Reasons for Obtaining a Fixed IP Address
Obtaining a fixed IP address can offer numerous benefits and is essential for various purposes. Whether you are a business owner, a gamer, or a technology enthusiast, having a fixed IP address can improve your online experience in several ways.
One of the primary reasons to obtain a fixed IP address is for remote access. With a fixed IP address, you can easily connect to your devices or network from anywhere in the world. This is particularly useful for businesses that require remote access to their servers, allowing employees to work efficiently and securely from home or while traveling.
Another advantage of a fixed IP address is enhanced security. When you have a fixed IP address, you can set up robust firewalls and access control lists (ACLs) to protect your network from unauthorized access. This helps safeguard sensitive data and prevent malicious hackers from infiltrating your system.
A fixed IP address is also beneficial for hosting websites or online services. If you run a website or an online application, having a fixed IP address allows your visitors to easily access your content. It eliminates the need for complicated domain setup and ensures a seamless experience for your users.
Moreover, a fixed IP address is valuable for setting up email servers. With a static IP, you can configure your email server to send and receive messages without the hassle of constantly updating DNS records. This ensures reliable email delivery and prevents your messages from being marked as spam.
Gamers can also benefit from a fixed IP address. It can provide a more stable and consistent connection, reducing latency and eliminating issues with NAT traversal that can hinder multiplayer gaming.
Additionally, acquiring a fixed IP address enables advanced networking capabilities. You can easily set up virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure remote access, establish site-to-site connections for connecting multiple locations, and implement network monitoring and management tools for better control of your network.
Overall, obtaining a fixed IP address offers increased convenience, security, and flexibility in the digital world. Whether it’s for remote access, hosting services, or gaming, a fixed IP address empowers you to have full control over your online activities and ensure seamless connectivity.
Choosing a Fixed IP Address
When it comes to choosing a fixed IP address, there are a few key factors to consider to ensure you make the right choice for your needs. Whether you are obtaining a fixed IP address through your internet service provider (ISP) or using a dynamic DNS service, here are some important considerations to keep in mind:
1. IPv4 or IPv6: Determine whether you prefer an IPv4 or IPv6 address. IPv4 addresses are the traditional 32-bit addresses and are still widely used. On the other hand, IPv6 addresses are 128 bits and offer a significantly larger address space to accommodate the growing number of connected devices.
2. Public or private address: Decide whether you need a public or private IP address. Public IP addresses are routable on the internet and allow direct access to your devices or network. Private IP addresses, such as those in the 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x ranges, are typically used within a private network and require network address translation (NAT) for internet access.
3. Static or dynamic assignment: Consider whether you need a static or dynamic assignment. A static IP address remains constant and does not change unless manually modified, providing stability and predictability. Dynamic IP addresses, as the name suggests, are assigned dynamically by a DHCP server and can change periodically.
4. Availability and cost: Check the availability and cost of obtaining a fixed IP address. Some ISPs may offer fixed IP address services as part of their packages or at an additional cost. Alternatively, you can consider dynamic DNS services that provide a fixed domain name that maps to your changing IP address.
5. Technical requirements: Assess any technical requirements you may have. For example, if you are hosting services or running specific applications, you may need to ensure that certain ports are open and properly configured to allow traffic to reach your devices.
Take the time to evaluate these aspects and determine the best fit for your specific needs. Consider consulting with your ISP or researching dynamic DNS service providers to gather all the necessary information before making a decision.
Remember, choosing the right fixed IP address is crucial as it will play a significant role in determining the stability, accessibility, and functionality of your online services or activities.
Obtaining a Fixed IP Address through Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
If you want to obtain a fixed IP address, one of the most common and straightforward methods is through your internet service provider (ISP). Here’s how you can go about it:
1. Contact your ISP: Start by reaching out to your ISP and inquire about their fixed IP address options. Most ISPs offer this service, although it may not be automatically included in your standard internet package. They will provide you with information on the availability, pricing, and any requirements for obtaining a fixed IP address.
2. Understand the terms: Take the time to understand the terms and conditions associated with the fixed IP address service provided by your ISP. It’s essential to know the duration of the contract, any additional fees or charges, and whether the IP address is truly static or subject to periodic changes.
