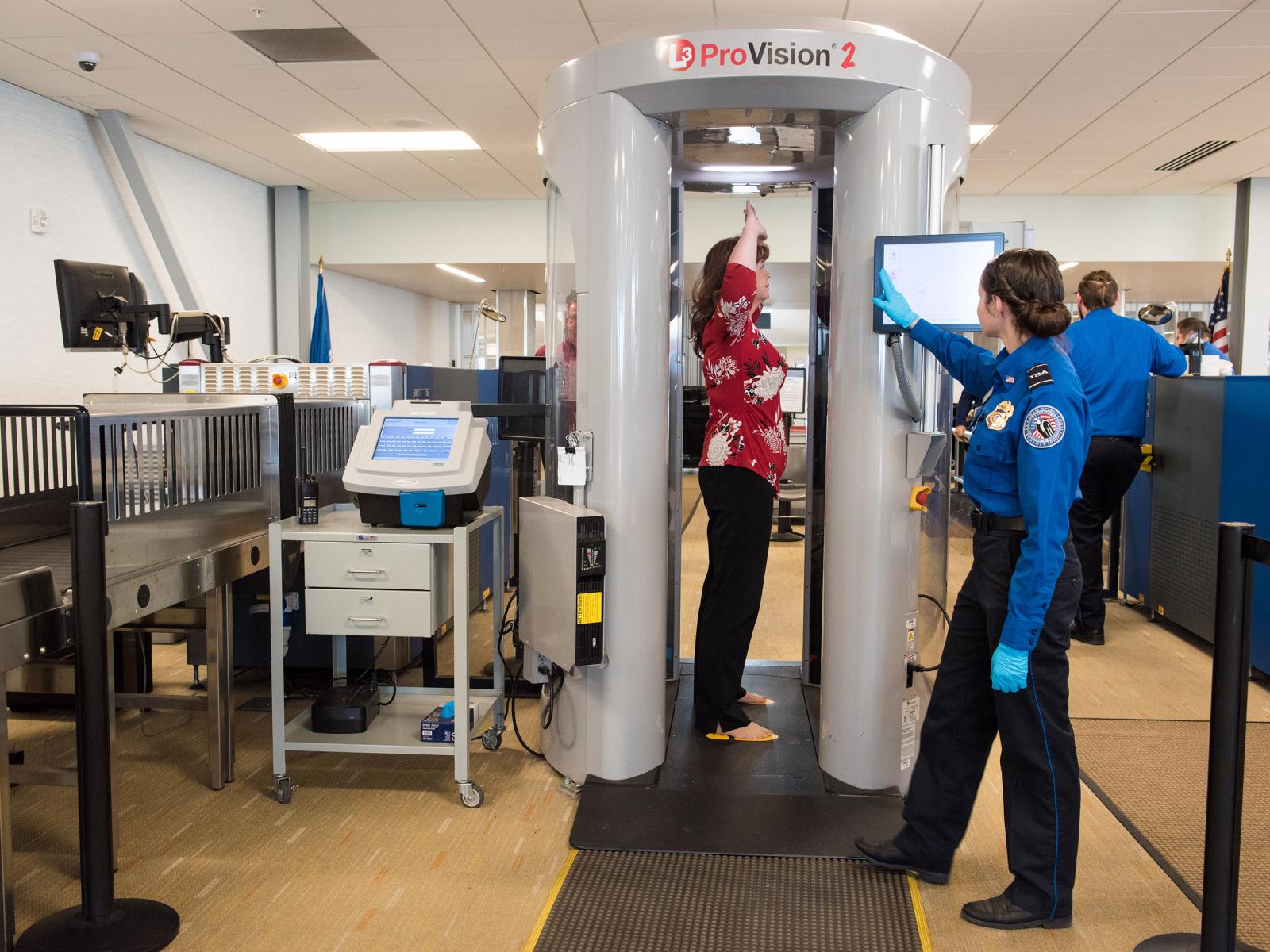
How Does an Airport Body Scanner Work?
An airport body scanner is a sophisticated security device that uses advanced imaging technology to detect any hidden objects or substances on a person’s body. There are two types of airport body scanners commonly used: millimeter-wave scanners and backscatter scanners.
