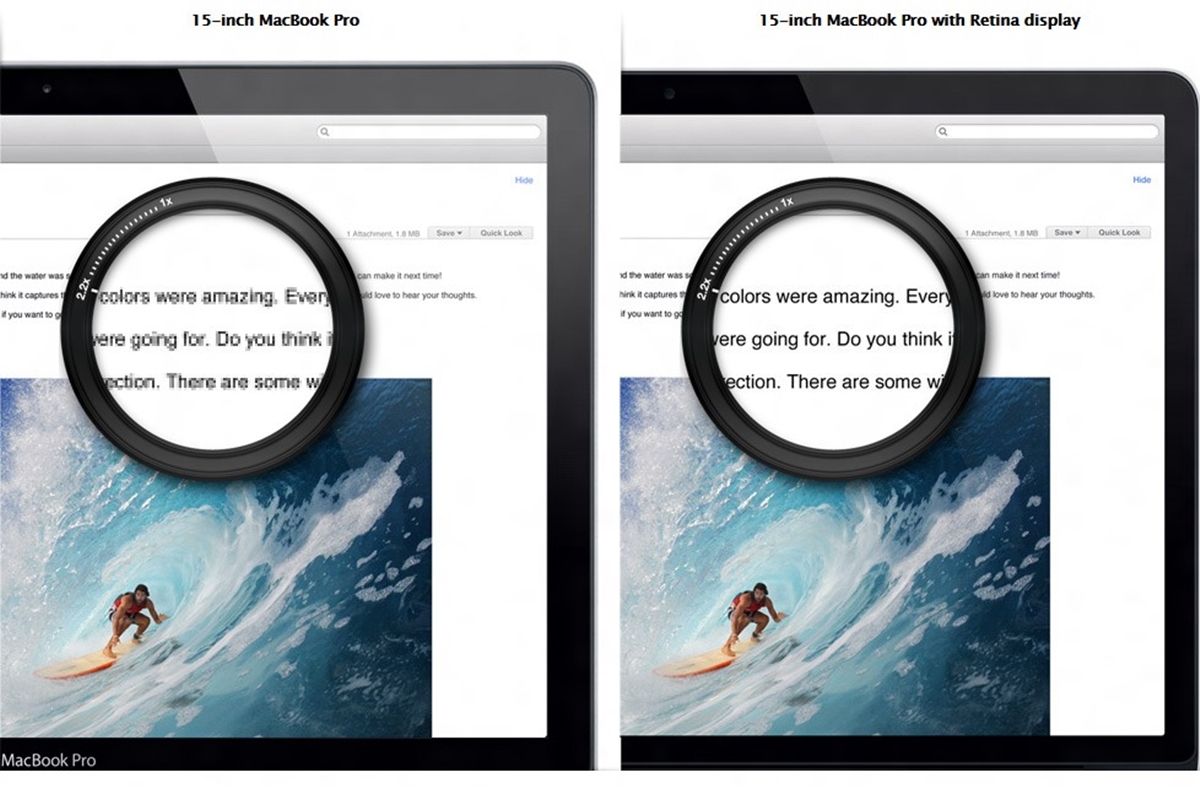
What Is Retina Display?
Retina display is a term coined by Apple Inc. to describe high-resolution screens that offer exceptional clarity and detail. It was first introduced in 2010 with the release of the iPhone 4 and has since been integrated into various Apple devices, including iPads, MacBooks, and iMacs. However, the term “retina display” has become widely used to refer to any high-resolution display, regardless of the manufacturer.
The key feature of a retina display is its high pixel density, which results in sharper and more vibrant images. The term “retina” is derived from the human eye and signifies that the display’s pixel density is so high that the average person would not be able to distinguish individual pixels at a normal viewing distance.
Retina displays achieve this high pixel density by packing a significant number of pixels into a relatively small physical area. This means that more pixels are concentrated in each inch of the display, resulting in clearer and more detailed images. The exact pixel density required to be considered a retina display varies depending on the device type and screen size.
Retina displays greatly enhance the user experience by providing exceptionally sharp text and graphics. This level of detail allows for a more immersive and lifelike viewing experience, whether you’re browsing the web, playing games, or editing photos and videos.
