What is Task Manager?
Task Manager is a system utility included in the Windows operating system that allows users to monitor and manage the various processes and applications running on their computer. It provides valuable insights into the performance and resource usage, helping users identify and troubleshoot issues that may be impacting their system’s efficiency and speed.
With Task Manager, users can view real-time information about the running processes, track CPU, memory, and disk usage, manage startup programs, monitor network activity, and end tasks or processes that are causing problems. It serves as a powerful tool for both regular users and technical professionals, allowing them to have better control over their system’s performance.
The Task Manager interface consists of multiple tabs, each providing detailed information about different aspects of the system. The default view shows the Processes tab, which displays a list of all currently running processes, along with their corresponding CPU and memory usage. This tab is particularly useful when identifying resource-hungry applications or determining if any processes are consuming an unusually high amount of system resources.
Another important tab is the Performance tab, which provides a comprehensive overview of CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization. Users can use this tab to monitor how their system is performing in real-time and identify any bottlenecks or issues that might be causing slowdowns or crashes.
Task Manager also includes additional tabs such as App History, Startup, Users, Details, Services, Networking, and Disk, each offering specific insights and controls for different aspects of the system.
Overall, Task Manager is a vital tool for managing and troubleshooting a Windows computer. It provides users with valuable information about the processes and services, allows them to control resource allocation, and helps them optimize system performance. Whether you are a regular user or a technical professional, Task Manager is an essential utility that can significantly enhance your computing experience.
Opening Task Manager
Opening Task Manager is a simple and straightforward process that can be done in several ways, depending on your preference and the version of Windows you are using. Here are some common methods to open Task Manager:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard simultaneously. This is the quickest and most direct way to open Task Manager, and it works on all versions of Windows.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Del and then click on “Task Manager” from the list of options. This method is applicable to Windows 7 and earlier versions.
- Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” from the context menu that appears. This method works on all versions of Windows.
- Press Windows + X to open the quick access menu, and then click on “Task Manager” in the list. This method is available on Windows 8 and later versions.
- Search for “Task Manager” in the Windows search bar and click on the displayed result.
Once Task Manager is launched, you will be presented with its user-friendly interface, which provides an overview of the system’s current processes and performance. The default tab that opens is the “Processes” tab, where you can view a list of all the running applications and background processes on your computer.
It’s worth noting that Task Manager can be customized according to your needs. You can resize the window, rearrange columns, sort processes by different criteria (e.g., CPU usage, memory usage, process name), and even end tasks or processes directly from the Task Manager window.
Furthermore, Task Manager can also be accessed in a more advanced mode, called “Task Manager for advanced users,” which provides additional information and features. To switch to this mode, click on the “More details” button at the bottom of the Task Manager window.
Opening Task Manager is the first step in utilizing its powerful features to monitor and manage the processes and performance of your Windows computer. Whether you need to troubleshoot issues, monitor resource usage, or close unresponsive applications, Task Manager is a valuable tool at your disposal.
The Processes Tab
The Processes tab in Task Manager provides a comprehensive view of all the running processes and applications on your Windows computer. It is one of the most frequently used tabs and offers valuable insights into the resource usage, performance, and impact of each process.
When you open the Processes tab, you will see a list of running processes with corresponding details such as the process name, PID (Process ID), CPU usage, memory usage, and more. By default, the processes are sorted by their current CPU usage, with the highest consuming processes displayed at the top.
Here are some key features and functions available in the Processes tab:
- End Task: You can right-click on a process and select “End Task” to terminate a specific process. This can be useful when an application becomes unresponsive or is causing system issues.
- Set Priority: By right-clicking on a process, you have the option to set its priority. This determines how much CPU time and resources the process will receive.
- Expand/Collapse Processes: You can click on the small arrow next to a process to expand it and view its associated subprocesses. This can be helpful in identifying which processes are linked to a particular application or service.
- Search Online: If you find a process that you’re not familiar with, you can right-click on it and select “Search Online” to quickly look up information about it on the internet.
- Resource Usage Details: You can click on the “CPU” or “Memory” column header to sort processes based on their resource usage. This allows you to identify any processes that may be consuming excessive CPU or memory and affecting system performance.
The Processes tab also provides options to customize the display and information presented. You can select which columns to show or hide, adjust the update speed of the displayed data, and even analyze the impact of each process on the system’s performance using graph views.