Millimeter-wave scanners operate by emitting harmless electromagnetic waves that are reflected off the body and produce a detailed image. These scanners use radio frequency waves to penetrate clothing, creating a 3D image that highlights any concealed items or abnormal shapes.
On the other hand, backscatter scanners emit low-level X-rays that pass through clothing but are blocked by the body’s surface. This creates a 2D image which can show object shapes, contours, and inconsistencies.
Regardless of the type, the scanner’s sensors receive and process the reflected waves or X-rays to generate a clear image of the individual. The images are created in real-time and displayed on a monitor, allowing security officers to quickly analyze the findings.
To ensure privacy and respect for individuals, the images produced by airport body scanners are designed to be generic and do not show explicit details of a person’s body. Instead, they highlight areas of concern for further inspection.
It’s important to note that airport body scanners use passive screening technology, which means they do not emit any harmful radiation during the scanning process. The electromagnetic waves or X-rays used in the scanning are at low levels that are considered safe for public health.
Types of Airport Body Scanners
There are two main types of airport body scanners that are commonly used in security checkpoints: millimeter-wave scanners and backscatter scanners.
Millimeter-wave scanners, also known as active scanners, use non-ionizing radio frequency waves to generate an image of the body. These scanners produce a 3D image by emitting low-power electromagnetic waves that are reflected off the body’s surface. The reflected waves are then analyzed by the scanner’s sensors to create a detailed image that highlights any concealed objects or anomalies. Millimeter-wave scanners are considered safe, as the level of radio frequency energy they emit is very low and harmless to the human body.
Backscatter scanners, on the other hand, use low-energy X-rays to generate their images. These scanners emit a small amount of X-ray radiation, which passes through clothing but is blocked by the body’s surface. The backscattered radiation that is reflected off the body is captured by the scanner’s sensors and converted into a 2D grayscale image. This type of scanner can show object shapes, contours, and inconsistencies on the body. It’s important to note that the level of radiation emitted by backscatter scanners is extremely low and considered safe for use.
Both types of scanners have their advantages and limitations. Millimeter-wave scanners provide a more detailed 3D image and are better at detecting concealed objects on the body, such as weapons or explosives. On the other hand, backscatter scanners are effective at revealing object shapes and contours but may not be as effective in detecting objects hidden within body cavities or non-metallic items.
It’s worth noting that the choice of which type of airport body scanner to use may vary based on factors such as cost, efficiency, and privacy concerns. Some airports may opt for a combination of both types to enhance security and optimize passenger screening.
What Does an Airport Body Scanner Look Like?
An airport body scanner is designed to be a compact and unobtrusive security device. It typically consists of a vertical panel with multiple sensors and a small footprint that allows it to fit within the limited space of a security checkpoint.
The appearance of an airport body scanner may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer, but there are some common features that can be observed:
1. Vertical Panel: The body scanner usually takes the form of a tall, vertical panel. It can be made of lightweight materials such as metal or plastic.
2. Sensors: The panel is equipped with multiple sensors that emit waves or X-rays on one side and receive the reflected signals on the other side. These sensors capture the data needed to generate the body image.
3. Display: There is a separate monitor or screen attached to the panel. This display allows security officers to view the generated image in real-time and analyze any potential threats or abnormalities.
4. Control Console: The scanner may have a control console located near the operator’s workstation. This console allows the operator to manage the scanning process, adjust settings, and review images.
5. Privacy Features: To address privacy concerns, airport body scanners are designed to ensure the anonymity of individuals being scanned. The scanned images are displayed on the monitor in a generic form that does not reveal explicit details of the person’s body.
6. Conveyor Belt: In some cases, the body scanner may be integrated with a conveyor belt or a designated area where passengers stand and are scanned. This allows for a smoother and more efficient screening process.
Overall, an airport body scanner is designed to blend seamlessly into the security checkpoint environment while providing accurate and reliable imaging capabilities. Its compact size and intuitive features enable security officers to conduct thorough screenings while maintaining passenger privacy and safety.
How Does an Airport Body Scanner Create an Image?
An airport body scanner utilizes advanced imaging technology to create a detailed image of a person’s body. The process involves capturing and analyzing the reflected waves or X-rays to generate an accurate representation.