It is important to note that not all displays with high resolutions can be categorized as retina displays. The term specifically refers to displays that meet the pixel density threshold set by Apple or other device manufacturers. The higher pixel density is what sets retina displays apart from standard displays.
Definition and Explanation
Retina display is a term that has become synonymous with high-resolution screens, known for their exceptional clarity and detail. The name “retina” is derived from the fact that these displays have pixel densities so high that the average human eye cannot discern individual pixels at a normal viewing distance.
The concept of retina display was first introduced by Apple Inc. with the launch of the iPhone 4 in 2010. At that time, it was a groundbreaking feature that revolutionized the smartphone industry. Since then, retina displays have become an integral part of Apple’s product lineup, including iPhones, iPads, MacBooks, and iMacs.
However, it is important to note that retina display is not exclusive to Apple devices. The term has been adopted more broadly to describe any high-resolution display that meets the pixel density threshold for exceptional clarity and detail.
Pixel density refers to the number of pixels per unit of area on a display. In the case of retina displays, a high pixel density is achieved by packing a large number of pixels into a relatively small physical area. This means that more pixels are crammed into each inch of the screen, resulting in sharper and more detailed images.
The pixel density required to qualify as a retina display varies depending on the device type and screen size. For example, a retina display on an iPhone may have a higher pixel density than on an iPad or MacBook, considering the difference in viewing distances.
Retina displays offer a host of benefits, primarily in terms of visual quality and user experience. With a retina display, text appears crisp and sharp, making reading on digital devices more comfortable and enjoyable. Images and videos also showcase exquisite detail and vibrant colors, enhancing the overall visual impact.
Retina displays have become increasingly popular, with many device manufacturers adopting the technology to deliver an immersive and visually stunning experience. Whether you’re playing games, watching movies, or editing photos and videos, a retina display elevates the level of realism and detail.
The next section will delve into the history and development of retina displays, exploring the advancements that have brought us to the current state of this technology.
History and Development
The history of retina displays can be traced back to the groundbreaking release of the iPhone 4 in 2010. It was during this time that Apple introduced the term “retina display” to describe its high-resolution screens.
Prior to the iPhone 4, most smartphones had displays with relatively low pixel densities, resulting in noticeable pixelation and lack of sharpness. Apple sought to address this issue by developing a screen with pixels so small and densely packed that they would be indistinguishable to the human eye at a typical viewing distance.
With the launch of the iPhone 4, Apple achieved this goal by introducing a display with a pixel density of 326 pixels per inch (PPI). This was a significant leap from the previous iPhone models, which had pixel densities in the range of 160-200 PPI.
The success of the iPhone 4’s retina display led Apple to expand its implementation to other devices in its product lineup. The next device to feature a retina display was the third-generation iPad, released in 2012, which had a pixel density of 264 PPI.
Over the years, as technology advanced and competition increased, other device manufacturers began to develop their own versions of high-resolution displays. These displays were often referred to as “retina-like” or “retina-equivalent” displays.
Today, retina displays are not limited to smartphones and tablets. They can be found in various devices, including laptops, desktop computers, and even some high-end televisions. The pixel densities and resolutions continue to increase with each new generation of devices, providing users with even greater clarity and detail.
Advancements in display technology have played a crucial role in the development of retina displays. These advancements include the use of in-plane switching (IPS) panels, which provide wider viewing angles and more accurate color reproduction, and the introduction of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays, which offer deeper blacks and more vibrant colors.
The relentless pursuit of higher pixel densities and improved visual quality drives the ongoing development of retina display technology. As device manufacturers strive to deliver more immersive and lifelike viewing experiences, we can expect future generations of retina displays to continue pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Next, we will explore how retina displays work and the underlying technology behind them.
How Retina Displays Work
Retina displays work by packing a high number of pixels into a small area, resulting in a high pixel density that produces sharp and detailed images. In order to understand how retina displays work, it’s important to grasp the basics of pixels and pixel density.
A pixel is the smallest unit of a digital image, and it consists of red, green, and blue subpixels that combine to create different colors. The more pixels a display has, the higher the level of detail it can produce. Pixel density refers to the number of pixels per inch (PPI) or pixels per centimeter (PPCM) on a screen.
Retina displays achieve their high pixel density by increasing the number of pixels in a given area. This means the pixels are physically smaller and more closely packed together. The goal is to make the pixels sufficiently small that they blend together, appearing as a smooth and continuous image to the human eye at a normal viewing distance.
