in preventing static electricity damage. Store sensors and detectors in anti-static bags or containers designed to dissipate static charges. These specialized storage solutions will shield the devices from potential static buildup and minimize the risk of damage.
During installation or maintenance, it is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations. Properly align and secure the connectors, ensuring a solid connection that minimizes the risk of static discharges.
Regular inspections are important to identify any signs of damage or wear on sensors and detectors. Look for cracked casings, loose connectors, or any visible abnormalities. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage and ensure accurate readings.
By following these precautions and handling sensors and detectors with care, you can reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure reliable and accurate operation in various applications.
LED and LCD Displays
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) are commonly used display technologies in various electronic devices, including televisions, monitors, smartphones, and digital signage. While these displays offer vibrant visuals, they are susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can result in visual artifacts, reduced brightness, or complete failure.
The delicate electronic components and precise circuitry within LED and LCD displays make them highly sensitive to static electricity. When a static discharge occurs near these displays, it can disrupt the electrical signals and affect the operation of the individual pixels or the backlighting system.
To protect LED and LCD displays from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before touching the displays is essential. Avoid touching the screen and the connectors without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can result in damage.
When cleaning LED and LCD displays, use a soft, anti-static cleaning cloth specifically designed for electronic screens. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh cleaning solutions, as they can exacerbate static-related issues or damage the protective coatings on the display surface.
Proper storage of LED and LCD displays is also essential in preventing static electricity damage. When storing or transporting these displays, they should be placed in anti-static bags or packaging designed to dissipate static charges. This minimizes the risk of static buildup and helps protect the displays from potential damage.
Whenever possible, avoid exposing LED and LCD displays to environments with extreme dryness or humidity, as these conditions can increase static discharge risks. Additionally, ensure that the displays are not in close proximity to sources of static electricity, such as carpets or synthetic materials that generate static charges.
By following these precautions and handling LED and LCD displays with care, you can reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure optimal visual performance and longevity of these essential electronic components.
Electric Motors and Servos
Electric motors and servos are critical components in various applications, including robotics, automation systems, and industrial machinery. While these devices are designed for precision and efficiency, they can be susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can lead to malfunctions or even permanent damage.
The sensitive electronic components and intricate wiring inside electric motors and servos make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these devices, it can disrupt the electrical signals and cause issues such as erratic movements, reduced motor performance, or complete failure.
To protect electric motors and servos from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices is essential. Avoid touching the exposed motor windings, connectors, or sensitive components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can have detrimental effects.
During installation or maintenance, ensure that the work surface and environment are free from static-prone materials such as carpets or synthetic fabrics. Use grounding mats or workbenches specifically designed to dissipate static charges and prevent the buildup of static electricity.
Proper storage is also important in preventing static electricity damage to electric motors and servos. When not in use, these devices should be stored in anti-static bags or containers to minimize the risk of static buildup and protect them from potential damage.
When connecting electric motors or servos, ensure that both the device and the peripheral equipment are powered off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the devices.
Regular inspections for any signs of damage or wear on electric motors and servos are crucial. Look for loose connections, burnt wiring, or visible abnormalities. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage to the components.
By following these precautions and handling electric motors and servos with care, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable and efficient operation of these crucial components in various applications.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Devices
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) devices are widely used for tracking and identification purposes in various industries, including supply chain management, asset tracking, and access control systems. These devices utilize radio waves for communication and data transmission. However, RFID devices are sensitive to static electricity discharges, which can cause malfunctions or even permanent damage.
The delicate components and circuitry inside RFID devices make them susceptible to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these devices, it can disrupt the radio waves and affect the transmission of data or the functioning of the device.
To protect RFID devices from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices is vital. Avoid touching the antennas, connectors, or sensitive components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can disrupt their operation.
When installing or replacing RFID devices, it is advisable to work in an ESD-safe environment. Anti-static workbenches, grounded mats, and proper grounding practices will help minimize the risk of static discharges and potential damage to these devices.
Proper storage is also essential in preventing static electricity damage. Store RFID devices in anti-static bags or containers designed to dissipate static charges. This specialized packaging will shield the devices from potential static buildup and minimize the risk of damage.
During maintenance or cleaning of RFID devices, use appropriate tools and materials that are designed for ESD protection. Avoid using abrasive materials or cleaners that can cause static buildup or damage the device’s sensitive components.
Regular inspections are important to identify any signs of damage or wear on RFID devices. Look for loose connections, cracked casings, or any visible abnormalities. Promptly address any issues to prevent further damage and ensure the proper functioning of the devices.
By following these precautions and handling RFID devices with care, you can reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable operation of these important devices in various applications.
Keyboards, Mice, and Other Input Devices
Keyboards, mice, and other input devices are essential components of our computer systems, enabling us to interact and input commands efficiently. However, these devices can be vulnerable to damage from static electricity discharges, which can disrupt their functionality and performance.