The specific steps involved in creating an image can vary depending on whether the scanner is a millimeter-wave scanner or a backscatter scanner.
Millimeter-wave scanners:
Millimeter-wave scanners emit low-power, non-ionizing radio frequency waves towards the person being scanned. These waves penetrate through clothing and are reflected off the body’s surface. The scanner’s sensors capture the reflected waves and process the data to generate a 3D image. This image highlights any concealed objects or anomalies that may be present on the body. The image created by the millimeter-wave scanner provides security officers with a detailed representation of the person’s body, aiding in the detection of potential threats.
Backscatter scanners:
Backscatter scanners use low-energy X-rays to create an image of the person being scanned. These scanners emit a small amount of X-ray radiation, which passes through the clothing but is blocked by the body’s surface. The backscattered radiation, reflected off the body, is captured by the scanner’s sensors. This data is then processed to generate a 2D grayscale image that shows object shapes, contours, and irregularities on the body’s surface. The resulting image allows security officers to identify any potential threats or concealed items.
Both types of scanners require sophisticated algorithms and advanced image processing techniques to analyze the captured data. These algorithms enhance the image quality, highlight anomalies, and distinguish potential threats from normal anatomical structures. The resulting image is displayed on a monitor for security officers to review and evaluate in real-time.
It’s important to note that while airport body scanners create detailed images for screening purposes, they are designed to prioritize passenger privacy. The images produced are generic and do not reveal explicit details of the person’s body. This ensures that the individual’s dignity and privacy are respected during the security screening process.
What Does the Airport Body Scanner Image Reveal?
An airport body scanner image reveals potential threats or abnormalities that may be present on a person’s body. While respecting passenger privacy, the scanner images are designed to highlight areas of concern that may require further inspection by security officers.
The scanner image provides security officers with important information about the individual’s body, such as the presence of concealed objects or deviations from normal anatomy. However, it’s important to note that the airport body scanner image does not reveal explicit details of the person’s body.
Instead, the image focuses on specific areas that could indicate a potential security risk. These areas may include anomalies in the shape or contour of the body, unusual density patterns, or the presence of foreign objects.
The airport body scanner image is carefully analyzed by trained security officers who are skilled at interpreting the images and identifying potential threats. They are trained to differentiate between normal anatomical structures and objects that may pose a risk to aviation security.
The image can reveal the presence of concealed weapons, explosives, drugs, or other prohibited items on the body. Additionally, the scanner image can also assist in identifying hidden objects within body cavities, such as swallowed items or objects concealed in body orifices.
It’s important to remember that the scanner image is one of several tools used in the airport security screening process. If a potential threat or anomaly is detected in the image, further investigation and additional screening procedures may be required, such as a physical pat-down search or thorough examination of personal belongings.
Overall, the airport body scanner image plays a crucial role in aviation security by enabling security officers to identify potential threats and ensure the safety of passengers and crew members.
Can the Airport Body Scanner See Through Clothes?
One common question that arises regarding airport body scanners is whether or not they can see through clothes. The answer is both yes and no, depending on the specific technologies used in the scanner.
Millimeter-wave scanners, which are the most commonly used type of airport body scanners, do not technically “see through” clothes. Instead, they use harmless radio frequency waves to penetrate clothing and create a 3D image of the body. These waves are designed to reflect off the body’s surface and provide information about the object’s shape and texture. However, the waves cannot penetrate the body or see beneath the clothing to reveal explicit details.
Backscatter scanners, on the other hand, use low-energy X-rays to create images. While these scanners can penetrate clothing to some extent, the level of detail they provide is limited. Backscatter scanners primarily highlight object shapes, contours, and irregularities on the body’s surface, rather than providing explicit visualizations of what lies beneath the clothing.
It is important to note that both types of scanners are designed to respect passenger privacy and ensure a balance between security needs and individual rights. The images generated by airport body scanners are generic and do not depict explicit details such as private body parts. Instead, they focus on identifying potential threats or anomalies that may warrant further inspection.
Additionally, security officers who review the scanner images are trained to interpret them for any signs of concealed objects or abnormalities without compromising passenger privacy. If a potential threat is identified, further inspection procedures, such as physical pat-down searches or enhanced screenings, may be implemented to ensure the safety of all individuals involved.