3. Provide the necessary information: Upon request, your ISP may ask for certain information such as your account details, the purpose or need for a fixed IP address, and any technical requirements you may have. Be prepared to provide these details to facilitate the process.
4. Configure your equipment: Once you have been assigned a fixed IP address by your ISP, you will need to configure your networking equipment accordingly. This may involve accessing your router’s settings and entering the provided IP address in the appropriate fields. Consult your ISP or refer to their documentation for instructions tailored to their specific setup.
5. Optional router upgrade: In some cases, if your current router does not support static IP addresses, you may need to upgrade to a compatible router. Your ISP can guide you in selecting a suitable router or may even offer one as part of their fixed IP address service.
6. Test and verify: After configuring your equipment, it’s crucial to test the connection to ensure that your fixed IP address is functioning correctly. Verify that the IP address assigned to you matches the one provided by your ISP and that you have the desired level of accessibility and stability.
Remember, the process of obtaining a fixed IP address through your ISP may vary depending on the specific provider and region. It’s advisable to check with your ISP for precise instructions and any additional details you may need.
By obtaining a fixed IP address through your ISP, you can enjoy the consistency and control that comes with having a dedicated and stable IP address for your internet activities.
Obtaining a Fixed IP Address through a Dynamic DNS Service
If your internet service provider (ISP) does not offer fixed IP address options or you prefer a more flexible solution, you can obtain a fixed IP address through a dynamic DNS (Domain Name System) service. Here’s how you can accomplish this:
1. Choose a dynamic DNS service provider: Start by selecting a dynamic DNS service provider that suits your needs. There are several reputable providers available, offering both free and paid options. Research different providers to compare features, reliability, and ease of use.
2. Create an account: Once you’ve chosen a dynamic DNS service provider, create an account with them. This typically involves providing your email address, choosing a username, and setting a password.
3. Configure your domain: After creating an account, configure your domain name. Depending on the provider, you may be able to choose from a selection of domain names or use a custom domain if you have one. Follow the provider’s instructions to set up your domain and associate it with your account.
4. Install the dynamic DNS client: Most dynamic DNS service providers offer a dynamic DNS client that automatically updates your IP address with your domain whenever it changes. Download and install the client software or configure it on your router if it has built-in support. This client monitors your IP address and sends updates to the service provider’s servers when changes occur.
5. Set up your router or device: If you’re using a router, access its settings and locate the dynamic DNS configuration section. Enter your dynamic DNS service provider’s settings, including your account credentials and domain information. If you’re using a device other than a router, follow the provider’s instructions to configure dynamic DNS settings specifically for that device.
6. Test the connection: After configuring the dynamic DNS settings, test the connection by accessing your domain from a different network or using a tool like ping or nslookup to verify that it resolves to your current IP address. Ensure that the IP address is updated promptly and accurately whenever it changes.
Obtaining a fixed IP address through a dynamic DNS service gives you the flexibility to work with changing IP addresses while maintaining a static domain name for easy access. It’s an excellent solution if you have a non-static IP address from your ISP or if you need to access devices or services remotely.
Note that dynamic DNS services require periodic renewal of your domain registration, and some providers offer additional features such as advanced DNS management and security options. Consider these factors and choose a reliable and reputable provider to ensure a smooth and dependable dynamic DNS experience.
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to Obtain a Fixed IP Address
If you’re looking for a secure and versatile way to obtain a fixed IP address, using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be an effective solution. A VPN allows you to route your internet traffic through a server located in a different geographical location, providing you with a fixed IP address assigned by the VPN provider. Here’s how you can use a VPN to obtain a fixed IP address:
1. Subscribe to a VPN service: Begin by selecting a reputable VPN service that offers dedicated or static IP address options. Research different providers to compare their features, server locations, and pricing.
2. Choose a server location: Once you’ve subscribed to a VPN service, choose a server location for your fixed IP address. Consider factors such as the proximity to your physical location, server availability, and any specific requirements you may have, such as accessing content restricted to certain regions.
