What is a SIM Card?
A Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card is a small, removable smart card that is inserted into a mobile device, such as a smartphone or tablet, to connect it to a mobile network. The SIM card securely stores the subscriber's identity and allows the user to access the network's services, including making calls, sending text messages, and using mobile data.
The SIM card contains essential information, such as the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) number, which uniquely identifies the subscriber to the network, as well as the Integrated Circuit Card Identifier (ICCID), which is a unique serial number for the SIM card itself. Additionally, the SIM card holds key authentication and encryption information, enabling secure communication with the mobile network.
SIM cards come in various sizes, including the standard SIM, micro-SIM, and nano-SIM, to accommodate different mobile devices. The SIM card's primary function is to authenticate the subscriber to the network and enable access to the carrier's services, making it an indispensable component of mobile communication.
The SIM card also stores contact information and text messages, allowing users to transfer their contacts and messages between devices by simply moving the SIM card. This feature is especially useful when upgrading to a new phone or replacing a lost or damaged device.
In essence, a SIM card serves as a crucial link between the mobile device and the mobile network, facilitating secure and personalized communication services for the subscriber. Understanding the role and significance of a SIM card is fundamental to comprehending its potential for tracking and securing mobile devices.
How Does a SIM Card Work?
A SIM card operates as a key component in the authentication and identification process within a mobile network. When a user inserts a SIM card into a compatible device and powers it on, the device communicates with the mobile network to establish a secure connection. The SIM card provides the necessary credentials to verify the user’s identity and grant access to the network’s services.
Upon initialization, the mobile device and the SIM card engage in a mutual authentication process with the mobile network. The SIM card presents its IMSI and authentication key to the network, which then challenges the SIM card to prove its authenticity. This challenge-response mechanism ensures that only valid SIM cards and authorized devices can access the network, safeguarding against unauthorized usage and fraudulent activities.
Once the authentication is successful, the SIM card enables the device to register with the network, allowing the user to make calls, send messages, and utilize mobile data services. The SIM card securely stores the user’s subscriber information and encryption keys, ensuring that communications are protected from interception and unauthorized access.
Furthermore, the SIM card plays a pivotal role in roaming scenarios, as it allows subscribers to connect to foreign networks while traveling. By authenticating with the visited network using the SIM card’s credentials, users can access voice and data services seamlessly, extending the reach of their home network to international destinations.
Overall, the SIM card acts as a trusted entity that validates the user’s identity and authorizes their access to the mobile network’s resources. Its robust security features and essential role in network authentication make it an integral part of mobile communication, ensuring that subscribers can enjoy reliable and secure connectivity wherever they go.
Why Would You Want to Track Your SIM Card?
Tracking your SIM card can be beneficial for several reasons, ranging from personal security to device recovery. Here are some compelling motives for monitoring the whereabouts of your SIM card:
- Security and Safety: By tracking your SIM card, you can enhance personal safety and security. In case of an emergency or unforeseen circumstances, knowing the location of your SIM card-equipped device can aid in obtaining assistance or notifying authorities of your whereabouts.
- Device Theft Prevention: Tracking your SIM card can serve as a deterrent to potential thieves. In the event of device theft, the ability to trace the SIM card’s location can assist law enforcement in recovering the stolen device and apprehending the culprits.
- Asset Management: For businesses and organizations, tracking SIM cards within company-issued devices can facilitate asset management and inventory tracking. Knowing the real-time location of devices can streamline operations and mitigate the risk of loss or misuse.
- Family Safety: Tracking family members’ SIM cards can provide peace of mind for parents and caregivers, allowing them to monitor the whereabouts of loved ones, especially in cases of minors or elderly family members who may require assistance.
- Geolocation Services: Leveraging SIM card tracking can enable location-based services, such as geotagging in photography, location sharing in messaging apps, and accessing location-specific information tailored to the user’s whereabouts.
