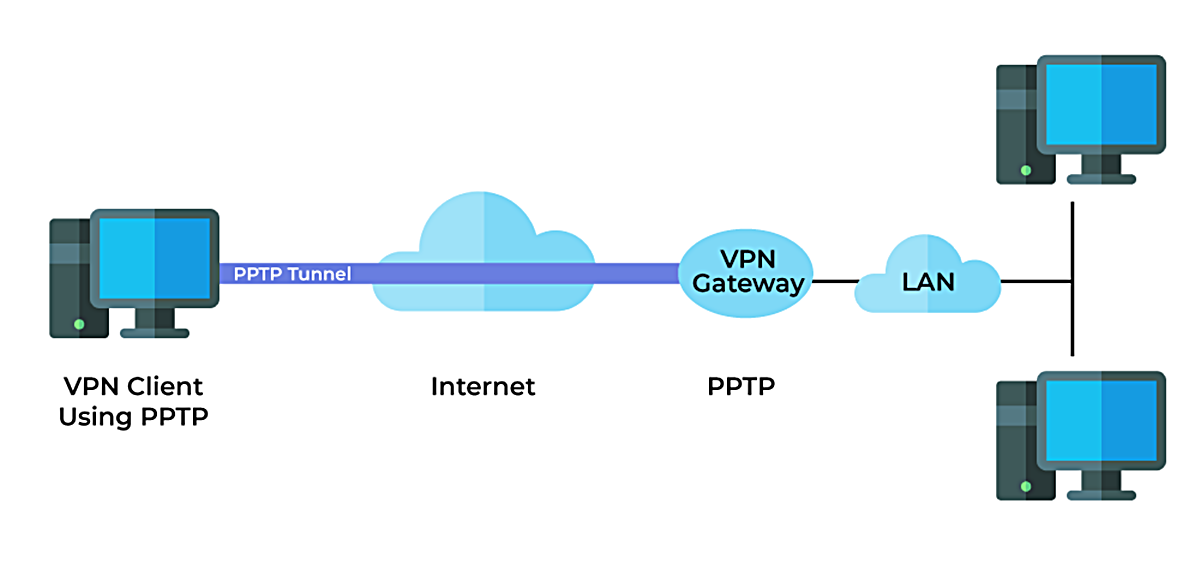
What is PPTP: Explaining the Basics
PPTP, which stands for Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, is a networking protocol used to establish secure encrypted tunnels between two devices over the internet. It was developed by Microsoft and was widely used in the early days of virtual private networks (VPNs). PPTP operates at the data link layer of the OSI model and encapsulates data in IP datagrams for transmission.
The main purpose of PPTP is to provide a secure connection between a client and a server, allowing data to be transmitted securely over a public network such as the internet. This is achieved by tunneling protocols such as PPTP that encapsulate the data in a secure packet, protecting it from unauthorized access.
One of the key features of PPTP is its simplicity. It is easy to set up and configure, making it a popular choice for users who value convenience and ease of use. PPTP is supported by most operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
The operation of PPTP involves two main components: the PPTP client and the PPTP server. The client initiates a connection to the server and establishes a secure tunnel for data transmission. The client and server authenticate each other using various methods, such as passwords or certificates, ensuring the security and integrity of the connection.
PPTP uses a combination of different protocols, including TCP/IP, GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation), and MPPE (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption). TCP/IP is responsible for routing and addressing, GRE encapsulates the data packets, and MPPE provides encryption to protect the data from being intercepted.
While PPTP was widely used in the past, it is important to note that it has some limitations and security concerns. The encryption used by PPTP is considered weak compared to more modern protocols like OpenVPN or IKEv2. Additionally, there have been reports of vulnerabilities in the PPTP protocol, which could potentially be exploited by attackers.
Despite its drawbacks, PPTP can still be a viable option in certain scenarios where compatibility and ease of use are prioritized over robust security. It remains a popular choice for home users or small businesses that require a simple and quick VPN solution.
In the next section, we will explore how PPTP works and delve into its technical details.
How Does PPTP Work: A Technical Overview
To understand how PPTP works, let’s dive into the technical details of this VPN protocol. PPTP utilizes various components and processes to establish a secure tunnel for data transmission.