3. Set up the VPN client: Install the VPN client software provided by your VPN service on your device. Follow the instructions provided by the service to configure the client with your credentials and server location. The VPN client will establish a secure connection to the VPN server.
4. Connect to the VPN server: Launch the VPN client and connect to the server location you’ve chosen. This will route all your internet traffic through the VPN server, assigning your device a fixed IP address associated with that server.
5. Verify your fixed IP address: Once the VPN connection is established, verify your fixed IP address by checking your current IP address using online tools or by accessing websites that display your IP information. It should reflect the IP address assigned by the VPN server in the chosen location.
6. Configure network applications: If necessary, configure network applications or services to utilize the fixed IP address provided by the VPN. This may involve specifying the IP address in the application settings or using port forwarding options available in the VPN client or router configurations.
Using a VPN to obtain a fixed IP address offers several advantages. It provides anonymity and security by encrypting your internet traffic, allowing you to bypass geo-restrictions, and ensures a stable and consistent IP address for your online activities. However, keep in mind that the availability of dedicated or static IP addresses may vary among different VPN providers, and additional fees may apply.
Before choosing a VPN service, assess your specific needs, such as whether you require a dedicated IP for personal or business use, and select a VPN provider that offers the features and reliability that align with your requirements.
Setting Up a Fixed IP Address on Windows
If you’re using a Windows operating system and want to configure a fixed IP address, you can follow these steps:
1. Open Network Settings: Open the “Settings” app by pressing the Windows key + I on your keyboard. Select “Network & Internet.”
2. Access Network Connections: In the Network & Internet settings, click on “Change adapter options.” This will display all the available network connections on your computer.
3. Select the appropriate network connection: Right-click on the network connection you want to set a fixed IP address for (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi) and choose “Properties.”
4. Configure TCP/IPv4 Properties: In the properties window, locate “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and double-click on it. This will open the TCP/IPv4 properties dialog box.
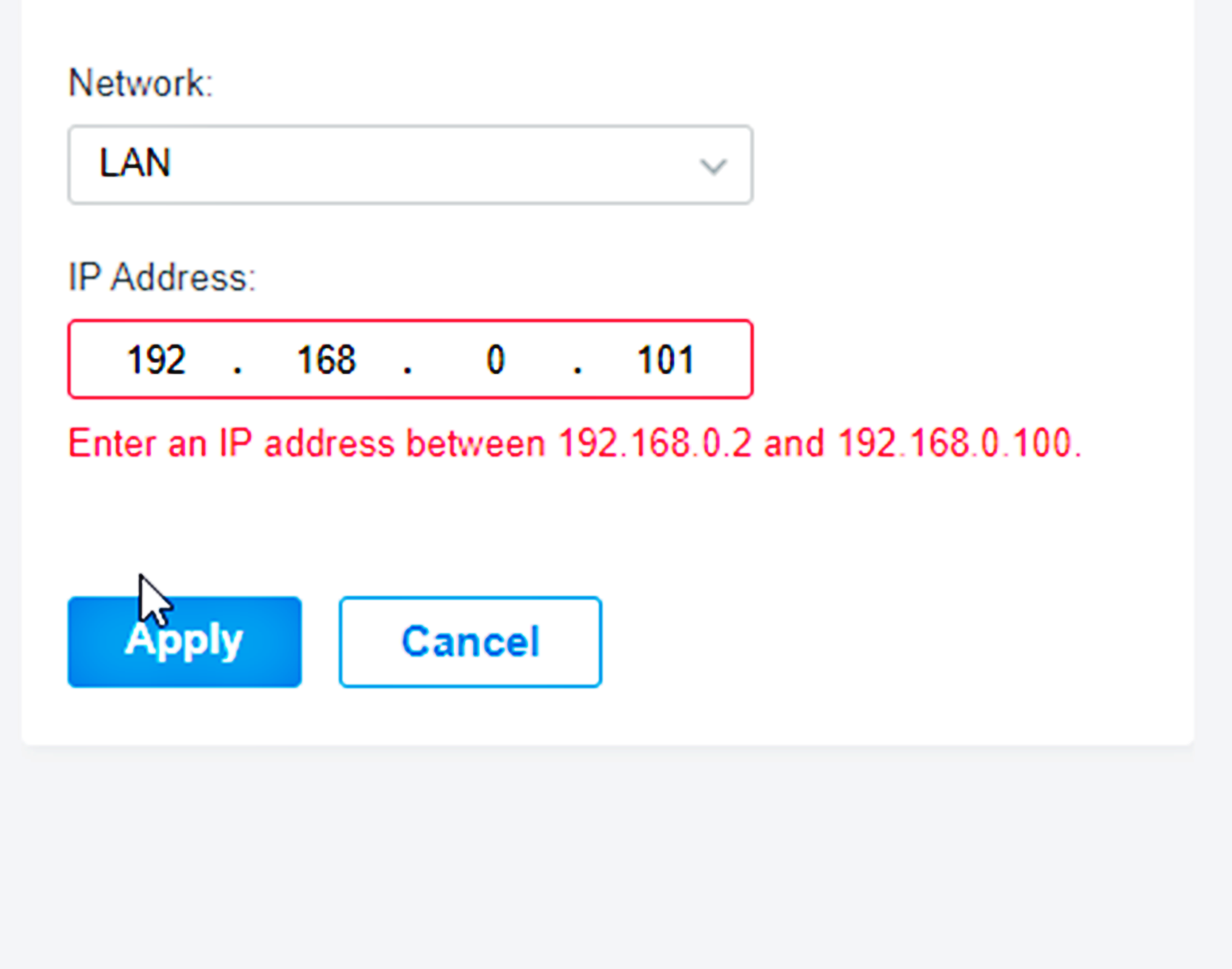
5. Specify the IP address: In the TCP/IPv4 properties dialog box, select the option to “Use the following IP address.” Enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and preferred DNS server. Make sure these values are appropriate for your network configuration. Note that the IP address you specify must be within the range specified by your network administrator or router.