Overall, the Processes tab in Task Manager is a powerful tool for managing and monitoring the running processes and applications on your Windows computer. It allows you to identify resource-intensive processes, terminate unresponsive applications, and gain insights into how each process is impacting system performance. If you’re experiencing slow response times, high CPU usage, or other performance issues, the Processes tab should be your go-to resource for troubleshooting and optimizing your system.
The Performance Tab
The Performance tab in Task Manager provides a detailed overview of the performance of your computer, including CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity, and network activity. It is a valuable tool for monitoring and analyzing system performance in real-time.
When you open the Performance tab, you will see multiple sections displaying graphs and charts for various hardware components and resources. Here are the key sections and features available in the Performance tab:
- CPU: The CPU section displays the current utilization of your computer’s processor. You can view the overall CPU usage as well as individual graphs for each processor core, if applicable. This section helps you monitor the CPU load and identify any processes or applications that are causing high CPU usage.
- Memory: The Memory section provides information about the RAM (Random Access Memory) usage on your computer. You can see the total available memory, the amount of memory in use, and the amount of memory that is free. This section helps you monitor memory usage and identify any processes or applications that may be consuming excessive memory.
- Disk: The Disk section shows the activity of your computer’s storage devices, such as hard drives or solid-state drives. You can view the current read and write speeds, as well as the percentage of disk utilization. This section allows you to monitor disk activity and identify any processes or applications that are causing high disk usage or slowing down your system.
- Network: The Network section displays real-time information about the network activity on your computer. You can see the current network utilization, both in terms of incoming and outgoing data. This section helps you monitor network performance and identify any processes or applications that may be consuming excessive network bandwidth.
Task Manager also provides options to customize the view in the Performance tab. You can select different graph types, display or hide specific hardware components, and even save performance data for later analysis.
The Performance tab is a powerful tool for troubleshooting and optimizing system performance. By monitoring the CPU, memory, disk, and network usage, you can identify potential bottlenecks, resource-hungry processes, or network-related issues that may be affecting the performance of your computer.
Whether you’re a regular user wanting to ensure your computer is running smoothly or a technical professional needing to diagnose performance problems, the Performance tab in Task Manager provides the necessary information and tools to help you monitor and optimize your system’s performance.
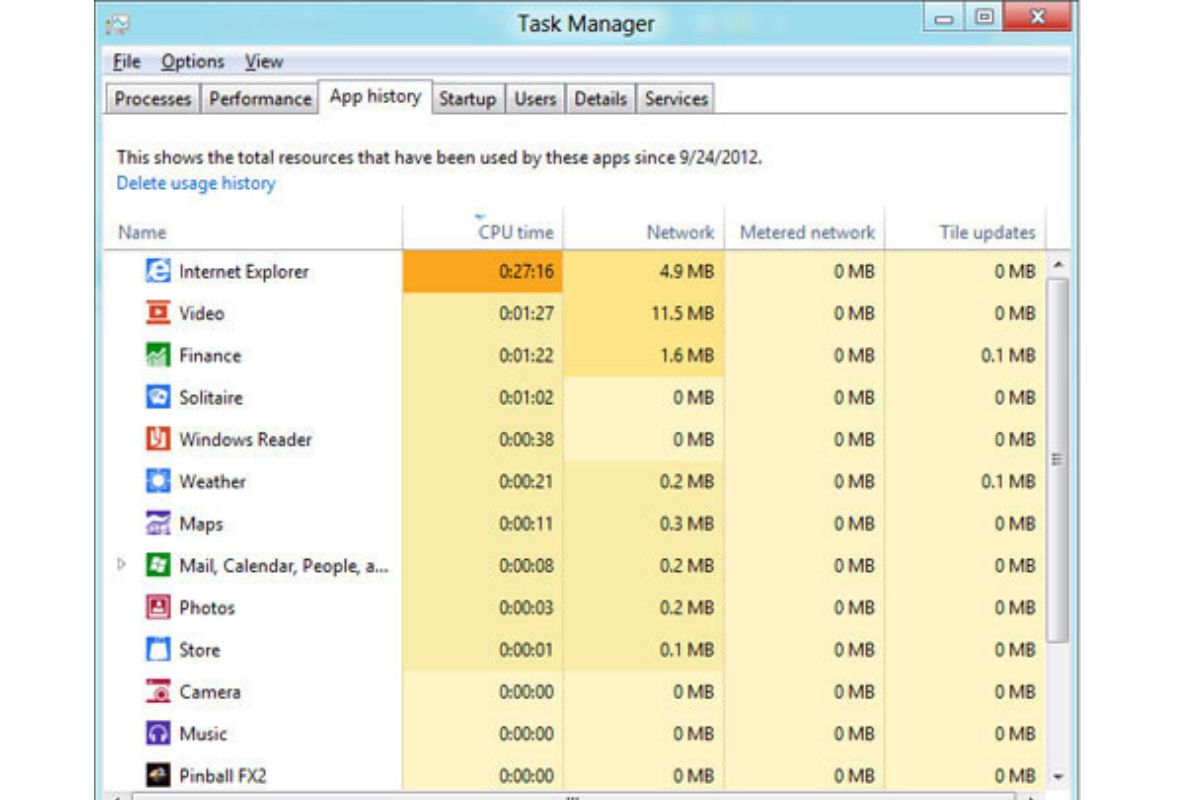
The App History Tab
The App History tab in Task Manager provides a comprehensive view of the resource usage history of applications on your Windows computer. It allows you to track the resource consumption of each application over time, helping you identify resource-hungry apps and optimize system performance.
When you open the App History tab, you will see a list of applications along with resource usage details such as CPU time, network usage, and metered network usage. This information is collected and displayed for each application based on their resource utilization history.
Here are the key features and information available in the App History tab:
- CPU Time: This column shows the total amount of CPU time used by each application since it was last reset. CPU time is a measure of the processor resources consumed by an application.