When a PPTP connection is established, the client sends a connection request to the PPTP server. This request is initiated using the control connection, which is established through a TCP/IP connection on port 1723. Once the control connection is established, PPTP uses the GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) protocol to encapsulate the data packets.
The encapsulated data packets are then sent through the secure tunnel, which is created by establishing a separate PPTP tunnel for data transmission. This tunnel is established by assigning a unique TCP connection on port 1723 for each client-server pair.
Within the data tunnel, the data packets are protected using MPPE (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption). MPPE provides encryption and authentication for secure transmission. It encrypts the data with a symmetrical encryption algorithm and generates cryptographic keys to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the transmitted data.
PPTP also utilizes the PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) for authentication and data link control. PPP is responsible for establishing and maintaining the connection between the PPTP client and server. It supports various authentication methods, including PAP (Password Authentication Protocol), CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol), and EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol).
During the authentication process, the client and server verify each other’s identity by exchanging credentials. This step ensures that only authorized users can establish a PPTP connection and access the network resources.
Overall, PPTP works by establishing a secure tunnel between the client and server using the GRE protocol, encapsulating data packets, and encrypting them with MPPE. This combination of protocols and encryption techniques ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the transmitted data.
Despite its technical intricacies, PPTP is known for its ease of setup and configuration. It is supported by most operating systems and can be quickly implemented, making it a preferred choice for users who prioritize convenience.
In the next section, we will explore the advantages of using PPTP as a VPN protocol and why it might be the right choice for your needs.
Advantages of PPTP: Why Choose This Protocol
PPTP, or Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for users in certain situations. Let’s explore some of the benefits of using PPTP as a VPN protocol.
1. Easy to Set Up and Use: One of the major advantages of PPTP is its simplicity. It is relatively easy to set up and configure, even for users with limited technical expertise. PPTP is supported by most operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
2. Compatibility: PPTP has widespread compatibility with different devices and platforms. It can be utilized on various devices, such as desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. This allows for seamless integration and usage across multiple devices.
3. Speed: PPTP is known for its fast connection speeds. It uses less processing power compared to other VPN protocols, resulting in a smoother and more efficient browsing experience. This makes it suitable for tasks that require real-time streaming or online gaming.
4. Broad Network Support: PPTP is supported by a wide range of network infrastructure, including routers and firewalls. This makes it easier to implement within existing network setups and ensures compatibility with different types of networks.
5. Low Overhead: PPTP has a relatively low overhead, meaning it requires less bandwidth for transmission. This can be advantageous for users with limited internet resources or those who want to minimize data usage while using a VPN.
6. Convenience: PPTP offers convenience for users who need a quick and straightforward VPN solution. Its ease of use, combined with its compatibility and fast connection speeds, makes it an attractive choice for home users or individuals who seek a hassle-free VPN experience.
It is important to consider these advantages when deciding whether PPTP is the right VPN protocol for your needs. However, it is essential to note that PPTP has its limitations and potential security concerns, as we will discuss in the following sections.
In the next section, we will explore the disadvantages of PPTP, which should be taken into account before making a decision on whether to use this protocol.
Disadvantages of PPTP: Limitations and Concerns
While PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) offers several advantages, it is important to be aware of its limitations and potential security concerns. Here are some of the notable disadvantages of using PPTP as a VPN protocol.
1. Weak Encryption: One of the main concerns with PPTP is its weak encryption. The encryption algorithm used, known as MPPE (Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption), has been shown to be susceptible to brute force attacks, making it less secure compared to other VPN protocols. As a result, sensitive data transmitted over a PPTP connection may be vulnerable to interception.
2. Less Secure Than Other VPN Protocols: PPTP is considered less secure compared to modern VPN protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard. It lacks advanced security features, such as the use of stronger encryption algorithms and more robust authentication methods. For users who prioritize high-level security, it is recommended to consider alternative protocols.
3. Potential Security Vulnerabilities: PPTP has been known to have security vulnerabilities in the past. These vulnerabilities could potentially be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to the network or intercept data. While patches and updates have been released to mitigate these vulnerabilities, it is still a concern for those looking for a secure VPN solution.