6. Save and apply the settings: After entering the IP address and other configuration details, click “OK” to save the settings. The system will apply the new configuration and assign the specified fixed IP address to the selected network connection.
It’s important to note that if you’re configuring a fixed IP address on a network that is managed by a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server, conflicts may occur if the IP address you specify is already assigned to another device on the network. Ensure that the IP address you choose is unique and not already in use.
To verify that the fixed IP address is set up correctly, you can open the command prompt and type “ipconfig” to view the network configuration details. Check if the assigned IP address matches the one you specified.
Remember to configure a fixed IP address only when necessary, such as for specific applications or network requirements. If you’re using a network that relies on DHCP, you can choose the option to obtain an IP address automatically, which is typically the default and recommended setting for most home and office networks.
By following these steps, you can easily set up a fixed IP address on a Windows computer and have more control over your network configuration.
Setting Up a Fixed IP Address on macOS
If you’re using a macOS system and want to configure a fixed IP address, you can follow these straightforward steps:
1. Open Network Preferences: Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of the screen and select “System Preferences.” In the System Preferences window, click on “Network.”
2. Select the network connection: From the list of available network connections on the left side, choose the connection for which you want to set a fixed IP address. It could be Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or any other active network interface.
3. Click on “Advanced”: After selecting the network connection, click on the “Advanced” button at the bottom right of the Network preferences window. This will open the advanced network settings for the selected connection.
4. Choose the TCP/IP tab: In the advanced network settings window, you’ll see multiple tabs. Click on the “TCP/IP” tab, which contains the options for configuring IP addresses.
5. Configure IPv4: In the TCP/IP tab, locate the “Configure IPv4” dropdown menu. Select the option “Manually” to manually set the IP address, subnet mask, router (gateway) address, and DNS server addresses. Enter the appropriate values based on your network configuration. Make sure the IP address you specify is unique and not already assigned to another device on the network.
6. Save the settings: After entering the IP address and other configuration details, click on “OK” to save the settings. Your system will apply the changes and assign the specified fixed IP address to the selected network connection.
Once the fixed IP address is set up, you can verify the configuration by opening the Terminal application and typing “ifconfig” or “ipconfig” command to view the network settings. Check if the assigned IP address matches the one you specified.