- Network Usage: This column displays the total amount of data sent and received by each application over a network connection since it was last reset. It provides insights into the network activity of applications and helps identify network-intensive apps.
- Metered Network Usage: This column shows the network usage, specific to metered connections, for each application. Metered connections are network connections with data usage restrictions, such as mobile broadband connections. This information is helpful for monitoring data usage on such connections and managing bandwidth consumption.
- Reset Usage: You can use the “Reset Usage” option to clear the resource usage statistics for all or selected applications. This allows you to start monitoring resource usage from a clean slate.
The App History tab enables you to evaluate the impact of different applications on system resources over time. By analyzing CPU time and network usage, you can assess the efficiency of various applications and make informed decisions about which ones may need optimization or closer monitoring.
While the App History tab provides valuable insights, it is important to note that not all applications will have data displayed in this tab. Only certain types of applications, such as Windows Store apps or universal apps, will have resource usage history recorded.
To summarize, the App History tab in Task Manager offers a historical view of resource usage for applications on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor CPU time and network usage, aiding in the identification of resource-intensive apps and optimization of system performance. Utilizing this information, you can make informed decisions about managing and optimizing the applications on your computer.
The Startup Tab
The Startup tab in Task Manager provides a convenient way to manage the programs that automatically start when you boot up your Windows computer. It allows you to enable or disable startup programs, helping you control the applications that run in the background and impact system performance.
When you open the Startup tab, you will see a list of programs that are set to launch automatically when your computer starts. Each program is displayed with its name, publisher, status (enabled or disabled), and startup impact rating. The startup impact rating indicates how much the program affects the startup time of your computer.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Startup tab:
- Enable/Disable Startup Programs: You can right-click on a program and select either “Enable” or “Disable” to control whether it starts automatically with your computer. Disabling unwanted or unnecessary startup programs can help speed up the boot time and reduce system resource usage.
- Startup Impact Rating: The Startup tab provides a rough estimate of how much each program impacts the startup time of your computer. Programs are categorized as Low, Medium, or High impact. This helps you identify programs that have a significant impact on startup and prioritize which ones to disable if necessary.
- Search Online: If you’re unsure about a specific startup program and need more information, you can right-click on it and select “Search Online” to perform a quick internet search to gather more details about the program and its purpose.
Managing startup programs is essential for optimizing system performance and reducing unnecessary resource consumption. Disabling programs that you don’t need to start automatically can significantly improve the boot time of your computer and free up system resources for other tasks.
It’s important to note that not all programs listed in the Startup tab should be disabled. Some applications may be necessary for the proper functioning of your system or important for specific tasks or software you use regularly. It’s recommended to exercise caution when disabling startup programs and only disable those that you are certain are unnecessary.