However, pixel density alone does not guarantee a true retina display. The screen’s resolution and viewing distance must also be taken into account. The viewing distance is the distance from which the display is typically viewed, and it varies depending on the device. For example, a typical viewing distance for smartphones is shorter than that for laptops or desktop monitors.
The size of the display and the resolution are also important factors in determining if a display can be considered retina. A higher resolution on a larger screen may result in a lower pixel density, which could affect the image’s sharpness and clarity.
The technology used in retina displays, such as advanced LCD or OLED panels, plays a crucial role in producing vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles. In addition, various image processing techniques are employed to optimize the image quality, such as subpixel rendering and anti-aliasing, which smooth out jagged edges and improve overall clarity.
It’s important to note that not all displays labeled as “retina” are created equal. Various manufacturers may have different pixel density thresholds, and some displays may use marketing terms similar to retina without meeting the true definition. Therefore, it’s recommended to compare specifications and reviews to ensure a display truly delivers the intended visual experience.
In the next section, we will explore the benefits and advantages of retina displays and how they enhance the user experience.
Benefits and Advantages of Retina Display
Retina displays offer a multitude of benefits and advantages that greatly enhance the visual experience for users. These high-resolution screens deliver exceptional clarity, sharpness, and detail, resulting in several key advantages:
1. Enhanced Image Quality: Retina displays produce incredibly sharp and vibrant images. The high pixel density ensures that the smallest details are visible, making photos, videos, and graphics appear more lifelike and realistic.
2. Crisp Text and Graphics: Reading text on a retina display is a pleasure. The high pixel density allows for smooth, clear, and well-defined text, reducing eye strain and creating a more comfortable reading experience. Graphics, icons, and user interface elements also benefit from the improved clarity, making them more visually appealing.
3. Improved Color Reproduction: Retina displays often utilize advanced technology, such as IPS or OLED panels, to achieve accurate color reproduction. This results in more vibrant, true-to-life colors, making images and videos appear richer and more vibrant.
4. Immersive Viewing Experience: Retina displays create a more immersive viewing experience, whether you’re watching movies, playing games, or browsing the web. The high level of detail and vivid colors draw you in, making everything on the screen feel more realistic and engaging.
5. Better Accessibility: Retina displays benefit individuals with visual impairments, as the high-resolution screens offer improved legibility and visibility. Text and images are crisp and clear, providing easier reading and comprehension for individuals with low vision.
6. Increased Productivity and Creativity: The clarity and detail offered by retina displays enhance productivity and creativity. Professionals working in design, photography, video editing, and other visual-intensive fields can accurately view and edit their work, ensuring precise detail and color accuracy.
7. Future-Proofing: With the rapid advancement of technology, retina displays provide a level of future-proofing. As content and applications continue to evolve, retina displays ensure compatibility and optimized visuals for future innovations.
Overall, retina displays offer significant advantages in terms of image quality, text clarity, color reproduction, immersion, accessibility, and productivity. Whether you’re using a smartphone, tablet, laptop, or desktop computer, the benefits of a retina display contribute to an enhanced visual experience.
Next, we will compare retina displays with non-retina displays, highlighting the differences and helping you understand why the pixel density of a display matters.
Retina Display vs. Non-Retina Display
The difference between a retina display and a non-retina display lies primarily in the level of pixel density and image quality. Let’s explore the distinctions between the two:
1. Pixel Density: Retina displays have a significantly higher pixel density compared to non-retina displays. This means that more pixels are packed into each inch of the screen, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image. Non-retina displays, on the other hand, have lower pixel densities, which can lead to pixelation and a less crisp visual experience.
2. Image Sharpness: Retina displays provide exceptional sharpness and clarity due to their high pixel density. Text and graphics appear smooth and well-defined, while images and videos showcase intricate details. Non-retina displays may appear slightly pixelated or less sharp, particularly when viewing fine details or smaller text.
3. Color Accuracy: The color reproduction on a retina display is often more accurate and vibrant compared to non-retina displays. Retina displays typically utilize advanced technologies, such as IPS or OLED panels, which offer better color saturation, wider color gamut, and improved viewing angles. Non-retina displays may exhibit less accurate colors and may have narrower viewing angles, resulting in distorted colors when viewed from the sides.