What Can’t the Airport Body Scanner See?
While airport body scanners are highly advanced and effective in detecting potential threats, there are some limitations to what they can see. These limitations are in place to ensure passenger privacy and to maintain a balance between security and individual rights.
Firstly, airport body scanners are specifically designed not to reveal explicit details of a person’s body. The images generated by these scanners are intentionally generic and do not provide a clear view of private body parts. Instead, the focus is on identifying any potential threats or anomalies that may be concealed on or within the body.
Furthermore, airport body scanners have varying abilities to detect non-metallic or low-density materials. While they can effectively detect most metallic items, such as weapons or firearms, they may not be as efficient in detecting plastic or liquid substances. The technology used in airport body scanners is primarily geared towards identifying solid objects, so certain non-metallic items may not be as easily visible in the scan.
Another limitation is that airport body scanners are unable to see beneath the skin or detect objects that are hidden internally, such as swallowed or implanted items. These scanners primarily analyze the external surface of the body and cannot penetrate the skin to identify objects that are concealed within body cavities or beneath the skin’s surface.
Moreover, airport body scanners may not be able to detect certain types of explosive materials or chemical substances that do not have a significant density or are concealed in a manner that makes them difficult to identify. While the scanners are designed to detect a wide range of potential threats, it is not foolproof and there is always the possibility that some substances may go undetected.
It’s important to remember that airport security is a multi-layered process, and body scanners are just one component of the overall screening procedures. If there are any suspicions or concerns about a passenger’s belongings or behavior, additional screening techniques, such as physical searches and explosive trace detection systems, may be employed to ensure the highest level of security.
Are There Privacy Concerns with Airport Body Scanners?
Privacy concerns have been a topic of discussion when it comes to airport body scanners. While these scanners are an important tool in ensuring aviation security, it is crucial to address any potential privacy issues that may arise.
One of the main concerns is the fear that airport body scanners may intrude on passengers’ privacy by revealing explicit details of their bodies. However, it’s important to note that the images generated by these scanners are intentionally designed to be generic and do not depict explicit visualizations of private body parts. The focus is on identifying potential threats or anomalies that may be concealed on or within the body, rather than providing visualizations of personal attributes.
To further protect passenger privacy, the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) has implemented measures to ensure that the individuals reviewing the scanner images are located in a remote location away from the screening area. They are unable to see the passenger being scanned and the scanner operator cannot view the image once the screening is complete, thus maintaining anonymity during the screening process.
Additionally, the images produced by airport body scanners are viewed in real-time by security officers who are specially trained to interpret the images. These officers have strict guidelines in place to ensure the protection of passenger privacy and are trained to focus on potential threats rather than personal details.
Another important aspect is the deletion of the scanned images. Once the image has been reviewed and cleared by security officers, it is immediately deleted from the system. This is done to safeguard passenger privacy and prevent any potential misuse of the images.
It’s worth noting that the use of airport body scanners is governed by strict regulations and legal frameworks to ensure privacy protection. These regulations usually include provisions that prohibit the storage or sharing of scanner images, as well as establishing penalties for any unauthorized use of such information.
Furthermore, alternative measures are available for individuals who may have concerns about going through an airport body scanner. Passengers have the option to request alternative screening methods, such as a physical pat-down, which ensures privacy while still meeting security requirements.
While privacy concerns are valid, it is important to recognize the efforts made to address them and maintain a balance between security and individual rights. The objective of airport body scanners is to enhance aviation security while respecting passenger privacy.
Are Airport Body Scanners Safe?
Ensuring the safety and well-being of passengers is of paramount importance when it comes to airport body scanners. Safety concerns surrounding these scanners primarily revolve around the potential health risks associated with their use.
It’s important to note that airport body scanners utilize non-ionizing radiation, which means they do not emit harmful levels of radiation that can cause damage to the body’s cells or DNA. Millimeter-wave scanners use low-power radio frequency waves, while backscatter scanners use low-energy X-rays. Both types of scanners adhere to established safety guidelines and regulations to ensure that the emitted radiation is within safe limits.
The radiation emitted by airport body scanners is significantly lower than the radiation a person is exposed to during a typical airplane flight or a dental X-ray. The levels of radiation are carefully controlled and kept well below any concerning thresholds to ensure passenger safety.