In addition to managing individual startup programs, the Task Manager’s Startup tab also provides a link to the “Open Task Manager” feature in the Startup section of the Windows Settings. This allows you to access an extended set of options for managing startup programs and their impact on your system.
In summary, the Startup tab in Task Manager offers a convenient way to manage the programs that automatically start with your Windows computer. By enabling or disabling startup programs, you can optimize system performance, reduce startup time, and allocate system resources more efficiently.
The Users Tab
The Users tab in Task Manager provides information about the users who are currently logged into your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor user activity, manage user sessions, and troubleshoot any issues related to user accounts.
When you open the Users tab, you will see a list of all logged-in users, along with their usernames and session status. Each user session is displayed separately, showing details such as session ID, session type, and the time when the session started.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Users tab:
- View User Information: The Users tab provides basic information about each logged-in user, including their username and session ID. You can use this information to identify who is currently using the computer.
- Monitor User Activity: By observing the session status and start time, you can monitor user activity and track how long each user has been logged in. This can be helpful for managing shared computers or identifying any unusual or unauthorized user logins.
- Disconnect User Sessions: If necessary, you have the option to disconnect a user session from the Users tab. This can be useful when troubleshooting issues related to a specific user account or when you need to forcefully terminate a user session.
- Manage User Accounts: Task Manager’s Users tab serves as a gateway to the user account management features in the Control Panel. By clicking on the “Open User Accounts” link, you can access additional options for managing user accounts, including creating new accounts, changing passwords, or modifying user permissions.
The Users tab is particularly helpful in environments where multiple users share a single computer or in scenarios where you suspect unauthorized access to your system. By keeping an eye on the Users tab, you can effectively manage user sessions, troubleshoot user-related issues, and ensure the security and integrity of your computer.
It’s important to note that the availability and functionality of the Users tab may vary depending on the edition of Windows you are using. Some advanced user management features may only be available in certain versions of Windows, such as enterprise or professional editions.
In summary, the Users tab in Task Manager provides valuable insights into the current logged-in users on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor user activity, manage user sessions, and access user account management options. By utilizing the Users tab, you can ensure the security and efficient utilization of your computer in multi-user environments.
The Details Tab
The Details tab in Task Manager provides a comprehensive view of the running processes on your Windows computer, offering detailed information about each process and giving you more control over their behavior and resource usage.
When you open the Details tab, you will see a list of all the processes currently running on your computer. Each process is displayed with its name, process ID (PID), CPU usage, memory usage, and other relevant details.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Details tab:
- Process Management: You can right-click on a process in the list to access various management options. These options include ending the process, setting priority, analyzing wait chain, searching online for more information, and more. This provides you with control over individual processes and allows you to troubleshoot any performance or stability issues related to a specific process.
- Column Selection: Task Manager allows you to select which columns to display in the Details tab. You can choose from a wide range of columns, such as process name, PID, CPU usage, memory usage, disk activity, and more, to customize the view based on your specific monitoring needs.
- Sorting and Filtering: You can sort the processes based on different criteria, such as CPU usage, memory usage, or process name, by clicking on the corresponding column header. Additionally, you can filter the process list by typing keywords in the search box, allowing you to quickly find specific processes.
- Create Dump File: Task Manager allows you to create a dump file for a selected process. This can be useful for further analysis or troubleshooting when diagnosing application crashes or system issues.
- Resource Usage and Performance: The Details tab provides insights into CPU and memory usage of each individual process, enabling you to identify resource-intensive processes and monitor their impact on system performance.
The Details tab offers an advanced level of process management and monitoring, giving you granular control over the running processes on your computer. It allows you to easily identify and troubleshoot resource-heavy or potentially problematic processes, ultimately enhancing system stability and performance.
It’s important to exercise caution when managing processes in the Details tab, as ending critical system processes or terminating processes without proper knowledge can lead to unexpected consequences. You should only modify or terminate processes if you are certain of their purpose and the potential impact on your system.
In summary, the Details tab in Task Manager provides a comprehensive view of running processes on your Windows computer. It offers advanced management options, customizable column selection, sorting, and filtering capabilities. By utilizing the features of the Details tab, you can effectively manage and monitor processes, troubleshoot issues, and optimize system performance.