The sensitive electronic components and circuitry inside keyboards, mice, and other input devices make them susceptible to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these devices, it can disrupt the electrical signals and cause issues such as unresponsive keys, erratic cursor movements, or complete failure of the device.
To protect keyboards, mice, and other input devices from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat before interacting with these devices is essential. Avoid touching the connectors, buttons, or sensitive components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can cause damage.
Proper cleaning and maintenance are also important in preventing static-related issues in input devices. Use soft, anti-static cloths or cleaning solutions specifically designed for electronic devices to remove dust or debris that may induce static buildup. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh cleaners that can damage the protective coatings on the device’s surface.
When connecting input devices to the computer or other devices, make sure that both the device and the computer are turned off. This reduces the risk of static discharge between the connectors and minimizes the chances of damage to the devices.
In environments with dry or low humidity conditions, the risk of static electricity buildup increases. Using a humidifier or anti-static sprays in the room can help reduce static charges and minimize the possibility of damage to the input devices.
Proper storage when not in use is also important to prevent static electricity damage. Store keyboards, mice, and other input devices in a cool, dry place to minimize exposure to static-prone materials or environments.
Regular inspections for any signs of damage or wear on input devices are crucial. Look for loose connectors, broken buttons, or any visible abnormalities. Repair or replace any damaged components promptly to prevent further issues.
By following these precautions and handling keyboards, mice, and other input devices with care, you can reduce the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable performance of these important components in your computing experience.
Medical Devices (Pacemakers, Hearing Aids, etc.)
Medical devices, such as pacemakers, hearing aids, and insulin pumps, play a critical role in managing and improving the health of individuals. Due to their delicate nature and sensitivity to electrical disturbances, these devices are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity discharges, which can jeopardize their functionality and pose risks to patients.
The intricate electronic components and circuitry within medical devices make them particularly vulnerable to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these devices, it can disrupt the electrical signals and cause malfunctions or errors in the device’s operation.
To protect medical devices from static electricity damage, it is crucial to handle them with extreme care. Proper grounding is essential before interacting with these devices. Ground yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat, and avoid touching the exposed connectors, buttons, or sensitive components without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can lead to damage.
When storing medical devices, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Some devices may require specific storage conditions or anti-static accessories to help dissipate static charges and prevent potential damage.
Regular inspections and maintenance of medical devices are essential for their proper function and longevity. Follow the recommended maintenance routines provided by the manufacturer, and promptly address any signs of wear, damage, or abnormal functionality. This ensures that the devices are operating safely and effectively.
It is crucial to inform healthcare professionals and providers about the use of medical devices that are sensitive to static electricity. They can provide guidance on how to properly handle and care for these devices to minimize the risk of static electricity damage.
Patients who rely on medical devices should also be mindful of their environment. Avoid situations that can generate static charges, such as wearing clothing made of synthetic fabrics or being in areas with excessive static electricity, to reduce the risk of static discharges around the devices.
By following these precautions and handling medical devices with extreme care, patients can help minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage, ensuring the reliable and safe operation of these essential healthcare technologies.
Other Electronic Components and Devices
Aside from the specific electronic components and devices mentioned earlier, there are numerous other electronic components and devices that can be susceptible to static electricity damage. These include resistors, capacitors, diodes, relays, and many more. While each component or device may have unique characteristics, they all share the vulnerability to static electricity discharges.
The delicate electronic components and intricate circuitry found in various electronic devices make them sensitive to static electricity damage. When a static discharge occurs near these components or devices, it can disrupt the electrical signals and cause malfunctions, inaccuracies, or even permanent damage.
To protect other electronic components and devices from static electricity damage, it is important to handle them with care. Grounding yourself by using an anti-static wristband or mat is essential before interacting with these components. Avoid touching the exposed pins, connectors, or sensitive parts without proper grounding, as even a small static shock can lead to damage.
Proper storage is also crucial in preventing static electricity damage. Components and devices should be stored in anti-static bags, containers, or cabinets designed to dissipate static charges. This helps protect them from potential static buildup and reduces the risk of damage.
When connecting or replacing electronic components, ensure that both the component and the device are powered off. This minimizes the risk of static discharges between the connectors and decreases the chances of damage to the components or devices.
Regular inspections for any signs of damage, wear, or abnormalities in electronic components and devices are important. Look for bent pins, cracked casings, or other visible issues. Replace or repair any damaged components promptly to prevent further damage and ensure the proper functionality of the devices.
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for handling, installation, and maintenance of electronic components and devices. These guidelines often provide specific instructions to protect them from static electricity and ensure optimal performance.
By handling other electronic components and devices with care, following proper grounding practices, and utilizing appropriate storage and maintenance techniques, you can minimize the risk of static electricity-induced damage and ensure the reliable operation of various electronic systems.