Moreover, extensive testing and evaluation of these scanners have been conducted to ensure their safety. These evaluations have been performed by independent agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, to verify the safety of the scanner technologies used in airports.
The safety of airport body scanners is also emphasized by the fact that millions of passengers go through these scanners without experiencing any health issues. The scanners are designed to emit low levels of radiation for a very short duration, minimizing any potential risk to passengers.
Furthermore, precautions are taken to ensure the safety of vulnerable individuals, such as pregnant women or those with medical concerns. Alternative screening options, such as physical pat-downs or hand-held metal detectors, are available for passengers who may have concerns about going through the airport body scanner.
While airport body scanners are considered safe, it is important that proper maintenance and calibration are carried out to ensure their continued safety and efficacy. Regular inspections and quality assurance measures are implemented to monitor the performance of the scanners and maintain compliance with safety standards.
Overall, the use of airport body scanners is subject to rigorous safety regulations and continual assessment to ensure that they pose no significant health risks to passengers. These scanners offer an effective and efficient way to enhance aviation security while prioritizing and maintaining passenger safety.
How Do Airport Security Officers Analyze the Scanner Images?
When it comes to airport security, analyzing the scanner images generated by airport body scanners is a critical task performed by trained security officers. These officers play a vital role in identifying potential threats and ensuring the safety of passengers and crew members.
Upon receiving the scanner image, security officers closely examine the details and anomalies present in the image. They are trained to interpret the images effectively and efficiently, often employing specific protocols and guidelines to aid in the analysis process.
The analysis of the scanner images involves several key steps:
1. Image Recognition: Security officers are trained to quickly recognize common objects and concealed items that may pose a security risk. By identifying specific shapes and patterns in the image, they can promptly distinguish between harmless objects, such as clothing or personal belongings, and potential threats.
2. Threat Assessment: Following object recognition, security officers assess the potential threat level associated with any identified objects or anomalies. They consider various factors, such as the shape, location, and density of the objects, to determine whether they pose a security risk that requires further investigation.
3. Collaboration and Communication: In complex or ambiguous cases, security officers may consult with their colleagues or supervisor to seek additional opinions or confirmation. Effective communication among security personnel ensures a thorough analysis of the scanner images and minimizes the chances of missing potential threats.
4. Decision-Making: Based on their analysis, security officers make informed decisions regarding the nature of potential threats. They may decide to conduct further screening procedures, such as a physical pat-down search, additional inspection of personal belongings, or applying explosive trace detection techniques, to obtain additional information and confirm any suspicions.
It is worth noting that the training of security officers includes regular updates and ongoing education to keep them well-informed about emerging threats and evolving security protocols. This continuous training helps officers improve their skills in analyzing scanner images and staying vigilant against new potential risks.
Moreover, to enhance consistency and accuracy, some airports have introduced automated image recognition software and algorithms. These tools assist security officers in quickly identifying potential threats while minimizing the margin of human error in the analysis process.
Can the Airport Body Scanner Detect Medical Devices or Implants?
Airport body scanners are designed to detect potential threats or anomalies on a person’s body, including concealed objects or substances. In the process of scanning, airport body scanners may detect the presence of medical devices or implants, depending on various factors.
Most medical devices and implants are made from materials that are visible to the scanners. If a medical device or implant contains metallic components, such as pacemakers, artificial joints, or plates, they are likely to be detected by the airport body scanners. These metallic components can reflect the waves or scatter the X-rays emitted by the scanner, leading to their identification on the scanner image.
However, it is worth noting that not all medical devices or implants may be readily visible to the airport body scanners. Devices or implants made from non-metallic materials, such as plastic or ceramic, may not be easily detected by the scanners as they do not significantly affect the scanner’s ability to penetrate or reflect waves.
In such cases, individuals with non-metallic medical devices or implants are advised to inform the security officers before going through the scanner. This allows the officers to carry out additional screening procedures, such as a physical pat-down or a manual inspection of the device, to ensure security while respecting privacy.
To facilitate the screening process, passengers with medical devices or implants are encouraged to carry medical documentation or identification to verify the presence and necessity of the device. This helps security officers understand the purpose and nature of the medical device, allowing for a smoother and more efficient screening experience.