The Services Tab
The Services tab in Task Manager provides a comprehensive overview of the background services running on your Windows computer. It allows you to manage and monitor system services, making it an essential tool for optimizing system performance and troubleshooting service-related issues.
When you open the Services tab, you will see a list of services that are currently running on your computer. Each service is displayed with its name, description, status (running or stopped), and the group it belongs to.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Services tab:
- Service Control: You can right-click on a service in the list to access a variety of control options. These options include starting, stopping, restarting, or disabling a service. This level of control allows you to manage the behavior and availability of services based on your specific needs.
- Service Details: Task Manager provides detailed information about each service in the list, including its description, service group, and process ID (PID). This information helps you understand the purpose and functionality of each service.
- Service Startup Mode: The Services tab displays the startup mode of each service, indicating how and when the service starts. The different startup modes include Automatic (started automatically with the system), Manual (started only when required), and Disabled (not started at all). This allows you to control the behavior and resource usage of services during system startup.
- Sorting and Filtering: You can sort the services based on different criteria, such as name, status, or startup type, by clicking on the corresponding column header. Additionally, you can filter the service list by typing keywords in the search box, making it easier to find specific services.
- Service Description: The Services tab provides a brief description of each service, helping you understand its purpose and significance in the overall system functionality. This information is useful when determining which services are essential for system operation and which ones can be disabled or modified.
The Services tab is an invaluable resource for managing and troubleshooting services on your Windows computer. It allows you to control and optimize the behavior of services, ensuring that they are running efficiently and not contributing to unnecessary resource usage or system issues.
While managing services in the Services tab, it’s important to exercise caution. Disable or modify services only if you are certain of their impact and have a thorough understanding of the consequences. Incorrectly modifying or disabling critical system services can result in system instability or loss of functionality.
In summary, the Services tab in Task Manager offers a comprehensive view of the background services running on your Windows computer. It provides control options, service details, startup modes, and sorting/filtering capabilities. By utilizing the features of the Services tab, you can effectively manage services, optimize system performance, and troubleshoot service-related issues.
The Networking Tab
The Networking tab in Task Manager provides real-time information about the network activity on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor network usage, identify bandwidth-consuming processes, and troubleshoot network-related issues.
When you open the Networking tab, you will see a detailed view of network utilization, including the processes and applications that are currently utilizing network resources. The tab displays network usage metrics such as total utilization, network adapter details, connection state, and the bandwidth used by each process.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Networking tab:
- Network Utilization Overview: The Networking tab provides a graphical representation of the overall network utilization. It visually depicts the amount of network traffic flowing in and out of your computer, giving you an instant understanding of the network activity.
- Processes and Network Usage: The tab displays a list of processes that are currently using network resources. You can identify which processes are consuming the most bandwidth and evaluate their impact on network performance. This information helps pinpoint network-intensive applications or potential bandwidth hogs.
- Sorting and Filtering: Task Manager allows you to sort the processes by different criteria, such as total utilization, sending or receiving data, or process name. You can also use the search box to filter the list and quickly find specific processes.
- Resource Usage Details: Selecting a process in the Networking tab displays additional details, including the remote address and port with which the process is communicating. This information can be helpful in diagnosing network connectivity issues or investigating suspicious network activity.
- End Task: If you identify a process that is consuming an excessive amount of network bandwidth or causing network-related problems, you can right-click on it and select “End Task” to terminate the process. This can help resolve network performance issues or troubleshoot problematic network connections.
The Networking tab is a powerful tool for monitoring and managing network activity on your Windows computer. It allows you to identify processes that are using network resources and determine if there are any unnecessary network connections or bandwidth bottlenecks.
It’s important to remember that network activity can vary depending on the applications and services running on your computer. Some processes may have legitimate reasons for using network resources, such as online streaming or file syncing services. However, abnormal or unexpected network usage can indicate potential security threats or network misconfigurations.
In summary, the Networking tab in Task Manager provides real-time insights into network activity on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor network utilization, identify bandwidth-consuming processes, and troubleshoot network-related issues. By utilizing the features of the Networking tab, you can effectively manage network resources, optimize network performance, and ensure a smooth and efficient network experience.
The Disk Tab
The Disk tab in Task Manager provides valuable information about the disk performance and usage on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor disk activity, identify processes that are using the disk heavily, and troubleshoot any disk-related issues.
