Choosing the Right Location for Installation
Choosing the Right Location for Installation
When it comes to installing a GPS tracker, selecting the optimal location is crucial for its effectiveness. Here are some key points to consider when choosing the right location for installation:
- Visibility: Ensure that the GPS tracker has a clear view of the sky to receive signals from satellites. Avoid installing it in areas obstructed by metal, concrete, or other dense materials that can interfere with signal reception.
- Protection from Weather: Shield the GPS tracker from direct exposure to harsh weather conditions such as heavy rainfall or extreme sunlight. Consider installing it in a weather-resistant casing or a location that provides natural protection.
- Accessibility: Select a location that is easily accessible for maintenance and retrieval, if necessary. This will facilitate future inspections, battery replacements, or any required adjustments.
- Concealment: While accessibility is important, it’s also essential to consider concealing the GPS tracker to prevent tampering or theft. Choose a location that is inconspicuous yet still meets the visibility and weather protection criteria.
- Legal Compliance: Before installation, ensure that you comply with local laws and regulations regarding the placement of GPS trackers. Some jurisdictions have specific guidelines on where and how GPS trackers can be installed.
By taking these factors into account, you can effectively determine the most suitable location for installing your GPS tracker, maximizing its performance and longevity.
Powering the GPS Tracker
Powering the GPS tracker is a fundamental step in the installation process. Here’s a comprehensive guide to ensure a seamless power setup for your GPS tracker:
Power Source: Identify the most suitable power source for your GPS tracker. Options may include the vehicle’s electrical system, an external battery, or a dedicated power source, depending on the type of tracker and its intended application.
Wiring: If hardwiring the GPS tracker to the vehicle’s electrical system, carefully route the wiring to conceal it from view and protect it from potential damage. Use appropriate wire connectors and insulation to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
Battery Considerations: For battery-powered trackers, select a high-quality, long-lasting battery that aligns with the tracker’s power requirements. Regularly monitor the battery’s status and replace it as needed to maintain uninterrupted tracking functionality.
Power Management: Implement power management features provided by the GPS tracker, such as sleep mode or power-saving settings, to optimize battery life and minimize power consumption when the tracker is not in active use.
Backup Power: Consider incorporating a backup power source, such as a secondary battery or an external power bank, to ensure continuous operation in the event of a primary power source failure or depletion.
By carefully addressing these power-related considerations, you can effectively establish a reliable and sustainable power setup for your GPS tracker, promoting consistent performance and minimal downtime.
Mounting the GPS Tracker
Properly mounting the GPS tracker is essential to ensure its stability and functionality. Consider the following guidelines for securely mounting your GPS tracker:
Secure Attachment: Utilize high-quality mounting hardware to securely affix the GPS tracker to the chosen location. This may involve brackets, adhesive mounts, or other specialized fixtures designed to withstand vibrations and environmental factors.
Orientation: Position the GPS tracker in a manner that aligns with its recommended orientation guidelines. This may involve ensuring that the device’s antennas or signal receivers are oriented correctly for optimal signal reception.
Vibration Dampening: If installing the GPS tracker in a vehicle or other dynamic environment, incorporate vibration-dampening measures to minimize the impact of mechanical vibrations on the tracker’s internal components and signal accuracy.
Environmental Protection: Shield the GPS tracker from potential environmental hazards, such as dust, moisture, or debris, by enclosing it in a protective housing or utilizing weather-resistant mounting solutions.
Stealthy Installation: When applicable, strive to mount the GPS tracker inconspicuously to deter tampering or theft, while still maintaining its accessibility for maintenance and inspection purposes.
By adhering to these mounting considerations, you can ensure that your GPS tracker is securely and effectively positioned, optimizing its performance and safeguarding it from external influences.
Connecting the GPS Tracker to the Platform
Establishing a seamless connection between the GPS tracker and the tracking platform is essential for real-time monitoring and data retrieval. Here’s a comprehensive guide to effectively link your GPS tracker to the platform:
Platform Compatibility: Ensure that the GPS tracker is compatible with the designated tracking platform. Verify the supported communication protocols, data formats, and integration methods to guarantee a harmonious connection.
Network Configuration: Configure the GPS tracker to communicate with the designated network, whether it’s a cellular network, satellite network, or other communication infrastructure. Verify the network settings and ensure proper signal strength for reliable connectivity.
Data Transmission: Verify that the GPS tracker is successfully transmitting location and telemetry data to the tracking platform. Confirm the frequency of data updates and the accuracy of the transmitted information to ensure optimal tracking performance.
Integration Testing: Conduct thorough testing to validate the integration between the GPS tracker and the tracking platform. Verify that location updates, status reports, and any custom data fields are accurately transmitted and displayed within the platform’s interface.
Security Measures: Implement robust security measures, such as encrypted communication channels and access controls, to safeguard the data transmitted between the GPS tracker and the platform from unauthorized interception or tampering.
By meticulously addressing these connectivity aspects, you can establish a reliable and secure link between your GPS tracker and the tracking platform, enabling comprehensive monitoring and management of the tracked assets or vehicles.
Testing the GPS Tracker
Thorough testing of the GPS tracker is essential to verify its functionality and accuracy. Here’s a comprehensive approach to testing your GPS tracker:
Signal Reception: Verify that the GPS tracker successfully acquires satellite signals and accurately determines its position. Assess its performance in various environments, including urban areas, remote locations, and areas with limited sky visibility.