Remember that using a fixed IP address should only be done when necessary and for specific purposes. In most cases, it’s recommended to leave the network settings to obtain an IP address automatically using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) unless you have specific network requirements or instructions from a network administrator.
By following these steps, you can easily set up a fixed IP address on macOS and have more control over your network configuration.
Setting Up a Fixed IP Address on Linux
If you are using a Linux-based operating system and want to set up a fixed IP address, the process typically involves modifying network configuration files. Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting up a fixed IP address on Linux:
1. Identify the network interface: Open a terminal and run the command `ifconfig` to list all available network interfaces. Note the name of the interface you want to set a fixed IP address for, such as eth0 or wlan0.
2. Edit the network configuration file: Open the relevant network configuration file in a text editor with root privileges. For example, on Ubuntu-based systems, the file path is usually `/etc/network/interfaces`, while on Red Hat-based systems, it is `/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-
3. Configure the interface: Within the network configuration file, look for the entry corresponding to the interface you identified in step 1. Modify the configuration by specifying the desired IP address, subnet mask, gateway (router) address, and DNS server addresses in the appropriate fields.
4. Save the changes: Save the file and exit the text editor.
5. Restart the network service: Depending on the Linux distribution you’re using, restart the network service to apply the changes. Use the command `sudo service networking restart` or `sudo systemctl restart network` to restart the network service.
Alternatively, you can also restart the system to ensure that the changes take effect.
After setting a fixed IP address, you can verify the configuration by running the command `ifconfig` or `ip addr show` in the terminal. Check if the assigned IP address matches the one you specified.
It’s important to note that Linux distributions may vary in terms of network configuration file locations and formats. Additionally, some distributions come with network management tools that provide graphical interfaces for configuring network settings, such as NetworkManager or systemd-networkd.
If you prefer a graphical approach, you can use these tools to configure a fixed IP address. Look for network settings or network configuration options in the system settings or menu.
Be cautious when modifying network configuration files, as incorrect changes can result in network connectivity issues. Make sure to keep a backup copy of any configuration files you modify.
By following these steps, you can easily set up a fixed IP address on your Linux system and have more control over your network configuration.
Setting Up a Fixed IP Address on Android
If you’re using an Android device and want to set up a fixed IP address, you can do so by following these steps:
1. Open the Wi-Fi settings: Go to the device’s Settings and tap on “Wi-Fi.”
2. Connect to a Wi-Fi network: Tap on the name of the Wi-Fi network you want to set a fixed IP address for and connect to it.
3. Modify network settings: Tap and hold the connected Wi-Fi network until a menu appears. Select “Modify network” or “Manage network settings” (the exact wording may vary based on the device and Android version).
4. Configure IP settings: In the network settings, scroll down and locate the “IP settings” dropdown. By default, it is set to “DHCP.” Change the setting to “Static” or “Manual.”
5. Enter the fixed IP address: After selecting the static IP setting, additional fields will appear to enter the IP address, Gateway, and DNS server information. Fill in these details based on your network configuration. Ensure that the IP address you specify is unique and does not conflict with other devices on the network.
6. Save the settings: Once you’ve entered the IP address and other information, tap on “Save” or “Apply” to save the changes.
After configuring the fixed IP address, the device will use this address whenever it connects to the specified Wi-Fi network. You can verify the configuration by accessing the Wi-Fi network settings again and checking if the IP address matches the one you specified.
Note that the steps provided above may vary slightly depending on the Android device manufacturer and version of Android. Some devices may have different interface designs or alternative terminology for menu options.
Setting up a fixed IP address on Android can be useful in situations where you require specific network access or when troubleshooting connectivity issues. Keep in mind that using a fixed IP address should only be done when necessary and for specific purposes.
If you want to set a fixed IP address for a mobile network (cellular data), consult your mobile network provider, as the ability to configure those settings may vary based on the provider’s policies and restrictions.
By following these steps, you can easily set up a fixed IP address on your Android device and have more control over your network configuration.