4. Viewing Experience: Retina displays provide a more immersive viewing experience. The high pixel density and improved image quality make the content on the screen appear more realistic and engaging. Non-retina displays, with their lower pixel densities, may lack the same level of visual impact and may not offer the same level of immersion.
5. Eye Comfort: Retina displays with their high pixel densities and sharp text rendering can reduce eye strain and fatigue, especially during prolonged reading or viewing sessions. Non-retina displays, when displaying smaller or less defined text, may cause more eye strain, making reading for longer periods less comfortable.
6. Compatibility: With the increasing prevalence of retina displays, developers and content creators are focusing on optimizing their products for high-resolution screens. This means that apps, websites, and multimedia content are often optimized for retina displays, resulting in a visually superior experience. Non-retina displays may not be able to fully take advantage of these optimizations, potentially resulting in a less visually appealing experience.
Overall, the key distinction between retina and non-retina displays lies in the level of pixel density, image clarity, color accuracy, and overall visual experience. While non-retina displays can still provide decent quality, retina displays offer a superior and more immersive visual experience across a wide range of devices.
In the next section, we will explore popular devices that feature retina displays and have become synonymous with high-resolution image quality.
Popular Devices with Retina Display
Retina displays have become widely popular and are now featured in a range of devices across different manufacturers. Here are some popular devices that are renowned for their high-resolution retina displays:
1. iPhone: Apple’s iPhone lineup has been synonymous with retina displays since the introduction of the iPhone 4. The latest models, such as the iPhone 12 Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max, feature Super Retina XDR displays with high pixel densities, offering exceptional image quality and vibrant colors.
2. iPad: Apple’s iPad series also boasts retina displays, providing a stunning visual experience for both work and entertainment. Models like the iPad Pro and iPad Air feature Liquid Retina displays, which offer excellent color accuracy and crisp image quality.
3. MacBook: Apple’s MacBook lineup includes retina displays, ensuring a sharp and detailed visual experience for users. The MacBook Pro and MacBook Air models feature Retina displays, which enhance the clarity of text, images, and videos for improved productivity and enjoyment.
4. iMac: Apple’s iMac computers are equipped with retina displays, delivering stunning visuals and precise color reproduction. The iMac models, such as the iMac Pro and iMac with Retina 5K display, showcase the power of high-resolution screens for professional creative work and immersive entertainment.
5. Samsung Galaxy: Samsung’s flagship smartphones, such as the Galaxy S21 and Galaxy Note20 series, feature Dynamic AMOLED displays with high pixel densities, resulting in vibrant colors and excellent contrast. These displays offer a visually captivating experience for multimedia consumption and gaming.
6. Google Pixel: Google’s Pixel smartphones, including the Pixel 5 and Pixel 4a, feature OLED displays with high pixel densities. These displays deliver deep blacks, vibrant colors, and sharp image quality, enhancing the overall visual experience.
7. Microsoft Surface: Microsoft’s Surface devices, such as the Surface Pro and Surface Laptop, offer high-resolution PixelSense displays. These displays feature excellent color accuracy and offer a precise and immersive visual experience for productivity tasks and multimedia consumption.
These are just a few examples of popular devices that feature retina displays. Many other manufacturers have also integrated high-resolution screens into their devices, providing users with stunning visuals and an exceptional viewing experience.
Next, let’s explore the intersection of retina display technology and accessibility, ensuring that high-resolution screens are accessible to all users.
Retina Display and Accessibility
Retina displays not only offer visually stunning and detailed images but also have the potential to improve accessibility for individuals with vision impairments. Here’s how retina display technology intersects with accessibility:
1. Improved Legibility: The high pixel density of retina displays ensures that text appears sharp and well-defined, making it easier for individuals with low vision to read. The clarity and crispness of the text can reduce eye strain and enhance legibility for people with visual impairments.
2. Enhanced Visual Content: Retina displays enhance the visibility of visual content, such as images, videos, and graphical user interfaces. The high pixel density and color accuracy help individuals with visual impairments perceive and comprehend visual information with more clarity.
3. Zoom and Magnification: Retina displays allow for zoom and magnification features to be more effective. When zooming into the screen, the high pixel density ensures that the magnified content remains sharp and clear, enabling individuals with visual impairments to view details without significant loss in quality.
