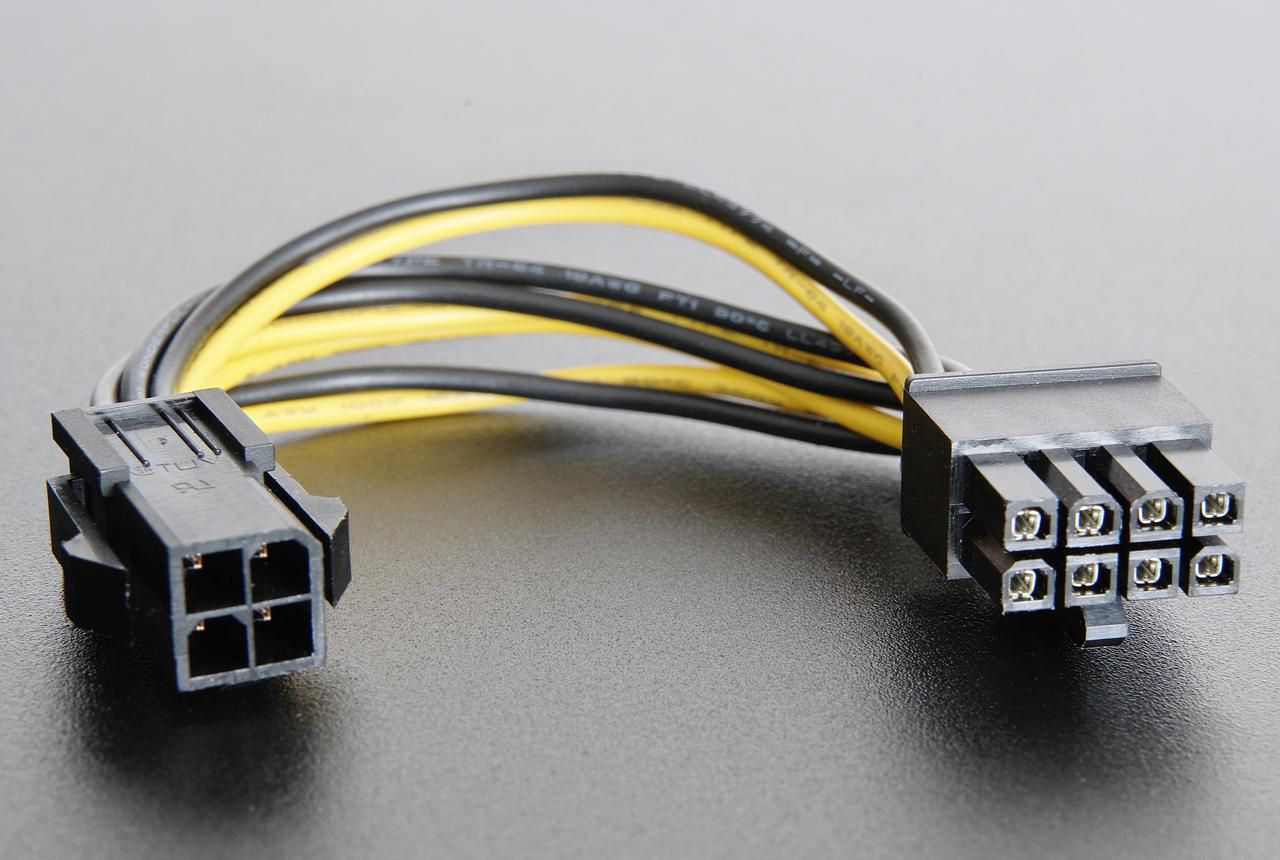
What is an ATX Power Connector?
An ATX power connector, short for Advanced Technology eXtended power connector, is a crucial component found on motherboards. It serves as the primary connection point for delivering power from the power supply unit (PSU) to the motherboard. This connector is standardized across most modern motherboards, ensuring compatibility and ease of use for PC builders and enthusiasts.
The ATX power connector is designed to provide the necessary voltage and current to various components on the motherboard, including the CPU, RAM, expansion cards, and other integrated circuits. It typically consists of multiple pins that deliver different voltages, such as +3.3V, +5V, +12V, and ground connections, ensuring stable and regulated power distribution throughout the system.