Setting Up a Fixed IP Address on iOS
If you’re using an iOS device and want to set up a fixed IP address, you can do so by following these steps:
1. Open the Wi-Fi settings: Navigate to the device’s Settings and tap on “Wi-Fi.”
2. Connect to a Wi-Fi network: Tap on the name of the Wi-Fi network you want to set a fixed IP address for and connect to it.
3. Tap on the (i) icon: Next to the connected Wi-Fi network, you’ll see an (i) icon. Tap on it to view the network details.
4. Configure IP settings: In the network details screen, scroll down and tap on “Configure IP.”
5. Change to Manual: By default, it is set to “Automatic.” Change the setting to “Manual.”
6. Enter the fixed IP address: Additional fields will appear to enter the IP address, Subnet Mask, Router (Gateway), and DNS server information. Fill in these details based on your network configuration. Ensure that the IP address you specify is unique and does not conflict with other devices on the network.
7. Save the settings: Once you’ve entered the IP address and other information, tap on “Save” or “Done” to save the changes.
After configuring the fixed IP address, the iOS device will use this address when connected to the specified Wi-Fi network. You can verify the configuration by accessing the Wi-Fi network settings again and checking if the IP address matches the one you specified.
Note that the steps provided above may vary slightly depending on the version of iOS you’re using. Apple often refines the interface and settings with each iOS update, but the general process remains similar.
Setting up a fixed IP address on iOS can be useful in specific scenarios where you require a consistent network address, such as accessing devices within your home network or configuring specific network permissions.
Remember that using a fixed IP address should only be done when necessary and for specific purposes. In most cases, it’s recommended to leave the network settings to obtain an IP address automatically using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
By following these steps, you can easily set up a fixed IP address on your iOS device and have more control over your network configuration.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Fixed IP Addresses
Setting up a fixed IP address can provide stability and control over your network connection. However, like any networking configuration, there may be occasional issues that can arise. Here are some common troubleshooting steps to resolve these issues:
1. IP Address Conflict: If you experience network connectivity problems or receive error messages related to IP address conflicts, it’s possible that another device on the network is using the same IP address. To resolve this, check for any duplicate IP addresses and ensure that each device has a unique address within the network.
2. Incorrect Configuration: Check the network configuration settings to ensure that the IP address, subnet mask, gateway (router), and DNS server addresses are entered correctly. Verify that the values match the requirements of your network and consult your network administrator or ISP if needed.
3. Firewall Blocking: If you are experiencing issues with internet connectivity or accessing certain services, check if your firewall settings are blocking traffic from the fixed IP address. Adjust the firewall rules to allow incoming and outgoing connections to and from the specific IP address.
4. Routing problems: If you are unable to access resources on other networks, it’s possible that there are routing issues. Ensure that your default gateway and subnet mask are configured correctly, and that routing tables are appropriately set up on your device and network infrastructure.
5. DNS Resolution Issues: If you encounter difficulties resolving domain names, verify that the DNS server addresses are correctly entered. Consider using alternative DNS servers, such as public DNS services like Google DNS or OpenDNS, as a troubleshooting step.
6. Power Cycling: In some cases, power cycling your networking equipment, including routers and modems, can help resolve various connectivity issues. Turn off the devices, wait a few seconds, and then power them back on to refresh the network connections.
7. Network Cable or Wi-Fi Signal Problems: Ensure that the network cables are securely connected or that you have a strong Wi-Fi signal. Physical issues with the network infrastructure can sometimes lead to intermittent connectivity problems.
8. Restart Network Services: Restarting network services on your device might help resolve issues. You can disable and then re-enable the network connection or restart the network interface via the command line or network settings, depending on your operating system.
9. Check for Software Updates: Keeping your device’s operating system and networking software up to date is crucial for resolving known bugs and security vulnerabilities. Check for updates and install any available patches or updates that may address the issues you are experiencing.
If you have exhausted these troubleshooting steps and are still experiencing problems with your fixed IP address, it may be helpful to seek further assistance from your network administrator, internet service provider (ISP), or consult relevant online forums and user communities for additional guidance.
Remember that each network environment is unique, and resolutions may vary depending on your specific setup and configuration.