When you open the Disk tab, you will see a detailed view of disk activity and utilization, including the processes that are interacting with your computer’s disks. The tab displays metrics such as total disk utilization, read and write speeds, and the percentage of disk usage for each process.
Here are the key features and functions available in the Disk tab:
- Disk Activity Overview: The Disk tab provides a graphical representation of the overall disk activity, showing the disk utilization and any spikes or fluctuations in disk usage. This helps you visualize disk performance and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Processes and Disk Usage: The tab displays a list of processes that are currently using the disk. You can see the percentage of disk usage for each process and determine which processes are consuming the most disk resources. This information is useful for identifying disk-intensive processes or potential disk-related performance issues.
- Sorting and Filtering: Task Manager allows you to sort the processes based on different criteria like disk utilization, read or write speeds, or process name. You can also use the search box to filter the list and quickly find specific processes.
- Resource Usage Details: Selecting a process in the Disk tab displays additional details, such as the total bytes read and written by the process. This information allows you to evaluate the extent of disk usage by individual processes and see which processes are responsible for the most disk activity.
- Ending Disk-Intensive Processes: If you notice a process that is causing excessive disk usage or hindering disk performance, you can right-click on it and select “End Task” to terminate the process. This can help alleviate disk-related performance issues or troubleshoot problematic disk activity.
The Disk tab is a valuable tool for monitoring and managing disk performance on your Windows computer. It allows you to identify processes that are placing a heavy load on your disks, which can help optimize system performance and improve overall responsiveness.
It’s important to note that disk activity can vary depending on the applications and services running on your computer. Some processes, such as antivirus scans or software installations, may temporarily increase disk activity. However, persistent or abnormally high disk usage might indicate a bottleneck or disk-related performance issue that needs attention.
In summary, the Disk tab in Task Manager provides insights into disk activity and utilization on your Windows computer. It allows you to monitor disk performance, identify disk-intensive processes, and troubleshoot disk-related issues. By utilizing the features of the Disk tab, you can effectively manage disk resources, optimize disk performance, and ensure smooth and efficient disk operations.
Ending Tasks and Processes
Task Manager provides a convenient way to end tasks and processes on your Windows computer. Terminating unresponsive or resource-hungry applications can help improve system performance, resolve software issues, and free up system resources. Here’s how to end tasks and processes using Task Manager:
1. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard simultaneously.
2. In the “Processes” or “Details” tab, locate the process or application that you want to end.
3. Right-click on the process or application and select “End Task” or “End Process”.
4. A confirmation prompt may appear warning you that ending the process will result in data loss or system instability. Review the prompt and click “End Process” or “End Now” to proceed.
5. In some cases, terminating a process may require administrative privileges. If prompted, confirm the action by clicking “Yes” in the User Account Control (UAC) dialog box.
6. The process or application will be terminated, and its associated windows or services will be closed.
It’s important to exercise caution when ending tasks and processes. Terminating critical system processes or necessary applications can lead to system instability or data loss. Make sure you are ending the correct process and consider saving any unsaved work before proceeding.
If a particular process or application is causing consistent issues or interfering with system performance, it may be helpful to investigate the root cause. Check for any available software updates, ensure compatibility with your operating system, or seek assistance from the application’s support if necessary.
Additionally, keep in mind that ending a process is not a long-term solution for addressing performance problems. If you consistently encounter issues with a specific process or application, it may be worth exploring other troubleshooting steps, such as adjusting settings, updating drivers, or seeking technical support.
In summary, Task Manager provides the functionality to end tasks and processes on your Windows computer. Ending unresponsive or resource-consuming processes can improve system performance and resolve software issues. However, always exercise caution when terminating processes and consider investigating the root cause of persistent problems for a more comprehensive solution.
Managing Startup Programs
Managing startup programs is essential for optimizing system performance and controlling which applications launch automatically when you start your Windows computer. Task Manager provides a user-friendly interface to enable or disable startup programs and streamline your computer’s boot process. Here’s how you can manage startup programs using Task Manager:
1. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard simultaneously.
2. Click on the “Startup” tab to view the list of programs that are set to launch during system startup.
3. Review the list of startup programs. You can see the name, publisher, and startup impact rating of each program.
4. To disable a startup program, right-click on it and select “Disable”. This prevents the program from launching automatically during system startup.