Location Accuracy: Validate the accuracy of the GPS tracker’s reported location by comparing it with known landmarks or addresses. Ensure that the reported positions align closely with the actual physical locations to confirm precise tracking.
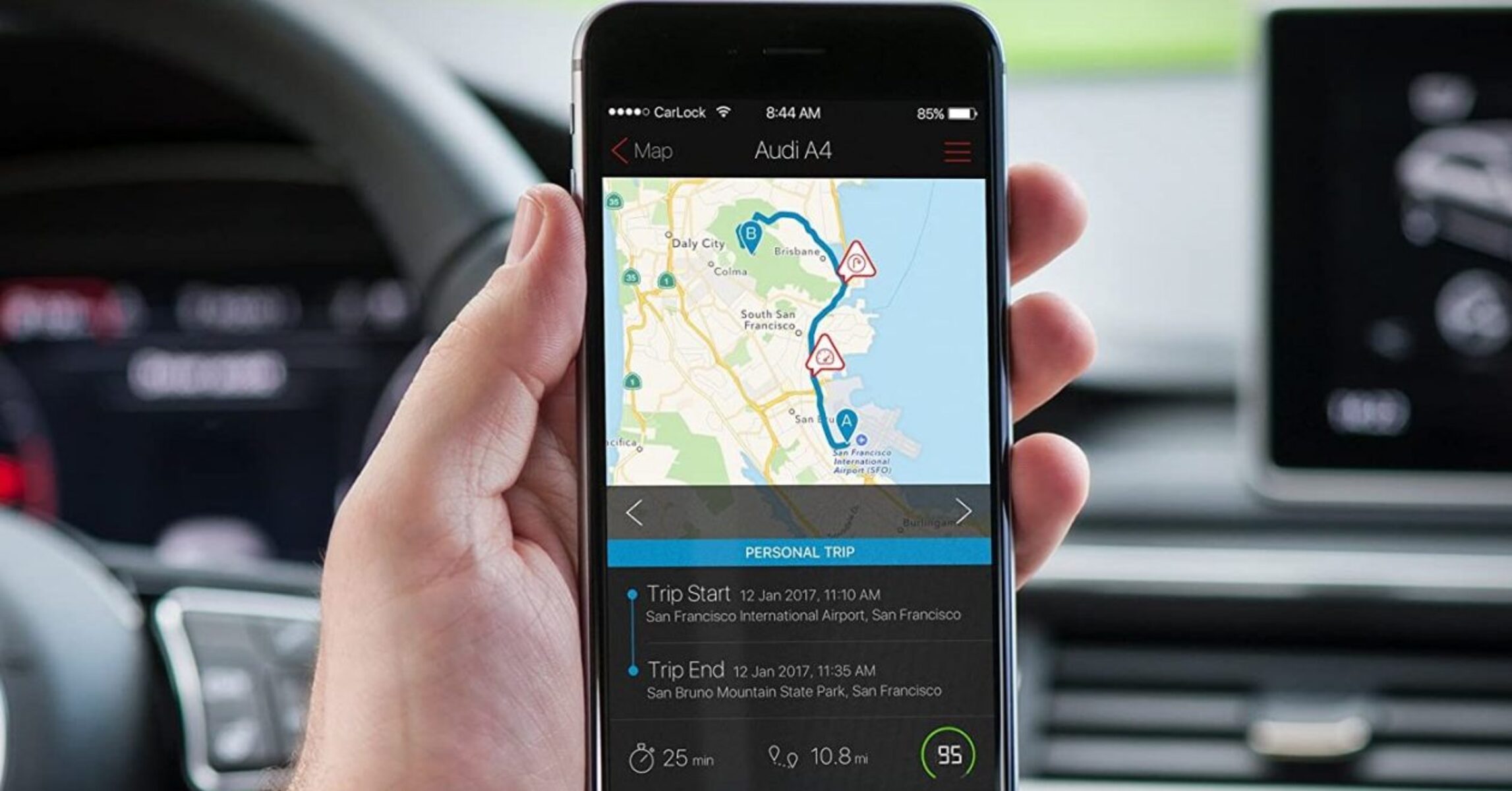
Real-Time Tracking: Monitor the GPS tracker’s real-time tracking capabilities by observing its updates on the tracking platform. Confirm that the reported movements align with the actual movements of the tracked asset or vehicle.
Alerts and Notifications: Test the GPS tracker’s alerting features, such as geofence breaches, excessive speed alerts, or unauthorized movement notifications, to ensure that the system triggers timely and accurate alerts as per the configured parameters.
Battery Performance: If applicable, assess the battery performance of the GPS tracker by monitoring its power consumption, battery life, and recharging intervals. Ensure that the tracker’s power management aligns with the expected operational requirements.
Data Integrity: Validate the integrity of the transmitted data, including timestamps, speed, heading, and any additional telemetry information. Confirm that the data presented on the tracking platform is consistent and reliable.
By conducting comprehensive testing encompassing these critical aspects, you can confidently affirm the operational readiness and reliability of your GPS tracker, ensuring its effectiveness in tracking and monitoring your assets or vehicles.