4. Blocked by Some Networks: PPTP traffic is often blocked by certain networks and firewalls due to its association with security vulnerabilities. This can limit the accessibility and usability of PPTP in certain environments, such as corporate networks or countries with strict internet censorship.
5. Compatibility Issues: Although PPTP is widely compatible, there may be compatibility issues with certain devices or operating systems, especially with newer versions. Some devices and operating systems may no longer support PPTP due to its security vulnerabilities, causing limitations in its usage.
6. Lack of Support: As PPTP is an older protocol, the level of support and development has significantly decreased in recent years. This means there may be limited resources available for troubleshooting issues or receiving updates to address security concerns.
Considering these limitations and concerns, it is crucial to evaluate the security requirements and priorities before deciding to use PPTP as a VPN protocol. Alternatives that offer stronger security measures and more robust features may be more suitable for users who require a higher level of security.
In the next section, we will compare PPTP with other VPN protocols to highlight the differences and help you make an informed decision.
PPTP vs. Other VPN Protocols: A Comparison
When selecting a VPN protocol, it is essential to compare the features and characteristics of different options. Let’s compare PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) with other popular VPN protocols to understand their differences.
1. Security: PPTP is known for its weak encryption and potential vulnerabilities. On the other hand, protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard offer stronger encryption algorithms, more robust authentication methods, and better overall security. These protocols prioritize data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity, making them a preferred choice for users who value high-level security.
2. Compatibility: PPTP is widely supported by various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. However, some newer operating systems and devices may no longer support PPTP due to its security concerns. OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard are also compatible with most platforms but provide broader support in terms of device compatibility.
3. Performance: PPTP is known for its fast connection speeds due to its lower overhead compared to other VPN protocols. However, protocols like WireGuard are designed to offer excellent performance by utilizing modern encryption and efficient protocols. They provide a balance between security and performance, making them an optimal choice for users who require both speed and security.
4. Flexibility: PPTP is simpler to set up and use, making it more convenient for users who prioritize ease of use. However, protocols like OpenVPN offer greater flexibility by allowing customization of encryption algorithms, authentication methods, and tunneling options. This flexibility provides advanced users with more control over their VPN configuration.
5. Support and Development: PPTP is an older protocol, and its level of support and development has significantly decreased in recent years. Conversely, protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, and WireGuard have active development communities, with regular updates, bug fixes, and security patches. This ongoing support ensures that the protocols remain up-to-date and secure.
When selecting a VPN protocol, it is important to consider your specific needs and priorities. If you value simplicity and compatibility, PPTP may be a suitable option. However, if security, performance, and flexibility are paramount, other protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard may be more appropriate.
In the next section, we will provide a step-by-step guide on setting up a PPTP VPN, so you can start using it for your connectivity needs.
Setting Up a PPTP VPN: Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up a PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) VPN is a straightforward process. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. Choose a PPTP-compatible VPN provider: Look for a reliable VPN provider that supports PPTP connections. Ensure they have servers in locations that meet your needs.
2. Subscribe to a VPN service: Sign up for a VPN service and choose a subscription plan that suits your requirements. Make sure the provider offers PPTP as one of their supported protocols.
3. Download and install the VPN client software: Most VPN providers offer dedicated software for their clients. Download the appropriate software for your operating system and follow the installation instructions.
4. Launch the VPN client software: After installation, launch the VPN client software on your device. You will typically find it in your Applications or Programs folder.
5. Enter login credentials: Provide your VPN username and password as provided by your VPN provider. These credentials are necessary to establish a secure connection to the VPN server.
6. Select a server location: Choose a server location from the available options provided by your VPN service. This selection will determine the geographical location from which your internet traffic will appear to originate.
7. Connect to the VPN server: Click on the “Connect” or “Connect to VPN” button within the client software. The software will establish a secure connection to the PPTP VPN server.
8. Verify the connection: Once connected, your VPN client software should display a notification confirming the successful connection. You can also verify your new IP address to ensure that your internet traffic is now being routed through the VPN server.
9. Test the VPN connection: Open a web browser and visit a website to ensure that your internet connection is now secure and your location is hidden. You can also perform a speed test to check the performance of your VPN connection.
Remember to disconnect from the VPN server when you no longer need the secure connection. Most VPN clients have a “Disconnect” or “Disconnect from VPN” button that you can use to end the secure connection.