5. To enable a disabled startup program, right-click on it and select “Enable”. This allows the program to launch automatically during system startup.
6. You can also adjust the startup impact rating column to sort the programs based on the impact they have on system startup. This helps you identify programs that significantly slow down the boot process.
7. If you are unsure about a specific startup program, right-click on it and select “Search online” to gather more information about it before deciding whether to enable or disable it.
Managing startup programs offers several benefits. Disabling unnecessary startup programs can reduce the time it takes for your computer to boot up and improve overall system performance. It also helps minimize the number of background processes running, freeing up system resources for the applications you genuinely need.
However, exercise caution when disabling startup programs. Some programs are essential for the proper functioning of your computer or specific software you use regularly. Disabling critical startup programs can result in the loss of functionality or prevent certain applications from working correctly.
Regularly reviewing and optimizing your startup programs can ensure a faster, more responsive computer. Over time, you may find that certain programs are no longer needed at startup, and disabling them can provide a smoother boot experience.
In addition to using Task Manager, you can also manage startup programs using the “Startup” section in the Windows Settings. This feature provides more advanced options to control the startup behavior of programs and services.
In summary, Task Manager offers a straightforward way to manage startup programs in Windows. By enabling or disabling startup programs, you can optimize system performance, reduce boot time, and allocate system resources more efficiently.
Monitoring Performance
Task Manager provides powerful performance monitoring tools that allow you to track the performance of your Windows computer in real-time. By monitoring performance metrics, you can gain valuable insights into system resource usage, identify bottlenecks, and optimize performance. Here’s how you can effectively monitor performance using Task Manager:
1. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard simultaneously.
2. By default, Task Manager opens in the “Processes” or “Details” tab, which displays the running processes and their resource utilization. You can observe the CPU and memory usage of processes to identify any resource-intensive applications.
3. Click on the “Performance” tab to access comprehensive performance monitoring tools.
4. In the Performance tab, you will find detailed graphs and charts for CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization. These graphical representations provide a visual overview of how your computer is utilizing these resources.
5. Switch between different performance views using the options available, such as “CPU”, “Memory”, “Disk”, and “Network”. Each view displays real-time graphs and metrics related to the respective resource.
6. Familiarize yourself with the key performance metrics displayed, such as CPU usage percentage, memory usage, disk read/write speeds, and network utilization. Keep an eye on these metrics to identify any abnormal spikes or consistently high resource usage.
7. Utilize the “Processes” or “Details” tab in conjunction with the performance graphs to correlate resource usage with specific processes or applications. This helps you pinpoint which processes are responsible for resource consumption.
8. For a more detailed view of resource utilization, you can customize the graph view by right-clicking on the graph and selecting the specific resource or performance metric you want to display.
9. Consider using the “Resource Monitor” feature, accessible through the Performance tab, for even more in-depth analysis of system resource usage and performance. Resource Monitor provides detailed information about CPU, memory, disk, and network activity at a granular level.
Monitoring performance using Task Manager allows you to proactively identify resource bottlenecks and troubleshoot performance issues. It provides you with the necessary information to optimize system performance, manage resource allocation, and ensure a smooth computing experience.
Keep in mind that performance monitoring is an ongoing process, especially in resource-intensive scenarios such as gaming or running demanding applications. Regularly monitoring performance allows you to make informed decisions regarding system optimization and resource management.
In summary, Task Manager provides powerful performance monitoring tools that enable you to track CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization in real-time. By monitoring performance metrics and correlating them with running processes, you can identify resource bottlenecks and optimize system performance for an efficient computing experience.
Troubleshooting with Task Manager
Task Manager is a valuable tool for troubleshooting various issues on your Windows computer. It provides insights into system resource usage, allows you to identify unresponsive applications or processes, and facilitates the management of startup programs. Here are some ways you can troubleshoot with Task Manager:
Ending Unresponsive Processes: If an application becomes unresponsive or freezes, you can use Task Manager to end the corresponding process. Open Task Manager, go to the “Processes” or “Details” tab, locate the unresponsive process, right-click on it, and select “End Task” or “End Process”. This helps regain control over your computer and resolves the issue.
