What is a Hotspot?
A hotspot refers to a physical location where people can access the internet, typically using Wi-Fi, through a wireless local area network (WLAN) with a router connected to an internet service provider. This convenient technology allows users to connect their devices, such as smartphones, laptops, or tablets, to the internet without the need for a physical wired connection.
Hotspots are commonly found in public places such as cafes, airports, hotels, and libraries, enabling individuals to stay connected while on the go. Additionally, many individuals and businesses use mobile hotspots, which are portable devices that create a Wi-Fi network using cellular data. These mobile hotspots provide internet access to multiple devices, making them valuable tools for remote work, travel, and leisure.
Hotspots play a crucial role in modern connectivity, offering flexibility and convenience for both personal and professional use. Whether it's staying productive during travel, conducting business remotely, or simply enjoying online entertainment, hotspots have become an integral part of our digital lifestyles.
In essence, a hotspot serves as a gateway to the digital world, providing seamless internet access to individuals and enabling them to stay connected wherever they may be. Understanding the fundamentals of hotspots and their functionality is essential for effectively managing and utilizing this technology to its fullest potential.
Why Disconnect Devices from a Hotspot?
Disconnecting devices from a hotspot is a crucial aspect of managing network resources, ensuring security, and optimizing the performance of the internet connection. While maintaining a stable and secure connection is essential, there are several compelling reasons to disconnect devices from a hotspot when necessary.
1. Bandwidth Management: When multiple devices are connected to a hotspot, the available bandwidth is distributed among them. Disconnecting inactive or unnecessary devices helps allocate more bandwidth to those in use, enhancing the overall speed and performance of the network. This is especially important in settings where high-speed internet access is critical, such as in business environments or during online meetings and video conferences.
2. Security Measures: Leaving devices connected to a hotspot, especially in public or shared environments, can pose security risks. By disconnecting unused devices, the potential for unauthorized access or data breaches is minimized. It’s an essential practice to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized individuals from exploiting the network.
3. Battery Conservation: In the case of mobile hotspots, disconnecting devices that are not actively using the internet helps conserve the battery life of the hotspot device. This is particularly beneficial when using a portable hotspot during travel or in situations where access to a power source may be limited.
4. Network Stability: Overloading a hotspot with too many connected devices can lead to network congestion and instability. Disconnecting unnecessary devices helps maintain a stable connection, reducing the likelihood of interruptions or connectivity issues for active users.
5. Privacy and Control: By disconnecting devices when they are no longer in use, hotspot owners can exercise greater control over their network and ensure privacy. This practice prevents unauthorized individuals from lingering on the network and provides a sense of security and ownership over the internet connection.
Overall, disconnecting devices from a hotspot is a proactive measure that contributes to efficient bandwidth utilization, enhanced security, improved network stability, and better overall user experience. By understanding the significance of managing connected devices, individuals and businesses can optimize their hotspot usage and mitigate potential risks associated with unmonitored connections.
Steps to Disconnect Devices from a Hotspot
Disconnecting devices from a hotspot can be a straightforward process, allowing users to manage their network resources effectively. Whether it’s freeing up bandwidth, enhancing security, or optimizing performance, the following steps outline the process of disconnecting devices from a hotspot:
1. Access the Hotspot Settings: To begin, access the settings or administrative interface of the hotspot device. This can typically be done by entering the device’s IP address into a web browser and logging in with the appropriate credentials. Alternatively, for mobile hotspots, access the device’s settings through the accompanying mobile app or web interface.
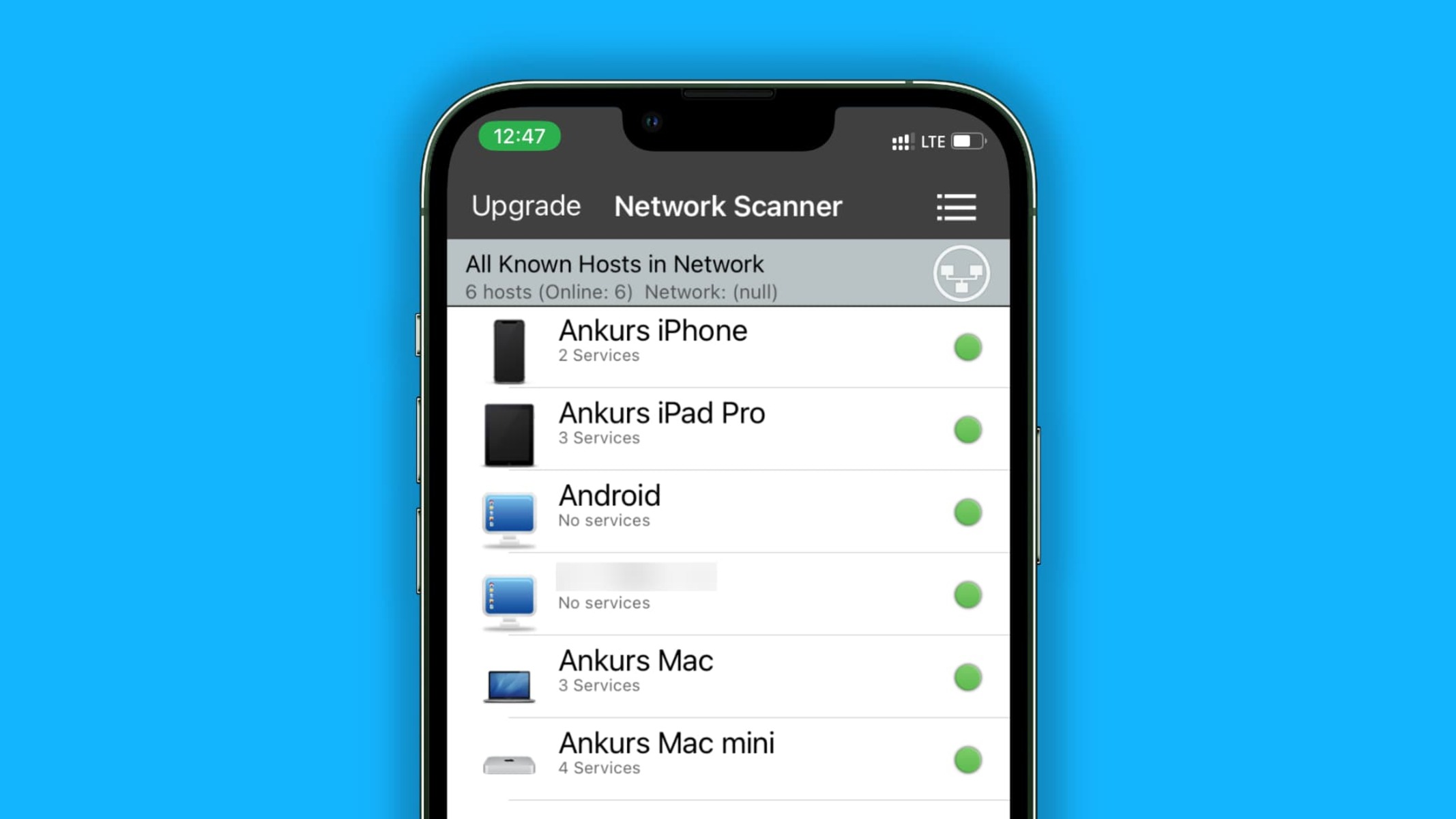
2. View Connected Devices: Once in the hotspot settings, locate the section that displays the currently connected devices. This may be listed as “Connected Devices,” “Client List,” or a similar designation, depending on the hotspot device or interface. Here, all connected devices, along with their respective IP or MAC addresses, should be visible.
3. Identify Devices to Disconnect: Review the list of connected devices and identify those that need to be disconnected. This may include devices that are no longer in use, belong to unauthorized users, or are consuming an excessive amount of bandwidth, impacting the overall network performance.
4. Select and Disconnect Devices: Most hotspot interfaces provide the option to select individual devices from the connected list and initiate a disconnection. This can typically be done by clicking on the device’s entry and choosing the “Disconnect” or similar option. Confirm the disconnection when prompted, and the selected device will be removed from the network.
5. Refresh or Reboot the Hotspot: After disconnecting the desired devices, consider refreshing the hotspot or rebooting it to ensure that the changes take effect. This step can help clear any lingering connections and optimize the network for the remaining connected devices.
6. Monitor and Manage Regularly: It’s important to monitor the connected devices periodically and manage the network proactively. Regularly reviewing and disconnecting inactive or unauthorized devices helps maintain network efficiency and security.
By following these steps, users can effectively disconnect devices from a hotspot, optimizing the network’s performance, security, and overall user experience. Proactive management of connected devices contributes to a more efficient and secure hotspot environment, aligning with best practices for network administration and utilization.
Managing Connected Devices
Effectively managing connected devices on a hotspot is essential for optimizing network performance, ensuring security, and providing a seamless user experience. By implementing proactive measures and leveraging the available tools and features, users can maintain control over their network resources and mitigate potential issues associated with excessive or unauthorized device connections.
1. Device Monitoring and Identification: Utilize the hotspot’s administrative interface or accompanying mobile app to monitor and identify connected devices. This includes reviewing the list of connected devices, identifying them by name or MAC address, and assessing their activity and bandwidth usage. Understanding the devices connected to the hotspot is crucial for effective management and security enforcement.
2. Bandwidth Allocation and Prioritization: Some advanced hotspot devices and management interfaces offer the capability to allocate and prioritize bandwidth for specific devices or types of traffic. This feature can be valuable in ensuring that essential devices or applications receive adequate bandwidth, especially in scenarios where network resources are limited or shared among multiple users.
3. Access Control and Security Measures: Implement access control measures, such as MAC address filtering or device blacklisting, to regulate which devices can connect to the hotspot. By maintaining a whitelist of authorized devices and blocking unauthorized ones, users can enhance the security of their network and prevent potential breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
4. Regular Review and Maintenance: Periodically review the list of connected devices and proactively manage them based on usage patterns, activity, and security considerations. Disconnect inactive devices, update access control lists, and ensure that the network remains optimized for the devices that require consistent and reliable connectivity.