It is worth noting that the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the VPN provider and the client software they offer. However, the general process outlined above should give you a good starting point for setting up a PPTP VPN.
In the next section, we will address common issues that users may encounter when using PPTP and provide troubleshooting tips to resolve them.
Troubleshooting PPTP: Common Issues and Solutions
While setting up and using a PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) VPN is typically straightforward, there may be instances when you encounter issues. Here are some common problems with PPTP connections and possible solutions to troubleshoot them:
1. Connection Drops: If your PPTP connection frequently drops or disconnects, it could be due to a weak internet connection. Try connecting to a different network or restarting your router. Also, check if your VPN client software is up to date.
2. Authentication Failure: If you receive an authentication error when connecting to the VPN server, double-check your username and password. Ensure they are entered correctly without any typos or spaces. If the issue persists, reset your VPN credentials or contact your VPN provider for assistance.
3. Blocked Ports: Some networks or firewalls may block PPTP traffic on port 1723, causing connection issues. Try connecting from a different network, such as a different Wi-Fi network or your mobile data network. Additionally, you can contact your network administrator to inquire about any firewall restrictions.
4. Compatibility Issues: If you are unable to establish a PPTP connection on a specific device or operating system, it might be due to compatibility issues. Ensure that your device and operating system support PPTP connections. If not, consider using a different VPN protocol that is compatible with your device.
5. ISP Interference: Some internet service providers (ISPs) may intentionally block or throttle PPTP connections. If you suspect your ISP is interfering with your VPN connection, contact them to inquire about any VPN-specific restrictions. Consider using a different ISP or a different VPN protocol if the issue persists.
6. VPN Server Issues: If you are unable to establish a connection to the VPN server, it could be due to server maintenance or temporary server issues. In such cases, try connecting to a different server location provided by your VPN provider.
7. Outdated Client Software: Ensure that you are using the latest version of your VPN client software. Developers frequently release updates to address bugs, security vulnerabilities, and compatibility issues. Update your client software to the latest version if available.
If you have exhausted these troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing issues with your PPTP connection, it is recommended to reach out to your VPN provider’s support team. They can provide specific guidance and address any further technical issues you may encounter.
Remember to provide detailed information about the problem you are facing and the steps you have already taken to troubleshoot. This will help the support team in resolving the issue more effectively.
In the next section, we will discuss the security aspects of PPTP and address whether it offers sufficient security for your needs.
PPTP Security: Is PPTP Secure Enough?
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) has long been regarded as having significant security vulnerabilities. As technology has advanced and more secure VPN protocols have emerged, the security of PPTP has been called into question. Let’s examine the security aspects of PPTP and whether it offers sufficient security for your needs.
1. Weak Encryption: PPTP uses the Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) protocol, which employs the RC4 encryption algorithm. RC4 has been shown to have vulnerabilities, making it less secure compared to more modern encryption algorithms used by other VPN protocols, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
2. Potential for Cryptanalysis Attacks: Due to the known vulnerabilities in the RC4 encryption algorithm, PPTP may be susceptible to cryptanalysis attacks. These attacks exploit weaknesses in the encryption scheme, potentially allowing an attacker to decipher the encrypted data.
3. Authentication Weaknesses: PPTP relies on basic authentication methods, such as passwords, which are more susceptible to brute force attacks. This increases the risk of unauthorized access to the VPN connection and potentially compromising the security of your data.
4. Security Vulnerabilities: PPTP has been found to have security vulnerabilities in the past, making it a less secure choice compared to other VPN protocols. These vulnerabilities have been exploited by attackers, leading to concerns about the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted over PPTP connections.
Given these issues, it is generally recommended to prioritize other VPN protocols, such as OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard, which offer stronger security measures. These protocols employ more robust encryption algorithms, advanced authentication methods, and have undergone rigorous security evaluations.
However, it’s important to note that PPTP may still be suitable for certain use cases where security is not the highest priority. For example, if you’re looking for a quick and easy way to access region-restricted content, PPTP may suffice. Additionally, PPTP may be a viable option if you’re connecting to a trusted network within a controlled environment, where the risk of malicious activity is low.