4. Accessibility Settings: Many devices with retina displays, including smartphones and computers, offer accessibility features specifically designed to assist users with visual impairments. These features, such as larger fonts, bold text, high contrast, and color filters, can be adjusted to meet individual accessibility needs.
5. VoiceOver and Screen Readers: Retina display devices often come equipped with built-in screen reader technology, such as Apple’s VoiceOver. These screen readers convert text and other on-screen elements into synthesized speech, providing an audio interface for individuals with visual impairments to navigate and interact with their devices.
6. Braille Support: Retina display devices can also support external Braille displays, allowing individuals with visual impairments to access information through tactile feedback. This integration enables users to read text, navigate interfaces, and interact with their devices using Braille input and output.
7. Usability for All: Retina displays, by delivering exceptional image quality and visual clarity, enhance the overall user experience for everyone. This includes individuals with varying levels of visual impairments, as well as individuals without impairments, who benefit from the enhanced visual aesthetics and legibility offered by retina displays.
While retina displays contribute to improved accessibility, it’s essential for developers and designers to ensure compatibility with accessibility standards and guidelines. This includes considering appropriate color contrast, scalable fonts, and the proper implementation of assistive technologies to further enhance the accessibility of content and interfaces.
In the next section, we will explore the difference between retina display and higher resolutions such as 4K and 8K, and discuss their respective advantages and use cases.
Retina Display vs. 4K and 8K Resolutions
Retina display, 4K, and 8K resolutions are all terms used to describe high-resolution displays. However, there are distinct differences between them in terms of pixel density, image quality, and use cases. Let’s explore the disparities:
1. Pixel Density: Retina displays generally have a high pixel density. The exact pixel density required to be classified as a retina display varies based on device type and screen size. On the other hand, 4K resolution refers to a display with approximately 4000 pixels horizontally, while 8K resolution refers to a display with approximately 8000 pixels horizontally. Higher resolution displays like 4K and 8K typically have even higher pixel densities than retina displays, resulting in finer detail and image clarity.
2. Image Quality: Retina displays are renowned for producing sharp and vibrant images. The high pixel density ensures that text, graphics, and visual content appear detailed and well-defined. Meanwhile, 4K and 8K resolutions offer even greater image quality due to the increased number of pixels. These higher resolutions provide more precise detail and exceptional visual clarity, making them ideal for professionals working in fields like photography, video editing, and graphic design.
3. Display Size and Viewing Distance: The pixel density required for a retina display depends on the device type and screen size. As the display size increases, maintaining a high pixel density becomes more challenging. In contrast, 4K and 8K resolutions are often associated with larger screens, such as televisions or computer monitors, where viewers tend to sit farther away. The higher resolutions of these displays compensate for the viewing distance, ensuring that the image remains detailed and sharp even at larger sizes.
4. Content Availability and Compatibility: Retina displays have become widely adopted by device manufacturers and are supported by a large ecosystem of applications and content optimized for high-resolution screens. On the other hand, while 4K and 8K resolutions offer superior image quality, content specifically designed and available in these resolutions is still relatively limited. However, with the increasing popularity of 4K and 8K displays, content in these resolutions is gradually becoming more accessible and widespread.
5. Intended Use Cases: Retina displays are suitable for a wide range of devices and use cases, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers. They offer excellent image quality for everyday tasks, such as browsing the web, viewing multimedia content, and general productivity. On the other hand, 4K and 8K resolutions are often found in larger displays, such as televisions and professional-grade monitors, aimed at specialized use cases. These resolutions excel in demanding tasks like video editing, gaming, and professional content creation.
While retina displays provide excellent image quality and are widely available on various devices, 4K and 8K resolutions offer even higher levels of detail, making them suitable for professionals and enthusiasts who require the utmost image clarity and precision. The choice between these technologies depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the user.
In the next section, we will address some common misconceptions about retina displays and provide clarification on these topics.
Common Misconceptions about Retina Display
Retina displays have gained widespread popularity and recognition for their high-resolution screens. However, there are some common misconceptions surrounding retina display technology. Let’s address these misconceptions and provide clarification:
1. Retina Display Equals High Resolution: While retina displays are known for their high pixel density, the term “retina” itself does not specify a specific resolution. Retina displays are characterized by their high pixel density, which results in sharp and detailed images, but the exact resolution can vary depending on the device and screen size.