Identifying High Resource Usage: Task Manager allows you to monitor resource usage, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network. If you notice unusually high resource consumption or performance issues, go to the corresponding tab in Task Manager and sort the processes by usage. This helps you identify resource-intensive processes, enabling you to take necessary action, such as closing unnecessary applications or troubleshooting specific processes.
Managing Startup Programs: Problems can arise when too many programs launch during system startup. Task Manager’s Startup tab provides an overview of the programs that start automatically when your computer boots up. By reviewing and disabling unnecessary startup programs, you can speed up the boot process and improve overall system performance.
Monitoring Performance: Task Manager’s Performance tab provides real-time insights into CPU, memory, disk, and network utilization. Monitoring these metrics helps you identify performance bottlenecks and troubleshoot any related issues. By observing the performance graphs and metrics, you can determine if resource contention is causing slowdowns or if specific processes are excessively consuming resources.
Analyzing Services: Task Manager’s Services tab displays the background services running on your computer. If you encounter issues related to specific services, you can use Task Manager to start, stop, or restart services. Ensure that critical services necessary for system functionality are running, and troubleshoot any problematic services that may be causing issues.
Checking Network Activity: If you experience slow internet speeds or network-related issues, Task Manager’s Networking tab provides insights into network utilization. You can monitor network activity, identify any processes or applications consuming high network bandwidth, and troubleshoot network connectivity problems.
Task Manager’s suite of troubleshooting features empowers you to track resource usage, identify problematic processes, and troubleshoot various issues on your Windows computer. By utilizing its capabilities, you can optimize system performance, resolve unresponsive application problems, and enhance the overall stability and efficiency of your computer.
Tips and Tricks for Task Manager
Task Manager is a powerful tool that offers a range of features to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot your Windows computer. Here are some tips and tricks to make the most out of Task Manager:
Customize Column View: Right-click on any column header in Task Manager to customize the view. You can choose which columns to display or hide, rearrange column order, and even resize column widths. Customizing the column view allows you to focus on the metrics and details that are most relevant to your needs.
Keyboard Shortcuts: Task Manager supports several keyboard shortcuts to quickly access specific features. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager directly, and press Ctrl + Alt + Del and select “Task Manager” to open it from the Windows Security screen. You can also navigate through tabs and control process termination using keyboard shortcuts such as Enter and Delete.
Taskbar Access: Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” to open Task Manager directly, without going through any additional menus or screens. This is a quick shortcut to access Task Manager when needed.
Resource Monitor: Task Manager provides a basic overview of system resource utilization, but for more detailed analysis, use the “Resource Monitor” feature. From Task Manager’s Performance tab, click on “Open Resource Monitor” to access Resource Monitor, which offers advanced capabilities for monitoring CPU, memory, disk, and network activity at a granular level.
Data Saving and Exporting: You can save and export the data displayed in Task Manager for offline analysis or record-keeping. Right-click anywhere in the Processes, Performance, or other tabs, and select “Save Selected Data” or “Save All Data” to save the information as a text file or CSV file. This is especially useful when gathering system diagnostic information or sharing details with technical support.
Always Verify Process Details: When managing or terminating processes, make sure you verify the process details carefully before taking any action. Mistakenly ending critical system processes can lead to system instability or loss of functionality. Confirm the process name, description, and other relevant details to ensure that you are interacting with the correct process.
Offline CPU Usage: Task Manager’s Performance tab displays real-time CPU usage, but it also shows “Offline” next to individual processor graphs if they are idle. This can be misleading; to view the actual CPU usage of all cores, right-click on the graph and select “Change graph to” and then “Logical processors”. This shows separate graphs for each CPU core, even when some cores are not actively processing tasks.
Utilize Resource Control Options: Right-click on a process or application in Task Manager to access various resource control options. Depending on the situation, you can set priority, manage affinity to specific CPU cores, or change the process’s I/O priority. These options can help optimize resource allocation and improve the responsiveness of specific processes.
Network Adapter Details: If you have multiple network adapters on your computer, Task Manager’s Networking tab provides valuable information about each adapter’s utilization. This allows you to identify the specific adapter that is experiencing heavy network traffic or connectivity issues.
By leveraging these tips and tricks, you can harness the full potential of Task Manager and efficiently monitor, manage, and troubleshoot your Windows computer. Task Manager is a versatile tool designed to enhance your computing experience and maintain optimal system performance.