Overall, the ability to track your SIM card offers a range of practical advantages, from enhancing personal security to optimizing asset management and location-based services. Whether for individual or organizational purposes, the capability to monitor the location of SIM card-equipped devices can provide valuable insights and peace of mind in various scenarios.
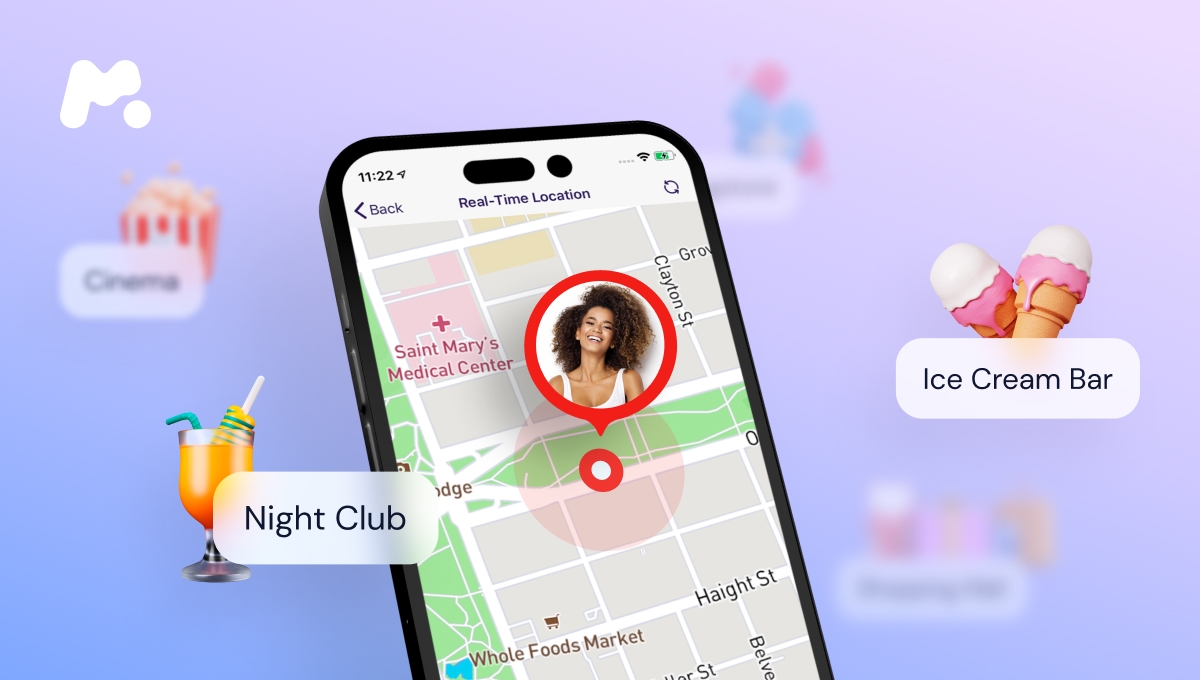
Can You Track Your SIM Card’s Location?
Tracking the precise location of a SIM card is a common inquiry, often associated with concerns about security, safety, and device management. While the SIM card itself does not have built-in GPS or location-tracking capabilities, the mobile device to which it is inserted can be used to determine its location through various methods:
- Cellular Network Triangulation: Mobile network operators can approximate the location of a SIM card-equipped device by triangulating its position based on the signals received from nearby cell towers. This method provides an estimated location within a certain radius and is commonly used for emergency services and network management.
- GPS-Enabled Devices: Smartphones and other GPS-enabled devices can utilize the Global Positioning System (GPS) to accurately determine their location. When a SIM card is inserted into a GPS-capable device, the device can provide real-time location data, which can be accessed through mapping and location-based services.
- Location-Based Services: Many mobile applications and services offer location tracking and geolocation features, leveraging the device’s GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular network data to provide accurate location information. These services often require user consent and may be subject to privacy settings and permissions.