This connector plays a pivotal role in ensuring the proper functioning of the motherboard and its associated components. Without a reliable power supply delivered through the ATX power connector, the system would fail to boot or operate efficiently, leading to potential hardware malfunctions and instability.
In essence, the ATX power connector acts as the lifeline of the motherboard, providing the necessary electrical power to drive the computing processes and facilitate seamless operation. Its standardized design and essential function make it an indispensable feature in modern computer systems, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the hardware.
In the next section, we will delve into the different types of ATX power connectors commonly used in the industry, shedding light on their specific characteristics and applications. Understanding the variations in ATX power connectors is crucial for selecting the appropriate power supply unit and ensuring compatibility with the motherboard.
Types of ATX Power Connectors
ATX power connectors come in several variations, each tailored to specific motherboard and power supply unit configurations. Understanding the different types of ATX power connectors is essential for selecting compatible hardware and ensuring seamless integration within the system.
1. 24-pin ATX Power Connector: This is the standard power connector found on modern motherboards. It consists of a 24-pin block that delivers various voltages and grounds to the motherboard. The 24-pin connector provides the primary power supply to the motherboard, ensuring stable operation and sufficient power delivery to all components.
2. 20-pin ATX Power Connector: Older motherboards may feature a 20-pin ATX power connector. While it is less common in modern systems, some legacy hardware still utilizes this connector. Adapters are available to convert a 20-pin connector to a 24-pin configuration, enabling compatibility with newer power supply units.
3. 4-pin CPU Power Connector: In addition to the main ATX power connector, many motherboards require a dedicated 4-pin connector to supply power to the CPU. This connector ensures that the processor receives adequate power for optimal performance and stability, especially in systems with high-power CPUs or overclocked configurations.
4. 8-pin CPU Power Connector: High-performance motherboards and CPUs often necessitate an 8-pin CPU power connector, providing additional power delivery for demanding processor requirements. This connector caters to power-hungry CPUs and is commonly found in gaming rigs, workstations, and enthusiast-grade systems.
5. PCIe Power Connectors: Some high-end graphics cards and expansion cards require dedicated PCIe power connectors directly from the power supply unit. These connectors deliver supplementary power to the graphics card, ensuring stable operation and optimal performance during intensive graphical tasks and gaming.
Understanding the specific requirements of the motherboard, CPU, and other components is crucial for selecting the appropriate ATX power connectors and power supply unit. Compatibility and proper power delivery are paramount in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of the system.
Pin Configuration of ATX Power Connectors
The pin configuration of ATX power connectors plays a critical role in delivering the necessary voltages and grounds to the motherboard and its components. Understanding the layout and function of the pins is essential for proper installation and power distribution within the system.
1. 24-pin ATX Power Connector: The 24-pin ATX power connector typically consists of multiple +3.3V, +5V, +12V, and ground pins, ensuring the delivery of essential voltages to the motherboard. This connector also includes the Power Good (PG) signal, which indicates that the power supply unit has stabilized and is providing reliable power to the system.
2. 4-pin CPU Power Connector: The 4-pin CPU power connector delivers dedicated power to the CPU, ensuring stable operation and optimal performance. It provides the necessary voltages to the processor, supporting its power requirements and contributing to efficient computing processes.
3. 8-pin CPU Power Connector: The 8-pin CPU power connector offers additional power delivery to high-performance CPUs, catering to their heightened power demands. This connector is designed to meet the requirements of advanced processors, especially in overclocked or high-power computing setups.
4. PCIe Power Connectors: PCIe power connectors feature multiple pins that deliver supplementary power to graphics cards and other expansion cards. These connectors ensure that high-performance GPUs receive the necessary power for intensive graphical tasks, gaming, and compute-intensive applications.
Understanding the pin configuration of ATX power connectors is crucial for proper installation and power supply unit compatibility. It enables users to ensure that the motherboard and its associated components receive the requisite voltages and grounds for reliable and efficient operation.
Next, we will explore the significance of ATX power connectors on motherboards, shedding light on their pivotal role in powering and sustaining the functionality of the hardware components.