Before deciding to use PPTP, assess your security requirements and evaluate the potential risks associated with using this protocol. If maintaining a high level of security is important to you, it is advisable to consider alternative VPN protocols that provide stronger encryption and more robust security features.
In the next section, we will explore some alternatives to PPTP and highlight VPN protocols that offer enhanced security options.
Alternatives to PPTP: VPN Protocols to Consider
If you are concerned about the security vulnerabilities of PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) or need a VPN protocol with stronger encryption and enhanced security features, there are several alternatives to consider. Let’s explore some popular VPN protocols that offer increased security options:
1. OpenVPN: OpenVPN is widely regarded as one of the most secure VPN protocols available. It uses the OpenSSL library and supports various encryption algorithms, including AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). OpenVPN is highly configurable, allowing for customization of security settings and authentication methods.
2. IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2): IKEv2 is a robust and secure VPN protocol that focuses on efficient and secure key exchange. It provides strong encryption and authentication, making it suitable for mobile devices and maintaining a stable connection even when switching between different networks.
3. WireGuard: WireGuard is a newer VPN protocol that aims to offer simplicity, speed, and high-level security. It utilizes modern cryptographic principles and algorithms, such as ChaCha20 for encryption and Curve25519 for key exchange. WireGuard’s minimal codebase allows for easier auditing and reduces the potential for security vulnerabilities.
4. L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol/IP Security): L2TP/IPsec combines the best of both L2TP and IPsec protocols to provide secure and reliable VPN connections. L2TP provides the tunneling functionality, while IPsec adds encryption and authentication capabilities. L2TP/IPsec is widely supported across various platforms and offers strong security features.
5. SoftEther: SoftEther is an open-source VPN protocol that supports multiple VPN protocols, including SSL-VPN, L2TP/IPsec, and OpenVPN. It offers a flexible and scalable solution with advanced security features. SoftEther provides high-speed performance and can bypass restrictive firewalls.
When selecting an alternative VPN protocol, consider your specific security requirements, ease of use, device compatibility, and the level of support available. It’s also essential to choose a VPN provider that supports the protocol you decide to use.
Remember, while these alternatives offer enhanced security features compared to PPTP, no protocol is completely foolproof. It is crucial to stay informed about potential vulnerabilities, regularly update your VPN client software, and follow best practices for online safety and privacy.
In the final section, we will provide some concluding thoughts to help you determine whether PPTP or an alternative VPN protocol is the right choice for your specific needs.
Final Thoughts: Is PPTP the Right Choice for You?
When considering whether PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is the right choice for your VPN needs, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of this protocol. Let’s summarize the key points and help you make an informed decision.
PPTP offers simplicity, ease of use, and compatibility with various operating systems. It provides fast connection speeds and is suitable for tasks that require real-time streaming or online gaming. Additionally, PPTP may be a viable option if you prioritize convenience and quick setup.
However, PPTP has some limitations and security concerns. It utilizes weak encryption and has been associated with vulnerabilities, potentially compromising the security of your data. Other VPN protocols, such as OpenVPN, IKEv2, WireGuard, or L2TP/IPsec, offer stronger security measures, advanced authentication methods, and more robust encryption algorithms.
To determine the right choice for you, consider the level of security required, the sensitivity of the data you will be transmitting, and your specific use cases. If security is paramount and you need a high level of protection for sensitive information, it is recommended to opt for alternative VPN protocols that provide better security features.
On the other hand, if you prioritize convenience, compatibility, and fast connection speeds over maximum security, and you are connecting to a trusted network within a controlled environment, PPTP may still be a suitable choice.
Keep in mind that technology is constantly evolving, and what may be considered secure today may become vulnerable in the future. It is essential to stay updated on the latest security practices and regularly evaluate your VPN protocols to ensure your data remains protected.
Regardless of the VPN protocol you choose, it is important to use a reputable VPN provider that offers strong encryption, a no-logs policy, and excellent customer support. Additionally, practice good online hygiene by using strong passwords, keeping your systems updated, and being cautious of phishing attempts.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your specific needs, priorities, and risk tolerance. By considering the advantages, disadvantages, and security implications, you can make an informed decision about whether PPTP or another VPN protocol is the right choice for you.
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights and helped you in selecting the most suitable VPN protocol for your requirements.