2. Retina Displays Are Limited to Apple Devices: While the term “retina display” was initially coined by Apple, it has now become a more general term used to describe high-resolution displays. Retina displays can be found in a range of devices from various manufacturers, providing exceptional image quality and clarity.
3. Retina Displays Always Require High Battery Consumption: While it is true that running a high-resolution display can consume more power, modern devices with retina displays have become more efficient in managing power consumption. Manufacturers have implemented technologies, such as power-saving OLED panels and optimized hardware, to ensure a balance between performance and battery life.
4. Retina Displays Are Only Beneficial for Younger Users: Retina displays offer enhanced visual experiences for users of all ages. The improved image quality, sharpness, and clarity provided by retina displays benefit individuals of all age groups, from young users engaging in multimedia content to older users who may have age-related vision changes.
5. High Resolution Is the Sole Factor for Display Quality: While high resolution is essential for display quality, other factors such as color accuracy, contrast ratio, and panel technology also contribute to the overall visual experience. Retina displays often incorporate advanced technologies, such as IPS or OLED panels, to enhance color reproduction, contrast, and viewing angles.
6. Retina Displays Guarantee Perfect Image Quality: While retina displays strive to provide exceptional image quality, the final result can still be influenced by factors such as content source, image scaling, and individual device performance. Additionally, user preferences and subjective assessments of image quality may vary.
7. Retina Displays Are Too Expensive: While retina displays may have initially been associated with high-end devices, advancements in manufacturing technology have resulted in broader availability and affordability. Retina displays can now be found in a wide range of devices, from smartphones to laptops, offering high-value visual experiences at various price points.
By addressing these misconceptions, it becomes clear that retina displays are a versatile and accessible technology that enhances the visual experience for users across different devices and price ranges.
In the next section, we will look into the future of retina display technology and potential advancements that lie ahead.
Future of Retina Display Technology
The future of retina display technology holds great promise for even more stunning visual experiences. Here are some potential advancements and trends to look forward to:
1. Higher Resolutions: As technology advances, we can expect even higher resolutions beyond 4K and 8K. Displays with pixel densities that exceed current limits will become more commonplace, offering unprecedented levels of detail and clarity.
2. Advanced Display Technologies: Future retina displays may incorporate innovative technologies such as micro-LED or mini-LED panels, which offer enhanced brightness, contrast ratios, and power efficiency. These technologies have the potential to push the boundaries of image quality even further.
3. Faster Refresh Rates: Displays with faster refresh rates, such as 120Hz or even 240Hz, provide smoother and more fluid visuals, especially during fast-paced gaming or high-motion content. Future retina displays are likely to embrace higher refresh rates, offering an enhanced viewing experience.
4. Foldable and Flexible Displays: Retina displays may evolve to include foldable and flexible form factors, enabling devices that can transform from a smartphone to a tablet or even larger screens. These displays will offer enhanced versatility and portability, revolutionizing the way we interact with digital content.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Retina displays will play a significant role in the advancement of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. High-resolution displays are crucial for creating immersive and realistic virtual environments, and future retina displays will likely offer improved visuals for AR and VR experiences.
6. Enhanced Color Accuracy and Dynamic Range: Retina displays will continue to improve color accuracy, offering wider color gamuts and better color reproduction. Additionally, advancements in HDR (High Dynamic Range) technology will enable retina displays to deliver richer, more vibrant colors and greater contrast ratios for more lifelike visuals.
7. Integration of Biometric Sensors: Future retina displays may include integrated biometric sensors, such as under-display fingerprint scanners or facial recognition technology. This integration will enhance device security and provide seamless authentication methods.
8. Energy Efficiency: Display technology will continue to focus on energy efficiency, optimizing power consumption while maintaining high image quality. Advancements in panel technology, backlighting, and power management will contribute to longer battery life without compromising visual excellence.
These potential advancements in retina display technology will shape the way we interact with digital content, providing more immersive and visually captivating experiences. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect retina displays to push the boundaries of what is possible, setting new standards for image quality and enhancing the overall visual landscape.
With each innovation and improvement in retina display technology, the future holds exciting possibilities for users across a wide range of devices and industries.