- Remote Device Management: Some mobile device management solutions and anti-theft applications offer remote tracking and location features for SIM card-equipped devices. These tools enable users to locate, lock, or remotely wipe their devices, providing added security and control in case of loss or theft.
It is important to note that the ability to track a SIM card’s location is contingent upon the device’s capabilities, network coverage, and user permissions. Additionally, privacy considerations and legal regulations may govern the use of location tracking and geolocation services, necessitating informed and responsible usage.
While the SIM card itself does not possess inherent location-tracking functionality, the devices to which it is linked can leverage various technologies and services to determine and share their locations. Understanding the available tracking methods and their implications is essential for utilizing location-based features effectively and responsibly.
How to Track Your SIM Card
Tracking the location of a SIM card involves leveraging the capabilities of the associated mobile device and utilizing location-based services and technologies. Here are several methods and considerations for tracking your SIM card:
- GPS-Enabled Devices: If your mobile device is equipped with GPS functionality, you can utilize location-tracking features to determine the real-time whereabouts of the device. Many smartphones offer built-in GPS capabilities, which can be accessed through mapping applications and location services.
- Location-Based Apps: Numerous mobile applications provide location-sharing and tracking features, allowing users to monitor the positions of their devices and share their locations with trusted contacts. These apps may require user consent and may offer additional functionalities such as geofencing and location history tracking.
- Mobile Device Management Solutions: Employing mobile device management (MDM) solutions or anti-theft applications can enable remote tracking and management of SIM card-equipped devices. These tools often offer features such as remote lock, wipe, and location tracking, providing added security and control in case of loss or theft.
- Network-Based Location Services: Mobile network operators can utilize cellular network data and triangulation techniques to approximate the location of SIM card-equipped devices. This method, known as network-based location services, can provide an estimated location within the coverage area of the mobile network.
- Privacy and Consent: When tracking a SIM card’s location, it is essential to consider privacy implications and obtain the necessary consent from the device’s user. Respecting privacy settings, permissions, and legal regulations is crucial when utilizing location-tracking features and services.
It is important to approach SIM card tracking with a responsible and informed mindset, considering the privacy and security implications of location monitoring. By leveraging the capabilities of GPS-enabled devices, location-based applications, and network-based services, users can track the whereabouts of their SIM card-equipped devices and enhance their security and management capabilities.
What to Do If Your SIM Card is Lost or Stolen
If you discover that your SIM card-equipped device is lost or stolen, taking prompt action is essential to safeguard your personal information and mitigate the risk of unauthorized usage. Here are the recommended steps to follow if your SIM card is lost or stolen:
- Report the Loss or Theft: Contact your mobile network operator immediately to report the loss or theft of your SIM card. Provide them with the necessary details, such as your account information and the affected phone number, to initiate the suspension of services associated with the SIM card.
- Secure Your Accounts: If your device contained sensitive information or access to online accounts, change the passwords for those accounts to prevent unauthorized access. This includes email, social media, and financial accounts linked to the lost or stolen device.
- Remote Lock and Wipe: If your device supports remote management features, such as remote lock and data wipe, use these functions to secure your personal data and prevent misuse of the device. Many anti-theft applications and mobile device management solutions offer these capabilities.
- Request a Replacement SIM Card: Contact your mobile network operator to request a replacement SIM card. Once the replacement SIM card is activated, you can continue using your existing phone number and services on a new SIM card-equipped device.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Keep a close eye on your accounts and billing statements for any unusual or unauthorized activity. Report any suspicious charges or usage to your mobile network operator and consider reviewing your device’s location history if available.
Being proactive and thorough in addressing the loss or theft of a SIM card-equipped device can help mitigate the potential impact of such incidents and protect your personal information. By promptly reporting the loss, securing your accounts, and taking advantage of remote management features, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and maintain control over your mobile services.