5. User Education and Policies: In shared or business environments, educating users about the proper use of the hotspot and establishing clear policies regarding device connectivity can contribute to effective device management. Communicate guidelines for connecting devices, data usage limits, and security best practices to promote responsible and efficient use of the network.
6. Remote Management and Automation: Explore hotspot devices and management solutions that offer remote management capabilities and automation features. This allows users to manage connected devices, enforce security measures, and optimize network settings from anywhere, enhancing convenience and control over the hotspot environment.
By implementing these strategies and leveraging the available features of hotspot devices and management interfaces, users can effectively manage connected devices, optimize network resources, and maintain a secure and efficient hotspot environment. Proactive device management contributes to a reliable and responsive network, aligning with best practices for network administration and user satisfaction.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While using a hotspot, users may encounter common issues that can affect connectivity and overall performance. Understanding how to troubleshoot these issues is essential for maintaining a reliable and efficient hotspot experience. By addressing these common challenges, users can minimize disruptions and optimize their network usage.
1. Slow or Intermittent Connectivity: If the hotspot connection is slow or intermittent, first ensure that the hotspot device is positioned in an area with strong signal reception. Additionally, consider the number of connected devices and their respective bandwidth usage. Disconnect inactive devices to free up bandwidth and improve overall connectivity for active users.
2. Device Connection Failures: When devices fail to connect to the hotspot, verify that the hotspot device is operational and within range. Restart the hotspot and the device attempting to connect, as this can resolve temporary connectivity issues. If the problem persists, check for any device-specific compatibility or configuration issues that may be preventing successful connections.
3. Network Overload and Congestion: In high-traffic environments, network overload and congestion can impact hotspot performance. Disconnect unnecessary devices and consider implementing bandwidth prioritization to ensure that essential applications or devices receive adequate resources, particularly during peak usage periods.
4. Security Concerns and Unauthorized Access: If there are suspicions of unauthorized access or security breaches, review the list of connected devices and ensure that only authorized devices are connected to the hotspot. Implement access control measures, such as MAC address filtering or device blacklisting, to prevent unauthorized access attempts and enhance network security.
5. Hotspot Device Overheating or Power Issues: Hotspot devices may encounter overheating or power-related issues, especially during extended usage or in high-temperature environments. Ensure that the hotspot device has proper ventilation and is not exposed to excessive heat. If power-related issues persist, consider using a dedicated power source or a portable power bank to ensure uninterrupted operation.
6. Firmware and Software Updates: Regularly check for firmware and software updates for the hotspot device, as outdated firmware or software can lead to performance issues and security vulnerabilities. Stay informed about the latest updates and ensure that the hotspot device is running the most current and stable version of its firmware and software.
By troubleshooting these common issues and implementing proactive measures to address them, users can maintain a reliable and responsive hotspot environment. Effective troubleshooting contributes to a seamless and uninterrupted connectivity experience, aligning with best practices for hotspot management and user satisfaction.
Best Practices for Managing Hotspot Connections
Effective management of hotspot connections involves implementing best practices to optimize network performance, enhance security, and provide a seamless user experience. By following these best practices, users can maximize the benefits of hotspot technology while mitigating potential challenges associated with network management and connectivity.
1. Regular Device Monitoring: Routinely monitor the list of connected devices to the hotspot, keeping track of their activity, bandwidth usage, and security status. This proactive approach allows for timely identification of unauthorized devices, inactive connections, and potential security threats, enabling swift action to maintain network integrity.
2. Disconnect Inactive Devices: Periodically disconnect devices that are inactive or no longer in use to free up bandwidth and optimize network resources. This practice contributes to a more responsive and efficient network, especially in environments with limited bandwidth or during peak usage periods.
3. Implement Access Control Measures: Utilize access control features, such as MAC address filtering and device blacklisting, to regulate which devices can connect to the hotspot. By maintaining a whitelist of authorized devices and preventing unauthorized access attempts, users can bolster network security and minimize the risk of data breaches or unauthorized usage.
4. Bandwidth Prioritization: If the hotspot supports bandwidth prioritization, allocate and prioritize network resources for essential devices or applications. This ensures that critical tasks or devices receive sufficient bandwidth, even in scenarios with multiple connected users or high network traffic.
5. Educate Users on Best Practices: In shared hotspot environments, educate users about best practices for device connectivity, data usage limits, and security measures. Clear communication of guidelines and policies fosters responsible usage and promotes a harmonious and efficient network environment.
6. Regular Firmware and Software Updates: Stay informed about firmware and software updates for the hotspot device, ensuring that it remains up to date with the latest security patches and performance enhancements. Regular updates minimize the risk of vulnerabilities and ensure optimal functionality of the hotspot device.
7. Network Optimization and Stability: Maintain a stable network environment by monitoring for network congestion, optimizing settings for performance, and addressing connectivity issues promptly. A stable and responsive network enhances the user experience and supports seamless connectivity for all connected devices.
By adhering to these best practices, users can effectively manage hotspot connections, optimize network resources, and uphold a secure and reliable connectivity environment. Proactive management and adherence to best practices contribute to a responsive and efficient hotspot experience, aligning with industry standards for network administration and user satisfaction.