Importance of ATX Power Connectors on Motherboards
The ATX power connectors play a pivotal role in powering and sustaining the functionality of motherboards and their associated components. Understanding the significance of these connectors is essential for appreciating their impact on the overall performance and reliability of computer systems.
1. Stable Power Delivery: ATX power connectors ensure stable and regulated power delivery to the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and other integrated circuits. This stable power supply is essential for maintaining the operational integrity of the hardware components, preventing malfunctions and system instability.
2. Component Functionality: The ATX power connectors enable the proper functioning of critical components such as the CPU, ensuring that they receive the requisite power for efficient operation. Without reliable power delivery through these connectors, the performance and stability of the entire system would be compromised.
3. System Boot and Operation: The ATX power connectors are instrumental in facilitating the booting process and sustaining the operation of the motherboard. They provide the initial power surge required to initiate the system and maintain continuous power delivery during operation, contributing to seamless computing experiences.
4. Hardware Protection: By delivering stable power to the motherboard and components, ATX power connectors play a crucial role in protecting hardware from voltage fluctuations and power surges. This safeguards the integrity of the system and reduces the risk of damage to sensitive electronic components.
5. Compatibility and Standardization: The standardized design of ATX power connectors ensures compatibility between power supply units and motherboards, simplifying the process of building and upgrading computer systems. This standardization promotes ease of use and interchangeability of hardware components.
6. System Reliability: The reliable power supply facilitated by ATX power connectors contributes to the overall reliability and performance of computer systems. It ensures that the hardware functions optimally, minimizing the risk of crashes, data loss, and hardware failures.
Understanding the importance of ATX power connectors is crucial for enthusiasts, system builders, and users seeking to optimize the performance and stability of their computer systems. These connectors serve as the backbone of power distribution within the hardware, influencing the overall functionality and longevity of the system.
In the subsequent section, we will delve into troubleshooting ATX power connector issues, providing insights into identifying and resolving common power-related challenges encountered in computer systems.
Troubleshooting ATX Power Connector Issues
While ATX power connectors are essential for powering motherboards and ensuring stable operation, issues related to these connectors can arise, impacting the functionality of the computer system. Understanding common troubleshooting methods is crucial for diagnosing and resolving ATX power connector issues effectively.
1. Check Power Supply Unit (PSU) Connections: Ensure that the power supply unit is properly connected to the ATX power connector on the motherboard. Verify that the 24-pin (or 20-pin) connector and the CPU power connectors are securely seated, with no loose connections or dislodged pins.
2. Inspect for Physical Damage: Examine the ATX power connectors for any signs of physical damage, such as bent pins, corrosion, or burns. Damaged connectors can impede proper power delivery and may require replacement to restore functionality.
3. Test with Alternate PSU: If available, testing the motherboard with an alternate power supply unit can help determine if the issue lies with the PSU or the motherboard’s power connectors. This can aid in isolating the source of the problem for targeted troubleshooting.
4. Verify Voltage Outputs: Utilize a multimeter to measure the voltage outputs of the ATX power connectors. Ensure that the +3.3V, +5V, and +12V rails are within the specified voltage ranges, indicating proper power delivery to the motherboard and components.
5. Reset BIOS/CMOS: In some cases, resetting the BIOS or CMOS settings can resolve power-related issues. Clearing the CMOS and resetting the BIOS to default settings can help address anomalies related to power management and hardware initialization.
6. Inspect for Thermal Issues: Overheating can impact the functionality of ATX power connectors and associated components. Ensure that adequate cooling is maintained within the system to prevent thermal issues that may affect power delivery and system stability.
7. Consult Manufacturer Documentation: Refer to the motherboard and power supply unit documentation for specific troubleshooting guidelines and recommendations. Manufacturers often provide detailed instructions for diagnosing and addressing power-related issues.
By employing these troubleshooting methods, users can identify and address ATX power connector issues, restoring the reliable operation of the motherboard and associated hardware components. Proper diagnosis and resolution of power-related challenges are essential for maintaining system stability and preventing potential hardware damage.
Understanding the intricacies of ATX power connectors and their troubleshooting methods empowers users to effectively manage power-related issues, ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of their computer systems.