It is important to remember that the primary aim of airport body scanners is to detect potential security threats, while ensuring the safety and comfort of passengers. Special considerations are made for individuals with medical devices or implants to balance security requirements with their specific needs.
If there are any concerns or uncertainties regarding the scanning process or the impact on medical devices, it is recommended to consult with healthcare providers, device manufacturers, or the airport authorities in advance to receive the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Can the Airport Body Scanner Identify Specific Objects or Substances?
Airport body scanners are designed to detect potential threats or anomalies on a person’s body, but they are not capable of identifying specific objects or substances with absolute certainty. While these scanners can highlight areas of concern, further investigation and additional screening measures may be necessary to determine the nature of the detected object or substance.
Airport body scanners primarily use advanced imaging technology, such as millimeter-wave scanners or backscatter scanners, to generate images of the body. These scanners focus on providing security officers with a clear view of potential threats or irregularities, rather than specific details about the detected objects or substances.
When a potential threat is detected on the scanner image, security officers must rely on their training and experience to determine the appropriate course of action. They may conduct further examinations, such as physical pat-down searches or enhanced screening techniques, to collect additional information about the identified object or substance.
It is important to note that while airport body scanners can indicate the presence of certain materials or substances, they cannot definitively identify them. For example, an airport body scanner may detect the presence of a dense object that requires further inspection, but it cannot specify whether the object is a weapon, an electronic device, or any other specific item.
Moreover, airport body scanners are primarily designed to identify threats related to security concerns, such as concealed weapons, explosives, or other prohibited items. They may not be optimized or calibrated to detect substances or materials that are unrelated to aviation security, such as illicit drugs or specific chemicals.
To address these limitations, airports often employ additional screening methods, such as explosive trace detection swabs or canine units, to further investigate and identify specific substances or materials that may pose a threat to aviation security.
It is worth noting that the primary objective of airport body scanners is to enhance aviation security by detecting potential threats and ensuring the safety of passengers and crew members. While the scanners provide valuable information to security officers, the identification of specific objects or substances may require additional screening techniques and procedures.
What Are the Alternatives to Airport Body Scanners?
Airport body scanners are just one component of a multi-layered security process implemented at airports worldwide. While they are effective in detecting potential threats, there are alternative screening methods available that can be used in conjunction with or in place of body scanners.
1. Metal Detectors: Metal detectors are widely used in airports to identify metallic objects on a person’s body. They emit a magnetic field and detect changes in that field caused by metal objects. Metal detectors are effective in detecting weapons, knives, or firearms, but they may not detect non-metallic items or explosives that do not contain significant amounts of metal. Therefore, they are often used together with body scanners for a more comprehensive screening process.
2. Physical Pat-Downs: Physical pat-down searches are a manual screening procedure conducted by trained security officers. They involve a comprehensive examination of a person’s body, including clothing, pockets, and extremities. Pat-downs are typically performed if an individual sets off a metal detector, refuses to go through a body scanner, or triggers suspicion during the screening process. Physical pat-downs provide a thorough check for any concealed items or anomalies that may pose a security risk.
3. Explosive Trace Detection (ETD): ETD is a screening technique that involves swabbing surfaces, such as bags or personal belongings, and testing them for the presence of explosive residue. The swabs are then analyzed using specialized equipment to identify any trace amounts of explosives. ETD is commonly used at security checkpoints to complement other screening methods and provide an additional layer of security.
4. Canine Units: Dogs trained to sniff out explosives or illicit substances are employed at airports as part of security measures. These highly trained canine units work alongside security officers to detect and alert on the presence of prohibited items or substances. Canine units provide an efficient and effective way to detect contraband and enhance overall security.
5. Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analysis and observation techniques are utilized to identify suspicious behaviors or indications of potential threats. Trained security officers observe individuals’ actions, body language, and interactions to detect patterns or abnormalities that may warrant further scrutiny. This approach relies on the expertise of skilled officers to identify potential risks based on observed behaviors rather than relying solely on technology.
It is important to understand that the combination and implementation of these alternative screening methods may vary depending on the country, airport, and specific security protocols in place. Airports often adapt their security measures based on the current threat landscape and evolving technologies to ensure the highest level of safety for passengers and crew members.